引言
在 GCaMP 实验中,使用 ImageJ 批量处理视频文件是一项重要任务,尤其是当文件数量较多时,操作流程稍有疏漏就可能导致错误。本教程将介绍如何在 ImageJ 中自动化处理一些 GCaMP 视频数据,包括以下内容:
- 视频 ROI 的选择: 在 GCaMP 实验中,准确选择信号和背景区域非常重要。
- 批量使用 Time Series Analyzer V3 处理: 自动化处理视频并导出 Time Series 数据。
- 生成可用于后续作图的 CSV 文件。
该项目最后附有合并的 Python 脚本文件,直接拖入 ImageJ 中即可运行。
文件准备
在开始操作前,需要整理好实验数据文件,并确保其目录结构规范。以下是项目文件夹的示例:
├─Final_Check
│ 2024-12-23 205725.mov
│ 2024-12-23 203914.mov
│ 2024-12-23 194717.mov
│ 2024-12-23 200121.mov文件说明:
- 原始文件:
.mov格式的视频文件,保存实验的原始数据。
环境准备
软件准备
- 下载并安装 ImageJ。
- 安装 Time Series Analyzer V3 插件:可以在 ImageJ 的插件库中找到并安装。
Python 环境准备
确保实验所需的 Python 脚本可以在 ImageJ 中运行。以下是一个简单测试代码:
- 打开 ImageJ 的 REPL(运行环境)。
- 在命令行中输入以下代码,检查是否能成功加载插件:
from ij import IJ
IJ.run("Time Series Analyzer V3", "");
如果插件可以正常运行,说明环境准备就绪。
拆解步骤
导入需要的包
import os
import shutil
from ij import IJ, WindowManager
from ij.plugin.frame import RoiManager
from ij.plugin import ZProjector
import os
import Time_Series_Analyzer_V3
import time
import subprocess
import sys
from java.lang import Runtime # 用于在 Jython 中执行系统命令
from javax.swing import JOptionPane
import csv
import re一、创建文件结构
代码部分
函数:创建文件结构并分类整理
setup_project_structure(folder_path2):在该目录下创建一个格式化的文件夹结构,并将视频移动到里面去。
def setup_project_structure(folder_path2):
"""
Create the directory structure for Project_Folder and organize necessary files into corresponding folders.
"""
# Define required file types for each category
required_files = {
"raw_data": [".mov", ".mp4"], # At least one .mov or .mp4 file is required
"converted_data": [".avi"]
}
# Define the root project folder
project_folder = os.path.join(folder_path2, "Project_Folder")
# Define the directory structure
folders = {
"raw_data": os.path.join(project_folder, "raw_data"), # Original video files
"converted_data": os.path.join(project_folder, "converted_data"), # Converted AVI files
"results": os.path.join(project_folder, "results"), # Output analysis results
"results_roi": os.path.join(project_folder, "results", "roi"), # ROI-related files
"results_gcamp": os.path.join(project_folder, "results", "gcamp_analysis"), # GCaMP analysis results
"results_figures": os.path.join(project_folder, "results", "figures") # Figures generated from data analysis
}
# Create the directory structure
for folder_name, folder_path in folders.items():
if not os.path.exists(folder_path): # Check if folder exists
os.makedirs(folder_path) # Create folder if it doesn't exist
print("Folder has been created or confirmed to exist: %s -> %s" % (folder_name, folder_path))
# Function to check if required video files exist (including in subfolders)
def has_required_files(folder_path, required_files):
"""
Check if the folder or its subfolders contain the necessary video files.
"""
for root, _, files in os.walk(folder_path): # Traverse the folder and subfolders
for file in files:
if file.endswith(tuple(required_files["raw_data"])): # Check for .mov or .mp4
return True
return False
# Check if required video files exist
if not has_required_files(folder_path2, required_files):
print("No valid .mov or .mp4 files found in the folder or its subfolders. The program has terminated.")
exit()
# Move files into corresponding folders
def move_files_to_folders(folder_path, folders, current_script="workflow.py"):
for filename in os.listdir(folder_path):
file_path = os.path.join(folder_path, filename)
# Skip directories
if os.path.isdir(file_path):
continue
# Skip the current script file
if filename == current_script:
continue
# Categorize files based on extensions
file_ext = os.path.splitext(filename)[-1].lower() # Get file extension
moved = False
for folder, extensions_or_files in required_files.items():
# Match file extension
if folder in ["raw_data", "converted_data"] and file_ext in extensions_or_files:
dest_folder = folders[folder]
shutil.move(file_path, os.path.join(dest_folder, filename))
print("Moved file: %s -> %s" % (filename, dest_folder))
moved = True
break
# Unclassified file warning
if not moved:
print("Unclassified file: %s, please handle manually." % filename)
# Start moving files
move_files_to_folders(folder_path2, folders)
print("\nThe directory structure has been created and the file classification is complete.")
主程序执行
folder_path2:刚储存视频文件的文件夹
# Main workflow
if __name__ == "__main__":
# ======= 1. Select Input Folder =======
folder_path2 = IJ.getDirectory("Choose an input folder.")
folder_path_project = os.path.join(folder_path2, "Project_Folder\\")
print("=== Setting up project structure ===\n")
setup_project_structure(folder_path2) # Create directories and organize files
print("\n=== Project structure setup complete ===\n")执行效果
运行后将在 folder_path2 目录下创建如下文件夹结构,并分类整理文件。
- converted_data: 储存处理过的avi视频
- raw_data: 储存原始mov文件
- results: 储存结果
- figures: 用于画图的文件
- gcamp_analysis: 储存中间产生的csv文件
- roi: 储存选择的ROI Region of Interest 区域
这样设计便于文件的规范化管理,提高后续批量处理的效率。
D:.
└─Project_Folder
├─converted_data
├─raw_data
└─results
├─figures
├─gcamp_analysis
└─roi二、选择ROI
代码部分
函数:创建ImageJ宏文件(.ijm),用于选择ROI区域
在这一部分,我们将编写一个ImageJ宏文件(.ijm),该文件用于打开AVI视频文件并选择感兴趣区域(ROI)。通过这种方式,我们能够在ImageJ中自动化ROI的选择,并将其保存以供后续分析使用。
ijm_script = """
// 1.0 Get input folders .
indir = getArgument();("Choose an input folder.");
avidir = indir + "converted_data\\\\"
roidir = indir + "results\\\\roi\\\\"
list = getFileList(avidir);
listroi = getFileList(roidir);
// 2.0 Get filelist of input folder
list = getFileList(avidir);
listroi = getFileList(roidir);
for (i = 0; i < list.length; i++) {
if (endsWith(list[i], ".avi")) {
// Check whether run before
norun = true;
if (endsWith(list[i], ".avi")) {
// Initialize control variables
for (j = 0; j < listroi.length; j++) {
roiVideoName = listroi[j].substring(0, listroi[j].lastIndexOf(".avi") + 4);
if (list[i]==roiVideoName) {
norun = false;
break;
}
}
}
if (norun) {
open(avidir + list[i]);
setTool("rectangle"); // Select Rectangle
roiManager("reset"); // clear ROI Manager
keepRunning = true;
roiIndex = 0; // Number initialized as 0
while (keepRunning) {
// Prompt the user to select the signal area
waitForUser("Draw the **Signal Area** ROI first, then click **OK**.\\n \\nDraw the **Background Area** ROI next, then click **OK**.\\n - Please draw them in pairs: Signal first, then Background.\\n \\n**The first ROI must be drawn during the activation frame** before clicking **OK**.\\n \\nTo stop:\\n - Draw a rectangle with width or height **less than 10 pixels** starting from the top-left corner (less than (100, 100)) and click **OK**.");
// Obtain the rectangular coordinates of the signal area
getSelectionBounds(x, y, width, height);
// Check if the user has drawn a too small rectangle
if ((width < 10 || height < 10) && x <= 100 && y <= 100) {
print("The SIGNAL rectangle is too small. Stopping...");
keepRunning = false;
break; // Exit the while loop
}
// If the user clicks Cancel, the entire loop will be stopped
if (width == 0 && height == 0) {
print("User canceled the process. Stopping...");
keepRunning = false;
break; // Exit the while loop
}
// Save the rectangular information of the signal area to the variable
signalX = x;
signalY = y;
signalWidth = width;
signalHeight = height;
// Add signal area to ROI Manager
roiManager("Add");
currentIndex = roiManager("count") - 1; // Get the ROI index just added
if (currentIndex < 0) {
print("Error: Failed to add SIGNAL ROI.");
keepRunning = false;
break;
}
roiManager("select", currentIndex);
if (currentIndex == 0) {
stimuliName = Roi.getName;
stimuliFrame = substring(stimuliName, 0, 4);
stimuliFrame = parseInt(stimuliFrame);
}
roiManager("rename", "Signal_" + roiIndex); // Manually control the numbering, named Signal-X
// **Lock the ROI of the signal area to prevent it from being dragged**
makeRectangle(signalX, signalY, signalWidth, signalHeight); // Restore signal area
run("Add Selection..."); // Save signal area as static selection
run("Duplicate...", "title=Fixed_Signal_ROI"); // Create a fixed copy
// Prompt the user to select the background area
waitForUser("Drag the rectangle to the BASE (background) area, and confirm.");
getSelectionBounds(baseX, baseY, baseWidth, baseHeight);
// Check if the user has drawn a background rectangle that is too small
if ((baseWidth < 10 || baseHeight < 10) && baseX <= 100 && baseY <= 100) {
print("The BASE rectangle is too small. Stopping...");
keepRunning = false;
break;
}
// If the user does not select the background area (clicks Cancel), stop the entire loop
if (baseWidth == 0 && baseHeight == 0) {
print("User canceled the process. Stopping...");
keepRunning = false;
break;
}
// Add background area to ROI Manager and mark it
roiManager("Add");
currentIndex = roiManager("count") - 1; // Retrieve the index of the background area
if (currentIndex < 0) {
print("Error: Failed to add BASE ROI.");
keepRunning = false;
break;
}
roiManager("select", currentIndex);
roiManager("rename", "Base_" + roiIndex); // Manually control the numbering, named Base_X
roiManager("save", roidir + list[i] + "_SF-" + stimuliFrame + ".all_ROIs.zip");
print("Signal and Base ROIs saved successfully.");
// Number increment to ensure signal and background correspondence
roiIndex++;
}
selectImage(list[i]); // Select current image
run("Close All"); //Close all images
}
}
}
"""
def create_ijm_file(output_dir):
# 自动生成 .ijm 文件
ijm_path = os.path.join(output_dir, "temp_script.ijm")
with open(ijm_path, "w") as f:
f.write(ijm_script)
return ijm_path主程序执行
# Main workflow
if __name__ == "__main__":
folder_path2 = IJ.getDirectory("Choose an input folder.")
