860.柠檬水找零
题目链接
思路:
情况一:账单是5,直接收下。
情况二:账单是10,消耗一个5,增加一个10
情况三:账单是20,优先消耗一个10和一个5,如果不够,再消耗三个5
class Solution {
public:
bool lemonadeChange(vector<int>& bills) {
int five = 0, ten = 0, twenty = 0;
for (auto bill : bills) {
if (bill == 5) {
five++;
}
if (bill == 10) {
if (five == 0) return false;
else {
five--;
ten++;
}
}
if (bill == 20) {
// 有10 没 5
if (ten >= 1 && five >= 1) {
ten--;
five--;
}
//没10 5 >3
else if (ten == 0 && five >= 3) {
five -= 3;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
};
总结:难度不大,需要静下心来完成,思考每种情况,就很容易解决这道题。
406.根据身高重建队列
**思路:**和分发糖果那道题类似,先进行一个维度上的排列,再对另一个维度进行排序。
首先对身高进行排序,从大到小排序,然后再对前面有几个进行选择插入。这里就要实现一个比较的方法,实现这个效果。
class Solution {
public:
static bool cmp(vector<int> &a, vector<int> &b) {
if (a[0] == b[0]) return a[1] < b[1];
return a[0] > b[0];
}
vector<vector<int>> reconstructQueue(vector<vector<int>>& people) {
sort(people.begin(), people.end(), cmp);
vector<vector<int>> que;
for (int i = 0; i < people.size(); i++) {
int pos = people[i][1];
que.insert(que.begin() + pos, people[i]);
}
return que;
}
};
明显看是使用C++中的list(底层链表实现)比vector(数组)效率高得多。对使用某一种语言容器的使用,特性的选择都会不同程度上影响效率。
// 版本二
class Solution {
public:
// 身高从大到小排(身高相同k小的站前面)
static bool cmp(const vector<int>& a, const vector<int>& b) {
if (a[0] == b[0]) return a[1] < b[1];
return a[0] > b[0];
}
vector<vector<int>> reconstructQueue(vector<vector<int>>& people) {
sort (people.begin(), people.end(), cmp);
list<vector<int>> que; // list底层是链表实现,插入效率比vector高的多
for (int i = 0; i < people.size(); i++) {
int position = people[i][1]; // 插入到下标为position的位置
std::list<vector<int>>::iterator it = que.begin();
while (position--) { // 寻找在插入位置
it++;
}
que.insert(it, people[i]);
}
return vector<vector<int>>(que.begin(), que.end());
}
};
452. 用最少数量的箭引爆气球
思路: 题目读起来很难受,但是实际做起来还是挺简单的。
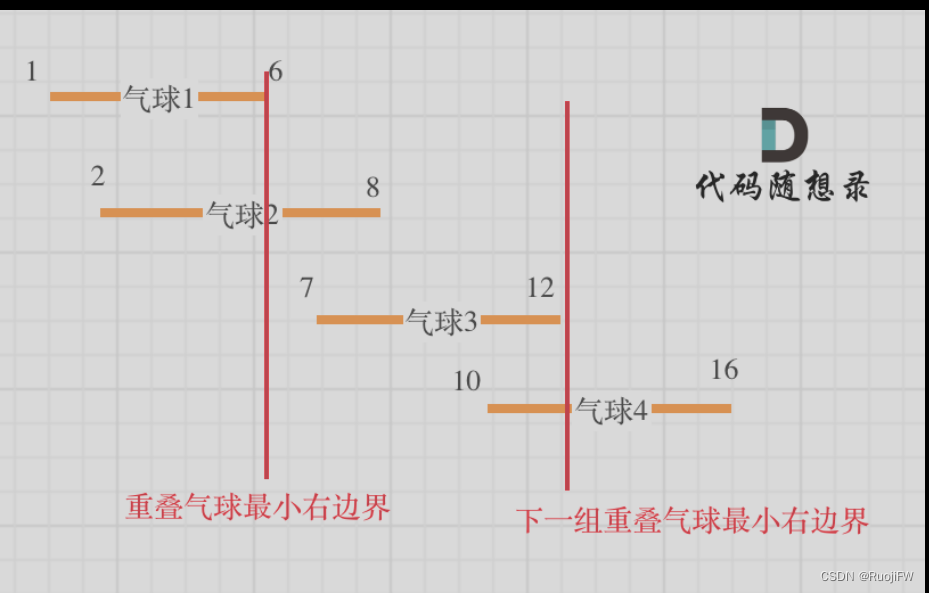
首先对气球的左边界进行从小到大的排序,然后如下图所示。接着遍历数组,对当前气球的右边界和上一个气球的左边界进行比较,如果一家超过了,那么一定需要一根箭,当重叠的时候,降新的用于判断的边界换成重叠时候最小的边界,继续下一轮判断。
class Solution {
private:
static bool cmp(const vector<int>& a, const vector<int>& b) {
return a[0] < b[0];
}
public:
int findMinArrowShots(vector<vector<int>>& points) {
if (points.size() == 0) return 0;
sort(points.begin(), points.end(), cmp);
int result = 1; // points 不为空至少需要一支箭
for (int i = 1; i < points.size(); i++) {
if (points[i][0] > points[i - 1][1]) { // 气球i和气球i-1不挨着,注意这里不是>=
result++; // 需要一支箭
}
else { // 气球i和气球i-1挨着
points[i][1] = min(points[i - 1][1], points[i][1]); // 更新重叠气球最小右边界
}
}
return result;
}
};
**总结:**理解起来很容易,但是自己想的时候感觉不容易想,不过边界排序这部分很熟悉了。




 文章介绍了三道编程题的解题思路,包括如何处理柠檬水找零的不同账单情况,根据身高和前面人数重构队列的算法,以及找出最少箭数引爆气球的逻辑。解题关键在于理解题意,正确排序和处理边界条件。
文章介绍了三道编程题的解题思路,包括如何处理柠檬水找零的不同账单情况,根据身高和前面人数重构队列的算法,以及找出最少箭数引爆气球的逻辑。解题关键在于理解题意,正确排序和处理边界条件。

















 1091
1091

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








