实现的功能
(1)实现基于DES和RSA算法的自动分配密钥加密聊天程序。
(2)实现密钥自动生成,并基于RSA算法进行密钥共享。
(3)实现基于DES加密的全双工通信,并且加密过程对用户是透明的。
一、安全加密模型
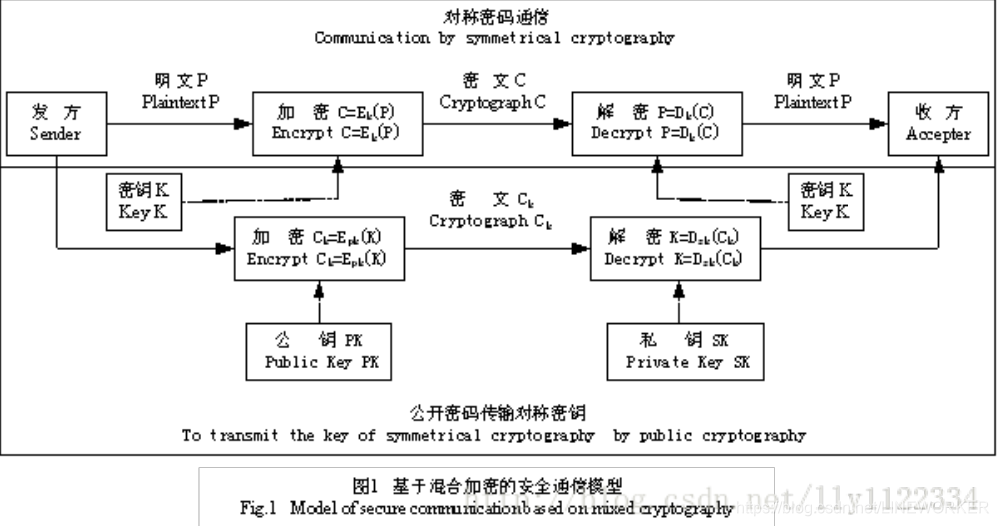
在这个模型中 E()代表加密,D()代表解密,我们要的是发方与收方之间的加密通信,这个加密通信是基于DES加密的,DES加密是对称加密(收发两方使用的秘钥相同),发方会产生DES秘钥,但是DES秘钥要怎么传递给收方呢? 这就要用到RSA非对称加密,直白的说,使用RSA加密就是加密的发放的秘钥。
RSA是非对称加密,发方使用收方的公钥加密自己的DES秘钥,然后传递给收方,收方再用自己的RSA私钥进行解密,获得DES秘钥。
二、代码
DES_BOX.py
# !/usr/bin/python3
# 说明: DES中用到的盒
IP_table = [58, 50, 42, 34, 26, 18, 10, 2,
60, 52, 44, 36, 28, 20, 12, 4,
62, 54, 46, 38, 30, 22, 14, 6,
64, 56, 48, 40, 32, 24, 16, 8,
57, 49, 41, 33, 25, 17, 9, 1,
59, 51, 43, 35, 27, 19, 11, 3,
61, 53, 45, 37, 29, 21, 13, 5,
63, 55, 47, 39, 31, 23, 15, 7]
IP_re_table = [40,8, 48, 16, 56, 24, 64, 32, 39,
7, 47, 15, 55, 23, 63, 31, 38, 6,
46, 14, 54, 22, 62, 30, 37,5, 45,
13, 53, 21, 61, 29, 36, 4, 44, 12,
52, 20, 60, 28, 35, 3, 43, 11, 51,
19, 59, 27, 34, 2, 42, 10, 50, 18,
58, 26, 33, 1, 41,9, 49, 17, 57, 25]
E = [32, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 4, 5,
6, 7, 8, 9, 8, 9, 10, 11,
12,13, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17,
16,17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 20, 21,
22, 23, 24, 25,24, 25, 26, 27,
28, 29,28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 1]
P = [16, 7, 20, 21, 29, 12, 28, 17,
1, 15, 23, 26, 5, 18, 31, 10,
2, 8, 24, 14, 32, 27, 3, 9,
19, 13, 30, 6, 22, 11, 4, 25]
S = [
[14, 4, 13, 1, 2, 15, 11, 8, 3, 10, 6, 12, 5, 9, 0, 7,
0, 15, 7, 4, 14, 2, 13, 1, 10, 6, 12, 11, 9, 5, 3, 8,
4, 1, 14, 8, 13, 6, 2, 11, 15, 12, 9, 7, 3, 10, 5, 0,
15, 12, 8, 2, 4, 9, 1, 7, 5, 11, 3, 14, 10, 0, 6, 13 ],
[15, 1, 8, 14, 6, 11, 3, 4, 9, 7, 2, 13, 12, 0, 5, 10,
3, 13, 4, 7, 15, 2, 8, 14, 12, 0, 1, 10, 6, 9, 11, 5,
0, 14, 7, 11, 10, 4, 13, 1, 5, 8, 12, 6, 9, 3, 2, 15,
13, 8, 10, 1, 3, 15, 4, 2, 11, 6, 7, 12, 0, 5, 14, 9],
[10, 0, 9, 14, 6, 3, 15, 5, 1, 13, 12, 7, 11, 4, 2, 8,
13, 7, 0, 9, 3, 4, 6, 10, 2, 8, 5, 14, 12, 11, 15, 1,
13, 6, 4, 9, 8, 15, 3, 0, 11, 1, 2, 12, 5, 10, 14, 7,
1, 10, 13, 0, 6, 9, 8, 7, 4, 15, 14, 3, 11, 5, 2, 12 ],
[7, 13, 14, 3, 0, 6, 9, 10, 1, 2, 8, 5, 11, 12, 4, 15,
13, 8, 11, 5, 6, 15, 0, 3, 4, 7, 2, 12, 1, 10, 14,9,
10, 6, 9, 0, 12, 11, 7, 13, 15, 1, 3, 14, 5, 2, 8, 4,
