import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
# 载入数据集
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data',one_hot=True)
# 不是一张张图片放入神经网络,定义一个批次,一次 100
batch_size = 100
# 计算一个有多少批次,整除
n_batch = mnist.train.num_examples // batch_size
# 命名空间
with tf.name_scope('input'):
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784],name='x-input')
y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10],name='y-input')
# 创建一个简单的神经网络
W = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784, 10]))
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]))
prediction = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(x,W)+b)
# 二次代价函数
# loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y-prediction))
# 交叉熵代价函数配合 softmax 使用
# 因为 prediction 是通过 softmax 来的,它是类别概率数组,所以不能直接用普通的交叉熵函数
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y, logits=prediction))
# 梯度下降法
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.2).minimize(loss)
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
# 结果存放在布尔型列表中
# tf.equal 相等返回 True,否则 False,argmax 比较 y 中哪个元素的值为 1,返回该元素下标
correct_predition = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y, 1), tf.argmax(prediction, 1))
# 求准确率
# tf.cast 将布尔型转换为32位浮点型,True -> 1.0,False -> 0.0,然后求平均值,如有 9 个 1,1 个 0,平均值为 0.9,准确率为 0.9
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_predition, tf.float32))
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter('logs/',sess.graph)
# 循环 21 个周期,每个周期批次为 100,每个周期将所有图片都训练一次
for epoch in range(1):
for batch in range(n_batch):
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x:batch_xs, y:batch_ys})
#训练完一个周期看下准确率
acc = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x:mnist.test.images,y:mnist.test.labels})
print('Iter ' + str(epoch) + ', Testing Accuracy' + str(acc))增添这几行
# 命名空间
with tf.name_scope('input'):
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784],name='x-input')
y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10],name='y-input')
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter('logs/',sess.graph)![]()
打开谷歌浏览器

在隐藏层添加命名空间
with tf.name_scope('layer'):
# 创建一个简单的神经网络
with tf.name_scope('weight'):
W = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784, 10]),name='W')
with tf.name_scope('biases'):
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]))
with tf.name_scope('wx_plus_b'):
wx_plus_b = tf.matmul(x,W)+b
with tf.name_scope('softmax'):
prediction = tf.nn.softmax(wx_plus_b)删除logs下生产的文件,重启notebook内核重新执行程序

给代价函数和计算准确率添加命名空间
# 二次代价函数
# loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y-prediction))
with tf.name_scope('loss'):
# 交叉熵代价函数配合 softmax 使用
# 因为 prediction 是通过 softmax 来的,它是类别概率数组,所以不能直接用普通的交叉熵函数
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y, logits=prediction))
with tf.name_scope('train'):
# 梯度下降法
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.2).minimize(loss)
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
with tf.name_scope('count_accuracy'):
with tf.name_scope('correct_predition'):
# 结果存放在布尔型列表中
# tf.equal 相等返回 True,否则 False,argmax 比较 y 中哪个元素的值为 1,返回该元素下标
correct_predition = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y, 1), tf.argmax(prediction, 1))
with tf.name_scope('accuracy'):
# 求准确率
# tf.cast 将布尔型转换为32位浮点型,True -> 1.0,False -> 0.0,然后求平均值,如有 9 个 1,1 个 0,平均值为 0.9,准确率为 0.9
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_predition, tf.float32)) 
双击打开查看


