数组的特点
1.一段连续的内存,只能存储相同类型的数据,只需要知道第一个索引的地址,就能快速找到其他数据
优点: 查找数据快速,时间复杂度为O(1)
缺点 添加,删除操作慢
为啥数组的索引是从0开始?
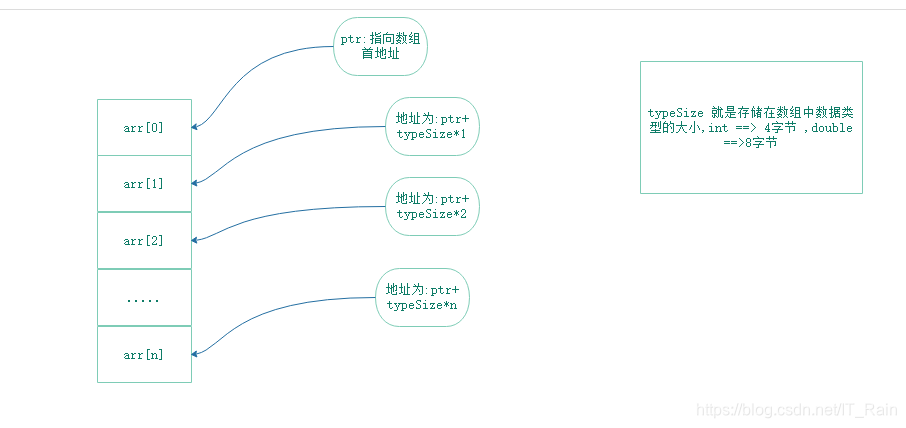
因为数组是连续的一段内存,而且数组的地址表示的是数组第一个数据的地址,比如有一个数组里面有n个数据
array[0] 的地址是 100001,
那么 array[1]的地址 就是 100001 + 数组类型的typeSize1,
array[2]的地址 就是 100001 + 数组类型的typeSize2,
array[n]的地址 就是 100001 + 数组类型的typeSize*n,
如果要用 1表示第一个数组的位置,那么
array[1] 就是 100001 + typeSize*(1-1)
array[2] 就是 100001 + typeSize*(2-1)
array[2] 就是 100001 + typeSize*(3-1)
array[n] 就是 100001 + typeSize*(n-1)
会多一个 减 的操作
模拟java ArrayList 数组结构
/**
* @program: javalearning
* @description: ${模拟数组}
* @author: Skipper
* @create: 2021-04-12 19:42
**/
public class MyArray {
/**
* 存储数据的数组
*/
Object [] data ;
/**
* 有效数据的长度
*/
private int size = 0;
/**
* 扩容因子(数组长度达到 size * expansionFactor 的时候 会触发扩容)
*/
final double expansionFactor = 0.75;
/**
* 默认数组长度(16)
*/
int defaultLength = 1 << 4;
/**
* 无参构造函数
*/
public MyArray() {
data = new Object[this.defaultLength];
}
/**
*
* @param defaultLength
*/
public MyArray(int defaultLength) {
this.defaultLength = defaultLength;
data = new Object[this.defaultLength];
}
/**
* 尾部添加
* @param o
* @return 返回所在的索引值
*/
public int add(Object o){
if (o == null){
return -1;
}
//先计算扩容,再添加
resize();
int index = size;
this.data[index] = o;
++size;
return index;
}
/**
* 往指定地方添加index
* @param index 时间复杂度为 O(n)
* @param o
* @return
*/
public boolean add(int index ,Object o){
if (!checkIndex(index) || o == null){
return false;
}
resize();
for (int i = size;i >index;--i){
this.data[i] = this.data[i-1];
}
this.data[index] = o;
++size;
return true;
}
/**
* 删除某个对象,返回对象所在的索引值 //时间复杂度为 O(n^2)
* @param o
* @return
*/
public int remove(Object o){
if (o == null){
return -1;
}
for (int i = 0;i< size;++i){
if (this.data[i].equals(o)){
if (remove(i) != null){
return i;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
/**
* 删除index 下标对应的对象 //时间复杂度为 O(n)
* @param
* @return 删除的对象
*/
public Object remove(int index){
if (!checkIndex(index)){
return null;
}
Object o = this.data[index];
for (int i = index;i< size-1;++i){
this.data[i] = this.data[i+1];
}
this.data[size-1] = null;
--size;
return o;
}
/**
* 赋值
* @param index
* @param o
* @return
*/
public boolean set(int index,Object o){
if (!checkIndex(index) || o == null){
return false;
}
this.data[index] = o;
return true;
}
/**
* 获取数据
* @param index
*/
public Object get(int index){
if (!checkIndex(index) ){
return null;
}
return this.data[index];
}
/**
* 清除
*/
public void clear(){
for (int i = 0;i< size;++i){
this.data[i] = null;
}
size =0;
}
/**
* 获取数组长度
* @return
*/
public int size(){
return this.size;
}
/**
* 判断数组越界
* @param index
* @return
*/
private boolean checkIndex( int index){
if (index <0 || index >= size){
return false;
}
return true;
}
/**
* 扩容
*/
private void resize(){
if (this.data == null){
return;
}
if (data.length * expansionFactor <= size){
int oldLength = data.length; //原来数组长度
int newLength = oldLength + (oldLength >> 1); //扩容后的数组长度 1.5倍扩容
data = Arrays.copyOf(data, newLength);
System.out.println("调用 resize oldLength =" + oldLength + " , newLength = " + newLength);
}
}
}
重要的操作就是 添加 ,删除 ,和 扩容
测试代码
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyArray array = new MyArray(50);
for (int i = 0;i< 100;++i){
array.add(i);
}
array.add(23,10);
for (int i = 0;i< array.size();++i){
System.out.println("数据" + array.get(i));
}
System.out.println("数组长度" + array.size());
int removeO = (int)array.remove(56);
System.out.println("removeO = " + removeO);
System.out.println("数组长度" + array.size());
int addIndex = array.add(195);
System.out.println("addIndex " + addIndex);
array.clear();
}





 本文档模拟了Java中的ArrayList实现,详细介绍了自定义数组的添加、删除、扩容等操作,并通过示例展示了其工作原理。核心操作包括尾部添加、指定位置插入、删除元素及扩容策略,同时提供了数组越界检查等辅助方法。
本文档模拟了Java中的ArrayList实现,详细介绍了自定义数组的添加、删除、扩容等操作,并通过示例展示了其工作原理。核心操作包括尾部添加、指定位置插入、删除元素及扩容策略,同时提供了数组越界检查等辅助方法。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








