学习资料:spring技术内幕、https://javadoop.com/post/spring-ioc
作者qq:767641495
一、IOC容器
IoC(Inversion of Control)是一种设计模式,是用来解耦组件复杂关系的利器,Spring的IoC是一种模式的实现。主要的两种大类的IoC容器为BeanFactory和ApplicationContext。
1、BeanFactory
BeanFactory是所有的IoC容器的基类,拥有容器最基本的功能。
它有一个很重要的实现类DefaultListableBeanFactory,被认为是一个成熟的工厂,经常被使用。
先来看看BeanFactory注释怎么说,信息量有点大,重点关注里面那个初始化顺序。

我们先从一个简单的BeanFactory的使用说起吧~
在使用一个IoC容器的时候,主要步骤为以下四步:
- 创建IoC配置文件的抽象资源,这个抽象资源包含了BeanDefinition的定义信息
- 创建一个BeanFactory
- 创建一个载入BeanDfinition的读取器,这里使用XMLBeanDefinitionReader对象来载入XML文件形式的BeanDefinition,通过一个回调配置给BeanFactory
- 从定以好的资源位置读入配置信息,具体的解析过程由XmlBeanDefinitionReader完成;完成整个载入 和注册Bean定义之后,需要的IoC容器就建立起来了。之后就可以使用IoC容器了
写一个简单的Demo可能更方便理解:
- 新建一个实体类MyUser
public class MyUser {
private String name;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
- 将bean写入xml
<bean id="myUser" class="com.demo.pojo.MyUser" name="u1">
<property name="name" value="hzh"/>
</bean>
- 写测试类
ClassPathResource res = new ClassPathResource("beans.xml");
DefaultListableBeanFactory factory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(factory);
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(res);
MyUser user = (MyUser) factory.getBean("u1");
System.out.println(user);
仔细看这个测试类,里面的每一步都与上面讲的主要步骤对应。
2、ApplicationContext
ApplicationContext是容器的高级形态,具有很多BeanFactory没有的功能。
老规矩,先上注释。

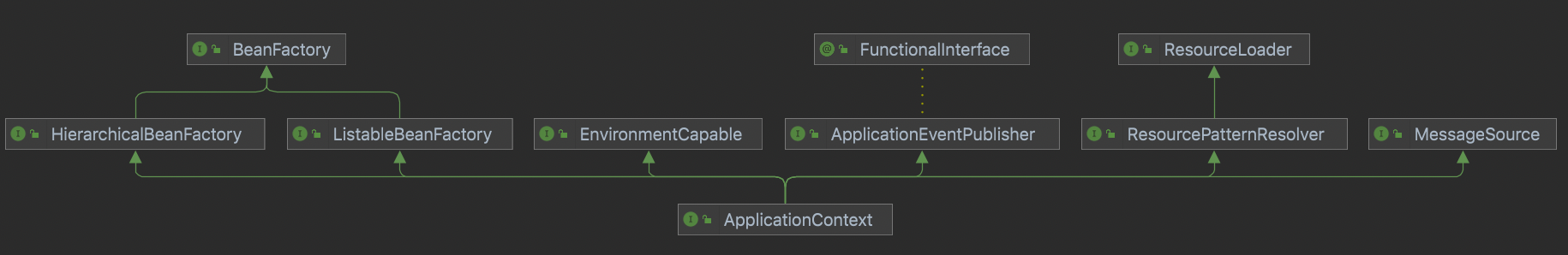
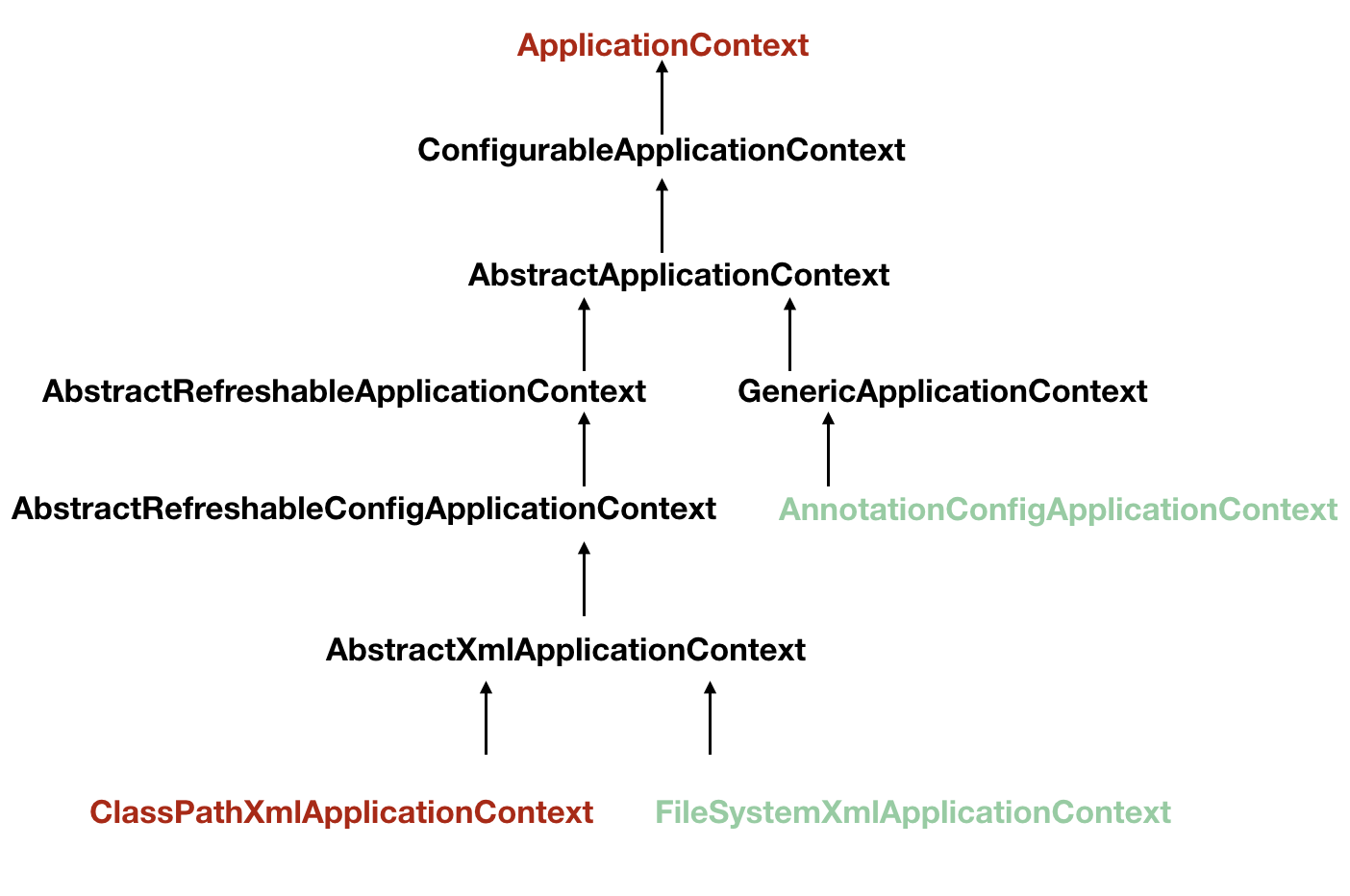
可以看到ApplicationContext中的父类以及实现类,实现类中用的比较多的就是AnnotationConfigApplicationContext,也就是基于注解的bean,也是如今springboot的使用类;还有就是传统的ClassPathXmlApplicationContext和FileSystemXmlApplicationContext这两个从xml文件中获取bean的类。
虽然ApplicationContext没有继承AutowireCapableBeanFactory,不过它通过组合的方式,可以通过getAutowireCapableBeanFactory()这个方法获取到这个工厂,实现自动装配。
沿用上面的demo,写一个新的测试类
ApplicationContext classPathXmlApplicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
MyUser user =(MyUser) classPathXmlApplicationContext.getBean("u2");
System.out.println(user);
可以发现我们省去了新建Reader并将Reader和factory绑定的步骤,这是因为ApplicationContext实现了ResourceLoader这个接口,使得它可以直接加载资源。
3、ApplicationContext的初始化过程
大致的流程分为三个基本过程——BeanDefinition的Resource定位、载入和注册。
先简单来聊聊这三步骤:
- Resource定位:其实就是找到你定义bean信息的文件,然后封装成Resource的形式,还记得我们刚刚讲过的第一步“创建IoC配置文件的抽象资源”嘛?就是这个。Resource实现了InputStreamSource接口,而这个接口中有InputStream,也就是我们可以读取配置文件。对于各种存在形式的Resource存在了不同的继承了Resource的子类,比如ClassPathResource, ServletContextResult, FileSystemResource等。
- BeanDefinition的载入:对xml文件中的内容进行解析,封装成IoC容器内部的数据结构BeanDefinition,所谓的Bean其实就是BeanDefinition的实例。
- 向Ioc容器注册BeanDefinition:通过调用BeanDefinitionRegistry接口,将上一步获得的BeanDefinition注入到一个HashMap中去。
补充:如果IoC容器中的Bean通过设置lazyinit属性进行懒加载,那么在初始化阶段就会进行依赖注入;如果没有,是在第一次调用getBean()方法的时候,进行依赖注入的。
我们以FileSystemXmlApplicationContext为例,来完整走一遍初始化流程。
Resource定位
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext构造函数
public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, @Nullable ApplicationContext parent) throws BeansException {
super(parent);
this.setConfigLocations(configLocations);
if (refresh) {
this.refresh();
}
}
可以看到这边先设置了配置的地址后,进行了一个refresh(),这个refresh()非常关键,是整个初始化的核心方法!这个方法是在FileSystemXmlApplicationContext的父类AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext中定义来看一下这个类的注释:

从注释中可以了解到,refresh()作用是重建一个新的内部bean工厂实例。可以看到这个抽象类要求子类实现loadBeanDefinitions方法,使用的IoC容器是DefaultListableBeanFactory,我们的FileSystemXmlApplicationContext对于的loadBeanDefinitions实现是在它的另一个父类AbstractXmlApplicationContext,对于loadBeanDefinitions的调用是在AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext中。
具体实现:
AbstractApplicationContext.java
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