folder_path_project = os.path.join(folder_path2, "Project_Folder\\")
# ======= 2. ROI Selection Step =======
print("=== Selecting ROI ===\n")
output_dir = ".\\temp" # Temporary directory
if not os.path.exists(output_dir):
os.makedirs(output_dir) # Create the directory if it doesn't exist
ijm_file = create_ijm_file(output_dir) # Generate the IJM file
IJ.runMacroFile(ijm_file, folder_path_project) # Run the IJM script
print("\n=== ROI Selection Complete ===\n")运行ijm后的操作步骤
1. 绘制信号区域 ROI → 点击确定
2. 绘制背景区域 ROI → 点击确定
3. 重复第 1 和第 2 步,成对绘制 ROI
4. 停止:绘制一个小矩形(宽/高 < 10)→ 点击确定-
绘制信号区域 ROI
- 首先,绘制一个矩形框,标记 信号区域。
- (第一个信号区域的 ROI 必须让视频停留在激活帧(Stimuli Frame)再单击 确定。因为GCaMP需要记录什么时候被激活,所有的数据都应当据此对齐)
- 绘制完成后,单击 确定(OK)。
- 首先,绘制一个矩形框,标记 信号区域。
-
制背景区域
- 接下来,拖动矩形框,标记 背景区域,大小与相对应的Signal区域需一致。
- 绘制完成后,单击 确定(OK)。
- 停止绘制规则
- 如果需要停止绘制,可以按照以下方式操作:
- 在绘制Signal区域的时候(因为Signal和Base要相对应)
- 从左上角(小于 (100, 100) 的区域)开始绘制一个矩形。
- 该矩形的 宽度或高度小于 10 像素。
- 绘制完成后,单击 确定 即可结束操作。
- 如果需要停止绘制,可以按照以下方式操作:
注意事项
- 信号区域和背景区域的匹配非常重要:每个信号区域都需要有一个对应的背景区域进行配对分析。
- 如果绘制时出现错误,可以删掉文件夹里相应的记录roi的zip文件重新运行。
- 停止绘制的触发条件是一个特殊的小矩形,但这个Jython环境我想半天也想不出来怎么停止合适。
三、运行GCaMP Series Analyzer V3对ROI区域执行分析
代码部分
函数:批量执行Time Series Analyzer V3
在这一部分,我们将创建一个函数gcamp_time_analyzer,该函数用于批量执行ImageJ中的Time Series Analyzer V3插件,分析AVI视频中的ROI区域。通过该插件,我们可以提取每个视频文件在不同时间点上的信号强度变化,并将分析结果保存为CSV文件。
- gcamp_time_analyzer(folder_path_project): 批量对Project_Folder下的avi视频和配套的ROI执行Time Series Analyzer V3 执行获取随时间序列的信号强度变化。处理后的csv会保存在gcamp_analysis 下
- folder_path_project: Project_Folder文件夹路径
def gcamp_time_analyzer(folder_path_project):
"""
This function analyzes GCamp time series data by iterating through .avi video files and corresponding .zip ROI files,
performing image analysis, and saving the results to .csv files.
Parameters:
folder_path_project (str): The path to the project folder where the directory structure will be created.
"""
avidir = folder_path_project + "converted_data\\"
roidir = folder_path_project + "results\\roi\\"
resultdir = folder_path_project + "results\\gcamp_analysis\\"
# 遍历文件夹,获取 .avi 和 .zip 文件
avi_files = [f for f in os.listdir(avidir) if f.endswith('.avi')]
zip_files = [f for f in os.listdir(roidir) if f.endswith('.zip') or f.endswith('.zip')]
csv_files = [f for f in os.listdir(resultdir) if f.endswith('.csv')]
# 遍历 .avi 文件
for avi_file in avi_files:
# 获取 .avi 文件的基本名(去掉后缀)
avi_base_name = os.path.splitext(avi_file)[0]
# 查找匹配的 .zip 文件
matching_zip = None
for zip_file in zip_files:
# 检查 .zip 文件名是否以 .avi 文件的基本名为前缀
if zip_file.startswith(avi_base_name):
matching_zip = zip_file
stimuli_frame = re.search(r'SF-(\d+)\.all_ROIs\.zip', zip_file)
stimuli_frame = stimuli_frame.group(1)
break
# 检查是否已经跑过这个文档了
for csv_file in csv_files:
# 检查 .csv 文件名是否以 .avi 文件的基本名为前缀
if csv_file.startswith(avi_base_name):
matching_zip = None
break
# 如果找到匹配的 .zip 文件
if matching_zip:
# 导入 ROI
IJ.run("ROI Manager...")
rm = RoiManager.getInstance()
rm.reset() # 重置 ROI 管理器
rm.open(os.path.join(roidir, matching_zip))
# 打开 .avi 文件
imp = IJ.openImage(os.path.join(avidir, avi_file))
imp.show()
# 等待图像窗口加载完成
time.sleep(2) # 确保图像已打开(视情况调整时间)
# 执行分析操作(根据你的需求调整)
analyzer = Time_Series_Analyzer_V3()
analyzer.getAverage()
# 等待 "Time Trace(s)" 窗口弹出
target_window_title = "Time Trace Average"
wait_time = 0
max_wait_time = 180 # 设置最大等待时间(秒)
# 检查目标窗口是否打开
while True:
open_windows = WindowManager.getImageTitles()
if target_window_title in open_windows:
break # 如果找到目标窗口,退出循环
time.sleep(1) # 等待 1 秒
wait_time += 1
if wait_time > max_wait_time:
break
# 保存结果
IJ.selectWindow("Time Trace(s)")
output_csv = os.path.join(resultdir, avi_base_name + "_Time_Table_SF-" + stimuli_frame +".csv")
IJ.saveAs("Results", output_csv)
print "Results saved to: {output_csv}"
time.sleep(2) # 确保图像已打开(视情况调整时间)
# 关闭所有打开的窗口
imp.close()
IJ.run("Close All")
IJ.selectWindow("Time Series V3_0");
IJ.run("Close");
else:
# 如果没有找到匹配的 .zip 文件
print "Skipping: {}, No ROI files found or Has run before".format(avi_file)
主程序执行
# Main workflow
if __name__ == "__main__":
folder_path2 = IJ.getDirectory("Choose an input folder.")
