<think>我们有一个包含两个3x2张量的列表,需要将其转换为一个形状为(2,3,2)的张量。
在PyTorch中,我们可以使用`torch.stack()`函数来实现。这个函数会将一个张量序列沿着新的维度进行拼接。
由于列表中有两个张量,我们希望在0维(即第一个维度)上堆叠,从而形成一个新的维度,使得最终张量的形状为(2,3,2)。
步骤:
1. 假设我们有一个列表`tensor_list`,其中包含两个形状均为(3,2)的张量。
2. 使用`torch.stack(tensor_list, dim=0)`,这样就可以在0维上堆叠,得到形状为(2,3,2)的张量。
注意:也可以使用`torch.cat`和`unsqueeze`的组合,但`torch.stack`更为直接。
示例代码:
假设有两个3x2的张量:
tensor1 = torch.tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]])
tensor2 = torch.tensor([[7, 8], [9, 10], [11, 12]])
将它们放入一个列表:tensor_list = [tensor1, tensor2]
然后使用torch.stack:
result = torch.stack(tensor_list, dim=0)
这样result的形状就是(2,3,2)。
验证:
result[0] 应该等于 tensor1
result[1] 应该等于 tensor2
另外,如果列表中的张量不在同一个设备上,需要先确保它们在同一个设备上。但一般情况下,我们假设它们都在同一个设备(如CPU)上。
因此,我们可以这样写:
</think>要将包含两个 $3 \times 2$ 张量的列表转换为 $2 \times 3 \times 2$ 的张量向量,可以使用 PyTorch 的 `torch.stack()` 函数。以下是详细步骤和代码实现:
### 解决方案
1. **创建示例张量列表**
假设有两个形状为 $(3,2)$ 的张量:
```python
import torch
# 创建两个 3x2 张量
tensor1 = torch.tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]])
tensor2 = torch.tensor([[7, 8], [9, 10], [11, 12]])
# 组成列表
tensor_list = [tensor1, tensor2]
```
2. **使用 torch.stack() 转换维度**
在维度 `dim=0` 上堆叠张量,形成新维度:
```python
# 沿第0维度堆叠(创建批次维度)
result_tensor = torch.stack(tensor_list, dim=0)
print(result_tensor.shape) # 输出: torch.Size([2, 3, 2])