// 来个锁,避免refresh()未结束,容器启动或者销毁
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// 准备工作,记录下容器的启动时间、标记“已启动”状态、处理配置文件中的占位符
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// 这步比较关键,这步完成后,配置文件就会解析成一个个 Bean 定义,注册到 BeanFactory 中,
// 当然,这里说的 Bean 还没有初始化,只是配置信息都提取出来了,
// 注册也只是将这些信息都保存到了注册中心
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// 设置 BeanFactory 的类加载器,添加几个 BeanPostProcessor,手动注册几个特殊的 bean
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Bean 如果实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口,那么在容器初始化以后,Spring 会负责调用里面的 postProcessBeanFactory 方法。这里是提供给子类的扩展点,到这里的时候,所有的 Bean 都加载、注册完成了,但是都还没有初始化。具体的子类可以在这步的时候添加一些特殊的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的实现类或做点什么
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// 调用 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 各个实现类的 postProcessBeanFactory(factory) 方法
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// 注册 BeanPostProcessor 的实现类,注意看和 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的区别
// 此接口两个方法: postProcessBeforeInitialization 和 postProcessAfterInitialization
// 两个方法分别在 Bean 初始化之前和初始化之后得到执行。注意,到这里 Bean 还没初始化
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// 初始化当前 ApplicationContext 的 MessageSource,国际化
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// 初始化当前 ApplicationContext 的事件广播器
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// 具体的子类可以在这里初始化一些特殊的 Bean
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// 注册事件监听器,监听器需要实现 ApplicationListener 接口
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// 初始化所有的 singleton beans
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// 最后,广播事件,ApplicationContext 初始化完成
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
}
这个方法完整初始化了ApplicationContext,我们先把关注点放在obtainFreshBeanFactory()中,它调用了refreshBeanFactory(),而refreshBeanFactory()中调用了customizeBeanFactory()和loadBeanDefinitions()两个方法。
AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext.java
protected void customizeBeanFactory(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
if (this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding != null) {
beanFactory.setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding);
}
if (this.allowCircularReferences != null) {
beanFactory.setAllowCircularReferences(this.allowCircularReferences);
}
}
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
if (this.hasBeanFactory()) {
this.destroyBeans();
this.closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.createBeanFactory();
beanFactory.setSerializationId(this.getId());
this.customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
this.loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
} catch (IOException var2) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + this.getDisplayName(), var2);
}
}
customizeBeanFactory()其实就是判断是否允许 Bean 定义覆盖和是否允许 Bean 间的循环依赖。BeanDefinition 的覆盖问题可能会有开发者碰到这个坑,就是在配置文件中定义 bean 时使用了相同的 id 或 name,默认情况下,allowBeanDefinitionOverriding 属性为 null,如果在同一配置文件中重复了,会抛错,但是如果不是同一配置文件中,会发生覆盖。
循环引用也很好理解:A 依赖 B,而 B 依赖 A。或 A 依赖 B,B 依赖 C,而 C 依赖 A。
默认情况下,Spring通过三级缓存机制,允许循环依赖的存在,当然如果你在 A 的构造方法中依赖 B,在 B 的构造方法中依赖 A 是不行的。
refreshBeanFactory()会先检测是否存在beanFactory,存在的话,会销毁所有bean然后关闭工厂,接着新建一个DefaultListableBeanFactory并将BeanDefinitions注入进入。也就是说所有的ApplicationContext中都有一个DefaultListableBeanFactory,之后所有的BeanFactory 相关的操作其实是委托给这个实例来处理的。
AbstractXmlApplicationContext.java
@Override
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException {
// Create a new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given BeanFactory.
XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
// Configure the bean definition reader with this context's
// resource loading environment.
beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment());
beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this);
beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this));
// Allow a subclass to provide custom initialization of the reader,
// then proceed with actually loading the bean definitions.
initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader);
loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader);
}
新建了一个BeanDefinitionReader将BeanDefinition载入BeanFactory
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws BeansException, IOException {
Resource[] configResources = getConfigResources();
if (configResources != null) {
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources);
}
String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations();
if (configLocations != null) {
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations);
}
}
获取configResources/configLocations,调用reader的loadBeanDefinitions
加载configResources是第二部分的事,后面再详细讲;先讲加载configLocations,最终会把configLocations给转换成Resource
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String location, Set<Resource> actualResources) {
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = getResourceLoader();
if (resourceLoader instanceof ResourcePatternResolver) {
// Resource pattern matching available.
Resource[] resources = ((ResourcePatternResolver) resourceLoader).getResources(location);
int count = loadBeanDefinitions(resources);
Collections.addAll(actualResources, resources);
return count;
}
else {
// Can only load single resources by absolute URL.
Resource resource = resourceLoader.getResource(location);
int count = loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
actualResources.add(resource);
return count;
}
}
getResources方法可以参考DefaultResourceLoader中的实现
public Resource getResource(String location) {
for (ProtocolResolver protocolResolver : getProtocolResolvers()) {
Resource resource = protocolResolver.resolve(location, this);
return resource;
}
if (location.startsWith("/")) {
return getResourceByPath(location);
}
else if (location.startsWith(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX)) {
return new ClassPathResource(location.substring(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX.length()), getClassLoader());
}
else {
try {
// Try to parse the location as a URL...
URL url = new URL(location);
return (ResourceUtils.isFileURL(url) ? new FileUrlResource(url) : new UrlResource(url));
}
catch (MalformedURLException ex) {
// No URL -> resolve as resource path.
return getResourceByPath(location);
}
}
}
可以看到,如果如果location就是一个path,会调用getResourceByPath();是URL的话,会调用URL的相关处理方法。getResourceByPath()在我们的第一个类FileSystemXmlApplicationContext中就实现过。
@Override
protected Resource getResourceByPath(String path) {
if (path.startsWith("/")) {
path = path.substring(1);
}
return new FileSystemResource(path);
}
至此,我们的第一小步终于完成了!
BeanDefinition的载入和解析
我们于第一步中获取到了Resource,现在我们需要做的是对Resource中的BeanDefinition的载入和解析。
接上文的“加载configResources”
@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource... resources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(resources, "Resource array must not be null");
int count = 0;
for (Resource resource : resources) {
count += loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
}
return count;
}
这里的loadBeanDefinitions(resource)在XmlBeanDefinitionReader中实现
@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
return loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource));
}
因为这个方法中异常处理以及非空判断过多,所以我将核心代码抽出来整理了一下:
public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) {
Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get();
currentResources = new HashSet<>(4);
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.set(currentResources);
InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream();
InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream);
inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding())
return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource());
}
protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource)
{
Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource);
int count = registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);
return count;
}
public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) {
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader();
int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount();
documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource));
return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore;
}
具体的解析是在BeanDefinitionParserDelegate类中完成的,这也是BeanDefinitionDocumentReader类的主要功能。最终,我们在XML文件中定义的BeanDefinition被解析成一棵DOM树,解析结果放入AbstractBeanDefinition对象并设置到BeanDefinitionHolder中。
BeanDefinition在IoC容器中的注册
在DefaultListableBeanFactory中实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry这个接口,这个接口的实现完成了BeanDefinition的注册,主要做的就是往DefaultListableBeanFactory中的HashMap里放数据。
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.hasText(beanName, "Bean name must not be empty");
Assert.notNull(beanDefinition, "BeanDefinition must not be null");
if (beanDefinition instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
try {
((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDefinition).validate();
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Validation of bean definition failed", ex);
}
}
BeanDefinition existingDefinition = this.beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
if (existingDefinition != null) {
if (!isAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding()) {
throw new BeanDefinitionOverrideException(beanName, beanDefinition, existingDefinition);
}
else if (existingDefinition.getRole() < beanDefinition.getRole()) {
// e.g. was ROLE_APPLICATION, now overriding with ROLE_SUPPORT or ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Overriding user-defined bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with a framework-generated bean definition: replacing [" +
existingDefinition + "] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
else if (!beanDefinition.equals(existingDefinition)) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with a different definition: replacing [" + existingDefinition +
"] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with an equivalent definition: replacing [" + existingDefinition +
"] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
}
else {
if (hasBeanCreationStarted()) {
// Cannot modify startup-time collection elements anymore (for stable iteration)
synchronized (this.beanDefinitionMap) {
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
List<String> updatedDefinitions = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames.size() + 1);
updatedDefinitions.addAll(this.beanDefinitionNames);
updatedDefinitions.add(beanName);
this.beanDefinitionNames = updatedDefinitions;
removeManualSingletonName(beanName);
}
}
else {
// Still in startup registration phase
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
this.beanDefinitionNames.add(beanName);
removeManualSingletonName(beanName);
}
this.frozenBeanDefinitionNames = null;
}
if (existingDefinition != null || containsSingleton(beanName)) {
resetBeanDefinition(beanName);
}
else if (isConfigurationFrozen()) {
clearByTypeCache();
}
}
到这里已经初始化了 Bean 容器(完成了refresh()中的obtainFreshBeanFactory()),<bean /> 配置也相应的转换为了一个个 BeanDefinition,然后注册到注册中心(HashMap),并且发送了注册事件。
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory)
接着回到之前的refresh(),下一个方法是prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory),在这里会手动注册一些特殊的bean并进行一些配置,其中我对Aware这个bean对容器的感知类进行了一些介绍。
/**
* Configure the factory's standard context characteristics,
* such as the context's ClassLoader and post-processors.
