题目:
Given n non-negative integers a1, a2, ..., an , where each represents a point at coordinate (i, ai). n vertical lines are drawn such that the two endpoints of line i is at (i, ai) and (i, 0). Find two lines, which together with x-axis forms a container, such that the container contains the most water.
Note: You may not slant the container and n is at least 2.

The above vertical lines are represented by array [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]. In this case, the max area of water (blue section) the container can contain is 49.
Example:
Input: [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]
Output: 49
题意:
给定一系列非负整数的序列,每个数代表一个数值的壁,两个壁与x轴组成一个容器,我们需要找到两个边能盛的最大水量。
解法:
首先,暴力法直接穷举是可以求解的,可是复杂度过高。
我们需要一种巧妙的方法,
我们建立前后两个指针,然后让他们分别从前往后,和从后往前搜索,直到他们相遇。
首先我们将最大值max初值设为0;之后两个指针lo 、 hi分别指向最左边和最右边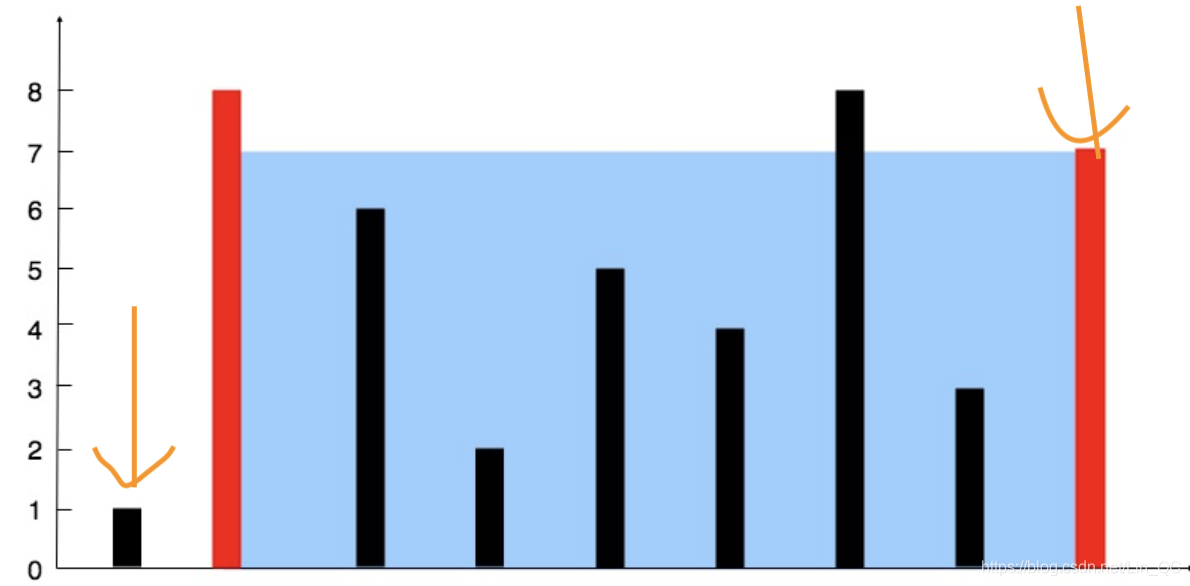
此时我们可以计算一次容量大小count=(hi - lo)* MIN(height[lo] , height[hi])
若比max大则 则 max =count
之后,我们比较height[lo] 和 height[hi]的大小
若 height[ lo] < height[hi] , lo++ (原理,假设移动长的那条边(也就是hi --),那么count出来的值只会更小,因为容量是根据短边来看,x轴的间距还变小了)
height[ lo] > height[hi] , hi -- (同理)
当 lo++ , 使height[lo] < height[hi] 变为 height[ lo] > height[hi],我们就可以执行hi --操作,在执行hi-- 操作前 ,我们是否需要计算一下count更新max值?
(这个其实依情况而定,我们需要在最开始设置一个叫lomax 和 himax的值,分别存储lo指针和hi指针遍历到的最高值
当出现lo++要变为 hi-- 时,我们首先查看一下当前的height[lo]是否比lomax大,如果没有 那么就没有必要计算count,道理跟之前的也差不多,如果没有lomax大(lomax肯定出现在该点之前,作为短边又比当前边长,所以计算出来的count必然会更大)而如果比lomax大,我们需要计算一下count,与max比较,按需填入
)
h--转换为lo++ 也是同理
代码:
class Solution {
public int maxArea(int[] height) {
int L = height.length, lo = 0, hi = L-1;
int max = 0;
while(lo<hi) {
int loMax = height[lo], hiMax = height[hi];
int candidate = (hi-lo) * (loMax<hiMax ? loMax : hiMax);
max = candidate > max ? candidate : max;
if(height[lo]<=height[hi])
while(lo<hi && height[lo]<=loMax) ++lo;
else
while(hi>lo && height[hi]<=hiMax) --hi;
}
return max;
}
}





 本文针对给定的一系列非负整数序列,介绍了一种高效算法来找出两个数值构成的容器能够盛放的最大水量。通过双指针技巧,避免了传统穷举方法的高复杂度,实现了快速求解。
本文针对给定的一系列非负整数序列,介绍了一种高效算法来找出两个数值构成的容器能够盛放的最大水量。通过双指针技巧,避免了传统穷举方法的高复杂度,实现了快速求解。
















 1096
1096

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








