前言
我在之前的博客中已经讲了堆的create、push、pop、destory,趁热打铁,我今天来讲一下堆排序 堆排序是一种很强大的排序方式,它的时间复杂度在O(N)的量级上,是可以和qsort的快排坐一桌的,不得不尝。
一、堆排序的思路
堆的特性使堆顶的数据总是最小或最大的(取决于是小堆还是大堆)
通过这个特性,我们首先想到的建堆思路是将一个数组中的元素像新插入的数据一样一个个的插入建堆(其实就是向上调整算法),再将数组中的数据一个一个pop出来
这种方式不是不行,但是存在效率上的问题
向上调整建堆方法的效率缺陷
向上调整算法是从儿子到父亲的调整算法
1、空间浪费:我们将数据一个一个pop出来后不可避免的要重新建一个数组来储存数据,在空间上是很大的浪费。
2、时间浪费 :向上调整算法在push是可靠的,但是在将数组建堆的时候被证明是低效的,采用这种方式无疑会造成时间上的浪费。
所以我们这里采用向下调整建堆,我接下来会分析为什么向上调整建堆比向下调整建堆时间复杂度高
二、向上调整建堆和向下调整建堆时间复杂度的比较
1、向上调整建堆时间复杂度的分析
向上调整建堆的思路是将数组中每一个数字当成刚刚插入进来的数据,相当于是在一直push
假如数组中的数据有N个,我们就执行了N次push操作。
但N次push操作不是我们想要的结果,我们还需要算出在这些push操作中最坏执行了几次操作,并将他们的总和算出来
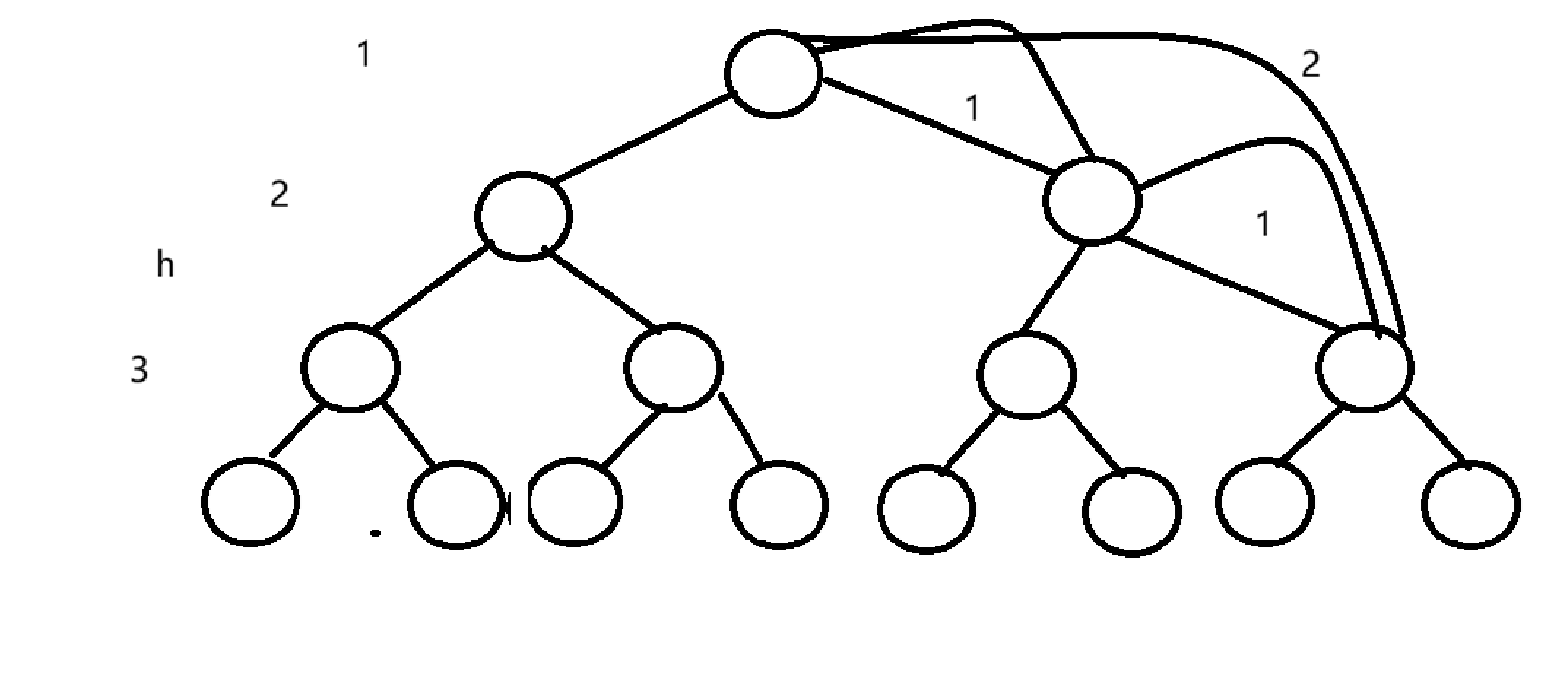
我们这里使用N是不好计算的,我们先采用h来进行计算,再使用N=2^h+1的关系来计算出执行次数和N之间的关系
从第二层开始看,第二层有2^1个元素,每个元素需要执行一次向上调整。
看第三层,第三层有2^2个元素,每个元素执行两次向上调整。
我们不难推出,如果按照每一层都是满的的理想情况来分析
在第h层,这一层有2^(h-1)个数据,每一个数据要执行(h-1)次向上调整
我们将每一层的次数求和求和
我们使用一下高中的数学知识:错位相减法
错位相减,可以算出
化简得:
我们将N=2^h带入得:h=log(N+1)
时间复杂度是N*logN
2、向下调整建堆时间复杂度的分析
向下调整建堆是将数组中的元素拆开来,一组一组的调整顺序
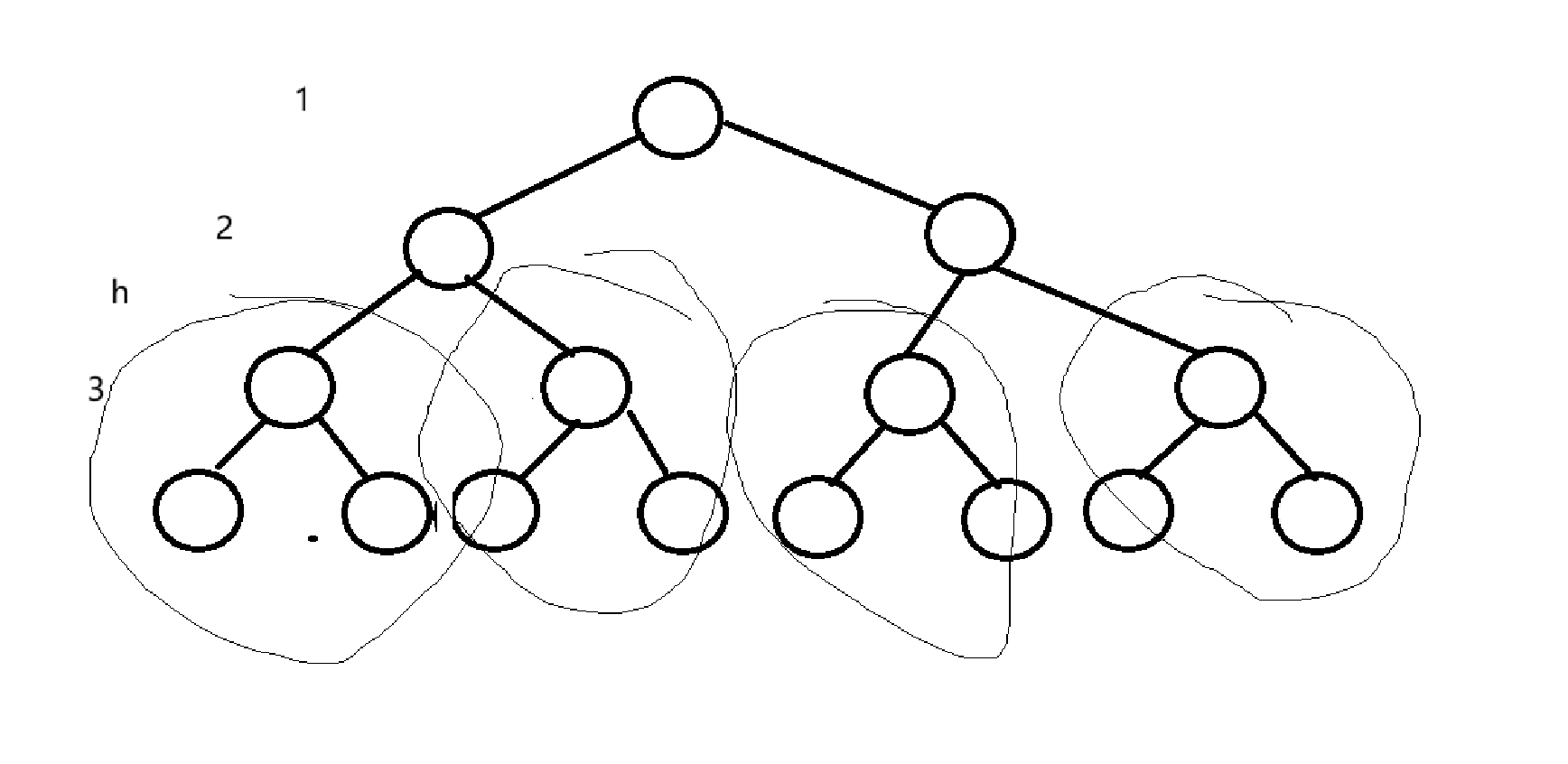
先调整最下面的一组
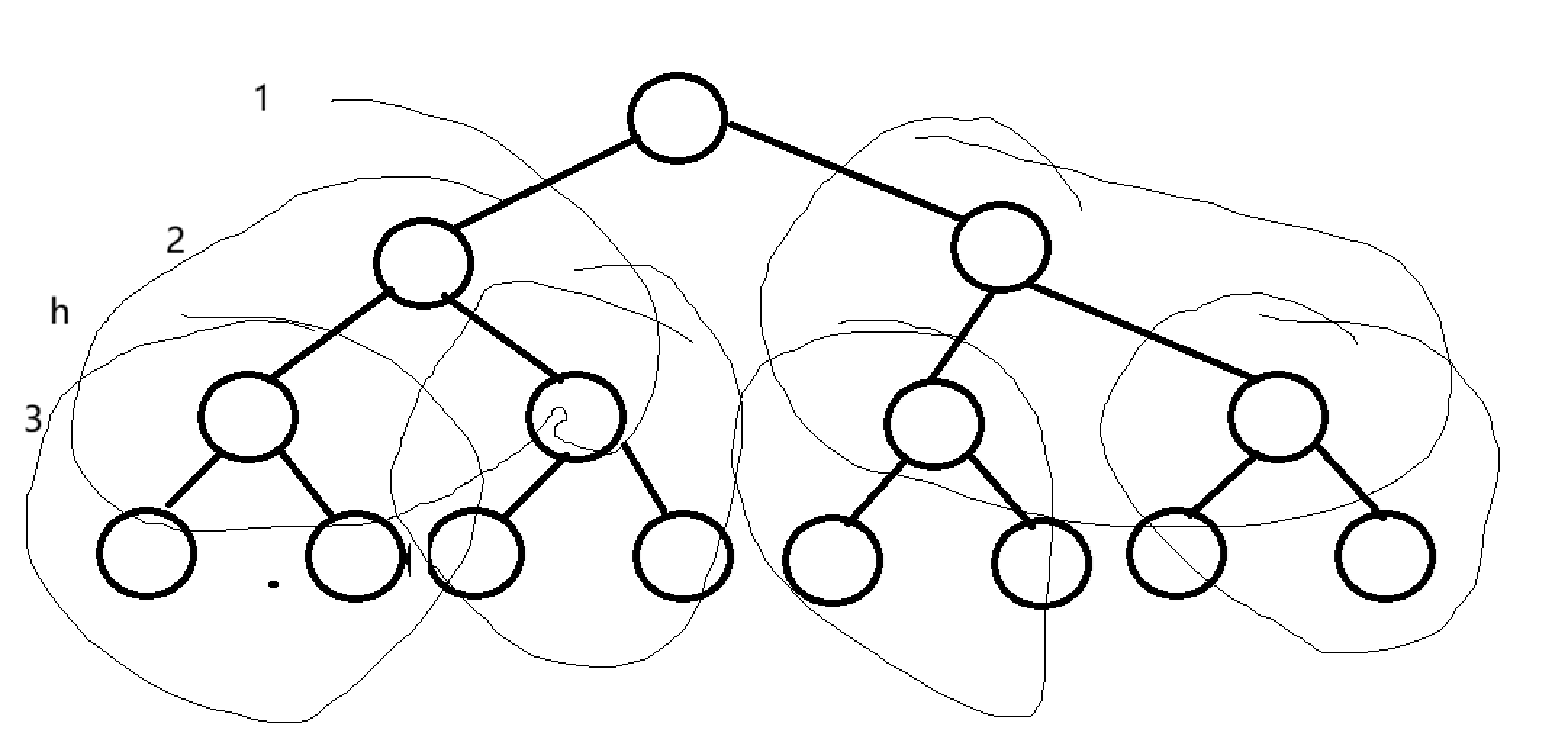
再调整上面一点的一组
我们经过计算得知,向下调整建堆的时间复杂度是O(N)(计算过程我就不写了)
3、反思
其实我们也可以直接分析,向上调整算法是大的乘大的,高度越往下乘的数越大
二向下调整是大的乘小的,越往下乘的越小
加起来肯定是向下调整建堆时间复杂度低
