给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表不存在相交节点,返回 null 。
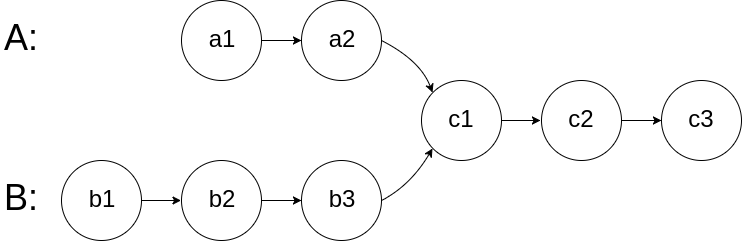
图示两个链表在节点 c1 开始相交:
题目数据 保证 整个链式结构中不存在环。
注意,函数返回结果后,链表必须 保持其原始结构 。
自定义评测:
评测系统 的输入如下(你设计的程序 不适用 此输入):
-
intersectVal- 相交的起始节点的值。如果不存在相交节点,这一值为0 -
listA- 第一个链表 -
listB- 第二个链表 -
skipA- 在listA中(从头节点开始)跳到交叉节点的节点数 -
skipB- 在listB中(从头节点开始)跳到交叉节点的节点数
评测系统将根据这些输入创建链式数据结构,并将两个头节点 headA 和 headB 传递给你的程序。如果程序能够正确返回相交节点,那么你的解决方案将被 视作正确答案 。
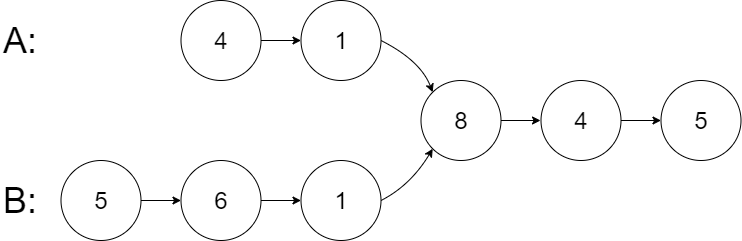
示例 1:
输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,6,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3 输出:Intersected at '8' 解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。 从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,6,1,8,4,5]。 在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。 — 请注意相交节点的值不为 1,因为在链表 A 和链表 B 之中值为 1 的节点 (A 中第二个节点和 B 中第三个节点) 是不同的节点。换句话说,它们在内存中指向两个不同的位置,而链表 A 和链表 B 中值为 8 的节点 (A 中第三个节点,B 中第四个节点) 在内存中指向相同的位置。
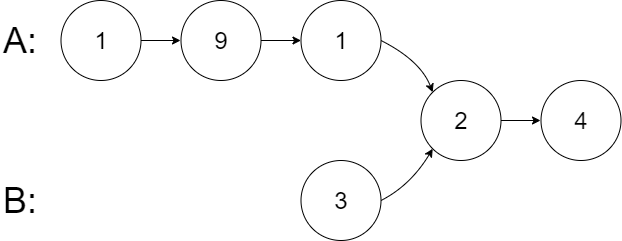
示例 2:
输入:intersectVal = 2, listA = [1,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1 输出:Intersected at '2' 解释:相交节点的值为 2 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。 从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [1,9,1,2,4],链表 B 为 [3,2,4]。 在 A 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 1 个节点。
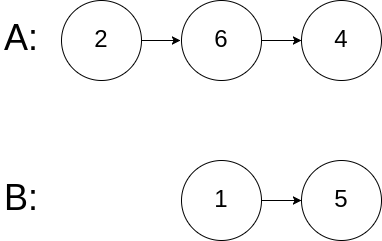
示例 3:
输入:intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2 输出:No intersection 解释:从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [2,6,4],链表 B 为 [1,5]。 由于这两个链表不相交,所以 intersectVal 必须为 0,而 skipA 和 skipB 可以是任意值。 这两个链表不相交,因此返回 null 。
提示:
-
listA中节点数目为m -
listB中节点数目为n -
1 <= m, n <= 3 * 104 -
1 <= Node.val <= 105 -
0 <= skipA <= m -
0 <= skipB <= n -
如果
listA和listB没有交点,intersectVal为0 -
如果
listA和listB有交点,intersectVal == listA[skipA] == listB[skipB]
进阶:你能否设计一个时间复杂度 O(m + n) 、仅用 O(1) 内存的解决方案?
法一:集合
任选一条链表遍历,遍历的同时将节点加入集合中。再遍历另一条链表,只要发现遍历到的节点已经存在于集合当中,那么这个节点就一定是相交的节点
C++
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
unordered_set<ListNode*>s;
while(headA) {
s.insert(headA);
headA=headA->next;
}
while(headB) {
if(s.find(headB)!=s.end()) {
return headB;
}
headB=headB->next;
}
return nullptr;
}
};Java
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
Set<ListNode>s = new HashSet<ListNode>();
ListNode temp=headA;
while(temp!=null) {
s.add(temp);
temp=temp.next;
}
temp=headB;
while(temp!=null) {
if(s.contains(temp)) {
return temp;
}
temp=temp.next;
}
return null;
}
}Go
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func getIntersectionNode(headA, headB *ListNode) *ListNode {
mp:=map[*ListNode]bool{}
for temp:=headA;temp!=nil;temp=temp.Next {
mp[temp]=true
}
for temp:=headB;temp!=nil;temp=temp.Next {
if(mp[temp]) {
return temp
}
}
return nil
}法二:走过你走过的路,只为与你相遇
A先跑200,再跑400,最后再跑800,和B先跑400,再跑200,最后再跑800是一样的。而且只要A和B速度相同,在跑完前600之后一定会相遇。
假设遍历A链表的指针名为a,遍历B链表的指针名为b:那么我们只需要让a和b先遍历完链表,如果遇到最后一个节点,就跳回到对方链表的开头即可,相当于走一遍对方走过的路程,这样只要链表有相交的地方,就必然会在相交的位置相遇。
C++
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
ListNode* a=headA;
ListNode* b=headB;
while(a!=b) {
a= a==nullptr?headB:a->next;
b= b==nullptr?headA:b->next;
}
return a;
}
};Java
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode a=headA;
ListNode b=headB;
while(a!=b) {
a= a==null?headB:a.next;
b= b==null?headA:b.next;
}
return a;
}
}Go
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func getIntersectionNode(headA, headB *ListNode) *ListNode {
a:=headA
b:=headB
for a!=b {
if(a==nil) {
a=headB
} else {
a=a.Next
}
if(b==nil) {
b=headA
} else {
b=b.Next
}
}
return a
}如果两个链表不相交怎么办?不相交的话,a走完B链表,同时b也走完了A链表,二者都为空,就会退出while循环,最终返回空





















 319
319

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