3, 15, 0, 6, 10, 1, 13, 8, 9, 4, 5, 11, 12, 7, 2, 14],
[2, 12, 4, 1, 7, 10, 11, 6, 8, 5, 3, 15, 13, 0, 14, 9,
14, 11, 2, 12, 4, 7, 13, 1, 5, 0, 15, 10, 3, 9, 8, 6,
4, 2, 1, 11, 10, 13, 7, 8, 15, 9, 12, 5, 6, 3, 0, 14,
11, 8, 12, 7, 1, 14, 2, 13, 6, 15, 0, 9, 10, 4, 5, 3],
[12, 1, 10, 15, 9, 2, 6, 8, 0, 13, 3, 4, 14, 7, 5, 11,
10, 15, 4, 2, 7, 12, 9, 5, 6, 1, 13, 14, 0, 11, 3, 8,
9, 14, 15, 5, 2, 8, 12, 3, 7, 0, 4, 10, 1, 13, 11, 6,
4, 3, 2, 12, 9, 5, 15, 10, 11, 14, 1, 7, 6, 0, 8, 13],
[4, 11, 2, 14, 15, 0, 8, 13, 3, 12, 9, 7, 5, 10, 6, 1,
13, 0, 11, 7, 4, 9, 1, 10, 14, 3, 5, 12, 2, 15, 8, 6,
1, 4, 11, 13, 12, 3, 7, 14, 10, 15, 6, 8, 0, 5, 9, 2,
6, 11, 13, 8, 1, 4, 10, 7, 9, 5, 0, 15, 14, 2, 3, 12],
[13, 2, 8, 4, 6, 15, 11, 1, 10, 9, 3, 14, 5, 0, 12, 7,
1, 15, 13, 8, 10, 3, 7, 4, 12, 5, 6, 11, 0, 14, 9, 2,
7, 11, 4, 1, 9, 12, 14, 2, 0, 6, 10, 13, 15, 3, 5, 8,
2, 1, 14, 7, 4, 10, 8, 13, 15, 12, 9, 0, 3, 5, 6, 11],
]
#key
PC_1 = [57, 49, 41, 33, 25, 17,9,
1, 58, 50, 42, 34, 26, 18,
10, 2, 59, 51, 43, 35, 27,
19, 11, 3, 60, 52, 44, 36,
63, 55, 47, 39, 31, 23, 15,
7, 62, 54, 46, 38, 30, 22,
14, 6, 61, 53, 45, 37, 29,
21, 13, 5, 28, 20, 12, 4]
PC_2 = [14, 17, 11, 24, 1, 5, 3, 28,
15, 6, 21, 10, 23, 19, 12, 4,
26, 8, 16, 7, 27, 20, 13, 2,
41, 52, 31, 37, 47, 55, 30, 40,
51, 45, 33, 48, 44, 49, 39, 56,
34, 53, 46, 42, 50, 36, 29, 32]
#秘钥左移的位数
SHIFT = [1,1,2,2,2,2,2,2,1,2,2,2,2,2,2,1]
test_rsa.py
from random import randrange
RSA_DEFAULT_EXPONENT = 65537
RSA_DEFAULT_MODULUS_LEN = 2048
first_50_primes = [3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31,
37, 41, 43, 47, 53, 59, 61, 67, 71, 73,
79, 83, 89, 97, 101, 103, 107, 109, 113, 127,
131, 137, 139, 149, 151, 157, 163, 167, 173, 179,
181, 191, 193, 197, 199, 211, 223, 227, 229, 233]
def generate_n_bit_odd(n: int):
'''Generate a random odd number in the range [2**(n-1)+1, 2**n-1]'''
assert n > 1
return randrange(2 ** (n - 1) + 1, 2 ** n, 2)
# The first 50 prime numbers after 2
def get_lowlevel_prime(n):
"""Generate a prime candidate not divisible by first primes"""
while True:
# Obtain a random odd number
c = generate_n_bit_odd(n)
# Test divisibility by pre-generated primes
for divisor in first_50_primes:
