第三学期地理信息系统实践成果,现在整理成博客存档。
插件仓库:github仓库
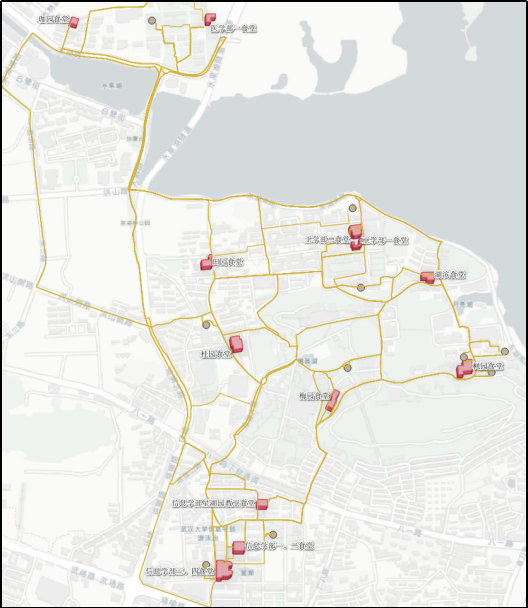
插件界面展示:
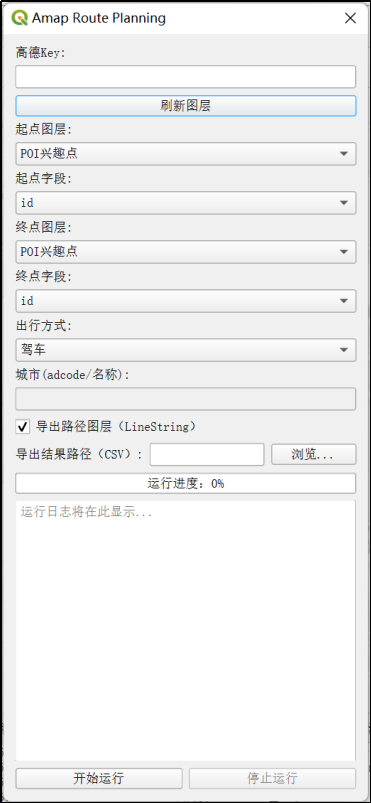
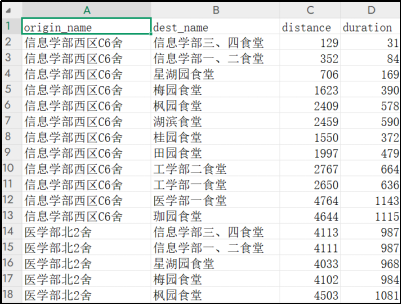
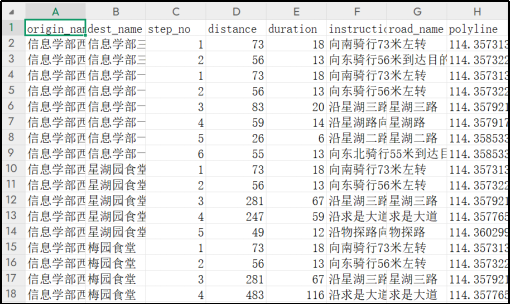
可以导出路径图层、csv表格。
目录
一、技术路线
1. 插件开发环境与框架构建
本次实验基于QGIS的Python插件开发体系展开,开发环境包括:
- QGIS 3.40.8 LTR
- Python 3.12
- Qt Designer
- PyQt与PyQGIS
- 高德地图 API
插件项目初始化通过Plugin Builder生成标准QGIS插件框架,开发过程中使用PyCharm IDE,并配置了QGIS的解释器路径,以实现PyQGIS模块的正常导入和调试运行。
2. 坐标转换处理策略
高德地图API返回的路径坐标为GCJ-02(火星坐标),无法直接叠加在常见的WGS84地图投影上。为实现准确可视化,采用以下方案:
(1) 在QGIS中安装了可以实现坐标转换的插件GeoHey Tools(参考了优快云上的博客:坐标系转换QGIS插件GeoHey_geohey toolbox-优快云博客);
(2) 阅读其源码,理解其GCJ-02→WGS84的逆向转换算法;
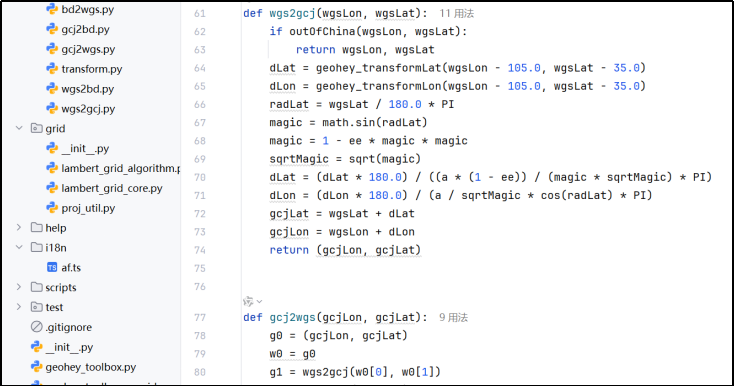
(3) 将API返回的路径点坐标手动转换为WGS84;
(4) 用转换后的坐标构造LineString图层,实现正确叠加显示。
二、开发过程
1. 插件框架搭建与环境配置
初期使用Plugin Builder构建插件项目框架,自动生成__init__.py、主逻辑 Route_Planning.py、对话框交互文件Route_Planning_dialog.py与.ui文件。图形界面通过 Qt Designer设计并用pyuic5工具转化为Python脚本。
界面控件包括:
- API Key输入框;
- 起点图层与终点图层选择;
- 出行方式下拉框;
- 导出路径图层与CSV输出路径设置;
- 运行按钮与进度条;
- 日志输出框。
开发环境包括QGIS 3.40.8 + Python 3.12,PyCharm作为调试平台,解释器使用QGIS自带的Python,通过.bat启动脚本在PyCharm中配置成功后可正常使用PyQGIS模块。
2. 高德地图API调用
采用以下接口实现路径调用:
https://restapi.amap.com/v3/direction/{mode}?origin=lng,lat&destination=lng,lat&key=API_KEY
支持驾车/步行/骑行/公交四种出行方式,返回路径时间(单位:秒)、距离(单位:米)及polyline坐标。插件流程如下:
(1) 遍历所有起点与终点组合;
def run(self):
from qgis.core import QgsCoordinateReferenceSystem, QgsCoordinateTransform, QgsPointXY
results = []
crs_wgs = QgsCoordinateReferenceSystem('EPSG:4326')
xform_to_wgs = QgsCoordinateTransform(self.crs_src, crs_wgs, QgsProject.instance())
xform_to_src = QgsCoordinateTransform(crs_wgs, self.crs_src, QgsProject.instance())
total = len(self.od_pairs)
for idx, (f1, f2) in enumerate(self.od_pairs):
if getattr(self, 'stop_flag', False):
self.log.emit('用户中断,提前结束')
break
try:
o_pt = f1.geometry().asPoint()