folder_path_project = os.path.join(folder_path2, "Project_Folder\\")
# ======= 3. GCaMP Time Analysis =======
print("\n=== GCaMP Time Analysis ===\n")
gcamp_time_analyzer(folder_path_project) # Perform GCaMP time analysis
print("\n=== GCaMP Time Analysis Complete ===\n")四、重新格式化csv文件
在完成GCaMP信号强度分析后,接下来的步骤是对Time Series Analyzer V3插件生成的CSV文件进行格式化处理。这一过程将帧数转换为时间(单位:秒),并添加必要的信息,如激活时间帧、视频名称以及帧率等。这样处理后的CSV文件将更具可读性,方便后续的分析和可视化。
代码部分
函数:格式化单个Time Series Analyzer V3结果的CSV文件
reformat_table函数用于对Time Series Analyzer V3插件生成的CSV文件进行格式化处理。它的主要任务是将CSV文件中的帧数转换为时间(秒),并为每个数据文件添加一些额外的列,比如激活时间帧、视频名称以及帧率信息。
- reformat_table(input_file, output_file): 对单一Time Series Analyzer V3产出的csv文件执行格式化操作,转换帧数为时间(s),添加激活时间帧、视频名称、帧率信息。
- input_file: Time Series Analyzer V3结果
- output_file: 格式化后的Time Series Analyzer V3结果
- integrate_gcamp_data(main_folder, output_file): 合并格式化后的csv,帧数转变为时间轴(s),并按照时间轴对齐。
- main_folder: 格式化后csv文件所在文件夹。(Project_Folder/results/gcamp_analysis)
- output_file: 合并文件路径。(Project_Folder/results/gcamp_analysis/formatted_consolidated_data.csv)
def reformat_table(input_file, output_file):
"""
将原始表格转换为指定格式,并保存为新文件。
参数:
- input_file: str,原始表格文件路径
- output_file: str,转换后的文件保存路径
输出:
- 无返回值,转换后的文件将保存到指定路径
"""
# 从文件名中提取信息
filename = os.path.basename(input_file)
video_name, fps, stimuli_frame = (
filename.split("_")[0],
filename.split("_")[1].split("-")[1],
filename.split("_")[-1].split("-")[-1].replace(".csv", ""),
)
# 读取原始表格数据
with open(input_file, 'r') as infile:
reader = csv.reader(infile)
headers = next(reader) # 读取第一行(表头)
data = list(reader) # 读取剩余内容
# 筛选 Signal 和 Base 列
signal_base_pairs = []
for col in headers:
if col.startswith("Signal"):
signal_base_pairs.append((col, col.replace("Signal", "Base")))
# 创建新的表格数据
formatted_data = [["Timepoint"]] # 新表头起始列
for i, (signal_col, base_col) in enumerate(signal_base_pairs):
formatted_data[0].extend(["Sample{}_fluorescence".format(i + 1),
"Sample{}_base".format(i + 1)])
# 将每一对 Signal 和 Base 的值合并到新表格
for row_index, row in enumerate(data):
new_row = [row_index + 1] # Timepoint 列从 1 开始
for signal_col, base_col in signal_base_pairs:
# 获取 Signal 和 Base 列的值
signal_index = headers.index(signal_col)
base_index = headers.index(base_col)
new_row.extend([row[signal_index], row[base_index]])
formatted_data.append(new_row)
# 写入新文件(添加表头信息)
with open(output_file, 'wb') as outfile:
outfile.write("# Video_name: {}\n".format(video_name))
outfile.write("# Stimuli_frame: {}\n".format(stimuli_frame))
outfile.write("# fps: {}\n".format(fps))
writer = csv.writer(outfile)
writer.writerows(formatted_data)
def integrate_gcamp_data(main_folder, output_file):
# 初始化一个空的字典来存储整合数据(按时间点)
timepoint_data = {}
header = ['Timepoint']
n_col = 0
# 遍历每个条件文件夹
for condition_folder in os.listdir(main_folder):
condition_path = os.path.join(main_folder, condition_folder)
if os.path.isdir(condition_path):
# 获取文件夹中的所有文件
for file_name in os.listdir(condition_path):
if file_name.endswith(".csv"):
file_path = os.path.join(condition_path, file_name)
# 读取 CSV 文件,跳过前三行注释
with open(file_path, 'r') as f:
# 读取前几行(假设注释在前3行)
header_lines = [f.readline().strip() for _ in range(3)]
# 获取Stimuli_frame(假设它在第二行并且格式为 '# Stimuli_frame: 471')
Video_name, stim_frame, fps = None, None, None
for line in header_lines:
if line.startswith('# Video_name'):
# 使用正则表达式提取 Video_name
match = re.search(r'#\s*Video_name:\s*([\d\-]+\s*[\d\:]+)', line)
if match:
Video_name = str(match.group(1)) # 提取并转换为整数
else:
print("Warning: Video_name in {} could not be parsed.".format(file_name))
elif line.startswith('# Stimuli_frame'):
# 使用正则表达式提取 Stimuli_frame
match = re.search(r'#\s*Stimuli_frame:\s*(\d+)', line)
if match:
stim_frame = int(match.group(1)) # 提取并转换为整数
else:
print("Warning: Stimuli frame in {} could not be parsed.".format(file_name))
elif line.startswith('# fps'):
# 使用正则表达式提取 fps
match = re.search(r'#\s*fps:\s*(\d+)', line)
if match:
fps = int(match.group(1)) # 提取并转换为整数
else:
print("Warning: fps in {} could not be parsed.".format(file_name))
# 读取 CSV 文件的实际数据,跳过前三行注释
with open(file_path, 'r') as f:
reader = csv.reader(f)
rows = list(reader)[3:] # 跳过前三行注释
# 创建一个新的数据列表
data = []
for row in rows:
# 从第二列开始处理(row[1:]),并尝试将每个值转换为浮动数字
processed_row = []
for i, value in enumerate(row[1:]): # 从第二列开始
try:
# 尝试将每个值转换为浮动类型
float_value = float(value)
processed_row.append(float_value)
except ValueError:
# 如果不能转换为浮动类型,则保留原始值或采取其他处理
processed_row.append(value)
# 添加到最终数据列表
data.append(processed_row)
# 获取时间点(Timepoint)
timepoints = [(float(t) - float(stim_frame)) / float(fps) for t in range(1, len(data) + 1)]
# 从第二列开始处理数据,偶数列为荧光,奇数列为背景
fluorescence_base = []
for i in range(0, len(data[0]), 2):
n_col = n_col + 1
# 偶数列是荧光数据,奇数列是背景数据
fluorescence_col = [float(row[i]) if isinstance(row[i], (int, float)) else 0.0 for row in data] # 确保转换为 float 类型
background_col = [float(row[i + 1]) if isinstance(row[i + 1], (int, float)) else 0.0 for row in data] # 确保转换为 float 类型
# 计算荧光信号 - 背景信号
fluorescence_base = [fluorescence - background for fluorescence, background in zip(fluorescence_col, background_col)]
header.append("{}".format(condition_folder) + "_{}_fluorescence-base_".format(file_name) + str(i/2))
# 将数据按 Timepoint 存入字典
for idx, timepoint in enumerate(timepoints):
if timepoint not in timepoint_data:
timepoint_data[timepoint] = []
for j in range(n_col-1):
timepoint_data[timepoint].append(None)
while len(timepoint_data[timepoint]) < n_col-1:
timepoint_data[timepoint].append(None)
# 添加每个条件的荧光基准数据
timepoint_data[timepoint].append(fluorescence_base[idx])
with open(output_file, 'wb') as f:
writer = csv.writer(f)
writer.writerow(header)
# 按 Timepoint 排序并写入数据行
for timepoint in sorted(timepoint_data.keys()):
row = [timepoint] + timepoint_data[timepoint]
writer.writerow(row)
print("Data has been successfully integrated and saved to {}".format(output_file))
主程序执行
- 4. CSV格式规范化
- 在此阶段,程序会自动对Time Series Analyzer V3生成的CSV文件进行格式化处理。格式化的内容包括将帧数转换为时间(秒),并为每个CSV文件添加额外的信息,如激活时间帧、视频名称和帧率等。这一操作确保了数据格式的统一,方便后续分析。
- 5. 执行分类操作(不同条件分组):
- 此时,程序会暂停执行,并弹出一个提示窗口,要求用户手动分类。用户需要在
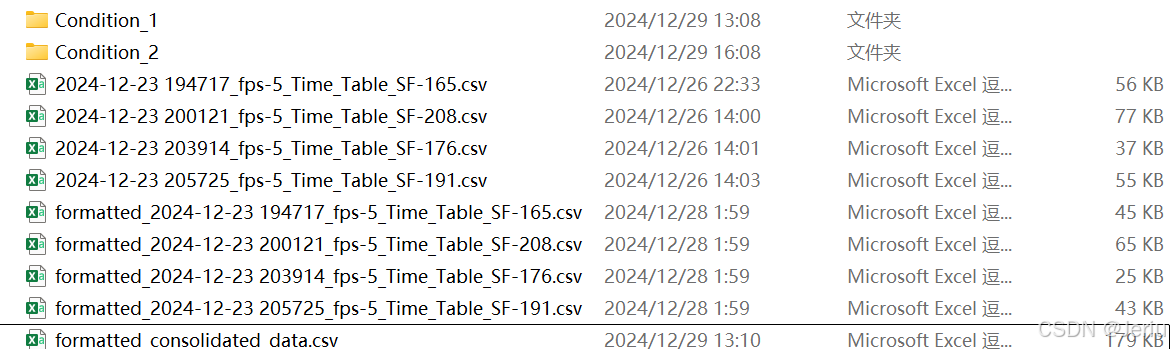
gcamp_analysis文件夹下创建以条件名命名的子文件夹,并将以formatted_开头的CSV文件放入相应的文件夹中。此时,用户需要根据实验条件对数据进行分组。 - 弹窗后手动分类:
- 手动放入Condition(其他命名也可)文件夹下:
-
./gcamp_analysis │ 2024-12-23 194717_fps-5_Time_Table_SF-165.csv │ 2024-12-23 200121_fps-5_Time_Table_SF-208.csv │ 2024-12-23 203914_fps-5_Time_Table_SF-176.csv │ 2024-12-23 205725_fps-5_Time_Table_SF-191.csv │ ├─Condition_1 │ formatted_2024-12-23 203914_fps-5_Time_Table_SF-176.csv │ formatted_2024-12-23 205725_fps-5_Time_Table_SF-191.csv │ └─Condition_2 formatted_2024-12-23 194717_fps-5_Time_Table_SF-165.csv formatted_2024-12-23 200121_fps-5_Time_Table_SF-208.csv
-
- 程序暂停并等待用户操作,按下OK程序继续运行:
- 此时,程序会暂停执行,并弹出一个提示窗口,要求用户手动分类。用户需要在
- 6. 整合所有不同条件下的数据,并输出合并的CSV文件
- 在完成手动分类操作后,程序将自动读取不同条件下的CSV文件,整合它们的数据,并输出一个合并后的CSV文件。合并后的文件会按照时间轴对齐,以便进一步分析。
# Main workflow
if __name__ == "__main__":
# ======= 1. Select Input Folder =======
folder_path2 = IJ.getDirectory("Choose an input folder.")
