Arc of Dream
Time Limit: 2000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65535/65535 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 2534 Accepted Submission(s): 777
Problem Description
An Arc of Dream is a curve defined by following function:
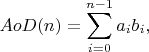
where
a 0 = A0
a i = a i-1*AX+AY
b 0 = B0
b i = b i-1*BX+BY
What is the value of AoD(N) modulo 1,000,000,007?
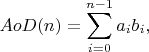
where
a 0 = A0
a i = a i-1*AX+AY
b 0 = B0
b i = b i-1*BX+BY
What is the value of AoD(N) modulo 1,000,000,007?
Input
There are multiple test cases. Process to the End of File.
Each test case contains 7 nonnegative integers as follows:
N
A0 AX AY
B0 BX BY
N is no more than 10 18, and all the other integers are no more than 2×10 9.
Each test case contains 7 nonnegative integers as follows:
N
A0 AX AY
B0 BX BY
N is no more than 10 18, and all the other integers are no more than 2×10 9.
Output
For each test case, output AoD(N) modulo 1,000,000,007.
Sample Input
1 1 2 3 4 5 6 2 1 2 3 4 5 6 3 1 2 3 4 5 6
Sample Output
4 134 1902
Author
Zejun Wu (watashi)
Source
Recommend
zhuyuanchen520 | We have carefully selected several similar problems for you:
5197
5196
5195
5194
5193
先将式子转化为递推式, Sn = Sn-1+an-1*bn-1, 其中an*bn也是递推式an*bn=ax*bx*an-1*bn-1+ax*by*an-1+ay*bx*bn-1+ay*by。
递推式可以转为矩阵快速幂O(n^3logk)复杂度,n*n的矩阵的k次幂
[sn an-1*bn-1 an-1 bn-1 1] = [ sn-1 an-2*an-2 an-2 bn-2 1]* [ [1 ax*bx ax*by ay*bx ay*by] [0 ax*bx ax*by ay*bx ay*by] [0 0 ax 0 ay] [0 0 0 bx by] [0 0 0 0 1]] //共5列
前两个矩阵为1*5,最后个矩阵为5*5.根据递推公式很容易列出第一个矩阵每一项对应的列的系数是什么,从而得到最后一个矩阵。
复杂度是O(5*5*5*logn)
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define M 1000000007
typedef unsigned long long ll;
typedef vector<ll> vec;
typedef vector<vec> mat;
mat mul(mat &a, mat &b)
{
mat c(a.size(), vec(b[0].size()));
for(int i = 0 ;i < a.size(); i++)
for(int j = 0; j < b.size(); j++)
for(int k = 0; k < b[0].size(); k++)
c[i][k] = (c[i][k]+a[i][j]*b[j][k])%M;
return c;
}
mat power(mat a, ll n)
{
mat b(a.size(), vec(a.size()));
for(int i = 0; i < a.size(); i++)
b[i][i] = 1;
while(n > 0){
if(n&1) b = mul(b,a);
a = mul(a, a);
n >>= 1;
}
return b;
}
int main()
{
ll n;
ll a0,ax,ay,b0,bx,by;
while(cin >> n){
cin >> a0 >> ax>> ay >> b0 >> bx >> by;
if(!n){
cout << 0 <<endl;
continue;
}
a0%=M,b0%=M,ax%=M,ay%=M,bx%=M,by%=M;
mat a(5, vec(5));
a[0][0] = 1;
a[1][0] = ax*bx%M,a[1][1] = ax*bx%M;
a[2][0] = ax*by%M, a[2][1]=ax*by%M,a[2][2] = ax;
a[3][0] = ay*bx%M, a[3][1]=ay*bx%M,a[3][3] = bx;
a[4][0] = by*ay%M, a[4][1] = by*ay%M, a[4][2] = ay, a[4][3] = by, a[4][4] = 1;
a = power(a, n-1);
mat fir(1, vec(5));
fir[0][0] = a0*b0%M, fir[0][1] = a0*b0%M, fir[0][2] = a0, fir[0][3] = b0, fir[0][4] = 1;
mat ans = mul(fir, a);
cout << ans[0][0] << endl;
}
return 0;
}







 本文介绍了一种通过矩阵快速幂方法解决弧梦曲线递推问题的算法。该算法利用矩阵运算将问题复杂度降低到O(5*5*5*logn),适用于求解大规模递推问题。文章提供了完整的C++代码实现。
本文介绍了一种通过矩阵快速幂方法解决弧梦曲线递推问题的算法。该算法利用矩阵运算将问题复杂度降低到O(5*5*5*logn),适用于求解大规模递推问题。文章提供了完整的C++代码实现。
















 182
182

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