完整程序
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
# 载入数据集
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data',one_hot=True)
# 不是一张张图片放入神经网络,定义一个批次,一次 100
batch_size = 100
# 计算一个有多少批次,整除
n_batch = mnist.train.num_examples // batch_size
# 命名空间
with tf.name_scope('input'):
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784],name='x-input')
y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10],name='y-input')
with tf.name_scope('layer'):
# 创建一个简单的神经网络
with tf.name_scope('weight'):
W = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784, 10]),name='W')
with tf.name_scope('biases'):
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]))
with tf.name_scope('wx_plus_b'):
wx_plus_b = tf.matmul(x,W)+b
with tf.name_scope('softmax'):
prediction = tf.nn.softmax(wx_plus_b)
# 二次代价函数
# loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y-prediction))
with tf.name_scope('loss'):
# 交叉熵代价函数配合 softmax 使用
# 因为 prediction 是通过 softmax 来的,它是类别概率数组,所以不能直接用普通的交叉熵函数
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y, logits=prediction))
with tf.name_scope('train'):
# 梯度下降法
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.2).minimize(loss)
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
with tf.name_scope('count_accuracy'):
with tf.name_scope('correct_predition'):
# 结果存放在布尔型列表中
# tf.equal 相等返回 True,否则 False,argmax 比较 y 中哪个元素的值为 1,返回该元素下标
correct_predition = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y, 1), tf.argmax(prediction, 1))
with tf.name_scope('accuracy'):
# 求准确率
# tf.cast 将布尔型转换为32位浮点型,True -> 1.0,False -> 0.0,然后求平均值,如有 9 个 1,1 个 0,平均值为 0.9,准确率为 0.9
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_predition, tf.float32))
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter('logs/',sess.graph)
# 循环 21 个周期,每个周期批次为 100,每个周期将所有图片都训练一次
for epoch in range(1):
for batch in range(n_batch):
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x:batch_xs, y:batch_ys})
#训练完一个周期看下准确率
acc = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x:mnist.test.images,y:mnist.test.labels})
print('Iter ' + str(epoch) + ', Testing Accuracy' + str(acc))删除logs下生产的文件,重启notebook内核重新执行程序
使用 tf.summary
with tf.name_scope('layer'):
# 创建一个简单的神经网络
with tf.name_scope('weight'):
W = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784, 10]),name='W')
variable_summaries(W)
with tf.name_scope('biases'):
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]))
variable_summaries(b)
with tf.name_scope('wx_plus_b'):
wx_plus_b = tf.matmul(x,W)+b
with tf.name_scope('softmax'):
prediction = tf.nn.softmax(wx_plus_b)
# 合并所有的 summary
merged = tf.summary.merge_all()
summary,_ = sess.run([merged,train_step], feed_dict={x:batch_xs, y:batch_ys})
writer.add_summary(summary, epoch)具体代码如下
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
# 载入数据集
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data',one_hot=True)
# 不是一张张图片放入神经网络,定义一个批次,一次 100
batch_size = 100
# 计算一个有多少批次,整除
n_batch = mnist.train.num_examples // batch_size
# 参数概要
def variable_summaries(var):
with tf.name_scope('summaries'):
mean = tf.reduce_mean(var)
# scalar 记录这个值,且起名字
tf.summary.scalar('mean', mean)
with tf.name_scope('summaries'):
stddev = tf.sqrt(tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(var - mean))) # 标准差
tf.summary.scalar('stddev', stddev)
tf.summary.scalar('max', tf.reduce_max(var))
tf.summary.scalar('min', tf.reduce_min(var))
tf.summary.histogram('histogram', var) # 直方图
# 命名空间
with tf.name_scope('input'):
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784],name='x-input')
y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10],name='y-input')
with tf.name_scope('layer'):
# 创建一个简单的神经网络
with tf.name_scope('weight'):
W = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784, 10]),name='W')
variable_summaries(W)
with tf.name_scope('biases'):
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]))
variable_summaries(b)
with tf.name_scope('wx_plus_b'):
wx_plus_b = tf.matmul(x,W)+b
with tf.name_scope('softmax'):
prediction = tf.nn.softmax(wx_plus_b)
# 二次代价函数
# loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y-prediction))
with tf.name_scope('loss'):
# 交叉熵代价函数配合 softmax 使用
# 因为 prediction 是通过 softmax 来的,它是类别概率数组,所以不能直接用普通的交叉熵函数
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y, logits=prediction))
# loss 只有一个值,没必要调用 variable_summaries 函数
tf.summary.scalar('loss', loss)
with tf.name_scope('train'):
# 梯度下降法
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.2).minimize(loss)
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
with tf.name_scope('count_accuracy'):
with tf.name_scope('correct_predition'):
# 结果存放在布尔型列表中
# tf.equal 相等返回 True,否则 False,argmax 比较 y 中哪个元素的值为 1,返回该元素下标
correct_predition = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y, 1), tf.argmax(prediction, 1))
with tf.name_scope('accuracy'):
# 求准确率
# tf.cast 将布尔型转换为32位浮点型,True -> 1.0,False -> 0.0,然后求平均值,如有 9 个 1,1 个 0,平均值为 0.9,准确率为 0.9
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_predition, tf.float32))
tf.summary.scalar('accuracy', accuracy)
# 合并所有的 summary
merged = tf.summary.merge_all()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter('logs/',sess.graph)
# 循环 21 个周期,每个周期批次为 100,每个周期将所有图片都训练一次
for epoch in range(11):
for batch in range(n_batch):
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
summary,_ = sess.run([merged,train_step], feed_dict={x:batch_xs, y:batch_ys})
writer.add_summary(summary, epoch)
#训练完一个周期看下准确率
acc = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x:mnist.test.images,y:mnist.test.labels})
print('Iter ' + str(epoch) + ', Testing Accuracy' + str(acc))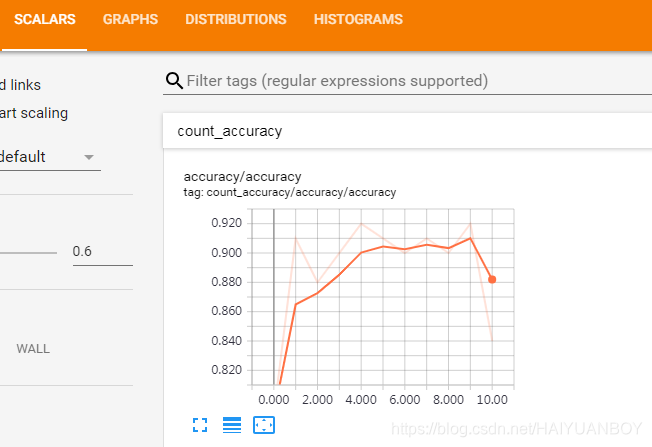

