目录
一、引言
上一篇博文详细介绍了什么是类以及类相关的重要内容,只说不练可不行。今天带大家用类的知识去实现日期计算器,具体要实现什么功能呢?这里图1.1是网上找到的日期计算器,图1.2是我们今天去实现的日期计算器的菜单。
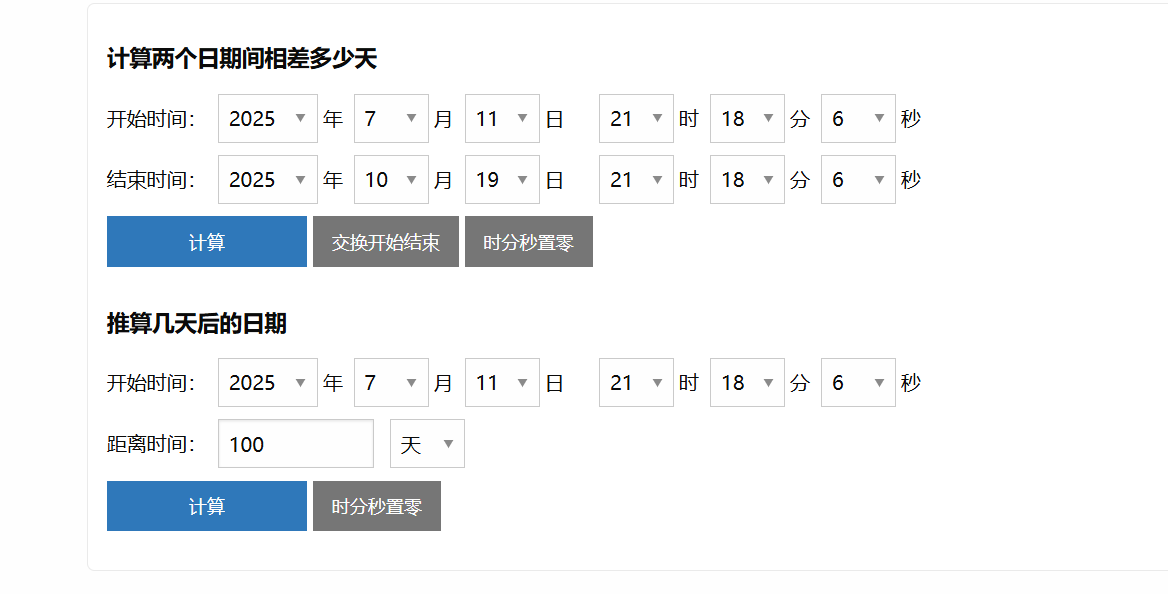
图1.1 日期计算器参考
void menu()
{
cout << "*********日期计算器*********" << endl;
cout << "***************************" << endl;
cout << "******1、几天后的日期*******" << endl;
cout << "******2、几天前的日期*******" << endl;
cout << "***3、日期与日期相差天数****" << endl;
cout << "*******4、日期比大小********" << endl;
cout << "**********5、结束***********" << endl;
cout << "***************************" << endl;
}图1.2 日期计算器菜单
二、完成日期类的基础创建
了解一个类首先得从它的成员变量入手,然后再去了解它的构造函数和析构函数,之后再去根据需求去了解相应的成员函数。
1.成员变量
这里日期类的成员变量显而易见的是年,月,日去记录日期,当然如果有什么特殊需求也可以根据需求增添成员变量,这里我的仅作参考。
class Date
{
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
2.构造函数和析构函数
构造函数支持函数重载,所以这里可以写多个构造函数,如默认构造和普通构造以及拷贝构造,不过我只写了全缺省的默认构造函数和拷贝构造函数,因为这里这两个构造函数就够我们后面接口使用了。
class Date
{
public:
// 全缺省的构造函数
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1)
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
if (!CheckDate())//检查日期
{
cout << "非法日期:";
ppfrint();//打印非法日期
}
}
// 拷贝构造函数
Date(const Date& d)
{
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
}
// 析构函数
~Date()
{
_year = _month = _day = 0;
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
这里用构造函数进行初始化的同时一定要去检查,输入的是否是合法的日期,不然输入个2005年13月40日这种日期出来,后面的接口必然出错,同时也没意义。用到了CheckDate函数和ppfrint函数,我们就需要写出来这两个函数。
class Date
{
public:
// 全缺省的构造函数
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1)
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
if (!CheckDate())//检查日期
{
cout << "非法日期:";
ppfrint();//打印非法日期
}
}
// 拷贝构造函数
Date(const Date& d)
{
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
}
// 析构函数
~Date()
{
_year = _month = _day = 0;
}
bool CheckDate()//检查日期
{
if (_month < 1 || _month>12 || _day<1 || _day>GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
{
return false;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
void ppfrint()//打印日期
{
cout << _year <<'/'<< _month <<'/'<< _day << endl;//中间用了符号/分开
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
3.运算符重载
在实现功能的接口之中,必然会用到很多运算符。这里我先实现了最简单的赋值运算符重载和比较日期的运算符重载以及输入输出运算符重载,这里比较运算符的重载使用了复用的方法,实现了一个>,其他比较基本上就都实现了,这里实现>的思路其实也很简单就是先比较年谁大,如果相等再去比较月谁大,如果相等再去比较日谁大。==的运算符重载就是年月日都相等这两个日期就相等。
class Date
{
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d);
friend istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d);
public:
// 全缺省的构造函数
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1)
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
if (!CheckDate())//检查日期
{
cout << "非法日期:";
ppfrint();//打印非法日期
}
}
// 拷贝构造函数
Date(const Date& d)
{
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
}
// 析构函数
~Date()
{
_year = _month = _day = 0;
}
bool CheckDate()//检查日期
{
if (_month < 1 || _month>12 || _day<1 || _day>GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
{
return false;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