d_pt = f2.geometry().asPoint()
o_wgs = xform_to_wgs.transform(QgsPointXY(o_pt))
d_wgs = xform_to_wgs.transform(QgsPointXY(d_pt))
o_gcj = self.wgs84_to_gcj02(o_wgs.x(), o_wgs.y())
d_gcj = self.wgs84_to_gcj02(d_wgs.x(), d_wgs.y())
if self.mode == 'transit':
distance, duration, polyline, steps = self.get_route_amap(o_gcj, d_gcj, self.mode, self.city)
else:
distance, duration, polyline, steps = self.get_route_amap(o_gcj, d_gcj, self.mode)
# polyline GCJ-02 -> WGS84 -> 工程坐标系
line_points = []
for lon_gcj, lat_gcj in polyline:
lon_wgs, lat_wgs = gcj2wgs(lon_gcj, lat_gcj)
pt_wgs = QgsPointXY(lon_wgs, lat_wgs)
pt_proj = xform_to_src.transform(pt_wgs)
line_points.append(pt_proj)
origin_attr = f1[self.origin_field]
dest_attr = f2[self.dest_field]
results.append({
'origin_attr': origin_attr,
'dest_attr': dest_attr,
'distance': distance,
'duration': duration,
'geometry': line_points,
'steps': steps
})
self.log.emit(f'OD({origin_attr})→({dest_attr}) 距离:{distance}m 用时:{duration}s 成功')
except Exception as e:
origin_attr = f1[self.origin_field]
dest_attr = f2[self.dest_field]
self.log.emit(f'OD({origin_attr}→{dest_attr}) 失败: {e}')
self.progress.emit(idx+1, total)
self.set_progress.emit(int((idx+1)/total*100))
import time
time.sleep(0.2)
self.finished.emit(results)(2) 构造API请求,提取路径字段(对于公交出行方式,还需要输入城市信息作为参数);
def get_route_amap(self, origin, destination, mode='driving', city=None):
if mode == 'bicycling':
url = f'https://restapi.amap.com/v4/direction/bicycling?origin={origin[0]},{origin[1]}&destination={destination[0]},{destination[1]}&key={self.amap_key}'
resp = requests.get(url).json()
if resp.get('errcode', 1) == 0 and resp['data']['paths']:
route = resp['data']['paths'][0]
distance = float(route['distance'])
duration = float(route['duration'])
points = []
steps = []
for idx, step in enumerate(route['steps']):
steps.append({
'step_no': idx+1,
