1、字符串转数组

List<String> collect = Arrays.stream(str.split(",")).collect(Collectors.toList());
2、两个集合的交集

List<String> collect = oldArray.stream()
.filter(old ->
newArray.stream().anyMatch(old::equals)
).collect(Collectors.toList());
3、获取第一个集合存在 ;第二个集合却不存在的元素

List<String> collect = oldArray.stream()
.filter(old ->
newArray.stream().noneMatch(old::equals)
).collect(Collectors.toList());
或者...
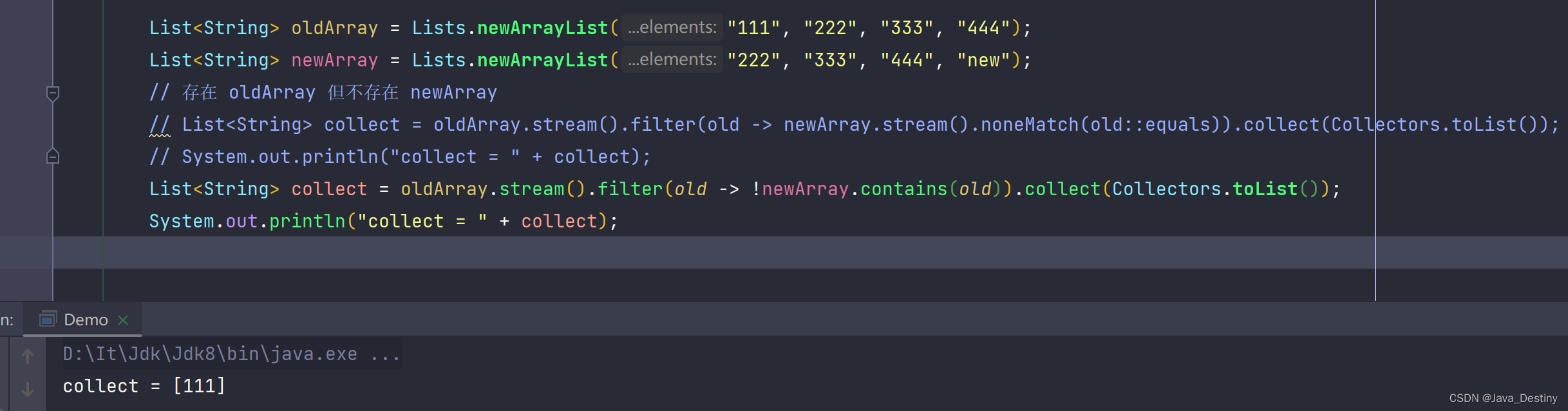
List<String> collect = oldArray.stream()
.filter(old ->
!newArray.contains(old)
).collect(Collectors.toList());
再或者...

List<String> collect = oldArray.stream()
.filter(old ->
newArray.stream().noneMatch(ss -> Objects.equals(old, ss))
).collect(Collectors.toList());
4、去重
普通去重...
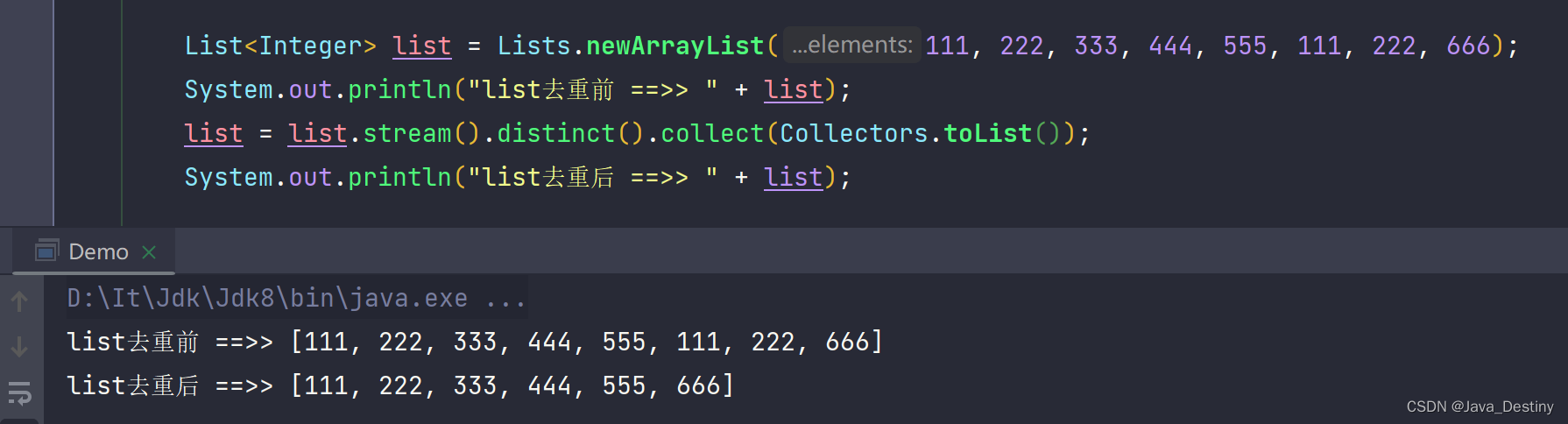
list = list.stream().distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
根据对象字段去重...