folder_path_project = os.path.join(folder_path2, "Project_Folder\\")
# ======= 4. CSV Formatting =======
print("\n=== CSV Formatting ===\n")
# Get the full path of the gcamp_analysis folder
gcamp_analysis_path = os.path.join(folder_path_project, 'results', 'gcamp_analysis')
if os.path.exists(gcamp_analysis_path):
# Iterate through all files in the gcamp_analysis folder
for file_name in os.listdir(gcamp_analysis_path):
if file_name.startswith('formatted_'): # Skip already formatted files
continue
if file_name.endswith('.csv'): # Process only CSV files
input_file = os.path.join(gcamp_analysis_path, file_name)
output_file = os.path.join(gcamp_analysis_path, 'formatted_' + file_name)
reformat_table(input_file, output_file) # Format the table
print("File reformatted: {}".format(file_name))
print("\n=== CSV Formatting Complete ===\n")
# ======= 5. Manual Classification =======
print("\n=== Manual Classification Step ===\n")
Runtime.getRuntime().exec('explorer "{}"'.format(gcamp_analysis_path)) # Open folder for user to classify files
time.sleep(2)
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(None, "Please complete the file classification in the folder and press OK to continue...")
print("\n=== Manual Classification Complete ===\n")
# ======= 6. File Integration =======
print("\n=== Starting File Integration ===\n")
output_path = os.path.join(gcamp_analysis_path, 'formatted_consolidated_data.csv')
integrate_gcamp_data(gcamp_analysis_path, output_path) # Integrate data
print("\n=== File Integration Complete ===\n")执行效果
1. Time Series Analyzer V3 结果:
首先,Time Series Analyzer V3的结果会经过reformat_table()处理。此时,程序会对每个CSV文件进行格式化,以下是格式化后的文件内容:
- 帧数转化为时间(秒):原本的帧数被转换为对应的时间(秒)。
- 添加激活时间帧:根据实验要求,标注每个视频的激活时间帧。
- 添加视频名称和帧率信息:在数据中加入视频名称和每秒的帧数(帧率)信息,以便后续追溯和分析。
Time Series Analyzer V3结果:
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> dataset = pd.read_csv("2024-12-23 194717_fps-5_Time_Table_SF-165.csv")
>>> dataset.head()
Signal_0 Base_0 Signal_1 Base_1 Average Err
0 62.000 62.000 62.000 73.65 64.913 2.522
1 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.00 1.000 0.000
2 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.00 1.000 0.000
3 25.652 22.486 20.294 18.56 21.748 1.324
4 25.466 22.470 20.320 18.60 21.714 1.282reformat_table()处理后,添加了注释信息:
# Video_name: 2024-12-23 194717
# Stimuli_frame: 165
# fps: 5
Timepoint Sample1_fluorescence Sample1_base Sample2_fluorescence Sample2_base
1 62 62 62 73.65
2 1 1 1 1
3 1 1 1 1
4 25.652 22.486 20.294 18.56
5 25.466 22.47 20.32 18.6
2. integrate_gcamp_data()处理后:
经过integrate_gcamp_data()处理后,多个条件下的CSV数据会被整合成一个统一的文件,主要效果如下:
- 数据合并:不同条件下的数据按照时间轴(秒)进行对齐,确保相同时间点的数据合并在同一行。
- 去重和标准化:合并的数据会去除冗余信息,并确保数据标准化,所有列对齐。
合并后的文件将包含以下信息:
- 时间列(秒):所有数据按照时间轴对齐。
- 不同条件的信号强度数据:不同条件下的数据被整合到一起,便于进行条件间的对比。
- 视频名称和激活帧:这些信息将被保留,帮助您了解数据来源及激活时点。
integrate_gcamp_data()处理后:
>>> dataset = pd.read_csv("formatted_consolidated_data.csv")
>>> dataset.head()
Timepoint ... Tre_formatted_2024-12-23 205725_fps-5_Time_Table_SF-191.csv_fluorescence-base_1
0 -41.4 ... NaN
1 -41.2 ... NaN
2 -41.0 ... NaN
3 -40.8 ... NaN
4 -40.6 ... NaN
[5 rows x 9 columns]五、数据标准化
在数据整合完成后,下一步是对数据进行标准化处理,以便对信号强度变化进行比较。标准化通常使用基线值(例如激活前的信号强度)来进行归一化操作。
我们使用normalize_csv()函数来执行数据的标准化。具体步骤如下:
函数:数据标准化处理
- normalize_csv(input_file, output_file, time_column="Timepoint", time_range=(-5, 0)):
- input_file (str): 输入文件路径,即上一步整合后的CSV文件。
- output_file (str): 输出文件路径,标准化后的数据将保存到该路径。
- time_column (str): 时间列的名称,默认为 "Timepoint",如果需要,可以更改为其他列名。
- time_range (tuple): 时间范围,用于选择用于计算基线值的时间区间。默认值为 (-5, 0),表示使用激活前5秒的平均值作为基线。
- 读取数据: 读取输入的CSV文件,将数据按行存储。
- 提取时间列和其他数据列: 查找时间列的位置,并确定其他需要进行标准化的列。
- 数据转换: 将数据中的非数字值(如空值、"NA"等)处理为
None,以避免干扰计算。 - 筛选时间范围内的数据: 仅选择时间在指定范围内的行,例如选择激活前5秒的数据。
- 计算基线平均值: 对每一列(信号强度数据列)在指定的时间范围内计算平均值作为基线值。
- 标准化处理: 对每个数据点进行标准化处理,按公式
(x - baseline_mean) / baseline_mean进行归一化。 - 保存输出: 将处理后的数据保存到指定的输出文件。
def normalize_csv(input_file, output_file, time_column="Timepoint", time_range=(-5, 0)):
"""
对指定 CSV 文件中的数据列进行归一化处理,并输出到新的文件。
参数:
input_file (str): 输入的 CSV 文件路径。
output_file (str): 输出的 CSV 文件路径。
time_column (str): 时间列的名称(默认是 "Timepoint")。
time_range (tuple): 时间范围,默认为 (-5, 0)。
"""
# 读取 CSV 文件
rows = []
with open(input_file, "r") as file:
reader = csv.reader(file)
rows = list(reader)
# 提取表头和数据
header = rows[0]
data = rows[1:]
for row in data:
while len(row) < len(header):
row.append('') # 添加None或空字符串('')
# 定义时间列和其他数据列
if time_column not in header:
raise ValueError("Time column '{}' not found in the file.".format(time_column))
time_index = header.index(time_column)
value_indices = [i for i in range(len(header)) if i != time_index]
# 将数据转换为 float,并处理空值为 None
data = [[float(cell) if cell != "" and cell != "NA" else None for cell in row] for row in data]
# 筛选时间范围内的数据
filtered_data = [row for row in data if row[time_index] is not None and time_range[0] <= row[time_index] <= time_range[1]]
# 计算每列的 baseline_mean
baseline_means = []
for col_index in value_indices:
valid_values = [row[col_index] for row in filtered_data if row[col_index] is not None]
if valid_values:
mean_value = sum(valid_values) / len(valid_values)
else:
mean_value = None
baseline_means.append(mean_value)
# 按公式 (x - baseline_mean) / baseline_mean 变换数据
for row in data:
for i, col_index in enumerate(value_indices):
if row[col_index] is not None and baseline_means[i] is not None:
baseline_mean = baseline_means[i]
row[col_index] = (row[col_index] - baseline_mean) / baseline_mean
# 写入处理后的数据到新的 CSV 文件
with open(output_file, "wb") as file:
writer = csv.writer(file)
writer.writerow(header) # 写入表头
for row in data:
# 转换 None 值回空字符串
writer.writerow([cell if cell is not None else "" for cell in row])
print("The data has been standardized and saved to {}".format(output_file))主程序运行
- 标准化数据: 使用
normalize_csv()函数对results/gcamp_analysis下的formatted_consolidated_data.csv文件进行标准化处理。 - 保存标准化结果: 将标准化后的数据保存到
results/figures文件夹中,方便后续用于绘图分析。
# Main workflow
if __name__ == "__main__":
# ======= 1. Select Input Folder =======
folder_path2 = IJ.getDirectory("Choose an input folder.")