'distance': step.get('distance'),
'duration': step.get('duration'),
'instruction': step.get('instruction'),
'road_name': step.get('road', ''),
'polyline': step.get('polyline', '')
})
for pt in step['polyline'].split(';'):
lon, lat = map(float, pt.split(','))
points.append((lon, lat))
return distance, duration, points, steps
else:
raise Exception('路径规划失败: ' + str(resp.get('errmsg', resp.get('info', '未知错误'))))
elif mode == 'transit':
if not city:
raise Exception('公交模式下城市不能为空')
url = f'https://restapi.amap.com/v3/direction/transit/integrated?origin={origin[0]},{origin[1]}&destination={destination[0]},{destination[1]}&city={city}&key={self.amap_key}'
resp = requests.get(url).json()
if resp['status'] == '1' and resp['route']['transits']:
transit = resp['route']['transits'][0]
distance = float(transit['distance'])
duration = float(transit['duration'])
steps = []
polyline = []
for idx, seg in enumerate(transit['segments']):
instr = ''
pl = ''
if 'bus' in seg and seg['bus']['buslines']:
instr = seg['bus']['buslines'][0]['name']
pl = seg['bus']['buslines'][0]['polyline']
elif 'walking' in seg and seg['walking']['steps']:
instr = '步行'
pl = ';'.join([step['polyline'] for step in seg['walking']['steps']])
steps.append({
'step_no': idx+1,
'instruction': instr,
'polyline': pl
})
for pt in pl.split(';'):
if pt:
lon, lat = map(float, pt.split(','))
polyline.append((lon, lat))
return distance, duration, polyline, steps
else:
raise Exception('公交路径规划失败: ' + resp.get('info', ''))
else:
url = f'https://restapi.amap.com/v3/direction/{mode}?origin={origin[0]},{origin[1]}&destination={destination[0]},{destination[1]}&key={self.amap_key}'
resp = requests.get(url).json()
if resp['status'] == '1' and resp['route']['paths']:
route = resp['route']['paths'][0]
distance = float(route['distance'])
duration = float(route['duration'])