if c % divisor == 0 and divisor ** 2 <= c:
break
else:
# The for loop did not encounter a break statement,
# so it passes low level primality test.
return c
def miller_rabin_primality_check(n, k=20):
'''Miller-Rabin Primality Test wwith specified round of test
Input:
n - n > 3, an odd integer to be tested for primality
k - the number of rounds of testing to perfor
Output:
True - passed (n is a strong probable prime)
False - failed (n is a composite)'''
# For a given odd integer n > 3, write n as (2^s)*d+1,
# where s and d are positive integers and d is odd.
assert n > 3
if n % 2 == 0:
return False
s, d = 0, n - 1
while d % 2 == 0:
d >>= 1
s += 1
for _ in range(k):
a = randrange(2, n - 1)
x = pow(a, d, n)
if x == 1 or x == n - 1:
continue
for _ in range(s):
x = pow(x, 2, n)
if x == n - 1:
break
else:
# The for loop did not encounter a break statement,
# so it fails the test, it must be a composite
return False
# Passed the test, it is a strong probable prime
return True
def get_random_prime(num_bits):
while True:
pp = get_lowlevel_prime(num_bits)
if miller_rabin_primality_check(pp):
return pp
def gcd(a, b):
'''Computes the Great Common Divisor using the Euclid's algorithm'''
while b:
a, b = b, a % b
return a
def lcm(a, b):
"""Computes the Lowest Common Multiple using the GCD method."""
return a // gcd(a, b) * b
def exgcd(a, b):
"""Extended Euclidean Algorithm that can give back all gcd, s, t
such that they can make Bézout's identity: gcd(a,b) = a*s + b*t
Return: (gcd, s, t) as tuple"""
old_s, s = 1, 0
old_t, t = 0, 1
while b:
q = a // b
s, old_s = old_s - q * s, s
t, old_t = old_t - q * t, t
a, b = b, a % b
return a, old_s, old_t
def invmod(e, m):
"""Find out the modular multiplicative inverse x of the input integer
e with respect to the modulus m. Return the minimum positive x"""
g, x, y = exgcd(e, m)
assert g == 1
# Now we have e*x + m*y = g = 1, so e*x ≡ 1 (mod m).
# The modular multiplicative inverse of e is x.
if x < 0:
x += m
return x
def uint_from_bytes(xbytes: bytes) -> int:
"""This works only for unsigned (non-negative) integers."""
return int.from_bytes(xbytes, 'big')
def uint_to_bytes(x: int) -> bytes:
"""This works only for unsigned (non-negative) integers.