如果 loss 震动得比较厉害,可能是学习率设置太大
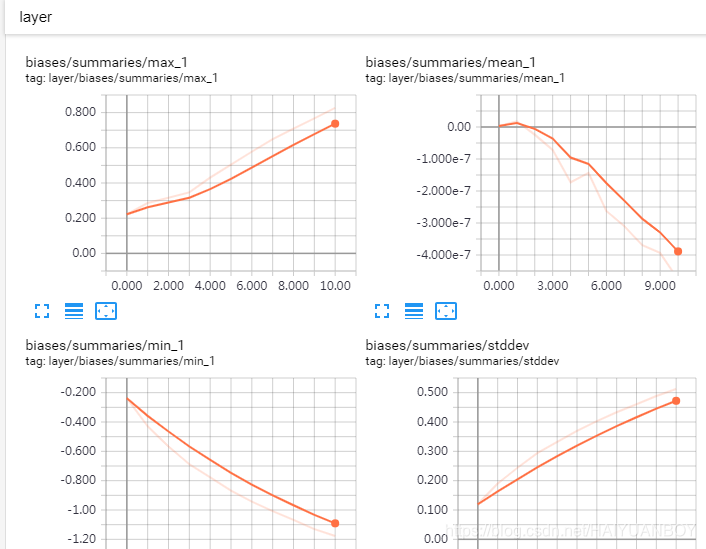
查看权值和偏置的 histogram 分布