folder_path_project = os.path.join(folder_path2, "Project_Folder\\")
gcamp_analysis_path = os.path.join(folder_path_project, 'results', 'gcamp_analysis')
# ======= 7. File Normalization =======
print("\n=== Starting File Integration ===\n")
input_file = os.path.join(gcamp_analysis_path, "formatted_consolidated_data.csv")
output_file = os.path.join(folder_path_project, 'results', "figures", "normalized_data.csv")
# 调用 normalize_csv 函数
normalize_csv(input_file, output_file)
print("\n=== File Integration Complete ===\n")执行效果:
- 标准化处理完成后,
formatted_consolidated_data.csv文件将被转换为标准化后的数据,并保存为normalized_data.csv文件。 - 输出文件:标准化后的文件保存在
results/figures/目录下,文件名为normalized_data.csv。这个文件可以直接用于绘图。
./results
├─figures
│ normalized_data.csv
│
├─gcamp_analysis
│ │ 2024-12-23 194717_fps-5_Time_Table_SF-165.csv
│ │ 2024-12-23 200121_fps-5_Time_Table_SF-208.csv
│ │ 2024-12-23 203914_fps-5_Time_Table_SF-176.csv
│ │ 2024-12-23 205725_fps-5_Time_Table_SF-191.csv
│ │ formatted_2024-12-23 194717_fps-5_Time_Table_SF-165.csv
│ │ formatted_2024-12-23 200121_fps-5_Time_Table_SF-208.csv
│ │ formatted_2024-12-23 203914_fps-5_Time_Table_SF-176.csv
│ │ formatted_2024-12-23 205725_fps-5_Time_Table_SF-191.csv
│ │ formatted_consolidated_data.csv
│ │
│ ├─Condition_1
│ │ formatted_2024-12-23 194717_fps-5_Time_Table_SF-165.csv
│ │ formatted_2024-12-23 200121_fps-5_Time_Table_SF-208.csv
│ │ formatted_2024-12-23 203914_fps-5_Time_Table_SF-176.csv
│ │ formatted_2024-12-23 205725_fps-5_Time_Table_SF-191.csv
│ │
│ └─Condition_2
│ formatted_2024-12-23 194717_fps-5_Time_Table_SF-165.csv
│ formatted_2024-12-23 200121_fps-5_Time_Table_SF-208.csv
│ formatted_2024-12-23 203914_fps-5_Time_Table_SF-176.csv
│ formatted_2024-12-23 205725_fps-5_Time_Table_SF-191.csv
│
└─roi
2024-12-23 200121_fps-2.avi_SF-207.all_ROIs.zip
2024-12-23 202758_fps-2.avi_SF-227.all_ROIs.zip合并步骤:把所有步骤合并到一个py文件内,直接在Imagej里打开运行
整合代码:
import os
import shutil
from ij import IJ, WindowManager
from ij.plugin.frame import RoiManager
from ij.plugin import ZProjector
import os
import Time_Series_Analyzer_V3
import time
import subprocess
import sys
from java.lang import Runtime # 用于在 Jython 中执行系统命令
from javax.swing import JOptionPane
import csv
import re
# 定义 ijm 内容为字符串
ijm_script = """
// 1.0 Get input folders .
indir = getArgument();("Choose an input folder.");
avidir = indir + "converted_data\\\\"
roidir = indir + "results\\\\roi\\\\"
list = getFileList(avidir);
listroi = getFileList(roidir);
// 2.0 Get filelist of input folder
list = getFileList(avidir);
listroi = getFileList(roidir);
for (i = 0; i < list.length; i++) {
if (endsWith(list[i], ".avi")) {
// Check whether run before
norun = true;
if (endsWith(list[i], ".avi")) {
// Initialize control variables
for (j = 0; j < listroi.length; j++) {
roiVideoName = listroi[j].substring(0, listroi[j].lastIndexOf(".avi") + 4);
if (list[i]==roiVideoName) {
norun = false;
break;
}
}
}
if (norun) {
open(avidir + list[i]);
setTool("rectangle"); // Select Rectangle
roiManager("reset"); // clear ROI Manager
keepRunning = true;
roiIndex = 0; // Number initialized as 0
while (keepRunning) {
// Prompt the user to select the signal area
waitForUser("Draw the **Signal Area** ROI first, then click **OK**.\\n \\nDraw the **Background Area** ROI next, then click **OK**.\\n - Please draw them in pairs: Signal first, then Background.\\n \\n**The first ROI must be drawn during the activation frame** before clicking **OK**.\\n \\nTo stop:\\n - Draw a rectangle with width or height **less than 10 pixels** starting from the top-left corner (less than (100, 100)) and click **OK**.");
// Obtain the rectangular coordinates of the signal area
getSelectionBounds(x, y, width, height);
// Check if the user has drawn a too small rectangle
if ((width < 10 || height < 10) && x <= 100 && y <= 100) {
print("The SIGNAL rectangle is too small. Stopping...");
keepRunning = false;
break; // Exit the while loop
}
// If the user clicks Cancel, the entire loop will be stopped
if (width == 0 && height == 0) {
print("User canceled the process. Stopping...");
keepRunning = false;
break; // Exit the while loop
}
// Save the rectangular information of the signal area to the variable
signalX = x;
signalY = y;
signalWidth = width;
signalHeight = height;
// Add signal area to ROI Manager
roiManager("Add");
currentIndex = roiManager("count") - 1; // Get the ROI index just added
if (currentIndex < 0) {
print("Error: Failed to add SIGNAL ROI.");
keepRunning = false;
break;
}
roiManager("select", currentIndex);
if (currentIndex == 0) {
stimuliName = Roi.getName;
stimuliFrame = substring(stimuliName, 0, 4);
stimuliFrame = parseInt(stimuliFrame);
}
roiManager("rename", "Signal_" + roiIndex); // Manually control the numbering, named Signal-X
// **Lock the ROI of the signal area to prevent it from being dragged**
makeRectangle(signalX, signalY, signalWidth, signalHeight); // Restore signal area
run("Add Selection..."); // Save signal area as static selection
run("Duplicate...", "title=Fixed_Signal_ROI"); // Create a fixed copy
// Prompt the user to select the background area
waitForUser("Drag the rectangle to the BASE (background) area, and confirm.");
getSelectionBounds(baseX, baseY, baseWidth, baseHeight);
// Check if the user has drawn a background rectangle that is too small
if ((baseWidth < 10 || baseHeight < 10) && baseX <= 100 && baseY <= 100) {
print("The BASE rectangle is too small. Stopping...");
keepRunning = false;
break;
}
// If the user does not select the background area (clicks Cancel), stop the entire loop
if (baseWidth == 0 && baseHeight == 0) {
print("User canceled the process. Stopping...");
keepRunning = false;
break;
}
// Add background area to ROI Manager and mark it
roiManager("Add");
currentIndex = roiManager("count") - 1; // Retrieve the index of the background area
if (currentIndex < 0) {
print("Error: Failed to add BASE ROI.");
keepRunning = false;
break;
}
roiManager("select", currentIndex);
roiManager("rename", "Base_" + roiIndex); // Manually control the numbering, named Base_X
roiManager("save", roidir + list[i] + "_SF-" + stimuliFrame + ".all_ROIs.zip");
print("Signal and Base ROIs saved successfully.");
// Number increment to ensure signal and background correspondence
roiIndex++;
}
selectImage(list[i]); // Select current image
run("Close All"); //Close all images
}
}
}
"""
def create_ijm_file(output_dir):
# 自动生成 .ijm 文件
ijm_path = os.path.join(output_dir, "temp_script.ijm")
with open(ijm_path, "w") as f:
f.write(ijm_script)
return ijm_path
def reformat_table(input_file, output_file):
"""
将原始表格转换为指定格式,并保存为新文件。
参数:
- input_file: str,原始表格文件路径
- output_file: str,转换后的文件保存路径
输出:
- 无返回值,转换后的文件将保存到指定路径
"""
# 从文件名中提取信息
filename = os.path.basename(input_file)
video_name, fps, stimuli_frame = (