It does not work for 0."""
if x == 0:
return bytes(1)
return x.to_bytes((x.bit_length() + 7) // 8, 'big')
class RSA:
"""Implements the RSA public key encryption/decryption with default
exponent 65537 and default key size 2048"""
def __init__(self, key_length=RSA_DEFAULT_MODULUS_LEN,
exponent=RSA_DEFAULT_EXPONENT, fast_decrypt=False):
global privite_key
self.e = exponent
self.fast = fast_decrypt
t = 0
p = q = 2
while gcd(self.e, t) != 1:
p = get_random_prime(key_length // 2)
q = get_random_prime(key_length // 2)
t = lcm(p - 1, q - 1)
self.n = p * q
self.d = invmod(self.e, t)
privite_key = self.d
if (fast_decrypt):
self.p, self.q = p, q
self.d_P = self.d % (p - 1)
self.d_Q = self.d % (q - 1)
self.q_Inv = invmod(q, p)
# 加密函数 self.e self.n为公钥
def encrypt(self, binary_data: bytes):
int_data = uint_from_bytes(binary_data)
global public_key,N
public_key=self.e
N=self.n
return pow(int_data, self.e, self.n)
# 解密函数 self.d self.n为私钥
def decrypt(self, encrypted_int_data: int):
int_data = pow(encrypted_int_data, self.d, self.n)
return self.e
def generate_signature(self, encoded_msg_digest: bytes):
"""Use RSA private key to generate Digital Signature for given
encoded message digest"""
int_data = uint_from_bytes(encoded_msg_digest)
return pow(int_data, self.d, self.n)
def generate_signature_fast(self, encoded_msg_digest: bytes):
# Use Chinese Remaider Theorem + Fermat's Little Theorem to
# do fast RSA signature generation
assert self.fast == True
int_data = uint_from_bytes(encoded_msg_digest)
s1 = pow(int_data, self.d_P, self.p)
s2 = pow(int_data, self.d_Q, self.q)
t = s1 - s2
if t < 0:
t += self.p
h = (self.q_Inv * t) % self.p
s = (s2 + h * self.q) % self.n
return s
def decrypt_fast(self, encrypted_int_data: int):
# Use Chinese Remaider Theorem + Fermat's Little Theorem to
# do fast RSA description
assert self.fast == True
m1 = pow(encrypted_int_data, self.d_P, self.p)
m2 = pow(encrypted_int_data, self.d_Q, self.q)
t = m1 - m2
if t < 0:
t += self.p
h = (self.q_Inv * t) % self.p
m = (m2 + h * self.q) % self.n
return uint_to_bytes(m)
def verify_signature(self, digital_signature: int):
"""Use RSA public key to decrypt given Digital Signature"""
int_data = pow(digital_signature, self.e, self.n)
return uint_to_bytes(int_data)
# ---- Test RSA class ----
alice = RSA(512, 3, True)
msg = b'Textbook RSA in Python'
ctxt = alice.encrypt(msg)
P1.py
import threading
import socket
import time
from test_rsa import *
from pyDes import des, PAD_PKCS5, ECB
##在RSA中,P1需要公钥,需要RSA的加密函数
##在DES中,需要使用RSA对DES的秘钥进行加密然后再传过去,然后用DES加密算法对发送的消息进行加解密
address = ('127.0.0.1', 5005) # 服务端地址和端口
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
s.bind(address) # 绑定服务端地址和端口
s.listen(5)
print('服务器已启动,等待客户端连接...')