颜色越深表示在此范围分布越多
可视化
在项目下创建 projector 文件夹,projector 下创建 data 和 projector 文件夹,data 下放图片 mnist_10k_sprite.png
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
# 载入数据集
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data',one_hot=True)
# 运行次数
max_steps = 1001
# 图片数量
image_num = 3000
# 文件路径
DIR = 'D:/notebook/py3/'
# 定义会话
sess = tf.Session()
# 载入图片,stack方法把图片追加进来
embedding = tf.Variable(tf.stack(mnist.test.images[:image_num]), trainable=False, name='embedding')
# 参数概要
def variable_summaries(var):
with tf.name_scope('summaries'):
mean = tf.reduce_mean(var)
# scalar 记录这个值,且起名字
tf.summary.scalar('mean', mean)
with tf.name_scope('summaries'):
stddev = tf.sqrt(tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(var - mean))) # 标准差
tf.summary.scalar('stddev', stddev)
tf.summary.scalar('max', tf.reduce_max(var))
tf.summary.scalar('min', tf.reduce_min(var))
tf.summary.histogram('histogram', var) # 直方图
#命名空间
with tf.name_scope('input'):
#这里的none表示第一个维度可以是任意的长度
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,784],name='x-input')
#正确的标签
y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,10],name='y-input')
#显示图片
with tf.name_scope('input_reshape'):
# -1 代表不确定的,任意的值,把 784 转化为 28 * 28,维度是 1,因为是黑白图片,彩色维度 3
image_shaped_input = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 28, 28, 1])
# 放 10 张图片
tf.summary.image('input', image_shaped_input, 10)
with tf.name_scope('layer'):
#创建一个简单神经网络
with tf.name_scope('weights'):
W = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784,10]),name='W')
variable_summaries(W)
with tf.name_scope('biases'):
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]),name='b')
variable_summaries(b)
with tf.name_scope('wx_plus_b'):
wx_plus_b = tf.matmul(x,W) + b
with tf.name_scope('softmax'):
prediction = tf.nn.softmax(wx_plus_b)
with tf.name_scope('loss'):
# 交叉熵代价函数配合 softmax 使用
# 因为 prediction 是通过 softmax 来的,它是类别概率数组,所以不能直接用普通的交叉熵函数
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y,logits=prediction))
tf.summary.scalar('loss',loss)
with tf.name_scope('train'):
#使用梯度下降法
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.5).minimize(loss)
#初始化变量
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
with tf.name_scope('accuracy'):
with tf.name_scope('correct_prediction'):
#结果存放在一个布尔型列表中
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y,1),tf.argmax(prediction,1))#argmax返回一维张量中最大的值所在的位置
with tf.name_scope('accuracy'):
#求准确率
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction,tf.float32))#把correct_prediction变为float32类型
tf.summary.scalar('accuracy',accuracy)
#产生metadata文件
if tf.gfile.Exists(DIR + 'projector/projector/metadata.tsv'):
tf.gfile.DeleteRecursively(DIR + 'projector/projector/metadata.tsv')
with open(DIR + 'projector/projector/metadata.tsv', 'w') as f:
labels = sess.run(tf.argmax(mnist.test.labels[:],1))
for i in range(image_num):
f.write(str(labels[i]) + '\n')
#合并所有的summary
merged = tf.summary.merge_all()
projector_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(DIR + 'projector/projector',sess.graph)
# 保存网络的模型
saver = tf.train.Saver()
config = projector.ProjectorConfig()
embed = config.embeddings.add()
embed.tensor_name = embedding.name
embed.metadata_path = DIR + 'projector/projector/metadata.tsv'
embed.sprite.image_path = DIR + 'projector/data/mnist_10k_sprite.png'
embed.sprite.single_image_dim.extend([28,28])
projector.visualize_embeddings(projector_writer,config)
for i in range(max_steps):
#每个批次100个样本
batch_xs,batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(100)
run_options = tf.RunOptions(trace_level=tf.RunOptions.FULL_TRACE)
run_metadata = tf.RunMetadata()
sess.run(train_step,feed_dict={x:batch_xs,y:batch_ys},options=run_options,run_metadata=run_metadata)
summary = sess.run(merged,feed_dict={x:batch_xs,y:batch_ys},options=run_options,run_metadata=run_metadata)
# 记录参数的变化
projector_writer.add_run_metadata(run_metadata, 'step%03d' % i)
projector_writer.add_summary(summary, i)
if i%100 == 0:
acc = sess.run(accuracy,feed_dict={x:mnist.test.images,y:mnist.test.labels})
print ("Iter " + str(i) + ", Testing Accuracy= " + str(acc))
# 保存模型
saver.save(sess, DIR + 'projector/projector/a_model.ckpt', global_step=max_steps)
projector_writer.close()
sess.close()运行
![]()

跑模型,查看迭代次数









 本文介绍了如何使用TensorFlow中的TensorBoard进行网络结构的可视化,包括清理logs文件、命名空间的使用、代价函数和准确率的命名、观察loss变化、权重和偏置的histogram分布以及设置projector进行数据可视化。通过这些步骤,可以更清晰地理解和调试模型。
本文介绍了如何使用TensorFlow中的TensorBoard进行网络结构的可视化,包括清理logs文件、命名空间的使用、代价函数和准确率的命名、观察loss变化、权重和偏置的histogram分布以及设置projector进行数据可视化。通过这些步骤,可以更清晰地理解和调试模型。
















 1298
1298

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