points = []
steps = []
for idx, step in enumerate(route['steps']):
steps.append({
'step_no': idx+1,
'distance': step.get('distance'),
'duration': step.get('duration'),
'instruction': step.get('instruction'),
'road_name': step.get('road', ''),
'polyline': step.get('polyline', '')
})
for pt in step['polyline'].split(';'):
lon, lat = map(float, pt.split(','))
points.append((lon, lat))
return distance, duration, points, steps
else:
raise Exception('路径规划失败: ' + resp.get('info', ''))
(3) 可选导出CSV表格,字段包括起点、终点ID、路径距离与时间;
def on_finished(self, results, export_layer, output_path, origin_field, dest_field):
self.dlg.set_run_enabled(True)
# 1. 路径图层(仅有有效路径时生成)
if export_layer and any(r['geometry'] for r in results):
import math
crs_authid = self.worker.crs_src.authid()
from qgis.core import QgsVectorLayer, QgsField, QgsFeature, QgsGeometry, QgsProject
fields = [QgsField(f'origin_{origin_field}', 10), QgsField(f'dest_{dest_field}', 10), QgsField('distance', 6, 'double'), QgsField('duration', 6, 'double')]
vl = QgsVectorLayer(f'LineString?crs={crs_authid}', 'AMAP路径规划', 'memory')
pr = vl.dataProvider()
pr.addAttributes(fields)
vl.updateFields()
feats = []
for r in results:
if r['geometry']:
# 过滤无效点
valid_points = [pt for pt in r['geometry'] if pt.x() is not None and pt.y() is not None and not math.isnan(pt.x()) and not math.isnan(pt.y())]
if not valid_points:
continue
feat = QgsFeature()
feat.setGeometry(QgsGeometry.fromPolylineXY(valid_points))
attrs = [r['origin_attr'], r['dest_attr'], r['distance'], r['duration']]
feat.setAttributes(attrs)
feats.append(feat)
if feats:
pr.addFeatures(feats)
vl.updateExtents()
QgsProject.instance().addMapLayer(vl)
self.dlg.append_log(f'已生成路径图层,共{len(feats)}条')
# 2. 导出OD汇总CSV
if output_path:
import csv
with open(output_path, 'w', newline='', encoding='utf-8') as f:
writer = csv.writer(f)