三、堆排序的实现
1、思路
堆排序的思路主要是升序建大堆,降序建小堆
我们接下来以升序排列做例子
建大堆可以将所有元素中的最大的元素放到堆顶,我们此时再将这个元素和最后一个元素交换,并视作这个元素不在数组中
此时我们在对堆进行一次向下调整,使剩下的数据中最大的数据被提上来,再交换
重复以上步骤,我们就可以做到每次将一个最大的数字放到数组的最后,执行完的时候,数组就已经是升序了
2、建堆
我们之前了解到向下调整算法,我们这里应该如何将它用于我们的建堆呢
我们先来回顾一下向下调整算法
这是向下调整算法的函数:
void AdjustDown_s(HpDataType* arr, int size,int parent)//向下调整-小堆
{
//这里多设置了一个接口,是为了方便以后数组建堆算法调用
int child = 0;
while (parent * 2 + 1 < size)
{
child = parent * 2 + 1;
int small = child;//假设法,避免了if else 的使用
if (child + 1 < size && arr[child] > arr[child + 1])
{
small = child + 1;
}
if (arr[small] < arr[parent])
{
Swap(&arr[small], &arr[parent]);
parent = small;//参数错了,原来是child,这里要注意
}
else//因为之前的数据都是有序地,只要在某一次验证中通过了,就不用进行接下来的验证了
{
break;
}
}
} 我们想要将数组接入函数,就需要适配接口,每一次传一个parent进来,第一个parnet就是我们找到的第一个父亲,之后将父亲的值依次--就行
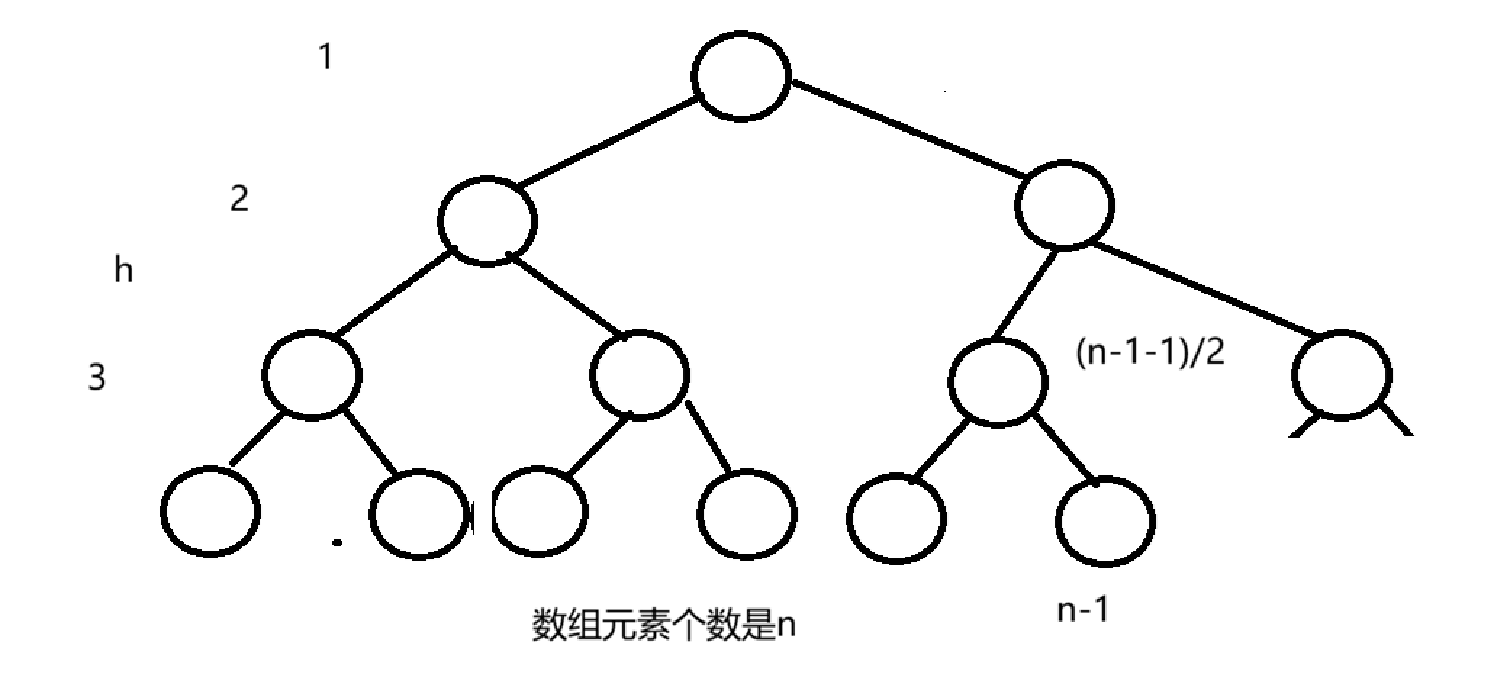
第一个parent就是(n-2)/2
void ToBigHP(HpDataType* arr, int size)
{
for (int i = (size - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
AdjustDown_b(arr, size, i);
}
}3、排序
我们现在实现排序
void ToUp(HpDataType* arr, int size)
{
ToBigHP(arr, size);
while (size > 0)
{
Swap(&arr[0], &arr[size - 1]);
size--;
AdjustDown_b(arr, size, 0);
}
}四、代码(包含上一期)