filename.split("_")[0],
filename.split("_")[1].split("-")[1],
filename.split("_")[-1].split("-")[-1].replace(".csv", ""),
)
# 读取原始表格数据
with open(input_file, 'r') as infile:
reader = csv.reader(infile)
headers = next(reader) # 读取第一行(表头)
data = list(reader) # 读取剩余内容
# 筛选 Signal 和 Base 列
signal_base_pairs = []
for col in headers:
if col.startswith("Signal"):
signal_base_pairs.append((col, col.replace("Signal", "Base")))
# 创建新的表格数据
formatted_data = [["Timepoint"]] # 新表头起始列
for i, (signal_col, base_col) in enumerate(signal_base_pairs):
formatted_data[0].extend(["Sample{}_fluorescence".format(i + 1),
"Sample{}_base".format(i + 1)])
# 将每一对 Signal 和 Base 的值合并到新表格
for row_index, row in enumerate(data):
new_row = [row_index + 1] # Timepoint 列从 1 开始
for signal_col, base_col in signal_base_pairs:
# 获取 Signal 和 Base 列的值
signal_index = headers.index(signal_col)
base_index = headers.index(base_col)
new_row.extend([row[signal_index], row[base_index]])
formatted_data.append(new_row)
# 写入新文件(添加表头信息)
with open(output_file, 'wb') as outfile:
outfile.write("# Video_name: {}\n".format(video_name))
outfile.write("# Stimuli_frame: {}\n".format(stimuli_frame))
outfile.write("# fps: {}\n".format(fps))
writer = csv.writer(outfile)
writer.writerows(formatted_data)
def gcamp_time_analyzer(folder_path_project):
avidir = folder_path_project + "converted_data\\"
roidir = folder_path_project + "results\\roi\\"
resultdir = folder_path_project + "results\\gcamp_analysis\\"
# 遍历文件夹,获取 .avi 和 .zip 文件
avi_files = [f for f in os.listdir(avidir) if f.endswith('.avi')]
zip_files = [f for f in os.listdir(roidir) if f.endswith('.zip') or f.endswith('.zip')]
csv_files = [f for f in os.listdir(resultdir) if f.endswith('.csv')]
# 遍历 .avi 文件
for avi_file in avi_files:
# 获取 .avi 文件的基本名(去掉后缀)
avi_base_name = os.path.splitext(avi_file)[0]
# 查找匹配的 .zip 文件
matching_zip = None
for zip_file in zip_files:
# 检查 .zip 文件名是否以 .avi 文件的基本名为前缀
if zip_file.startswith(avi_base_name):
matching_zip = zip_file
stimuli_frame = re.search(r'SF-(\d+)\.all_ROIs\.zip', zip_file)
stimuli_frame = stimuli_frame.group(1)
break
# 检查是否已经跑过这个文档了
for csv_file in csv_files:
# 检查 .csv 文件名是否以 .avi 文件的基本名为前缀
if csv_file.startswith(avi_base_name):
matching_zip = None
break
# 如果找到匹配的 .zip 文件
if matching_zip:
# 导入 ROI
IJ.run("ROI Manager...")
rm = RoiManager.getInstance()
rm.reset() # 重置 ROI 管理器
rm.open(os.path.join(roidir, matching_zip))
# 打开 .avi 文件
imp = IJ.openImage(os.path.join(avidir, avi_file))
imp.show()
# 等待图像窗口加载完成
time.sleep(2) # 确保图像已打开(视情况调整时间)
# 执行分析操作(根据你的需求调整)
analyzer = Time_Series_Analyzer_V3()
analyzer.getAverage()
# 等待 "Time Trace(s)" 窗口弹出
target_window_title = "Time Trace Average"
wait_time = 0
max_wait_time = 180 # 设置最大等待时间(秒)
# 检查目标窗口是否打开
while True:
open_windows = WindowManager.getImageTitles()
if target_window_title in open_windows:
break # 如果找到目标窗口,退出循环
time.sleep(1) # 等待 1 秒
wait_time += 1
if wait_time > max_wait_time:
break
# 保存结果
IJ.selectWindow("Time Trace(s)")
output_csv = os.path.join(resultdir, avi_base_name + "_Time_Table_SF-" + stimuli_frame +".csv")
IJ.saveAs("Results", output_csv)
print "Results saved to: {output_csv}"
time.sleep(2) # 确保图像已打开(视情况调整时间)
# 关闭所有打开的窗口
imp.close()
IJ.run("Close All")
IJ.selectWindow("Time Series V3_0");
IJ.run("Close");
else:
# 如果没有找到匹配的 .zip 文件
print "Skipping: {}, No ROI files found or Has run before".format(avi_file)
def integrate_gcamp_data(main_folder, output_file):
# 初始化一个空的字典来存储整合数据(按时间点)
timepoint_data = {}
header = ['Timepoint']
n_col = 0
# 遍历每个条件文件夹
for condition_folder in os.listdir(main_folder):
condition_path = os.path.join(main_folder, condition_folder)
if os.path.isdir(condition_path):
# 获取文件夹中的所有文件
for file_name in os.listdir(condition_path):
if file_name.endswith(".csv"):
file_path = os.path.join(condition_path, file_name)
# 读取 CSV 文件,跳过前三行注释
with open(file_path, 'r') as f:
# 读取前几行(假设注释在前3行)
header_lines = [f.readline().strip() for _ in range(3)]
# 获取Stimuli_frame(假设它在第二行并且格式为 '# Stimuli_frame: 471')
Video_name, stim_frame, fps = None, None, None
for line in header_lines:
if line.startswith('# Video_name'):
# 使用正则表达式提取 Video_name
match = re.search(r'#\s*Video_name:\s*([\d\-]+\s*[\d\:]+)', line)
if match:
Video_name = str(match.group(1)) # 提取并转换为整数
else:
print("Warning: Video_name in {} could not be parsed.".format(file_name))
elif line.startswith('# Stimuli_frame'):
# 使用正则表达式提取 Stimuli_frame
match = re.search(r'#\s*Stimuli_frame:\s*(\d+)', line)
if match:
stim_frame = int(match.group(1)) # 提取并转换为整数
else:
print("Warning: Stimuli frame in {} could not be parsed.".format(file_name))
elif line.startswith('# fps'):
# 使用正则表达式提取 fps
match = re.search(r'#\s*fps:\s*(\d+)', line)
if match:
fps = int(match.group(1)) # 提取并转换为整数
else:
print("Warning: fps in {} could not be parsed.".format(file_name))
# 读取 CSV 文件的实际数据,跳过前三行注释
with open(file_path, 'r') as f:
reader = csv.reader(f)
rows = list(reader)[3:] # 跳过前三行注释
# 创建一个新的数据列表
data = []
for row in rows:
# 从第二列开始处理(row[1:]),并尝试将每个值转换为浮动数字
processed_row = []
for i, value in enumerate(row[1:]): # 从第二列开始
try:
# 尝试将每个值转换为浮动类型
float_value = float(value)
processed_row.append(float_value)
except ValueError:
# 如果不能转换为浮动类型,则保留原始值或采取其他处理
processed_row.append(value)
# 添加到最终数据列表
data.append(processed_row)
# 获取时间点(Timepoint)
timepoints = [(float(t) - float(stim_frame)) / float(fps) for t in range(1, len(data) + 1)]
# 从第二列开始处理数据,偶数列为荧光,奇数列为背景
fluorescence_base = []
for i in range(0, len(data[0]), 2):
n_col = n_col + 1
# 偶数列是荧光数据,奇数列是背景数据
fluorescence_col = [float(row[i]) if isinstance(row[i], (int, float)) else 0.0 for row in data] # 确保转换为 float 类型
background_col = [float(row[i + 1]) if isinstance(row[i + 1], (int, float)) else 0.0 for row in data] # 确保转换为 float 类型
# 计算荧光信号 - 背景信号
fluorescence_base = [fluorescence - background for fluorescence, background in zip(fluorescence_col, background_col)]
header.append("{}".format(condition_folder) + "_{}_fluorescence-base_".format(file_name) + str(i/2))
# 将数据按 Timepoint 存入字典
for idx, timepoint in enumerate(timepoints):
if timepoint not in timepoint_data:
timepoint_data[timepoint] = []
for j in range(n_col-1):
timepoint_data[timepoint].append(None)
while len(timepoint_data[timepoint]) < n_col-1:
timepoint_data[timepoint].append(None)
# 添加每个条件的荧光基准数据
timepoint_data[timepoint].append(fluorescence_base[idx])
with open(output_file, 'wb') as f:
writer = csv.writer(f)
writer.writerow(header)
# 按 Timepoint 排序并写入数据行
for timepoint in sorted(timepoint_data.keys()):
row = [timepoint] + timepoint_data[timepoint]
writer.writerow(row)
print("Data has been successfully integrated and saved to {}".format(output_file))
def setup_project_structure(folder_path2):
"""
Create the directory structure for Project_Folder and organize necessary files into corresponding folders.