conn, addr = s.accept() # 返回客户端地址和一个新的 socket 连接 服务在这里处于阻塞状态
print('[+] Connected with', addr)
print('开始初始化...')
def send():
time.sleep(5)
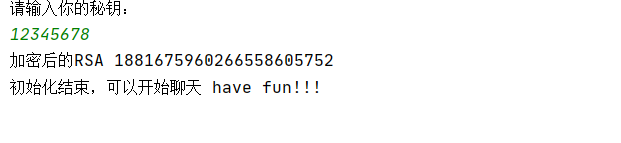
print("请输入你的秘钥:")
key = input().replace(' ', '')
global GLO_KEY
GLO_KEY=key
key1=pow(int(key), int(public_key), int(N))
print("加密后的RSA",key1)
key1=str(key1)
#print('对秘钥进行加密',key1)
conn.sendall(key1.encode())
#conn.sendall(key.encode())
print("初始化结束,可以开始聊天 have fun!!!")
while True:
send = input('').encode()
if send=='我们结束吧'.encode():
break
conn.close()
des_obj = des(key, ECB, key, padmode=PAD_PKCS5)
secret_bytes = des_obj.encrypt(send)
#print("密文",secret_bytes)
#对数据进行加密
conn.sendall(secret_bytes)
conn.close()
s.close()
def my():
global public_key,N
public_key=conn.recv(1024)
public_key=public_key.decode()
print("收到对方的public_key",public_key)
N=conn.recv(1024)
N=N.decode()
print("收到对方的N",N)
while True:
data = conn.recv(1024)
# 对数据进行解密
des_obj = des(str(GLO_KEY), ECB, str(GLO_KEY), padmode=PAD_PKCS5)
data = des_obj.decrypt(data)
print('', data.decode())
if __name__ == '__main__':
#服务器部分
p = threading.Thread(target=my)
p.start()
send()
P2.py
import threading
import socket
import time
import sys
from test_rsa import *
from pyDes import des, PAD_PKCS5, ECB
##在RSA中,P2需要私钥,需要RSA的解密函数
##在DES中,需要DES的加密解密函数
address = ('127.0.0.1', 5005) # 服务端地址和端口
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
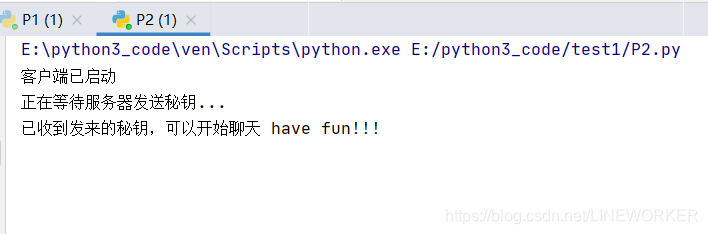
print("客户端已启动")
try:
s.connect(address) # 尝试连接服务端
except Exception:
print('[!] Server not found ot not open')
sys.exit()
def send():
msg_key=str(public_key)
msg_n=str(N)
s.sendall(msg_key.encode())
time.sleep(2)
s.sendall(msg_n.encode())
while True:
send = input('').encode()
if send == '我们结束吧'.encode(): # 自定义结束字符串
break
des_obj = des(str(GLO_KEY), ECB, str(GLO_KEY), padmode=PAD_PKCS5)
secret_bytes = des_obj.encrypt(send)
s.sendall(secret_bytes)
s.close()
def my():
print("正在等待服务器发送秘钥...")
global DES_KEY
DES_KEY = s.recv(1024)
DES_KEY = DES_KEY.decode()
DES_KEY = pow(int(DES_KEY),int(privite_key),int(N))
#print('收到的秘钥:', DES_KEY)
global GLO_KEY
GLO_KEY=DES_KEY
print("已收到发来的秘钥,可以开始聊天 have fun!!!")