list.stream().collect(Collectors.collectingAndThen(
Collectors.toCollection(
() -> new TreeSet<>(Comparator.comparing(Test::getId))
), ArrayList::new)
);
5、过滤并去重

list.stream()
// 过滤
.filter(item -> item.equals("11"))
// 去重
.distinct()
.collect(Collectors.toList());
6、 多条件过滤

7、合并两个list并去重

8、替代嵌套循环

9、字符串转集合并转换类型

10、 排序
普通排序...

根据对象属性排序...

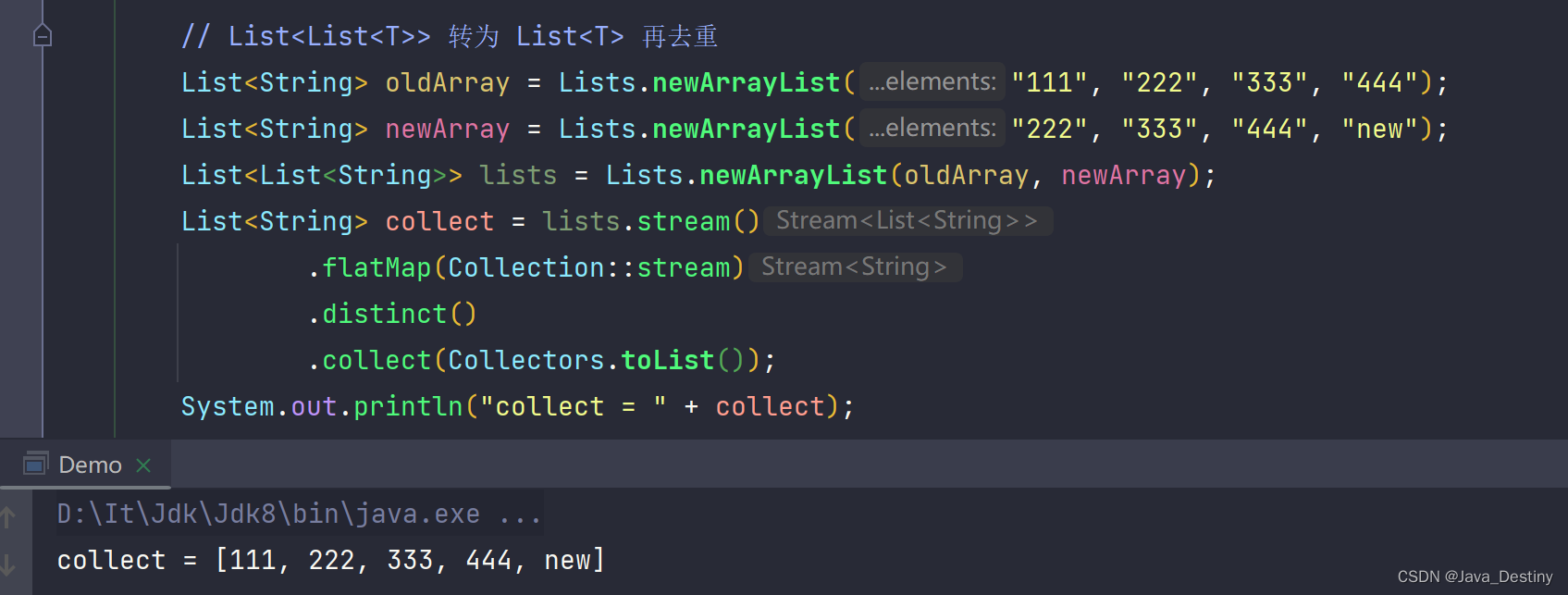
11、 List<List<T>> 转为 List<T>
12、多个字符串转为集合 并合并成一个List
list = [ "1,2" , "3,4,5,6" ] 转为 list = [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 ]

13、List转Map

或...