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<time.h>
typedef int HpDataType;
typedef struct HP
{
HpDataType* arr;
int size;
int capacity;
}HP;
HP* HPIint();//初始化堆
void DestoryHP(HP* hp);//销毁堆
void HPPush(HP* hp,int val);//向堆中插入数据
void AdjustUp_s(HpDataType* arr, int size);//向上调整
void AdjustDown_s(HpDataType* arr, int size, int parent);
void AdjustDown_b(HpDataType* arr, int size, int parent);
void AdjustUp_b(HpDataType* arr, int size);//向上调整-大堆
void Swap(HpDataType* p1, HpDataType* p2);//交换两个数
HpDataType HPPop(HP* hp);//返回最顶端的数
bool HPIsEmpty(HP* hp);//判断堆是否是空的
void ToSmallHP(HpDataType* arr, int size);//将一个数组转化为小堆
void ToBigHP(HpDataType* arr, int size);//将一个数组转化为大堆
void ToUp(HpDataType* arr, int size);//将一个数组升序排列
void ToDown(HpDataType* arr, int size);//将一个数组降序排列
void CreaRanNum();//生成随机数
void FindMaxK(int k);//找到前k个最大数#include"hp.h"
HP* HPIint()
{
HP* hp = (HP*)malloc(sizeof(HP));
if (NULL == hp)
{
perror("malloc");
return NULL;
}
hp->capacity = 4;
hp->arr = (HpDataType*)malloc(sizeof(HpDataType) * hp->capacity);
hp->size = 0;
return hp;
}
void Swap(HpDataType* p1, HpDataType* p2)
{
HpDataType* temp = 0;
temp = *p1;
*p1 = *p2;
*p2 = temp;
}
void AdjustUp_s(HpDataType* arr, int size)//向上调整-小堆