* @param beanFactory the BeanFactory to configure
*/
protected void prepareBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// 设置 BeanFactory 的类加载器,我们知道 BeanFactory 需要加载类,也就需要类加载器,
// 这里设置为加载当前 ApplicationContext 类的类加载器
beanFactory.setBeanClassLoader(getClassLoader());
// 设置 BeanExpressionResolver
beanFactory.setBeanExpressionResolver(new StandardBeanExpressionResolver(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
//
beanFactory.addPropertyEditorRegistrar(new ResourceEditorRegistrar(this, getEnvironment()));
// 添加一个 BeanPostProcessor,这个 processor 比较简单:
// 实现了 Aware 接口的 beans 在初始化的时候,这个 processor 负责回调,
// 这个我们很常用,如我们会为了获取 ApplicationContext 而 implement ApplicationContextAware
// 注意:它不仅仅回调 ApplicationContextAware,还会负责回调 EnvironmentAware、ResourceLoaderAware 等,看下源码就清楚了
// aware类指的是Bean对容器的感知,即通过bean可以获取实现了对应aware接口的信息
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this));
// 下面几行的意思就是,如果某个 bean 依赖于以下几个接口的实现类,在自动装配的时候忽略它们,
// Spring 会通过其他方式来处理这些依赖。
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EnvironmentAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EmbeddedValueResolverAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ResourceLoaderAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationEventPublisherAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(MessageSourceAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationContext.class);
/**
* 下面几行就是为特殊的几个 bean 赋值,如果有 bean 依赖了以下几个,会注入这边相应的值,
* 之前我们说过,"当前 ApplicationContext 持有一个 BeanFactory",这里解释了第一行。
* ApplicationContext 还继承了 ResourceLoader、ApplicationEventPublisher、MessageSource
* 所以对于这几个依赖,可以赋值为 this,注意 this 是一个 ApplicationContext
* 那这里怎么没看到为 MessageSource 赋值呢?那是因为 MessageSource 被注册成为了一个普通的 bean
*/
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(BeanFactory.class, beanFactory);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ResourceLoader.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationEventPublisher.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationContext.class, this);
// 这个 BeanPostProcessor 也很简单,在 bean 实例化后,如果是 ApplicationListener 的子类,那么将其添加到 listener 列表中,可以理解成:注册 事件监听器
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(this));
// 这里涉及到特殊的 bean,名为:loadTimeWeaver
// ltw 是 AspectJ 的概念,指的是在运行期进行织入,这个和 Spring AOP 不一样,
if (beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
// Set a temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
/**
* 从下面几行代码我们可以知道,Spring 往往很 "智能" 就是因为它会帮我们默认注册一些有用的 bean,
* 我们也可以选择覆盖
*/
// 如果没有定义 "environment" 这个 bean,那么 Spring 会 "手动" 注册一个
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment());
}
// 如果没有定义 "systemProperties" 这个 bean,那么 Spring 会 "手动" 注册一个
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemProperties());
}
// 如果没有定义 "systemEnvironment" 这个 bean,那么 Spring 会 "手动" 注册一个
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemEnvironment());
}
}
下一个重要的方法是finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory),这里初始化了所有的singleton beans。
// 初始化剩余的 singleton beans
protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// 初始化名字为 ConversionService 的 Bean。
// 它用来将前端传过来的参数和后端的 controller 方法上的参数进行绑定的时候用。
if (beanFactory.containsBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME) &&
beanFactory.isTypeMatch(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class)) {
beanFactory.setConversionService(
beanFactory.getBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class));
}
// Register a default embedded value resolver if no bean post-processor
// (such as a PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer bean) registered any before:
// at this point, primarily for resolution in annotation attribute values.
if (!beanFactory.hasEmbeddedValueResolver()) {
beanFactory.addEmbeddedValueResolver(new StringValueResolver() {
@Override
public String resolveStringValue(String strVal) {
return getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(strVal);
}
});
}
// 先初始化 LoadTimeWeaverAware 类型的 Bean
// 这是 AspectJ 相关的内容
String[] weaverAwareNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(LoadTimeWeaverAware.class, false, false);
for (String weaverAwareName : weaverAwareNames) {
getBean(weaverAwareName);
}
// Stop using the temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(null);
// 没什么别的目的,因为到这一步的时候,Spring 已经开始预初始化 singleton beans 了,
// 肯定不希望这个时候还出现 bean 定义解析、加载、注册。
beanFactory.freezeConfiguration();
// 开始初始化
beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();
}
@Override
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
}
// this.beanDefinitionNames 保存了所有的 beanNames
List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<String>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
// 下面这个循环,触发所有的非懒加载的 singleton beans 的初始化操作
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
// 合并父 Bean 中的配置,注意 <bean id="" class="" parent="" /> 中的 parent
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
// 非抽象、非懒加载的 singletons。如果配置了 'abstract = true',那是不需要初始化的
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
// 处理 FactoryBean
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
// FactoryBean 的话,在 beanName 前面加上 ‘&’ 符号。再调用 getBean,getBean 方法
final FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
// 判断当前 FactoryBean 是否是 SmartFactoryBean 的实现,此处忽略,直接跳过
boolean isEagerInit;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) {
isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Boolean>() {
@Override
public Boolean run() {
return ((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit();
}
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean &&
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit());
}
if (isEagerInit) {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
else {
// 对于懒加载的 Bean,只要调用 getBean(beanName) 这个方法就可以进行预实例化
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
// 到这里说明所有的非懒加载的 singleton beans 已经完成了初始化
// 如果我们定义的 bean 是实现了 SmartInitializingSingleton 接口的,那么在这里得到回调
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) {
final SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() {
@Override
public Object run() {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
return null;
}
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
}
}
}
}
### 4、IoC容器的依赖注入
getBean()
首先再次强调一下,依赖注入的过程是用户第一次向IoC容器索要Bean时触发或者通过lazy-init属性进行预实例化。以AbstractBeanFactory中的getBean为例,我删除了其中一些判空和异常处理的代码。
@Override
public Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException {
return doGetBean(name, null, null, false);
}
protected <T> T doGetBean(
String name, @Nullable Class<T> requiredType, @Nullable Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly)
throws BeansException {
String beanName = transformedBeanName(name);
Object bean;
// 从缓存中拿bean,拿不到就创建
// 这里说下 args ,虽然看上去一点不重要。前面我们一路进来的时候都是 getBean(beanName),
// 所以 args 传参其实是 null 的,但是如果 args 不为空的时候,那么意味着调用方不是希望获取 Bean,而是创建 Bean
// Eagerly check singleton cache for manually registered singletons.
Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) {
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, null);
}
else {
// Fail if we're already creating this bean instance:
// We're assumably within a circular reference.
if (isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName);
}
// 取不到bean就从双亲factory那里去递归取
// Check if bean definition exists in this factory.
BeanFactory parentBeanFactory = getParentBeanFactory();
if (parentBeanFactory != null && !containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) {
// Not found -> check parent.
String nameToLookup = originalBeanName(name);
if (parentBeanFactory instanceof AbstractBeanFactory) {
return ((AbstractBeanFactory) parentBeanFactory).doGetBean(
nameToLookup, requiredType, args, typeCheckOnly);
}
else if (args != null) {
// Delegation to parent with explicit args.
return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, args);
}
else if (requiredType != null) {
// No args -> delegate to standard getBean method.
return parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, requiredType);
}
else {
return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup);
}
}
if (!typeCheckOnly) {
markBeanAsCreated(beanName);
}
try {
// 根据beanName拿到BeanDefinition
RootBeanDefinition mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
checkMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanName, args);
// 递归获取依赖bean
// Guarantee initialization of beans that the current bean depends on.
String[] dependsOn = mbd.getDependsOn();
if (dependsOn != null) {
for (String dep : dependsOn) {
if (isDependent(beanName, dep)) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Circular depends-on relationship between '" + beanName + "' and '" + dep + "'");
}
registerDependentBean(dep, beanName);
try {
getBean(dep);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"'" + beanName + "' depends on missing bean '" + dep + "'", ex);
}
}
}
// 真正创建singleton bean的实例,调用ObjectFactory的createBean方法
// Create bean instance.
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> {
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there
// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.
// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
// 创建Prototype类型的bean
else if (mbd.isPrototype()) {
// It's a prototype -> create a new instance.
Object prototypeInstance = null;
try {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
prototypeInstance = createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(prototypeInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
else {
String scopeName = mbd.getScope();
Scope scope = this.scopes.get(scopeName);
try {
Object scopedInstance = scope.get(beanName, () -> {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(scopedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
}
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
cleanupAfterBeanCreationFailure(beanName);
throw ex;
}
}
// 对Bean的类型检查
// Check if required type matches the type of the actual bean instance.
if (requiredType != null && !requiredType.isInstance(bean)) {
try {
T convertedBean = getTypeConverter().convertIfNecessary(bean, requiredType);
if (convertedBean == null) {
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass());
}
return convertedBean;
}
}
return (T) bean;
}
createBean()
getBean后会调用createBean(),createBean()的实现在AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory中,Bean对象会根据BeanDefinition生成。从类名也可以发现,这个是通过@Autowired 注解注入属性值的地方。
protected Object doCreateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// Instantiate the bean.
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();
Class<?> beanType = instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass();
if (beanType != NullBean.class) {
mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType;
}
// Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition.
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {
if (!mbd.postProcessed) {
try {
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Post-processing of merged bean definition failed", ex);
}
mbd.postProcessed = true;
}
}
// Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references
// even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware.
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
}
addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));
}
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) {
throw (BeanCreationException) ex;
}
else {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex);
}
}
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false);
if (earlySingletonReference != null) {
if (exposedObject == bean) {
exposedObject = earlySingletonReference;
}
else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) {
String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName);
Set<String> actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(dependentBeans.length);
for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) {
if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) {
actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean);
}
}
if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName,
"Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" +
StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) +
"] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " +
"wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " +
"bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " +
"'getBeanNamesForType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example.");
}
}
}
}
// Register bean as disposable.
try {
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex);
}
return exposedObject;
}
createBeanInstance()
真正创建Bean实例的方法
protected BeanWrapper createBeanInstance(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args) {
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point.
Class<?> beanClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
// 工厂方法实例化
if (beanClass != null && !Modifier.isPublic(beanClass.getModifiers()) && !mbd.isNonPublicAccessAllowed()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Bean class isn't public, and non-public access not allowed: " + beanClass.getName());
}
Supplier<?> instanceSupplier = mbd.getInstanceSupplier();
if (instanceSupplier != null) {
return obtainFromSupplier(instanceSupplier, beanName);
}
if (mbd.getFactoryMethodName() != null) {
return instantiateUsingFactoryMethod(beanName, mbd, args);
}
// Shortcut when re-creating the same bean...
boolean resolved = false;
boolean autowireNecessary = false;
if (args == null) {
synchronized (mbd.constructorArgumentLock) {
if (mbd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod != null) {
resolved = true;
autowireNecessary = mbd.constructorArgumentsResolved;
}
}
}
if (resolved) {
if (autowireNecessary) {
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, null, null);
}
else {
return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd);
}
}
// 构造器实例化
// Candidate constructors for autowiring?
