【分支限界法】布线问题
印刷电路板将布线区域划分成n×m个方格如图a所示。精确的电路布线问题要求确定连接方格a的中点到方格b的中点的最短布线方案。在布线时,电路只能沿直线或直角布线,如图b所示。为了避免线路相交,已布了线的方格做了封锁标记,其它线路不允穿过被封锁的方格。
一个布线的例子:图中包含障碍。起始点为a,目标点为b。
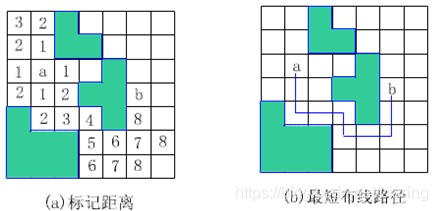
解此问题的队列式分支限界法从起始位置a开始将它作为第一个扩展结点。与该扩展结点相邻并且可达的方格成为可行结点被加入到活结点队列中,并且将这些方格标记为1,即从起始方格a到这些方格的距离为1。
接着,算法从活结点队列中取出队首结点作为下一个扩展结点,并将与当前扩展结点相邻且未标记过的方格标记为2,并存入活结点队列。这个过程一直继续到算法搜索到目标方格b或活结点队列为空时为止。即加入剪枝的广度优先搜索。
// Position.cpp : 此文件包含 "main" 函数。程序执行将在此处开始并结束。
//
#include <iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
template<class Type>
class Position
{
public:
Position(Type x, Type y) :row(x), col(y) {}
Position() {}
template<class Type>
friend bool FindPath(Position<Type>, Position<Type>, Type& Path, Position<Type>*&,Type **grid);
private:
Type row,
col;
};
template<class Type>
bool FindPath(Position<Type> start, Position<Type> end, Type& Pathlen, Position<Type>* &path, Type** grid)
{
Position<Type> offset[4];
(offset[0]).row = 0, (offset[0]).col = 1;
(offset[1]).row = 0, (offset[1]).col = -1;
(offset[2]).row = 1, (offset[2]).col = 0;
(offset[3]).row = -1, (offset[3]).col = 0;
Position<Type> here, nbr;
here.col = start.col;
here.row = start.row;
grid[here.row][here.col] = 2;
queue< Position<Type>> Q;
do {
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
nbr.row = here.row + offset[i].row;
nbr.col = here.col + offset[i].col;
if ((nbr.row>=1&& nbr.row<=7)&& (nbr.col >= 1 && nbr.col <= 7)&& (grid[nbr.row][nbr.col] == 0))
{
grid[nbr.row][nbr.col] = grid[here.row][here.col] + 1;
if (nbr.row == end.row && nbr.col == end.col)
break;
Q.push(nbr);
}
}
if (nbr.row == end.row && nbr.col == end.col)
break;
if (Q.empty())
return false;
here = Q.front();
Q.pop();
}while (true);
for (int i = 1; i < 8; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < 8; j++)
{
cout << grid[i][j] << "\t";
}
cout << endl;
}
here = end;
Pathlen = grid[end.row][end.col] - 2;
path = new Position<Type>[Pathlen];
for (int j = Pathlen - 1; j >= 0; j--)
{
path[j] = here;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
nbr.row = here.row + offset[i].row;//行
if ((nbr.row >= 1 && nbr.row <= 7) && (nbr.col >= 1 && nbr.col <= 7)&&grid[nbr.row][nbr.col] == j + 2)
break;
}
here = nbr;
}
for (int j = Pathlen - 1; j >= 0; j--)
{
cout << path[j].row << " " << path[j].col << endl;
}
return true;
}
int main()
{
Position<int> start(3,2);
Position<int> end(4, 6);
int Pathlen = 0;
Position<int>* path = nullptr;
int** grid;
grid = new int* [8];
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
grid[i] = new int[8];
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 8; j++)
grid[i][j] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
grid[i][0] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
grid[0][i] = 1;
grid[5][1] = 1, grid[6][1] = 1, grid[7][1] = 1;
grid[6][2] = 1, grid[7][2] = 1;
grid[6][3] = 1, grid[7][3] = 1;
grid[3][5] = 1, grid[4][4] = 1, grid[4][5] = 1, grid[5][5] = 1;
grid[1][3] = 1, grid[2][3] = 1, grid[2][4] = 1;
cout << FindPath<int>(start, end, Pathlen, path, grid) << endl;;
return 0;
}
 使用分支限界法解决电路布线问题
使用分支限界法解决电路布线问题





 本文介绍了如何运用队列式分支限界法解决印刷电路板上的布线问题。起始点和目标点固定,路径需遵循直线和直角规则,并避免穿过已封锁的方格。算法从起始点开始,逐步扩展至目标点,通过更新和存储相邻未标记方格的距离来寻找最短布线方案。程序示例展示了具体的实现过程,包括路径长度计算和路径回溯。
本文介绍了如何运用队列式分支限界法解决印刷电路板上的布线问题。起始点和目标点固定,路径需遵循直线和直角规则,并避免穿过已封锁的方格。算法从起始点开始,逐步扩展至目标点,通过更新和存储相邻未标记方格的距离来寻找最短布线方案。程序示例展示了具体的实现过程,包括路径长度计算和路径回溯。
















 4389
4389

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








