#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
double Trapezoid(double(*fun)(double x), double a, double b, int n)
{
double result = 0.0;
if(a > b)
swap(a, b);
result = (fun(a) + fun(b))/2;
double h = (1.0/n) * (b-a);
cout << setw(5) << a << setw(10) << fun(a) << endl;
for(int k=1; k<n; k++)
{
cout << setw(5) << a+k*h << setw(10)<< fun(a+k*h) <<endl;
result += fun(a + k*h);
}
cout << setw(5) << b << setw(10) << fun(b) << endl;
result *= h;
return result;
}
double Simpson(double(*fun)(double x), double a, double b, int n)
{
double result = 0.0;
if(a > b)
swap(a, b);
double h = (1.0/n) * (b-a);
result += (fun(a) - fun(b));
double x = a;
for(int k=1; k<=n; k++)
{
x += h/2;
result += 4*fun(x);
x += h/2;
result += 2*fun(x);
}
return (result*h)/6;
}
double function(double x)
{
if(x == 0)
return 1;
else
return sin(x)/x;
}
int main()
{
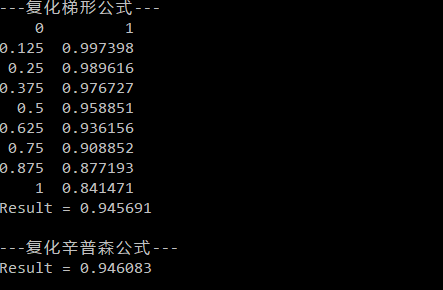
cout << "---复化梯形公式---" << endl;
cout << "Result = " << Trapezoid(function, 0, 1, 8) << endl;
cout << endl;
cout << "---复化辛普森公式---" << endl;
cout << "Result = " << Simpson(function, 0, 1, 4) << endl;
return 0;
}






 本文深入探讨了复化辛普森公式在数值积分中的应用,通过实例解析其计算过程,阐述了如何利用这一方法高效准确地估算函数积分。复化辛普森公式结合了线性与二次插值,提供了比简单矩形法和梯形法更高的精度。
本文深入探讨了复化辛普森公式在数值积分中的应用,通过实例解析其计算过程,阐述了如何利用这一方法高效准确地估算函数积分。复化辛普森公式结合了线性与二次插值,提供了比简单矩形法和梯形法更高的精度。

















 2371
2371

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