header = [f'origin_{origin_field}', f'dest_{dest_field}', 'distance', 'duration']
writer.writerow(header)
for r in results:
row = [r['origin_attr'], r['dest_attr'], r['distance'], r['duration']]
writer.writerow(row)
self.dlg.append_log(f'已导出CSV:{output_path}')
# 3. 导出step表格
if output_path:
steps_path = output_path.replace('.csv', '_steps.csv')
with open(steps_path, 'w', newline='', encoding='utf-8') as f:
writer = csv.writer(f)
writer.writerow([f'origin_{origin_field}', f'dest_{dest_field}', 'step_no', 'distance', 'duration', 'instruction', 'road_name', 'polyline'])
for r in results:
for step in r.get('steps', []):
writer.writerow([
r['origin_attr'], r['dest_attr'], step.get('step_no'), step.get('distance'), step.get('duration'),
step.get('instruction'), step.get('road_name'), step.get('polyline')
])
self.dlg.append_log(f'已导出step表格:{steps_path}')
self.dlg.append_log('分析完成')(4) 支持进度条与日志输出、失败记录处理;
def on_progress(self, done, total):
percent = int(done / total * 100) if total else 0
self.dlg.set_progress(percent)
def on_error(self, msg):
self.dlg.append_log(msg)
self.dlg.set_run_enabled(True)3. 坐标偏移问题处理
发送请求时,工程坐标系可以先转换成WGS84坐标系,再调取高德地图官方API转换为火星坐标,用于写入路径规划API参数。
def wgs84_to_gcj02(self, lon, lat):
url = f'https://restapi.amap.com/v3/assistant/coordinate/convert?locations={lon},{lat}&coordsys=gps&key={self.amap_key}'
resp = requests.get(url).json()
if resp['status'] == '1':
lon_gcj, lat_gcj = map(float, resp['locations'].split(','))
return lon_gcj, lat_gcj
else:
raise Exception('坐标转换失败: ' + resp.get('info', ''))但高德API返回坐标为GCJ-02火星坐标系,高德官方未提供相关接口进行转换,不能直接用于WGS84投影地图。为实现路径图层的准确叠加与分析,采用如下策略:
- 阅读网络博客,在QGIS插件库中查找坐标转换工具;
- 发现GeoHey Tools插件提供GCJ-02 → WGS84坐标逆转换功能;
- 阅读插件源码,理解其算法原理,将其坐标转换过程提炼总结集成到自身插件中。
插件使用了一个迭代反向校正算法,用于从GCJ-02坐标还原出近似WGS84坐标,实现方式如下:
- 初始设定:将输入的GCJ坐标g0作为初始猜测值w0。
- 迭代逼近:使用当前猜测值w0转换为GCJ坐标g1(调用wgs2gcj)。