while True:
data = s.recv(1024)
#对数据进行解密
des_obj = des(str(DES_KEY), ECB, str(DES_KEY), padmode=PAD_PKCS5)
data = des_obj.decrypt(data)
print('', data.decode())
if __name__ == '__main__':
p = threading.Thread(target=my)
p.start()
send()
三、运行结果
P1为服务器,也就是图中发方,P2为客户端,相当于图中收方,但是他们之间是能够进行全双工通信的,不是一个只能收,一个只能发。
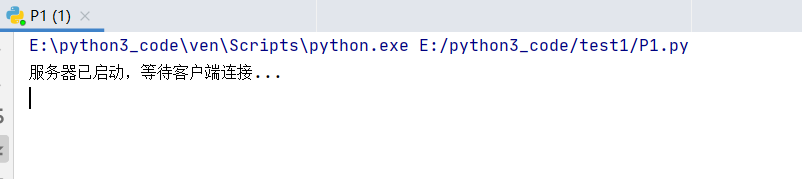
1.首先启动服务器,等待客户端连接
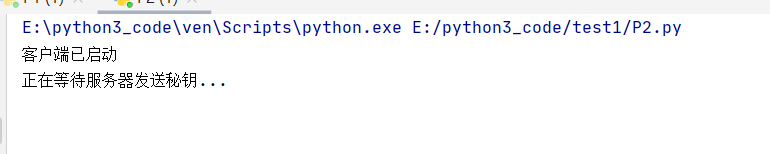
2.启动客户端
3.这时的服务器受到了客户端发来的公钥 和 大整数N
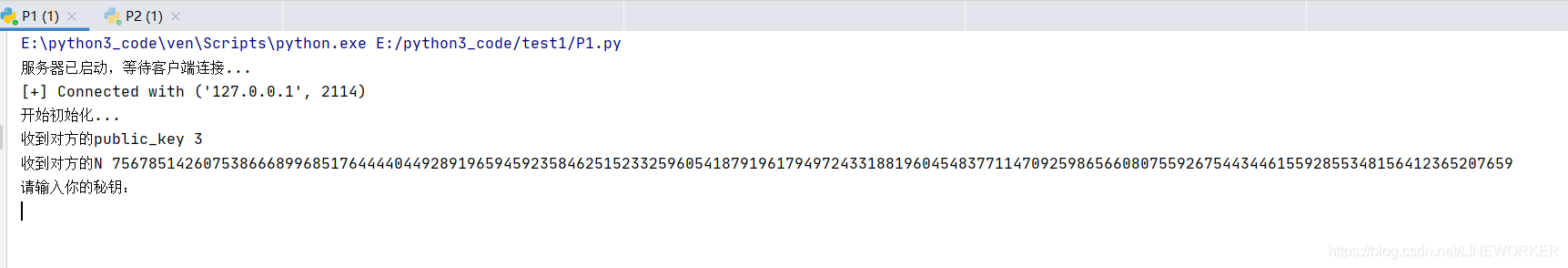
4.服务器将用这些对自己的DES秘钥进行加密
这里需要注意的是DES秘钥长度固定为64bit,也就是8个字符,在输入时需要注意。

按回车,就可以通信啦
测试汉字:

测试字符串:
P1:
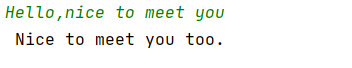
p2:

总结
一开始想直接用Python中的DES包和RSA包直接对数据进行加密,奈何格式不是很匹配,变换格式有些许麻烦,索性直接创建了两个Python文件来进行DES和RSA加密。





 本文详细介绍了如何实现一个基于DES和RSA的加密聊天程序,包括密钥生成、共享与透明加密过程。通过RSA非对称加密传递DES对称密钥,确保通信安全。同时,展示了P1和P2客户端的交互流程,实现实时双向通信。
本文详细介绍了如何实现一个基于DES和RSA的加密聊天程序,包括密钥生成、共享与透明加密过程。通过RSA非对称加密传递DES对称密钥,确保通信安全。同时,展示了P1和P2客户端的交互流程,实现实时双向通信。
















 9247
9247