Constructor<?>[] ctors = determineConstructorsFromBeanPostProcessors(beanClass, beanName);
if (ctors != null || mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR ||
mbd.hasConstructorArgumentValues() || !ObjectUtils.isEmpty(args)) {
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, ctors, args);
}
// Preferred constructors for default construction?
ctors = mbd.getPreferredConstructors();
if (ctors != null) {
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, ctors, null);
}
// 默认构造函数实例化
// No special handling: simply use no-arg constructor.
return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd);
}
protected BeanWrapper instantiateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
try {
Object beanInstance;
final BeanFactory parent = this;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
beanInstance = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() {
@Override
public Object run() {
return getInstantiationStrategy().instantiate(mbd, beanName, parent);
}
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
// 实例化
beanInstance = getInstantiationStrategy().instantiate(mbd, beanName, parent);
}
// 包装一下,返回
BeanWrapper bw = new BeanWrapperImpl(beanInstance);
initBeanWrapper(bw);
return bw;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Instantiation of bean failed", ex);
}
}
@Override
public Object instantiate(RootBeanDefinition bd, String beanName, BeanFactory owner) {
// 如果不存在方法覆写,那就使用 java 反射进行实例化,否则使用 CGLIB,方法覆写
// 注意,spring新版本里反过来,优先使用CGLIB,若不通过配置指定,不使用java反射
if (bd.getMethodOverrides().isEmpty()) {
Constructor<?> constructorToUse;
synchronized (bd.constructorArgumentLock) {
constructorToUse = (Constructor<?>) bd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod;
if (constructorToUse == null) {
final Class<?> clazz = bd.getBeanClass();
if (clazz.isInterface()) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(clazz, "Specified class is an interface");
}
try {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
constructorToUse = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedExceptionAction<Constructor<?>>() {
@Override
public Constructor<?> run() throws Exception {
return clazz.getDeclaredConstructor((Class[]) null);
}
});
}
else {
constructorToUse = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor((Class[]) null);
}
bd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod = constructorToUse;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(clazz, "No default constructor found", ex);
}
}
}
// 利用构造方法进行实例化
return BeanUtils.instantiateClass(constructorToUse);
}
else {
// 存在方法覆写,利用 CGLIB 来完成实例化,需要依赖于 CGLIB 生成子类,这里就不展开了。
// tips: 因为如果不使用 CGLIB 的话,存在 override 的情况 JDK 并没有提供相应的实例化支持
return instantiateWithMethodInjection(bd, beanName, owner);
}
}
和AOP一样,具体对Bean的实例化有两种方法。一种是CGLIB,在SimpleInstantiationStrategy类中;一种是通过JVM反射,使用BeanUtils。
populateBean()
依赖注入核心函数,在之前的AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory类中,
其中有对Autowired的处理
protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable BeanWrapper bw) {
if (bw == null) {
if (mbd.hasPropertyValues()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Cannot apply property values to null instance");
}
else {
// Skip property population phase for null instance.
return;
}
}
// 到这步的时候,bean 实例化完成(通过工厂方法或构造方法),但是还没开始属性设值
// Give any InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors the opportunity to modify the
// state of the bean before properties are set. This can be used, for example,
// to support styles of field injection.
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
if (!ibp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) {
return;
}
}
}
}
PropertyValues pvs = (mbd.hasPropertyValues() ? mbd.getPropertyValues() : null);
// 自动装配代码
int resolvedAutowireMode = mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode();
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME || resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues(pvs);
// 通过名字找到所有属性值,如果是 bean 依赖,先初始化依赖的 bean。记录依赖关系
// Add property values based on autowire by name if applicable.
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME) {
autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
// 通过类型装配
// Add property values based on autowire by type if applicable.
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
pvs = newPvs;
}
boolean hasInstAwareBpps = hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors();
boolean needsDepCheck = (mbd.getDependencyCheck() != AbstractBeanDefinition.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE);
PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = null;
if (hasInstAwareBpps) {
if (pvs == null) {
pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues();
}
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
PropertyValues pvsToUse = ibp.postProcessProperties(pvs, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
if (filteredPds == null) {
filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
}
// 这里有个非常有用的 BeanPostProcessor 进到这里: AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor,对采用 @Autowired、@Value 注解的依赖进行设值
pvsToUse = ibp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
return;
}
}
pvs = pvsToUse;
}
}
}
if (needsDepCheck) {
if (filteredPds == null) {
filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
}
checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs);
}
if (pvs != null) {
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs);
}
}
调用applyPropertyValues具体对属性解析然后注入
protected void applyPropertyValues(String beanName, BeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw, PropertyValues pvs) {
if (pvs.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && bw instanceof BeanWrapperImpl) {
((BeanWrapperImpl) bw).setSecurityContext(getAccessControlContext());
}
MutablePropertyValues mpvs = null;
List<PropertyValue> original;
if (pvs instanceof MutablePropertyValues) {
mpvs = (MutablePropertyValues) pvs;
if (mpvs.isConverted()) {
// Shortcut: use the pre-converted values as-is.
try {
bw.setPropertyValues(mpvs);
return;
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Error setting property values", ex);
}
}
original = mpvs.getPropertyValueList();
}
else {
original = Arrays.asList(pvs.getPropertyValues());
}
TypeConverter converter = getCustomTypeConverter();
if (converter == null) {
converter = bw;
}
BeanDefinitionValueResolver valueResolver = new BeanDefinitionValueResolver(this, beanName, mbd, converter);
// Create a deep copy, resolving any references for values.
List<PropertyValue> deepCopy = new ArrayList<>(original.size());
boolean resolveNecessary = false;
for (PropertyValue pv : original) {
if (pv.isConverted()) {
deepCopy.add(pv);
}
else {
String propertyName = pv.getName();
Object originalValue = pv.getValue();
if (originalValue == AutowiredPropertyMarker.INSTANCE) {
Method writeMethod = bw.getPropertyDescriptor(propertyName).getWriteMethod();
if (writeMethod == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Autowire marker for property without write method: " + pv);
}
originalValue = new DependencyDescriptor(new MethodParameter(writeMethod, 0), true);
}
Object resolvedValue = valueResolver.resolveValueIfNecessary(pv, originalValue);
Object convertedValue = resolvedValue;
boolean convertible = bw.isWritableProperty(propertyName) &&
!PropertyAccessorUtils.isNestedOrIndexedProperty(propertyName);
if (convertible) {
convertedValue = convertForProperty(resolvedValue, propertyName, bw, converter);
}
// Possibly store converted value in merged bean definition,
// in order to avoid re-conversion for every created bean instance.
if (resolvedValue == originalValue) {
if (convertible) {
pv.setConvertedValue(convertedValue);
}
deepCopy.add(pv);
}
else if (convertible && originalValue instanceof TypedStringValue &&
!((TypedStringValue) originalValue).isDynamic() &&
!(convertedValue instanceof Collection || ObjectUtils.isArray(convertedValue))) {
pv.setConvertedValue(convertedValue);
deepCopy.add(pv);
}
else {
resolveNecessary = true;
deepCopy.add(new PropertyValue(pv, convertedValue));
}
}
}
if (mpvs != null && !resolveNecessary) {
mpvs.setConverted();
}
// Set our (possibly massaged) deep copy.