- 根据误差(g1 - g0)对坐标进行修正,得到新的WGS坐标w1。
- 计算修正前后的差值delta。
- 循环直到修正量delta非常小(小于1e-6),表示收敛到足够精确的WGS坐标。
- 返回最终的WGS坐标w1。
将路径图层导出后通过写好的转换函数统一进行转换:

调用的tramform.py:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# 本文件来自amap_route_planning插件,仅用于GCJ-02与WGS84坐标转换
# 原作者: GeoHey
# 仅保留坐标转换相关函数,供高德路径插件调用
from __future__ import print_function
from builtins import zip
import math
from math import sin, cos, sqrt, fabs, atan2
from math import pi as PI
a = 6378245.0
f = 1 / 298.3
b = a * (1 - f)
ee = 1 - (b * b) / (a * a)
def outOfChina(lng, lat):
return not (72.004 <= lng <= 137.8347 and 0.8293 <= lat <= 55.8271)
def geohey_transformLat(x, y):
ret = -100.0 + 2.0 * x + 3.0 * y + 0.2 * y * y + 0.1 * x * y + 0.2 * sqrt(fabs(x))
ret = ret + (20.0 * sin(6.0 * x * PI) + 20.0 * sin(2.0 * x * PI)) * 2.0 / 3.0
ret = ret + (20.0 * sin(y * PI) + 40.0 * sin(y / 3.0 * PI)) * 2.0 / 3.0
ret = ret + (160.0 * sin(y / 12.0 * PI) + 320.0 * sin(y * PI / 30.0)) * 2.0 / 3.0
return ret
def geohey_transformLon(x, y):
ret = 300.0 + x + 2.0 * y + 0.1 * x * x + 0.1 * x * y + 0.1 * sqrt(fabs(x))
ret = ret + (20.0 * sin(6.0 * x * PI) + 20.0 * sin(2.0 * x * PI)) * 2.0 / 3.0
ret = ret + (20.0 * sin(x * PI) + 40.0 * sin(x / 3.0 * PI)) * 2.0 / 3.0
ret = ret + (150.0 * sin(x / 12.0 * PI) + 300.0 * sin(x * PI / 30.0)) * 2.0 / 3.0
return ret
def wgs2gcj(wgsLon, wgsLat):
if outOfChina(wgsLon, wgsLat):
return wgsLon, wgsLat
dLat = geohey_transformLat(wgsLon - 105.0, wgsLat - 35.0)
dLon = geohey_transformLon(wgsLon - 105.0, wgsLat - 35.0)
radLat = wgsLat / 180.0 * PI
magic = math.sin(radLat)
magic = 1 - ee * magic * magic
sqrtMagic = sqrt(magic)
dLat = (dLat * 180.0) / ((a * (1 - ee)) / (magic * sqrtMagic) * PI)
dLon = (dLon * 180.0) / (a / sqrtMagic * cos(radLat) * PI)
gcjLat = wgsLat + dLat
gcjLon = wgsLon + dLon
return (gcjLon, gcjLat)
def gcj2wgs(gcjLon, gcjLat):