void ppfrint()//打印日期
{
cout << _year <<'/'<< _month <<'/'<< _day << endl;//中间用了符号/分开
}
// 赋值运算符重载
// d2 = d3 -> d2.operator=(&d2, d3)
Date& operator=(const Date& d)
{
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
return *this;
}
// >运算符重载
bool operator>(const Date& d)
{
if (_year > d._year)
{
return true;
}
else if (_year == d._year)
{
if (_month > d._month)
{
return true;
}
else if (_month == d._month)
{
if (_day > d._day)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
// ==运算符重载
bool operator==(const Date& d)
{
if (_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day == d._day)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
// >=运算符重载
bool operator >= (const Date& d)
{
return *this > d || *this == d;
}
// <运算符重载
bool operator < (const Date& d)
{
if ((*this) == d)
{
return false;
}
else
{
return !((*this) > d);
}
}
// <=运算符重载
bool operator <= (const Date& d)
{
return *this < d || *this == d;
}
// !=运算符重载
bool operator != (const Date& d)
{
return !((*this) == d);
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d)
{
out << d._year << "年" << d._month << "月" << d._day << "日" << endl;
return out;
}
istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d)
{
while (1)
{
cout << "请输入年月日:";
in >> d._year >> d._month >> d._day;
if (!d.CheckDate())
{
cout << "输入为非法日期" << endl;
cout << "请重新输入" << endl;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
return in;
}三、完成日期类相应接口的实现
1.几天后的日期
思路:在实现几天后的日期这个接口,其实是去重载+=运算符。通过这个+=运算符去计算一个日期+多少天后的日期是多少。这里实现+=运算符的重载的思路是先把加的天数全加到_day(日)上面去,如果加上去之后这里的_day大于了当前月的天数,就得让_day去减去当月的天数,再让_month月增加一月,一直循环,直到_day小于当月的天数为止。这里有种情况要特殊讨论,就是当月是十二月增加一月之后就变成十三月了,这肯定不符合规定,所以我们单独考虑这情况让十三月变成一月,然后年再加一年即可。
Date& operator+=(int day)
{
if (day > 0)
{
_day += day;
while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
{
_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
_month++;
if (_month > 12)
{
_year++;
_month = 1;
}
}
}
else
{
*this -= (-day);
}
return *this;
}
// 日期+天数
Date operator+(int day)
{
Date tmp = *this;
tmp += day;
return tmp;
}
// 前置++
Date& operator++()
{
*this += 1;
return *this;
}
// 后置++
Date operator++(int)
{
Date tmp = *this;
*this += 1;
return tmp;
}这里的+,前置++,后置++运算符重载,复用了+=运算符就一起实现了。这里还有一个叫GetMonthDay的函数其实就是年有闰年和平年的区别,闰年2月有29天,平年2月有28天,肯定需要区分,就使用了这个函数去获取每月的天数。
// 获取某年某月的天数
int GetMonthDay(int year, int month)
{
static int a[13] = { -1, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30,31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31 };
if (month == 2 && (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year
% 400 == 0))
{
return 29;
}
else if (month == 2)
{
return 28;
}
return a[month];
}我这里使用的是一个数组去记录每月的天数,然后区分开2月的情况,数组多了一个值是为了让数组的下标与年份相配。
2.几天前的日期
思路:在实现几天前的日期这个接口,其实是去重载-=运算符。通过这个-=运算符去计算一个日期-多少天后的日期是多少。这里我发现网上找的日期计算器支持-负天数的情况,所以我也是一样先判断了一下day的正负,如果是负数的情况下直接复用我们前面的+=即可。如果是正数我先把这个数减在_day(日)上面,如果_day是大于0的那么我就直接返回,不需要其他计算。如果_day是小于等于0的情况,我就需要进一步计算。这里进一步计算整体思路让_day去加当前月的上一月的天数,月再减去一月,一直循环直到_day大于0。不过有一种特殊情况要单独列出来,当当前月是一月,一月的上一月应该是十二月,而不是0月。一月减去一月之后变成十二月,年也得减去一年。