14、 两个list根据属性合并

或者...

15、用流来分页

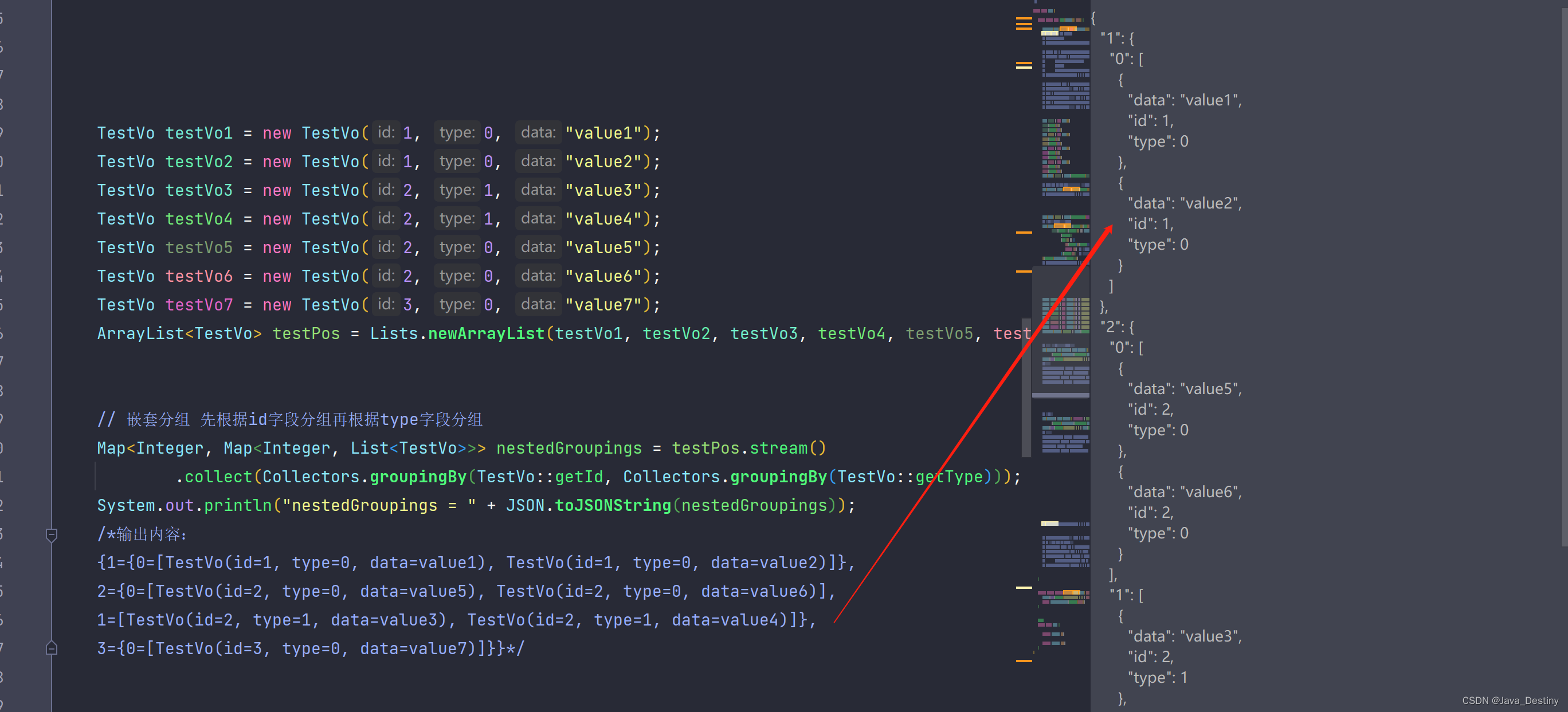
16、分组

嵌套分组
17、 先分组,再对分组里的集合经行判断,返回分组的key以及判断的结果

18、根据List中的对象中的List的值来分组
对象:
实现:

效果:
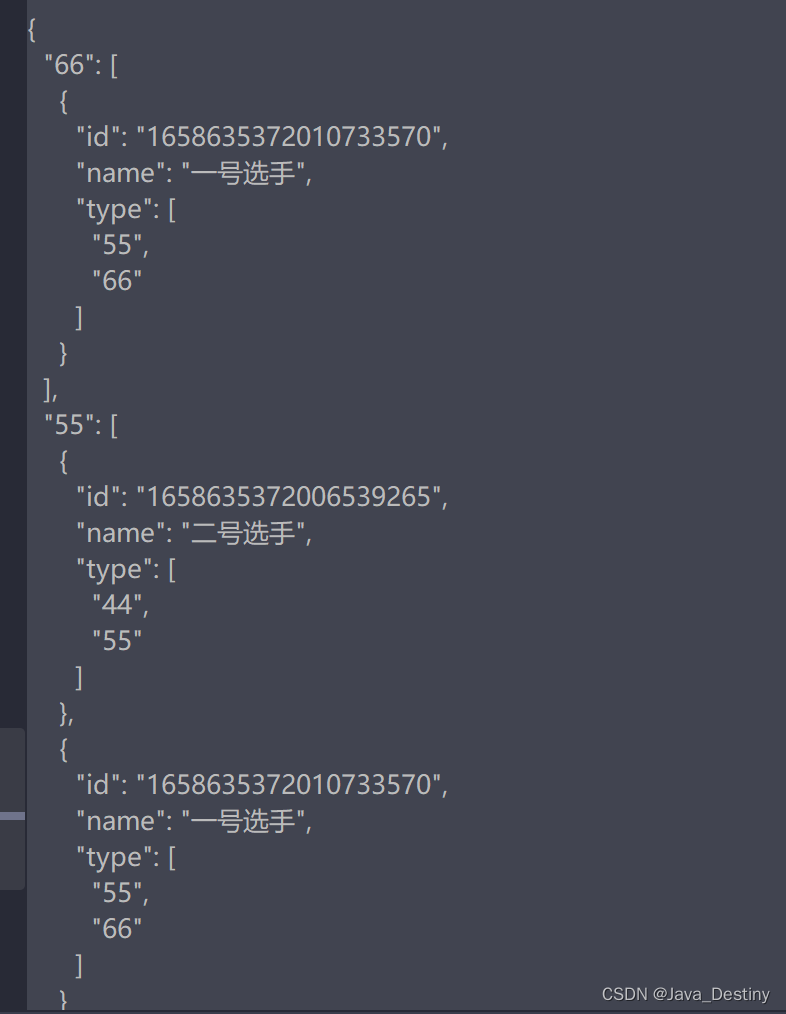
Map<String, List<Test>> test = list.stream()
// 过滤掉 type 为空的对象
.filter(p -> !CollectionUtils.isEmpty(p.getType()))
// 将每个 Test 拆分成多个键值对,其中键为 type,值为 Test 对象
.flatMap(p -> p.getType().stream()
.map(type -> new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(type, p)))
// 将拆分后的键值对按照键分组,并将每个键对应的值放入一个列表中
.collect(Collectors.toMap(AbstractMap.SimpleEntry::getKey,
// 创建一个只包含当前值的列表
e -> new ArrayList<>(Collections.singletonList(e.getValue())),
// 合并两个值(即两个列表)为一个列表
(l1, l2) -> {
l1.addAll(l2);
return l1;
}));
19.根据list中某个字段去重后并拼接


随手笔记
未完待续。。。。




 本文介绍了多种Java8的流处理和集合操作方法,包括字符串转数组、计算集合交集、去重、过滤、多条件过滤、合并列表并去重、排序、List到Map的转换、根据属性合并列表、流式分页、分组及复杂逻辑处理等。这些技巧有助于优化代码,提高效率。
本文介绍了多种Java8的流处理和集合操作方法,包括字符串转数组、计算集合交集、去重、过滤、多条件过滤、合并列表并去重、排序、List到Map的转换、根据属性合并列表、流式分页、分组及复杂逻辑处理等。这些技巧有助于优化代码,提高效率。
















 695
695

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