{
int child = size - 1;
int parent = 0;
while (child > 0)
{
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
if (arr[parent] > arr[child])
{
Swap(&arr[parent], &arr[child]);
}
child = parent;
}
}
void AdjustDown_s(HpDataType* arr, int size,int parent)//向下调整-小堆
{
//这里多设置了一个接口,是为了方便以后数组建堆算法调用
int child = 0;
while (parent * 2 + 1 < size)
{
child = parent * 2 + 1;
int small = child;//假设法,避免了if else 的使用
if (child + 1 < size && arr[child] > arr[child + 1])
{
small = child + 1;
}
if (arr[small] < arr[parent])
{
Swap(&arr[small], &arr[parent]);
parent = small;//参数错了,原来是child,这里要注意
}
else//因为之前的数据都是有序地,只要在某一次验证中通过了,就不用进行接下来的验证了
{
break;
}
}
}
void AdjustUp_b(HpDataType* arr, int size)//向上调整-大堆
{
//这个可以改为
int child = size - 1;
int parent = 0;
while (child > 0)
{
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
if (arr[parent] < arr[child])
{
Swap(&arr[parent], &arr[child]);
}
child = parent;
}
}
void AdjustDown_b(HpDataType* arr, int size,int parent)//向下调整-大堆
{
int child = 0;
while (parent * 2 + 1 < size)
{
child = parent * 2 + 1;
int big = child;
if (child + 1 < size && arr[child] < arr[child + 1])
{
big = child + 1;
}
if (arr[big] > arr[parent])