// 日期-=天数
Date& operator-=(int day)
{
if (day > 0)
{
_day -= day;
while (_day <= 0)
{
if (_month == 1)
{
_day += GetMonthDay(_year, 12);
_month--;
}
else
{
_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month - 1);
_month--;
}
if (_month < 1)
{
_year--;
_month = 12;
}
}
}
else
{
*this += (-day);
}
return *this;
}
Date operator-(int day)
{
Date tmp = *this;
tmp -= day;
return tmp;
}
// 后置--
Date operator--(int)
{
Date tmp = *this;
*this -= 1;
return tmp;
}
// 前置--
Date& operator--()
{
*this -= 1;
return *this;
}这里的-,前置--,后置--运算符重载,复用了+=运算符就一起实现了。
3.日期-日期
这里的日期减去日期是日期计算器最有难度的地方,有很多种方法去实现,这里我实现了两种方法。
法1:思路:这个方法比较偷懒简洁,但是效率很低,就是我先假定减数日期为较大的用一个max指向,被减数日期为较小的用一个min指向,这个时候符号变量是正数,如果比较大小不对,就交换一下即可max和min的指向即可。然后设置一个n去记录差的天数,进入循环当min和max相等循环停止,使用++运算符重载一直让min去加,n也++,加到相等了n的值就是它们的差值再去乘以符号变量即可。
int operator-(const Date& d) const
{
Date max = *this;
Date min = d;
int flag = 1;
if (*this < d)
{
max = d;
min = *this;
flag = -1;
}
int n = 0;
while (min != max)
{
++min;
++n;
}
return n * flag;
}法2:思路:这个方法思路难一点,不过效率高一点。我是通过先判断两个日期年相等不,不相等我让减数日期的年去改变和被减数日期的年相等,然后让记录天数的tmp加上年的天数,这里要区分闰年还是平年,减数日期年大于被减数日期年我就加正数,相反加负数。月和日的计算和这个基本上差不多,大家看代码就可以看懂了。注意一下:这里的月去计算的时候是为了让两个月相等,那么当减数日期月大于被减数日期月的时候就需要从减数日期的当月的上一个月开始减,因为当月还没过完,而当减数日期月小于被减数日期月的时候就需要从减数日期的当月开始加,因为当月对于被减数日期已经过完了。例如:减数日期是2004年05月10日,被减数日期是2004年03月20日,为了让月相等就需要让tmp去加4月份和3月份的天数,减数日期变成2004年3月10日。
// 日期-日期
int operator-(const Date& d)
{
int tmp = 0;
Date hmp = *this;
while (hmp._year != d._year)
{
if (hmp._year > d._year)
{
if ((hmp._year % 4 == 0 && hmp._year % 100 != 0) ||
(hmp._year % 400 == 0))
{
tmp += 366;
}
else
{
tmp += 365;
}
hmp._year--;
}
else
{
if (((hmp._year + 1) % 4 == 0 &&
(hmp._year + 1) % 100 != 0) || ((hmp._year + 1) % 400 == 0))
{
tmp += (-366);
}
else
{
tmp += (-365);
}
hmp._year++;
}
}
while (hmp._month != d._month)
{
if (hmp._month > d._month)
{
tmp += GetMonthDay(hmp._year,hmp._month-1);
hmp._month--;
}
else
{
tmp-= GetMonthDay(hmp._year,hmp._month);
hmp._month++;
}
}
while (hmp._day != d._day)
{
if (hmp._day > d._day)
{
tmp += (hmp._day - d._day);
hmp._day = d._day;
}
else
{
tmp -= (hmp._day - d._day);
hmp._day = d._day;
}
}
return tmp;
}4.日期比较大小
这个接口其实意义不是很大,前面的比较运算符重载已经实现了这个功能,这里菜单加上这个功能让功能多一点更加完善而已。
四、整体代码
主函数代码:
int main()
{
menu();
int year = 0, month = 0, day = 0;
cout << " 请输入当前日期或者你想查询的日期 " << endl;
cin >> year >> month >> day;
Date MAX(year, month, day);
cout << " 请输入你想完成的日期计算 " << endl;
int caoz = 0;
cin >> caoz;
switch (caoz)
{
case(1):
{
cout << " 当前操作为几天后的日期,请输入几天后的 " << endl;
int dayt = 0;
cin >> dayt;
MAX += dayt;
printf("当前日期%d天后为--", dayt);
MAX.ppfrint();
}
case(2):
{
cout << " 当前操作为几天前的日期,请输入几天前的 " << endl;
int monday = 0;
cin >> monday;
MAX -= monday;
printf("当前日期%d天前为--", monday);
MAX.ppfrint();
break;
}
case(3):
{
