一、FileOutputStream
FileOutputStream类,即文件输出流,是用于将数据写入 File的输出流。
它的构造方法主要有两个:

使用以上这两个构造方法创建 FileOutputStream对象,写数据时会自动覆盖前面写过的数据。要避免这种情况,可以使用下面这种构造方法,在第二个参数填入true就能实现追加写入。

我们使用到FileOutputStream类中的write()和close()方法,如下所示:

二、FileInputStream
FileInputStream类 从文件系统中的某个文件中获得输入字节。
它的构造方法和上面的类似,如图所示:

我们主要使用到FileInputStream类中read()方法读取数据,如下所示:

- int read():读取一个字节并返回,没有字节返回-1.
- int read(byte[]): 读取一定量的字节数,并存储到字节数组中,返回读取到的字节数。
三、文件复制、图片复制、视频复制——代码实现
接下来我们将使用FileInputStream和FileOutputStream来实现文件的复制操作。
import java.io.*;
public class FileInputStreamCopy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 文件对象
File wordFile = new File("D:\\programming\\IDEA\\save\\docx\\03 虚拟仪器报告-实验三.doc");
File pictureFile = new File("D:\\programming\\IDEA\\save\\docx\\QQ图片20210901172834.jpg");
File videoFile = new File("D:\\programming\\IDEA\\save\\docx\\VID_20210502_143040.mp4");
// 文件复制
wordCopy(wordFile);
// 图片复制
pictureCopy(pictureFile);
// 视频复制
videoCopy(videoFile);
}
public static void wordCopy(File file){
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
// 准备好复制过来的文件的新名字
String[] names = file.getPath().split("\\.");
String name = names[0]+"Copy."+names[1]; // 重命名
try {
// 文件字节输出、输出流对象
fis = new FileInputStream(file);
fos = new FileOutputStream(name);
// 读数据
int len = 0;
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
while ((len=fis.read(bytes))!=-1){
// 写数据
fos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
// 释放资源
fis.close();
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void pictureCopy(File file){
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
// 为复制过来的文件准备新名字
String[] names = file.getPath().split("\\.");
String name = names[0]+"Copy."+names[1]; // 新名字
try {
// 文件字节输入输出流
fis = new FileInputStream(file);
fos = new FileOutputStream(name);
// 读数据
int len=0;
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
while ((len=fis.read(bytes))!=-1){
fos.write(bytes,0, len);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
// 释放资源
try {
fis.close();
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void videoCopy(File file){
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
// 为复制过来的文件重命名
String[] names = file.getPath().split("\\.");
String name = names[0]+"Copy."+names[1];
try {
// 文件字节输入输出对象
fis = new FileInputStream(file);
fos = new FileOutputStream(name);
// 读数据
int len=0;
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
while ((len=fis.read(bytes))!=-1){
// 写数据
fos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
// 释放资源
fis.close();
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
没有运行程序前:
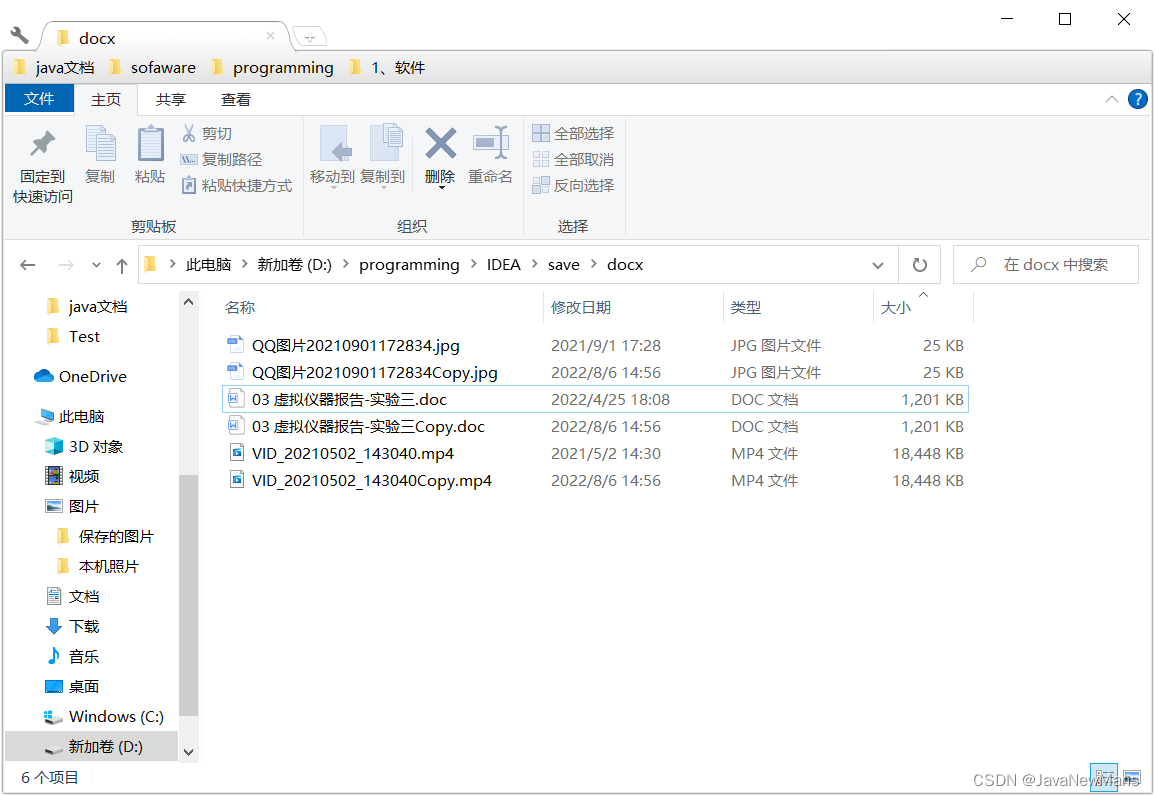
运行程序效果图:





 本文介绍了如何使用Java中的FileOutputStream和FileInputStream进行文件复制操作。详细阐述了FileOutputStream的构造方法及write、close方法,以及FileInputStream的read方法。通过实例展示了如何实现文件、图片和视频的复制功能。
本文介绍了如何使用Java中的FileOutputStream和FileInputStream进行文件复制操作。详细阐述了FileOutputStream的构造方法及write、close方法,以及FileInputStream的read方法。通过实例展示了如何实现文件、图片和视频的复制功能。
















 705
705

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