g0 = (gcjLon, gcjLat)
w0 = g0
g1 = wgs2gcj(w0[0], w0[1])
w1 = tuple([x[0]-(x[1]-x[2]) for x in zip(w0,g1,g0)])
delta = tuple([x[0] - x[1] for x in zip(w1, w0)])
while (abs(delta[0]) >= 1e-6 or abs(delta[1]) >= 1e-6):
w0 = w1
g1 = wgs2gcj(w0[0], w0[1])
w1 = tuple([x[0]-(x[1]-x[2]) for x in zip(w0,g1,g0)])
delta = tuple([x[0] - x[1] for x in zip(w1, w0)])
return w1
def gcj2bd(gcjLon, gcjLat):
z = sqrt(gcjLon * gcjLon + gcjLat * gcjLat) + 0.00002 * sin(gcjLat * PI * 3000.0 / 180.0)
theta = atan2(gcjLat, gcjLon) + 0.000003 * cos(gcjLon * PI * 3000.0 / 180.0)
bdLon = z * cos(theta) + 0.0065
bdLat = z * sin(theta) + 0.006
return (bdLon, bdLat)
def bd2gcj(bdLon, bdLat):
x = bdLon - 0.0065
y = bdLat - 0.006
z = sqrt(x * x + y * y) - 0.00002 * sin(y * PI * 3000.0 / 180.0)
theta = atan2(y, x) - 0.000003 * cos(x * PI * 3000.0 / 180.0)
gcjLon = z * cos(theta)
gcjLat = z * sin(theta)
return (gcjLon, gcjLat)
def wgs2bd(wgsLon, wgsLat):
gcj = wgs2gcj(wgsLon, wgsLat)
return gcj2bd(gcj[0], gcj[1])
def bd2wgs(bdLon, bdLat):
gcj = bd2gcj(bdLon, bdLat)
return gcj2wgs(gcj[0], gcj[1])
这一步是整个路径插件开发中最具技术挑战的部分,需在多个坐标系间来回校验坐标误差,确保插件输出路径具有可视化与分析价值。
三、插件功能成果
- 实现了调用高德地图API,支持驾车、步行、骑行、公交四种出行方式的路径规划;
- 用户可选起点/终点图层,插件自动遍历所有OD点组合并完成路径计算;
- 输出字段包括路径时间、距离、polyline坐标;
- 支持导出CSV表格结果及可视化路径图层;
- 采用QGIS多线程机制实现进度条与日志输出,提升用户体验;
- 对于高德返回的火星坐标系(GCJ-02),通过解析GeoHey插件源码,自主实现逆变换模块,确保路径图层在地图上准确叠加。
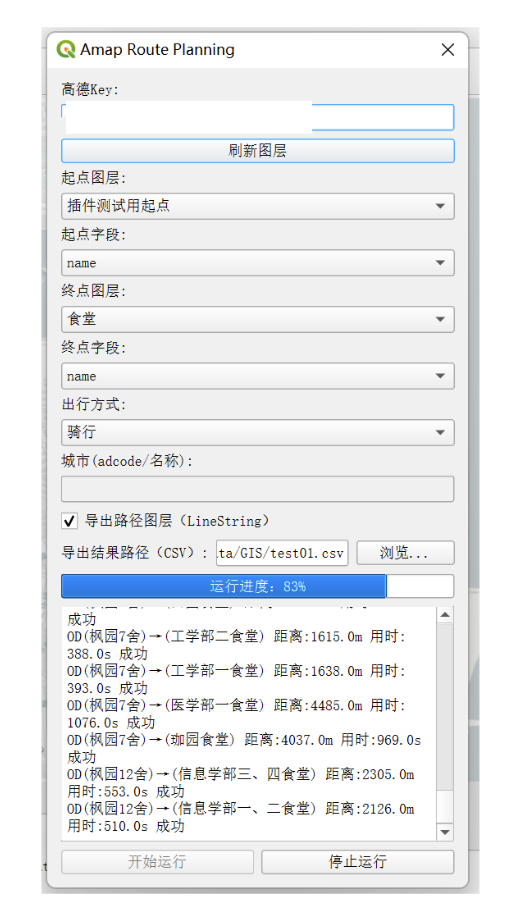
四、如何使用
我打算检查检查代码再修一修readme之后发布到QGIS插件市场,这里简单展示下怎么克隆我的库到本地后使用该插件。
找到项目所在文件夹:
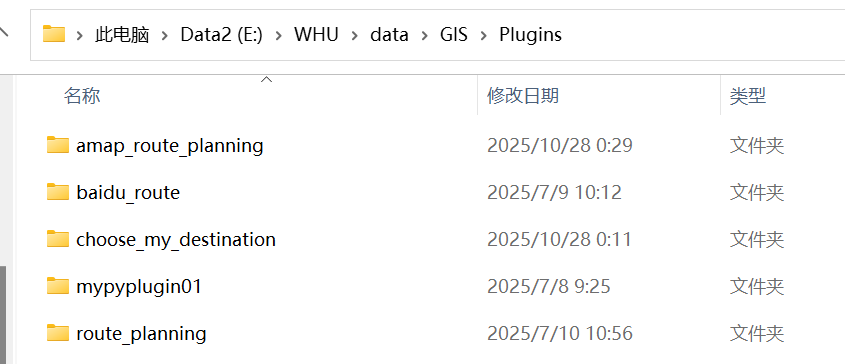
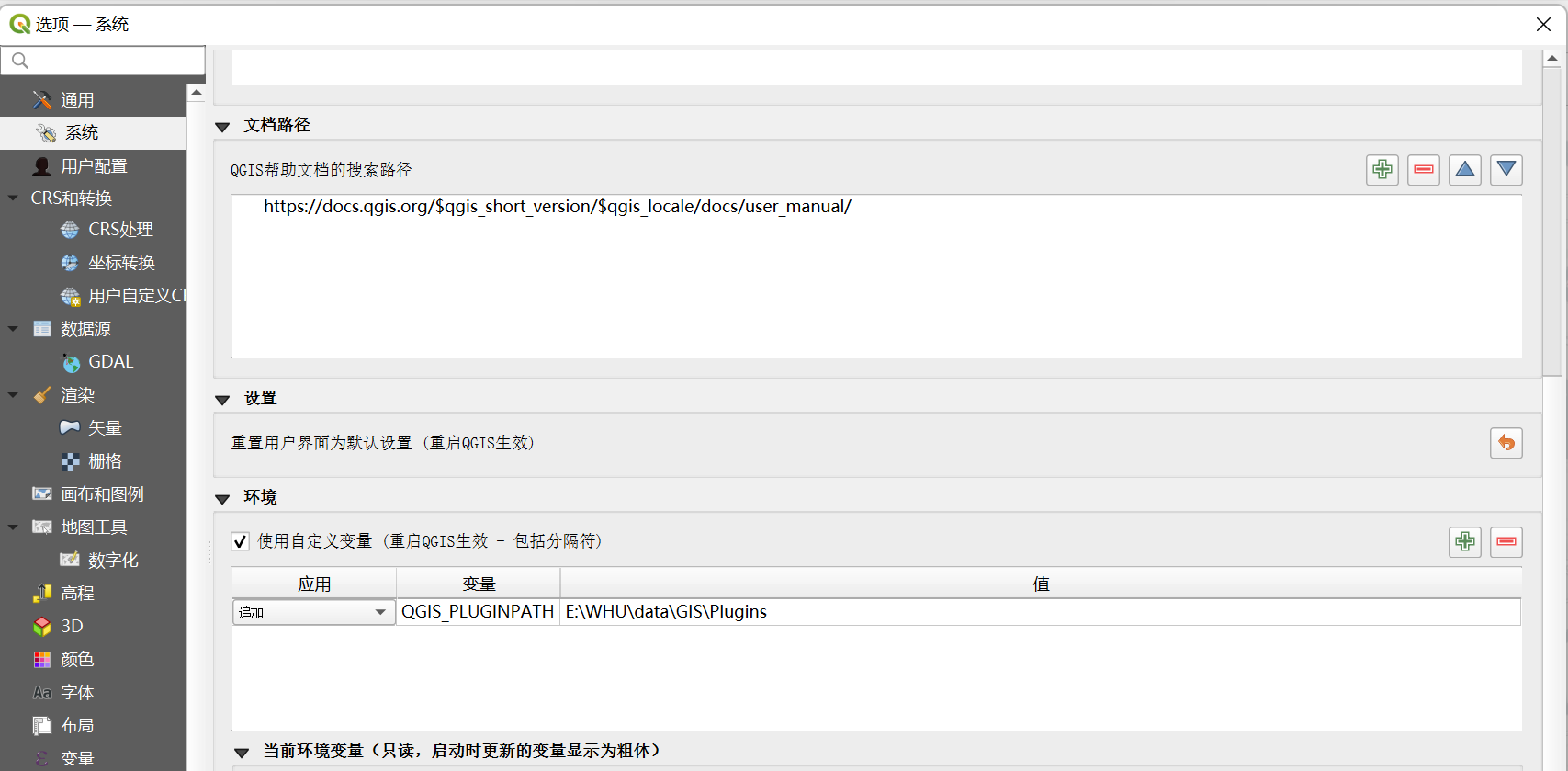
在“设置-选项-系统-环境”中选择“使用自定义变量”,追加“QGIS_PLUGINPATH”,将项目所在文件夹地址写入,使系统自动识别自定义插件的路径,这样自定义插件就会显示在插件列表中了(记得重启QGIS)。
五、后记
转眼间大学生活也快结束,整理点以前做的东西纪念纪念我的四年本科生活。开发这个插件已经是几个月前的事情了,文章难免会出现一些纰漏,欢迎指正和提出改进意见。




















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