cout << " 当前操作为日期与日期的相差,请输入想要与当前日期相差的日期 " << endl;
int year1 = 0, month1 = 0, day1 = 0;
cin >> year1 >> month1 >> day1;
Date MINI(year1, month1, day1);
int tel = MAX - MINI;
printf("相差 %d 天", tel);
break;
}
case(4):
{
cout << " 当前操作为日期比大小,请输入想要与当前日期比较的日期 " << endl;
int year2 = 0, month2 = 0, day2 = 0;
cin >> year2 >> month2 >> day2;
Date MINII(year2, month2, day2);
if (MAX > MINII)
{
cout << "较大日期为:" << endl;
MAX.ppfrint();
}
else
{
cout << "较大日期为:" << endl;
MINII.ppfrint();
}
}
case(5):
{
break;
}
default:
{
cout << "输入异常,自动结束" << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}类的相关代码:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Date
{
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d);
friend istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d);
public:
// 全缺省的构造函数
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1)
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
if (!CheckDate())
{
cout << "非法日期:";
ppfrint();
}
}
// 拷贝构造函数
// d2(d1)
Date(const Date& d)
{
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
}
// 赋值运算符重载
// d2 = d3 -> d2.operator=(&d2, d3)
Date& operator=(const Date& d)
{
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
return *this;
}
// 析构函数
~Date()
{
_year = _month = _day = 0;
}
bool CheckDate()
{
if (_month < 1 || _month>12 || _day<1
|| _day>GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
{
return false;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
// 获取某年某月的天数
int GetMonthDay(int year, int month)
{
static int a[13] = { -1, 31, 28, 31, 30,
31, 30,31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31 };
if (month == 2 && (year % 4 == 0 &&
year % 100 != 0) || (year% 400 == 0))
{
return 29;
}
else if (month == 2)
{
return 28;
}
return a[month];
}
void dateflash(int year, int month, int day)
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
if (!CheckDate())
{
cout << "非法日期:";
ppfrint();
}
}
Date& operator+=(int day)
{
if (day > 0)
{
_day += day;
while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
{
_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
_month++;
if (_month > 12)
{
_year++;
_month = 1;
}
}
}
else
{
*this -= (-day);
}
return *this;
}
// 日期+天数
Date operator+(int day)
{
Date tmp = *this;
tmp += day;
return tmp;
}
// 日期-天数
Date operator-(int day)
{
Date tmp = *this;
tmp -= day;
return tmp;
}
// 日期-=天数
Date& operator-=(int day)
{
if (day > 0)
{
_day -= day;
while (_day <= 0)
{
if (_month == 1)
{
_day += GetMonthDay(_year, 12);
_month--;
}
else
{
_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month - 1);
_month--;
}
if (_month < 1)
{
_year--;
_month = 12;
}
}
}
else
{
*this += (-day);
}
return *this;
}
// 前置++
Date& operator++()
{
*this += 1;
return *this;
}
// 后置++
Date operator++(int)
{
Date tmp = *this;
*this += 1;
return tmp;
}
//后置--
Date operator--(int)
{
Date tmp = *this;
*this -= 1;
return tmp;
}
// 前置--
Date& operator--()
