 #include
#include
#include<stdio.h>
#define ISLEAPYEAR(x) x % 100 != 0 && x % 4 == 0 || x % 400 == 0 ? 1 : 0 //简洁写法
using namespace std;
int DaysOfMonth(int month, int year)
{
switch(month)
{
case 1: case 3: case 5: case 7: case 8: case 10: case 12:
return 31;
break;
case 4: case 6: case 9: case 11:
return 30;
break;
case 2:
if(ISLEAPYEAR(year)) return 29;
else return 28;
}
}
class Date //注意不要加括号
{
public:
int year;
int month;
int day;
Date() //初始化日期为0/1/1 作为基准
{
year = 0;
month = 1;
day = 1;
}
void update() //将日期加一天
{
day++;
if(day > DaysOfMonth(month, year))
{
day = 1;
month ++;
if(month > 12)
{
month = 1;
year ++;
}
}
}
};
int Abs(int x)
{
return (x >= 0 ? x : -1*x);
}
int buf[6001][13][32]; //用来存储每个日期与基准日期的差值
int main()
{
Date temp;
int count = 0;
while(temp.year < 6000)
{
buf[temp.year][temp.month][temp.day] = count;
temp.update();
count ++;
}
int time1,time2;
int y1, m1, d1, y2, m2, d2,t;
while(scanf("%8d", &time1) != EOF) //此处注意对于格式的控制
{
scanf("%8d", &time2);
if(time1>time2)
{
t=time1;time1=time2;time2=t;
}
y1=time1/10000;
y2=time2/10000; //用取余数的方法得到
m1=time1%10000/100;
m2=time2%10000/100;
d1=time1%100;
d2=time2%100;
cout << Abs(buf[y2][m2][d2] - buf[y1][m1][d1] + 1) << endl;
}
return 0;
}
更好的办法
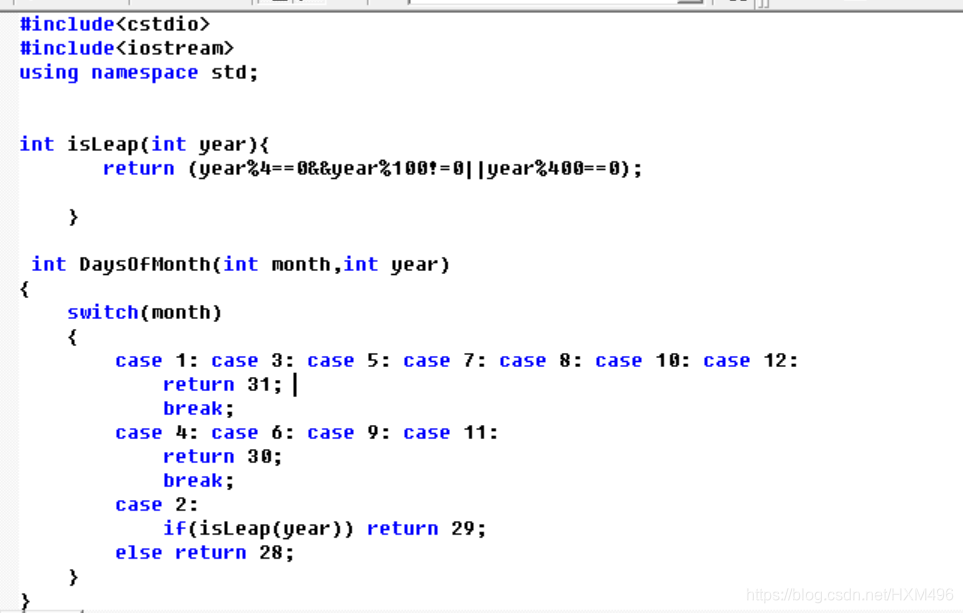

#include
#include
using namespace std;
int isLeap(int year){
return (year%40&&year%100!=0||year%4000);
} //true可作为1,自动类型提升
int DaysOfMonth(int month,int year)
{
switch(month)
{
case 1: case 3: case 5: case 7: case 8: case 10: case 12:
return 31;
break;
case 4: case 6: case 9: case 11:
return 30;
break;
case 2:
if(isLeap(year)) return 29;
else return 28;
}
}
int main(){
int time1,y1,m1,d1;
int time2,y2,m2,d2;
int ans = 1;
while(scanf("%d%d",&time1,&time2)!=EOF){
if(time1>time2){
int temp = time1;time1 =time2;time2=temp;
}
ans=1;
y1 = time1/10000;
y2 = time2/10000;
m1 = time1%10000/100;
m2 = time2%10000/100;
d1 = time1%100;
d2 = time2%100;
while(!(y1==y2&&m1==m2&&d1==d2)){ //time2不变,动time1
d1++;
if(d1>DaysOfMonth(m1,y1)){
d1=1;m1++;
if(m1>12){
m1=1;
y1++;
}
}
ans++;
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}





















 1471
1471

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