{
Swap(&arr[big], &arr[parent]);
parent = big;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void HPPush(HP* hp, int val)
{
if (hp->size == hp->capacity)
{
hp->capacity += 4;
HP* ret = realloc(hp->arr, hp->capacity*sizeof(HpDataType));
if (NULL != ret)
{
hp->arr = ret;
}
}
hp->arr[hp->size] = val;
hp->size++;
AdjustUp_s(hp->arr,hp->size);
}
HpDataType HPPop(HP* hp)
{
if (HPIsEmpty(hp))
{
printf("\n警告,堆现在是空的\n");
return -1;
}
else
{
HpDataType ret = hp->arr[0];
Swap(&hp->arr[0], &hp->arr[hp->size - 1]);
hp->size--;//代表被换下的数据已经是失效的了
AdjustDown_s(hp->arr, hp->size , 0);
return ret;
}
}
void DestoryHP(HP* hp)
{
free(hp->arr);
free(hp);
}
bool HPIsEmpty(HP* hp)
{
if (hp->size == 0)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
void ToSmallHP(HpDataType* arr, int size)
{
for (int i = (size - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
AdjustDown_s(arr, size, i);
}
}
void ToBigHP(HpDataType* arr, int size)
{
for (int i = (size - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
AdjustDown_b(arr, size, i);
}
}
void ToUp(HpDataType* arr, int size)
{
ToBigHP(arr, size);
while (size > 0)
{
Swap(&arr[0], &arr[size - 1]);
size--;