{
*this -= 1;
return *this;
}
// >运算符重载
bool operator>(const Date& d)
{
if (_year > d._year)
{
return true;
}
else if (_year == d._year)
{
if (_month > d._month)
{
return true;
}
else if (_month == d._month)
{
if (_day > d._day)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
// ==运算符重载
bool operator==(const Date& d)
{
if (_year == d._year && _month == d._month
&& _day == d._day)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
// >=运算符重载
bool operator >= (const Date& d)
{
return *this > d || *this == d;
}
// <运算符重载
bool operator < (const Date& d)
{
if ((*this) == d)
{
return false;
}
else
{
return !((*this) > d);
}
}
// <=运算符重载
bool operator <= (const Date& d)
{
return *this < d || *this == d;
}
// !=运算符重载
bool operator != (const Date& d)
{
return !((*this) == d);
}
// 日期-日期
int operator-(const Date& d)
{
int tmp = 0;
Date hmp = *this;
while (hmp._year != d._year)
{
if (hmp._year > d._year)
{
if ((hmp._year % 4 == 0 && hmp._year % 100 != 0)
|| (hmp._year % 400 == 0))
{
tmp += 366;
}
else
{
tmp += 365;
}
hmp._year--;
}
else
{
if (((hmp._year + 1) % 4 == 0 &&
(hmp._year + 1) % 100 != 0) || ((hmp._year + 1) % 400 == 0))
{
tmp += (-366);
}
else
{
tmp += (-365);
}
hmp._year++;
}
}
while (hmp._month != d._month)
{
if (hmp._month > d._month)
{
tmp += GetMonthDay(hmp._year,hmp._month-1);
hmp._month--;
}
else
{
tmp-= GetMonthDay(hmp._year,hmp._month);
hmp._month++;
}
}
while (hmp._day != d._day)
{
if (hmp._day > d._day)
{
tmp += (hmp._day - d._day);
hmp._day = d._day;
}
else
{
tmp -= (hmp._day - d._day);
hmp._day = d._day;
}
}
return tmp;
}
//int operator-(Date& d)
//{
// Date max = *this;
// Date min = d;
// int flag = 1;
// if (*this < d)
// {
// max = d;
// min = *this;
// flag = -1;
// }
// int n = 0;
// while (min != max)
// {
// ++min;
// ++n;
// }
// return n * flag;
//}
void ppfrint()
{
cout << _year <<'/'<< _month <<'/'<< _day << endl;
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d)
{
out << d._year << "年" << d._month << "月" << d._day << "日" << endl;
return out;
}
istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d)
{
while (1)
{
cout << "请输入年月日:";
in >> d._year >> d._month >> d._day;
if (!d.CheckDate())
{
cout << "输入为非法日期" << endl;
cout << "请重新输入" << endl;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
return in;
}
void menu()
{
cout << "*********日期计算器********" << endl;
cout << "***************************" << endl;
cout << "******1、几天后的日期******" << endl;
cout << "******2、几天前的日期******" << endl;
cout << "***3、日期与日期相差天数***" << endl;
cout << "*******4、日期比大小*******" << endl;
cout << "**********5、结束**********" << endl;
cout << "***************************" << endl;
}五、总结
日期计算器的实现可以很好对类和对象进行复习,而且对于日期减去日期的接口对我们的日常生活也是有需要的,希望我的实现思路能够帮助到你,有些思路我想尽可能说清楚就会有一些冗余,希望大家不要介意,有错误的地方也请温柔的指出来谢谢。人生最多三万多天,希望我们都能够努力过好每一天,加油!






















 554
554

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