try {
bw.setPropertyValues(new MutablePropertyValues(deepCopy));
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Error setting property values", ex);
}
}
可以看到上方实际上是在BeanDefinitionValueResolver中对BeanDefinition进行解析的,最后在BeanWrapper的实现类中将对象的深拷贝通过set注入进去。
BeanDefinitionValueResolver.java
private Object resolveReference(Object argName, RuntimeBeanReference ref) {
try {
Object bean;
Class<?> beanType = ref.getBeanType();
if (ref.isToParent()) {
BeanFactory parent = this.beanFactory.getParentBeanFactory();
if (parent == null) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
this.beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), this.beanName,
"Cannot resolve reference to bean " + ref +
" in parent factory: no parent factory available");
}
if (beanType != null) {
bean = parent.getBean(beanType);
}
else {
bean = parent.getBean(String.valueOf(doEvaluate(ref.getBeanName())));
}
}
else {
String resolvedName;
if (beanType != null) {
NamedBeanHolder<?> namedBean = this.beanFactory.resolveNamedBean(beanType);
bean = namedBean.getBeanInstance();
resolvedName = namedBean.getBeanName();
}
else {
resolvedName = String.valueOf(doEvaluate(ref.getBeanName()));
bean = this.beanFactory.getBean(resolvedName);
}
this.beanFactory.registerDependentBean(resolvedName, this.beanName);
}
if (bean instanceof NullBean) {
bean = null;
}
return bean;
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
this.beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), this.beanName,
"Cannot resolve reference to bean '" + ref.getBeanName() + "' while setting " + argName, ex);
}
}
private Object resolveManagedArray(Object argName, List<?> ml, Class<?> elementType) {
Object resolved = Array.newInstance(elementType, ml.size());
for (int i = 0; i < ml.size(); i++) {
Array.set(resolved, i, resolveValueIfNecessary(new KeyedArgName(argName, i), ml.get(i)));
}
return resolved;
}
private List<?> resolveManagedList(Object argName, List<?> ml) {
List<Object> resolved = new ArrayList<>(ml.size());
for (int i = 0; i < ml.size(); i++) {
resolved.add(resolveValueIfNecessary(new KeyedArgName(argName, i), ml.get(i)));
}
return resolved;
}
这里列举了对另一个bean的引用方法的解析以及几类数据结构的解析方法,可以看到几类数据结构的注入方法中调用了resolveValueIfNecessary。
@Nullable
public Object resolveValueIfNecessary(Object argName, @Nullable Object value) {
// We must check each value to see whether it requires a runtime reference
// to another bean to be resolved.
if (value instanceof RuntimeBeanReference) {
RuntimeBeanReference ref = (RuntimeBeanReference) value;
return resolveReference(argName, ref);
}
else if (value instanceof RuntimeBeanNameReference) {
String refName = ((RuntimeBeanNameReference) value).getBeanName();
refName = String.valueOf(doEvaluate(refName));
if (!this.beanFactory.containsBean(refName)) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Invalid bean name '" + refName + "' in bean reference for " + argName);
}
return refName;
}
else if (value instanceof BeanDefinitionHolder) {
// Resolve BeanDefinitionHolder: contains BeanDefinition with name and aliases.
BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder = (BeanDefinitionHolder) value;
return resolveInnerBean(argName, bdHolder.getBeanName(), bdHolder.getBeanDefinition());
}
else if (value instanceof BeanDefinition) {
// Resolve plain BeanDefinition, without contained name: use dummy name.
BeanDefinition bd = (BeanDefinition) value;
String innerBeanName = "(inner bean)" + BeanFactoryUtils.GENERATED_BEAN_NAME_SEPARATOR +
ObjectUtils.getIdentityHexString(bd);
return resolveInnerBean(argName, innerBeanName, bd);
}
else if (value instanceof DependencyDescriptor) {
Set<String> autowiredBeanNames = new LinkedHashSet<>(4);
Object result = this.beanFactory.resolveDependency(
(DependencyDescriptor) value, this.beanName, autowiredBeanNames, this.typeConverter);
for (String autowiredBeanName : autowiredBeanNames) {
if (this.beanFactory.containsBean(autowiredBeanName)) {
this.beanFactory.registerDependentBean(autowiredBeanName, this.beanName);
}
}
return result;
}
else if (value instanceof ManagedArray) {
// May need to resolve contained runtime references.
ManagedArray array = (ManagedArray) value;
Class<?> elementType = array.resolvedElementType;
if (elementType == null) {
String elementTypeName = array.getElementTypeName();
if (StringUtils.hasText(elementTypeName)) {
try {
elementType = ClassUtils.forName(elementTypeName, this.beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader());
array.resolvedElementType = elementType;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// Improve the message by showing the context.
throw new BeanCreationException(
this.beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), this.beanName,
"Error resolving array type for " + argName, ex);
}
}
else {
elementType = Object.class;
}
}
return resolveManagedArray(argName, (List<?>) value, elementType);
}
else if (value instanceof ManagedList) {
// May need to resolve contained runtime references.
return resolveManagedList(argName, (List<?>) value);
}
else if (value instanceof ManagedSet) {
// May need to resolve contained runtime references.
return resolveManagedSet(argName, (Set<?>) value);
}
else if (value instanceof ManagedMap) {
// May need to resolve contained runtime references.
return resolveManagedMap(argName, (Map<?, ?>) value);
}
else if (value instanceof ManagedProperties) {
Properties original = (Properties) value;
Properties copy = new Properties();
original.forEach((propKey, propValue) -> {
if (propKey instanceof TypedStringValue) {
propKey = evaluate((TypedStringValue) propKey);
}
if (propValue instanceof TypedStringValue) {
propValue = evaluate((TypedStringValue) propValue);
}
if (propKey == null || propValue == null) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
this.beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), this.beanName,
"Error converting Properties key/value pair for " + argName + ": resolved to null");
}
copy.put(propKey, propValue);
});
return copy;
}
else if (value instanceof TypedStringValue) {
// Convert value to target type here.