AdjustDown_b(arr, size, 0);
}
}
void ToDown(HpDataType* arr, int size)
{
ToSmallHP(arr, size);
while (size > 0)
{
Swap(&arr[0], &arr[size - 1]);
size--;
AdjustDown_s(arr, size,0);
}
}
void CreaRanNum()
{
FILE* file = NULL;
fopen_s(&file, "text.txt", "w");
if (NULL == file)
{
perror("fopen_s fail");
return NULL;
}
int n = 10000;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
fprintf(file, "%d\n", (rand() + i) % 100000);
}
fclose(file);
file = NULL;
}
void FindMaxK(int k)
{
FILE* file = NULL;
fopen_s(&file, "text.txt", "r");
if (NULL == file)
{
perror("fopen_s fail");
return;
}
int ret = 0;
int* arr = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * k);
if (NULL == arr)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
ret = fscanf_s(file, "%d\n", &arr[i]);
}
//输入前k个数据
ToSmallHP(arr, k);
//将前k个数据搞成小堆的形式
int n = 0;
while ((ret = fscanf_s(file, "%d\n", &n)) > 0)
{
if (n > arr[0])
{
arr[0] = n;
AdjustDown_s(arr, k, 0);
}
}
int copy = k;
while (k > 0)
{
Swap(&arr[0], &arr[k - 1]);
k--;
AdjustDown_s(arr, k, 0);
}
k = copy;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
}




















 1085
1085

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