"""
# Define required file types for each category
required_files = {
"raw_data": [".mov", ".mp4"], # At least one .mov or .mp4 file is required
"converted_data": [".avi"]
}
# Define the root project folder
project_folder = os.path.join(folder_path2, "Project_Folder")
# Define the directory structure
folders = {
"raw_data": os.path.join(project_folder, "raw_data"), # Original video files
"converted_data": os.path.join(project_folder, "converted_data"), # Converted AVI files
"results": os.path.join(project_folder, "results"), # Output analysis results
"results_roi": os.path.join(project_folder, "results", "roi"), # ROI-related files
"results_gcamp": os.path.join(project_folder, "results", "gcamp_analysis"), # GCaMP analysis results
"results_figures": os.path.join(project_folder, "results", "figures") # Figures generated from data analysis
}
# Create the directory structure
for folder_name, folder_path in folders.items():
if not os.path.exists(folder_path): # Check if folder exists
os.makedirs(folder_path) # Create folder if it doesn't exist
print("Folder has been created or confirmed to exist: %s -> %s" % (folder_name, folder_path))
# Function to check if required video files exist (including in subfolders)
def has_required_files(folder_path, required_files):
"""
Check if the folder or its subfolders contain the necessary video files.
"""
for root, _, files in os.walk(folder_path): # Traverse the folder and subfolders
for file in files:
if file.endswith(tuple(required_files["raw_data"])): # Check for .mov or .mp4
return True
return False
# Check if required video files exist
if not has_required_files(folder_path2, required_files):
print("No valid .mov or .mp4 files found in the folder or its subfolders. The program has terminated.")
exit()
# Move files into corresponding folders
def move_files_to_folders(folder_path, folders, current_script="workflow.py"):
for filename in os.listdir(folder_path):
file_path = os.path.join(folder_path, filename)
# Skip directories
if os.path.isdir(file_path):
continue
# Skip the current script file
if filename == current_script:
continue
# Categorize files based on extensions
file_ext = os.path.splitext(filename)[-1].lower() # Get file extension
moved = False
for folder, extensions_or_files in required_files.items():
# Match file extension
if folder in ["raw_data", "converted_data"] and file_ext in extensions_or_files:
dest_folder = folders[folder]
shutil.move(file_path, os.path.join(dest_folder, filename))
print("Moved file: %s -> %s" % (filename, dest_folder))
moved = True
break
# Unclassified file warning
if not moved:
print("Unclassified file: %s, please handle manually." % filename)
# Start moving files
move_files_to_folders(folder_path2, folders)
print("\nThe directory structure has been created and the file classification is complete.")
def normalize_csv(input_file, output_file, time_column="Timepoint", time_range=(-5, 0)):
"""
对指定 CSV 文件中的数据列进行归一化处理,并输出到新的文件。
参数:
input_file (str): 输入的 CSV 文件路径。
output_file (str): 输出的 CSV 文件路径。
time_column (str): 时间列的名称(默认是 "Timepoint")。
time_range (tuple): 时间范围,默认为 (-5, 0)。
"""
# 读取 CSV 文件
rows = []
with open(input_file, "r") as file:
reader = csv.reader(file)
rows = list(reader)
# 提取表头和数据
header = rows[0]
data = rows[1:]
for row in data:
while len(row) < len(header):
row.append('') # 添加None或空字符串('')
# 定义时间列和其他数据列
if time_column not in header:
raise ValueError("Time column '{}' not found in the file.".format(time_column))
time_index = header.index(time_column)
value_indices = [i for i in range(len(header)) if i != time_index]
# 将数据转换为 float,并处理空值为 None
data = [[float(cell) if cell != "" and cell != "NA" else None for cell in row] for row in data]
# 筛选时间范围内的数据
filtered_data = [row for row in data if row[time_index] is not None and time_range[0] <= row[time_index] <= time_range[1]]
# 计算每列的 baseline_mean
baseline_means = []
for col_index in value_indices:
valid_values = [row[col_index] for row in filtered_data if row[col_index] is not None]
if valid_values:
mean_value = sum(valid_values) / len(valid_values)
else:
mean_value = None
baseline_means.append(mean_value)
# 按公式 (x - baseline_mean) / baseline_mean 变换数据
for row in data:
for i, col_index in enumerate(value_indices):
if row[col_index] is not None and baseline_means[i] is not None:
baseline_mean = baseline_means[i]
row[col_index] = (row[col_index] - baseline_mean) / baseline_mean
# 写入处理后的数据到新的 CSV 文件
with open(output_file, "wb") as file:
writer = csv.writer(file)
writer.writerow(header) # 写入表头
for row in data:
# 转换 None 值回空字符串
writer.writerow([cell if cell is not None else "" for cell in row])
print("The data has been standardized and saved to {}".format(output_file))
# Main workflow
if __name__ == "__main__":
# ======= 1. Select Input Folder =======
folder_path2 = IJ.getDirectory("Choose an input folder.")
folder_path_project = os.path.join(folder_path2, "Project_Folder\\")
print("=== Setting up project structure ===\n")
setup_project_structure(folder_path2) # Create directories and organize files
print("\n=== Project structure setup complete ===\n")
# ======= 2. ROI Selection Step =======
print("=== Selecting ROI ===\n")
output_dir = ".\\temp" # Temporary directory
if not os.path.exists(output_dir):
os.makedirs(output_dir) # Create the directory if it doesn't exist
ijm_file = create_ijm_file(output_dir) # Generate the IJM file
IJ.runMacroFile(ijm_file, folder_path_project) # Run the IJM script
print("\n=== ROI Selection Complete ===\n")
# ======= 3. GCaMP Time Analysis =======
print("\n=== GCaMP Time Analysis ===\n")
gcamp_time_analyzer(folder_path_project) # Perform GCaMP time analysis
print("\n=== GCaMP Time Analysis Complete ===\n")
# ======= 4. CSV Formatting =======
print("\n=== CSV Formatting ===\n")
# Get the full path of the gcamp_analysis folder
gcamp_analysis_path = os.path.join(folder_path_project, 'results', 'gcamp_analysis')
if os.path.exists(gcamp_analysis_path):
# Iterate through all files in the gcamp_analysis folder
for file_name in os.listdir(gcamp_analysis_path):
if file_name.startswith('formatted_'): # Skip already formatted files
continue
if file_name.endswith('.csv'): # Process only CSV files
input_file = os.path.join(gcamp_analysis_path, file_name)
output_file = os.path.join(gcamp_analysis_path, 'formatted_' + file_name)
reformat_table(input_file, output_file) # Format the table
print("File reformatted: {}".format(file_name))
print("\n=== CSV Formatting Complete ===\n")
# ======= 5. Manual Classification =======
print("\n=== Manual Classification Step ===\n")
Runtime.getRuntime().exec('explorer "{}"'.format(gcamp_analysis_path)) # Open folder for user to classify files
time.sleep(2)
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(None, "Please complete the file classification in the folder and press OK to continue...")