TypedStringValue typedStringValue = (TypedStringValue) value;
Object valueObject = evaluate(typedStringValue);
try {
Class<?> resolvedTargetType = resolveTargetType(typedStringValue);
if (resolvedTargetType != null) {
return this.typeConverter.convertIfNecessary(valueObject, resolvedTargetType);
}
else {
return valueObject;
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// Improve the message by showing the context.
throw new BeanCreationException(
this.beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), this.beanName,
"Error converting typed String value for " + argName, ex);
}
}
else if (value instanceof NullBean) {
return null;
}
else {
return evaluate(value);
}
}
可以看到这个方法里对各种类型的数据结构都进行了解析。解析完成后就要注入了是在BeanWrapper的实现类BeanWrapperImpl中完成注入的,新版本可以参考AbstractNestablePropertyAccessor的processKeyedProperty的方法。
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private void processKeyedProperty(PropertyTokenHolder tokens, PropertyValue pv) {
Object propValue = getPropertyHoldingValue(tokens);
PropertyHandler ph = getLocalPropertyHandler(tokens.actualName);
if (ph == null) {
throw new InvalidPropertyException(
getRootClass(), this.nestedPath + tokens.actualName, "No property handler found");
}
Assert.state(tokens.keys != null, "No token keys");
String lastKey = tokens.keys[tokens.keys.length - 1];
if (propValue.getClass().isArray()) {
Class<?> requiredType = propValue.getClass().getComponentType();
int arrayIndex = Integer.parseInt(lastKey);
Object oldValue = null;
try {
if (isExtractOldValueForEditor() && arrayIndex < Array.getLength(propValue)) {
oldValue = Array.get(propValue, arrayIndex);
}
Object convertedValue = convertIfNecessary(tokens.canonicalName, oldValue, pv.getValue(),
requiredType, ph.nested(tokens.keys.length));
int length = Array.getLength(propValue);
if (arrayIndex >= length && arrayIndex < this.autoGrowCollectionLimit) {
Class<?> componentType = propValue.getClass().getComponentType();
Object newArray = Array.newInstance(componentType, arrayIndex + 1);
System.arraycopy(propValue, 0, newArray, 0, length);
setPropertyValue(tokens.actualName, newArray);
propValue = getPropertyValue(tokens.actualName);
}
Array.set(propValue, arrayIndex, convertedValue);
}
catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new InvalidPropertyException(getRootClass(), this.nestedPath + tokens.canonicalName,
"Invalid array index in property path '" + tokens.canonicalName + "'", ex);
}
}
else if (propValue instanceof List) {
Class<?> requiredType = ph.getCollectionType(tokens.keys.length);
List<Object> list = (List<Object>) propValue;
int index = Integer.parseInt(lastKey);
Object oldValue = null;
if (isExtractOldValueForEditor() && index < list.size()) {
oldValue = list.get(index);
}
Object convertedValue = convertIfNecessary(tokens.canonicalName, oldValue, pv.getValue(),
requiredType, ph.nested(tokens.keys.length));
int size = list.size();
if (index >= size && index < this.autoGrowCollectionLimit) {
for (int i = size; i < index; i++) {
try {
list.add(null);
}
catch (NullPointerException ex) {
throw new InvalidPropertyException(getRootClass(), this.nestedPath + tokens.canonicalName,
"Cannot set element with index " + index + " in List of size " +
size + ", accessed using property path '" + tokens.canonicalName +
"': List does not support filling up gaps with null elements");
}
}
list.add(convertedValue);
}
else {
try {
list.set(index, convertedValue);
}
catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new InvalidPropertyException(getRootClass(), this.nestedPath + tokens.canonicalName,
"Invalid list index in property path '" + tokens.canonicalName + "'", ex);
}
}
}
else if (propValue instanceof Map) {
Class<?> mapKeyType = ph.getMapKeyType(tokens.keys.length);
Class<?> mapValueType = ph.getMapValueType(tokens.keys.length);
Map<Object, Object> map = (Map<Object, Object>) propValue;
// IMPORTANT: Do not pass full property name in here - property editors
// must not kick in for map keys but rather only for map values.
TypeDescriptor typeDescriptor = TypeDescriptor.valueOf(mapKeyType);
Object convertedMapKey = convertIfNecessary(null, null, lastKey, mapKeyType, typeDescriptor);
Object oldValue = null;
if (isExtractOldValueForEditor()) {
oldValue = map.get(convertedMapKey);
}
// Pass full property name and old value in here, since we want full
// conversion ability for map values.
Object convertedMapValue = convertIfNecessary(tokens.canonicalName, oldValue, pv.getValue(),
mapValueType, ph.nested(tokens.keys.length));
map.put(convertedMapKey, convertedMapValue);
}
else {
throw new InvalidPropertyException(getRootClass(), this.nestedPath + tokens.canonicalName,
"Property referenced in indexed property path '" + tokens.canonicalName +
"' is neither an array nor a List nor a Map; returned value was [" + propValue + "]");
}
}
在Bean的创建和对象依赖注人的过程中,需要依据BeanDefinition中的信息来递归地完
成依赖注入。从上面的几个递归过程中可以看到,这些递归都是以getBean为入口的。
递归是在上下文体系中查找需要的Bean和创建Bean的递归调用,另一个递归是在依赖注人
时,通过递归调用容器的getBean方法,得到当前Bean的依赖Bean,同时也触发对依赖Bean
的创建和注入。在对Bean的属性进行依赖注入时,解析的过程也是一个递归的过程。这样,
根据依赖关系,一层一层地完成Bean的创建和注入,直到最后完成当前Bean的创建。有了这
个顶层Bean的创建和对它的属性依赖注人的完成,意味着和当前Bean相关的整个依赖链的注
入也完成了。
在Bean创建和依赖注入完成以后,在IoC容器中建立起一系列依靠依赖关系联系起来的
Bean,这个Bean己经不是简单的Java对象了。该Bean系列以及Bean之间的依赖关系建立完
成以后,通过IoC容器的相关接口方法,就可以非常方便地供上层应用使用了。
5、IoC基本实现原理总结
- 资源定位:BeanFactory通过ResourceLoader去定位Resource,ApplicationContext因为实现了资源定位接口,可以直接定位Resource。通过Resource接口可以获取在xml或yml等文件中配置bean信息的IO流。
- 容器初始化:通过refresh()方法,对容器进行初始化。通过BeanDefinitionReader读取解析Resource中的BeanDefinition信息并建立IoC内部的AbstractBeanDefinition,在注册的时候,这些信息会被维护在一个HashMap中。最后注入设置过懒加载的Bean。
- 依赖注入:当用户第一次向IoC容器请求Bean时,执行依赖注入,递归地将Bean依赖的Bean进行创建和注入。





















 250
250

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