```
### 完整代码示例
```python
import torch
# 步骤1: 创建两个 3x2 张量组成的列表
tensor1 = torch.tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]])
tensor2 = torch.tensor([[7, 8], [9, 10], [11, 12]])
tensor_list = [tensor1, tensor2]
# 步骤2: 堆叠为 2x3x2 张量
result = torch.stack(tensor_list, dim=0)
# 验证结果
print("输入列表长度:", len(tensor_list)) # 输出: 2
print("转换后张量形状:", result.shape) # 输出: torch.Size([2, 3, 2])
print("张量内容:\n", result)
"""
输出:
tensor([[[ 1, 2],
[ 3, 4],
[ 5, 6]],
[[ 7, 8],
[ 9, 10],
[11, 12]]])
"""
```
### 关键说明
1. **`torch.stack()` 工作机制**
- 在指定维度(`dim=0`)上添加新维度
- 数学表达:若输入张量 $A \in \mathbb{R}^{3 \times 2}$, $B \in \mathbb{R}^{3 \times 2}$,则输出为:
$$
\text{result} = \begin{bmatrix} A \\ B \end{bmatrix} \in \mathbb{R}^{2 \times 3 \times 2}
$$
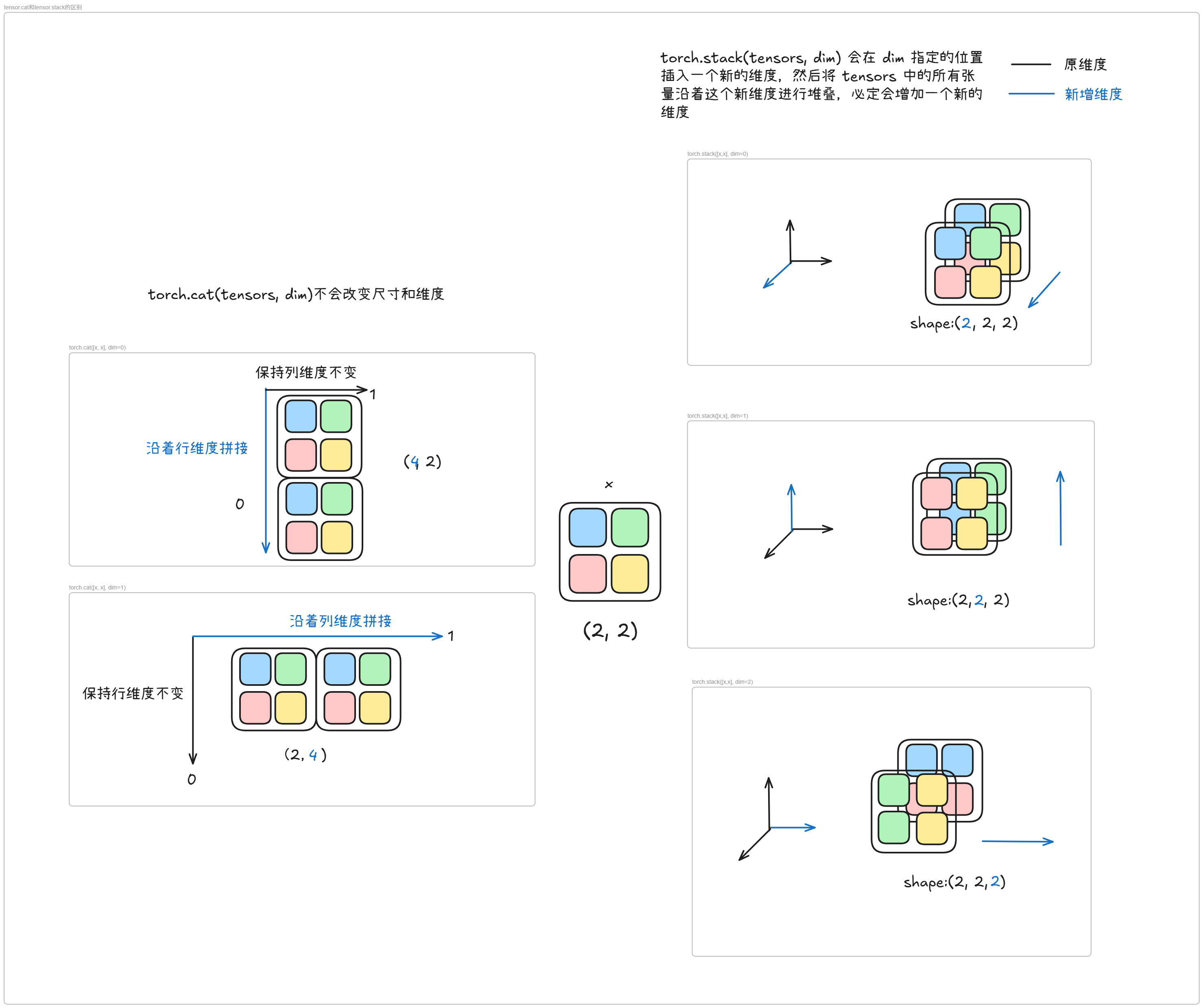
- 与 `torch.cat()` 的区别:`cat` 拼接现有维度,`stack` 创建新维度[^2]
2. **维度选择**
- `dim=0`:创建批次维度(最常用)
- `dim=1`:在行维度堆叠(形状变为 $3 \times 2 \times 2$)
- `dim=2`:在列维度堆叠(形状变为 $3 \times 2 \times 2$)
### 错误处理建议
若遇到维度不匹配错误,需检查:
```python
# 验证列表中所有张量形状一致
assert all(t.shape == tensor_list[0].shape for t in tensor_list), "张量形状不一致"
```
 Pytorch中tensor.cat和tensor.stack的区别
Pytorch中tensor.cat和tensor.stack的区别






















 4183
4183

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








