目录
在活动之间传递消息
在具体的应用中有时候需要在活动之间传递消息,比如之前讲过在Java代码中利用Intent.setFlags方法设置后面页面的启动模式。那么这个Intent类到底是干嘛用的?Intent是各个组件交流的桥梁,既能在Activity之间沟通也能在Activity与Service或Broadcast之间交流。Intent主要有三部分的工作,一是表明本次通信的请求从哪来往哪去、怎么去;一是发起方携带数据,接收方从Intent中解析数据;一是若发送方想要知道接收方的处理结果,Intent需要负责让接收方返回应答的内容。
1.显式Intent与隐式Intent
Intent有两种方式,一种是显式Intent即有明确的来源活动以及目标活动,属于精确匹配;另一种是隐式Intent即无明确的目标活动只给出一个动作字符串让系统自动匹配,属于模糊匹配。
1.1显式Intent
显示Intent意图主要有三种方式,一种是通过Intent的构造函数指定意图,一种是调用Intent对象的setFlags方法指定,一种是调用Intent对象的setComponent方法指定。下面是代码示例。在xml中有三个按钮,分别对应三种方式。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".ActivityLifeCycle.IntentActivity"
android:orientation="vertical">
<Button
android:id="@+id/button_1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="构造函数指定意图" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button_2"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="setClass方法指定意图" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button_3"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="setComponent方法指定意图" />
</LinearLayout>下面是部分代码,获取三个按钮实例,注册点击监听器,若一个页面存在多个按钮可以将监听器实现与当前页面实例上,如下面所示,通过view.getId区分点击源来自哪个按钮。
public class IntentActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_intent);
Button button_1,button_2,button_3;
button_1 = findViewById(R.id.button_1);
button_2 = findViewById(R.id.button_2);
button_3 = findViewById(R.id.button_3);
button_1.setOnClickListener(this);
button_2.setOnClickListener(this);
button_3.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
if(view.getId() == R.id.button_1){
Intent intent = new Intent(IntentActivity.this,FirstLifeCycleActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
}
else if(view.getId() == R.id.button_2){
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setClass(IntentActivity.this,FirstLifeCycleActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
}
else {
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setComponent(new ComponentName(IntentActivity.this, FirstLifeCycleActivity.class));
startActivity(intent);
}
}
}效果图如下,点击每个按钮都会跳转至同一个页面。


1.2隐式Intent
有些时候APP并不想向外暴露活动名称,只给定一个事先设定好的标志,这样就可以按图索骥找到与标志一样的活动。隐式Intent起到了标记过滤的作用,而这个标志可以是自己定义的动作也可以是系统已有的系统动作。
| 动作常量 | 含义说明 | 典型场景 |
|---|---|---|
| ACTION_MAIN | 应用程序入口 | 应用启动图标触发的界面 |
| ACTION_VIEW | 显示指定数据 | 查看网页、图片、联系人等 |
| ACTION_EDIT | 编辑指定数据 | 编辑联系人、文档等 |
| ACTION_PICK | 从列表中选择某项并返回所选的数据 | 选择联系人、图片等 |
| ACTION_GET_CONTENT | 让用户选择数据,并返回所选数据 | 文件选择器 |
| ACTION_DIAL | 显示拨号面板 | 拨打电话(不直接拨打) |
| ACTION_CALL | 直接向指定用户打电话 | 直接发起呼叫(需权限) |
| ACTION_SEND | 向其他人发送数据 | 分享文本、图片、文件等 |
| ACTION_SENDTO | 向其他人发送消息 | 发送短信、邮件等 |
| ACTION_INSERT | 插入数据 | 插入日历事件、联系人等 |
| ACTION_DELETE | 删除数据 | 删除数据 |
| ACTION_SEARCH | 执行搜索 | 应用内搜索或全局搜索 |
| ACTION_WEB_SEARCH | 执行 Web 搜索 | 网页搜索 |
示例代码如下,对于自定义动作,在AndroidManifest文件中要在目标页面的Activity中添加自定义动作,示例代码中动作字符串为IntentActivity同时要添加category的属性值为android.intent.category.DEFAULT,这是隐式Intent必须添加的属性。
//页面布局文件代码
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".ActivityLifeCycle.IntentActivity"
android:orientation="vertical">
<Button
android:id="@+id/button_1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="利用系统动作跳转至浏览器" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button_2"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="利用自定义动作跳转新页面" />
</LinearLayout>
//AndroidManifest.xml中的部分代码
<activity
android:name=".ActivityLifeCycle.FirstLifeCycleActivity"
android:exported="true"
android:launchMode="standard">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="IntentActivity"/>
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>部分Java代码,系统动作的示例是打开百度网页,自定义动作的示例是打开新页面。
public class IntentActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_intent);
Button button_1,button_2;
button_1 = findViewById(R.id.button_1);
button_2 = findViewById(R.id.button_2);
button_1.setOnClickListener(this);
button_2.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
if(view.getId() == R.id.button_1){
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setAction(Intent.ACTION_VIEW);
intent.setData(Uri.parse("http://baidu.com"));
startActivity(intent);
}
else if(view.getId() == R.id.button_2){
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setAction("IntentActivity");
startActivity(intent);
}
}
}2.活动数据交互
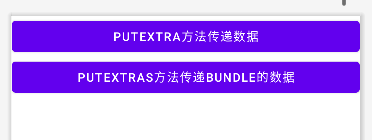
上面所讲只是基本的页面跳转而不带什么数据,若需要传递数据可以调用Intent实例的putExtra方法以及putExtras方法。第一个方法的参数可以为各种类型,包括整型,浮点型,字符串等。第二个方法的参数有Bundle类型,该类可以看做一个包裹,将各种类型的数据装进去在打包一次性交给Intent。下面是代码示例,
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".ActivityLifeCycle.IntentActivity"
android:orientation="vertical">
<Button
android:id="@+id/button_1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="putExtra方法传递数据" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button_2"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="putExtras方法传递Bundle的数据" />
</LinearLayout>来源页面的部分Java代码。
public class IntentActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_intent);
Button button_1,button_2;
button_1 = findViewById(R.id.button_1);
button_2 = findViewById(R.id.button_2);
button_1.setOnClickListener(this);
button_2.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
if(view.getId() == R.id.button_1){
Intent intent = new Intent(IntentActivity.this,FirstLifeCycleActivity.class);
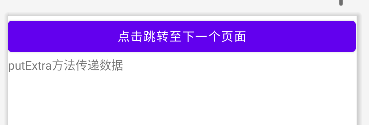
intent.putExtra("data","putExtra方法传递数据");
startActivity(intent);
}
else if(view.getId() == R.id.button_2){
Intent intent = new Intent(IntentActivity.this,FirstLifeCycleActivity.class);
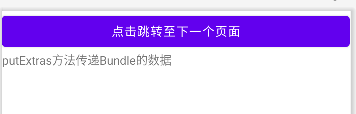
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putString("data","putExtras方法传递Bundle的数据");
intent.putExtras(bundle);
startActivity(intent);
}
}
}目标页面的部分代码。
public class FirstLifeCycleActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private TextView textView;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_first_life_cycle);
textView = findViewById(R.id.textView);
if(getIntent().getStringExtra("data") != null){
textView.setText(getIntent().getStringExtra("data"));
}
if(getIntent().getExtras() != null){
Bundle bundle = getIntent().getExtras();
bundle.getString("data");
textView.setText(bundle.getString("data"));
}
}
}效果图如下,依次点击按钮可以看到数据能够正确被传递到新页面。





















 1106
1106

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