print("\n=== Manual Classification Complete ===\n")
# ======= 6. File Integration =======
print("\n=== Starting File Integration ===\n")
output_path = os.path.join(gcamp_analysis_path, 'formatted_consolidated_data.csv')
integrate_gcamp_data(gcamp_analysis_path, output_path) # Integrate data
print("\n=== File Integration Complete ===\n")
# ======= 7. File Normalization =======
print("\n=== Starting File Integration ===\n")
input_file = os.path.join(gcamp_analysis_path, "formatted_consolidated_data.csv")
output_file = os.path.join(folder_path_project, 'results', "figures", "normalized_data.csv")
# 调用 normalize_csv 函数
normalize_csv(input_file, output_file)
print("\n=== File Integration Complete ===\n")
# ======= 8. Workflow Completed =======
print("\n=== Workflow Complete ===")
文件结构:
./Final_Check
└─Project_Folder
├─converted_data
│ 2024-12-23 205725_fps-2.avi
│ 2024-12-23 203914_fps-2.avi
│ 2024-12-23 194717_fps-2.avi
│ 2024-12-23 200121_fps-2.avi
│
├─raw_data
│ 2024-12-23 205725.mov
│ 2024-12-23 203914.mov
│ 2024-12-23 194717.mov
│ 2024-12-23 200121.mov
│
└─results
├─figures
│ gcamp_signal_over_time.pdf
│ normalized_data.csv
│
├─gcamp_analysis
│ │ 2024-12-23 194717_fps-5_Time_Table_SF-165.csv
│ │ 2024-12-23 200121_fps-5_Time_Table_SF-208.csv
│ │ 2024-12-23 203914_fps-5_Time_Table_SF-176.csv
│ │ 2024-12-23 205725_fps-5_Time_Table_SF-191.csv
│ │ formatted_2024-12-23 194717_fps-5_Time_Table_SF-165.csv
│ │ formatted_2024-12-23 200121_fps-5_Time_Table_SF-208.csv
│ │ formatted_2024-12-23 203914_fps-5_Time_Table_SF-176.csv
│ │ formatted_2024-12-23 205725_fps-5_Time_Table_SF-191.csv
│ │ formatted_consolidated_data.csv
│ │
│ ├─Condition_1
│ │ formatted_2024-12-23 203914_fps-5_Time_Table_SF-176.csv
│ │ formatted_2024-12-23 205725_fps-5_Time_Table_SF-191.csv
│ │
│ └─Condition_2
│ formatted_2024-12-23 194717_fps-5_Time_Table_SF-165.csv
│ formatted_2024-12-23 200121_fps-5_Time_Table_SF-208.csv
│
└─roi
2024-12-23 205725_fps-5_Time_Table_SF-191.all_ROIs.zip
2024-12-23 203914_fps-5_Time_Table_SF-176.all_ROIs.zip
2024-12-23 194717_fps-5_Time_Table_SF-165.all_ROIs.zip
2024-12-23 200121_fps-5_Time_Table_SF-208.all_ROIs.zipPLUS:MATLAB绘图
% 弹出文件选择对话框,让用户选择一个CSV文件
[filename, pathname] = uigetfile('*.csv', 'Select a CSV file');
% 构建完整的文件路径
fullpath = fullfile(pathname, filename);
% 读取所选的CSV文件
data = readtable(fullpath);
% % 定义时间列名称
% time_column = 'Timepoint';
%
% % 获取时间掩码 (时间范围 -5 到 0)
% time_mask = data.(time_column) >= -5 & data.(time_column) <= 0;
%
% % 获取需要归一化的列(排除时间列)
% value_columns = data.Properties.VariableNames;
% value_columns(strcmp(value_columns, time_column)) = []; % 排除时间列
%
% % 遍历每一列进行处理
% for i = 1:length(value_columns)
% col_name = value_columns{i}; % 当前列名称
%
% % 计算时间范围内的基线平均值
% baseline_mean = mean(data{time_mask, col_name});
%
% % 按要求归一化列
% data{:, col_name} = (data{:, col_name} - baseline_mean) / baseline_mean;
% end
%
% % 将结果写回新的文件
% writetable(data, fullfile(pathname, 'formatted_normalized_data.csv'));
% 提取时间点(第一列)
timepoints = data.Timepoint;
% 提取所有样本列
sample_data = data{:, 2:end};
% 提取列名,并解析出条件名
col_names = data.Properties.VariableNames(2:end);
conditions = cellfun(@(x) strtok(x, '_'), col_names, 'UniformOutput', false); % 提取组别
unique_conditions = unique(conditions); % 获取所有唯一的组别
% 初始化存储均值和 SEM 的矩阵
mean_data = [];
sem_data = [];
% 遍历每个组别,计算均值和 SEM
for i = 1:length(unique_conditions)
% 获取当前组别的列索引
condition = unique_conditions{i};
condition_idx = strcmp(conditions, condition);
% 当前组别的所有样本数据
condition_data = sample_data(:, condition_idx);
% 计算组别均值和 SEM
condition_mean = mean(condition_data, 2, 'omitnan'); % 按行计算均值
condition_sem = std(condition_data, 0, 2, 'omitnan') ./ sqrt(sum(~isnan(condition_data), 2)); % SEM = std / sqrt(n)
% 存储结果
mean_data = [mean_data, condition_mean];
sem_data = [sem_data, condition_sem];
end
% 创建折线图
figure;
hold on;
% 设置颜色映射
num_conditions = length(unique_conditions);
colors = lines(max(num_conditions, 7)); % 确保足够的颜色数量
% 绘制每个条件的平均值和误差条
for i = 1:num_conditions
% 当前条件
condition = unique_conditions{i};
% 筛选非 NaN 值的索引
valid_idx = ~isnan(mean_data(:, i)) & ~isnan(sem_data(:, i)); % 修复列索引错误
% 筛选有效时间点、均值和误差条
valid_timepoints = timepoints(valid_idx);
valid_mean = mean_data(valid_idx, i);
valid_sem = sem_data(valid_idx, i);
% 绘制均值曲线
plot(valid_timepoints, valid_mean, 'LineWidth', 1.5, 'Color', colors(i, :), 'DisplayName', condition);
hold on; % 确保所有条件绘制在同一图上
% 添加误差条
fill([valid_timepoints; flip(valid_timepoints)], ...
[valid_mean - valid_sem; flip(valid_mean + valid_sem)], ...
colors(i, :), 'FaceAlpha', 0.3, 'EdgeColor', 'none');
end
% 图例和样式
legend('Location', 'best', 'Interpreter', 'none');
xlabel('Time (s)');
ylabel('Normalized Fluorescence (\DeltaF/F)');
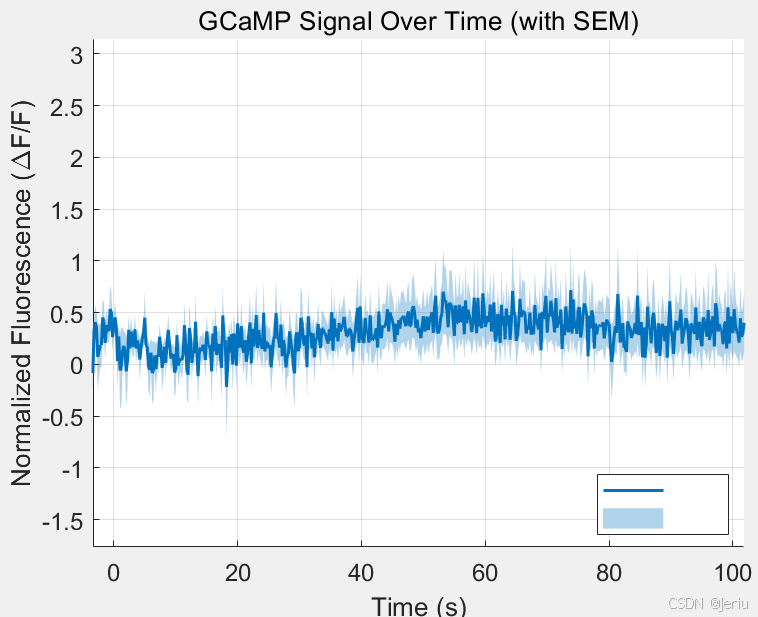
title('GCaMP Signal Over Time (with SEM)');
grid on;
set(gca, 'FontSize', 12);
hold off;
% 设置文件保存路径和文件名
pdf_filename = fullfile(pathname, 'gcamp_signal_over_time.pdf'); % 替换 pathname 为你的文件夹路径
% 保存当前图像为 PDF
saveas(gcf, pdf_filename);
% 或者使用更高质量的导出方式
exportgraphics(gcf, pdf_filename, 'ContentType', 'vector');




















 1088
1088

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








