Intersection
Time Limit: 4000/4000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 512000/512000 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 119 Accepted Submission(s): 49
Problem Description
Matt is a big fan of logo design. Recently he falls in love with logo made up by rings. The following figures are some famous examples you may know.

A ring is a 2-D figure bounded by two circles sharing the common center. The radius for these circles are denoted by r and R (r < R). For more details, refer to the gray part in the illustration below.
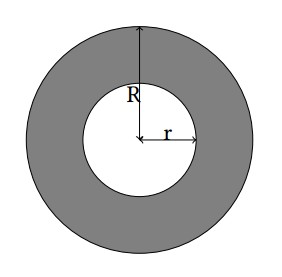
Matt just designed a new logo consisting of two rings with the same size in the 2-D plane. For his interests, Matt would like to know the area of the intersection of these two rings.

A ring is a 2-D figure bounded by two circles sharing the common center. The radius for these circles are denoted by r and R (r < R). For more details, refer to the gray part in the illustration below.

Matt just designed a new logo consisting of two rings with the same size in the 2-D plane. For his interests, Matt would like to know the area of the intersection of these two rings.
Input
The first line contains only one integer T (T ≤ 10
5), which indicates the number of test cases. For each test case, the first line contains two integers r, R (0 ≤ r < R ≤ 10).
Each of the following two lines contains two integers x i, y i (0 ≤ x i, y i ≤ 20) indicating the coordinates of the center of each ring.
Each of the following two lines contains two integers x i, y i (0 ≤ x i, y i ≤ 20) indicating the coordinates of the center of each ring.
Output
For each test case, output a single line “Case #x: y”, where x is the case number (starting from 1) and y is the area of intersection rounded to 6 decimal places.
Sample Input
2 2 3 0 0 0 0 2 3 0 0 5 0
Sample Output
Case #1: 15.707963 Case #2: 2.250778
Source
Recommend
圆环相交 --->大圆交大圆(如果相交) - 2 * 大圆交小圆 (如果相交) + 小圆交小圆(如果相交)
重现赛不知道哪里写错了一直WA,赛后推翻重写就AC了
圆环相交 --->大圆交大圆(如果相交) - 2 * 大圆交小圆 (如果相交) + 小圆交小圆(如果相交)
重现赛不知道哪里写错了一直WA,赛后推翻重写就AC了
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <list>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const double pi = acos(-1);
struct point
{
double x, y;
};
double calc_area(point a, point b, double r1, double r2)
{
double d = sqrt((a.x - b.x) * (a.x - b.x) + (a.y - b.y) * (a.y - b.y));
if (r1 - r2 - d >= 0)
{
return pi * r2 * r2;
}
double ang1 = acos((r1 * r1 + d * d - r2 * r2) / (2 * r1 * d));
double ang2 = acos((r2 * r2 + d * d - r1 * r1) / (2 * r2 * d));
return ang1 * r1 * r1 + ang2 * r2 * r2 - 0.5 * r1 * d * sin(ang1) - 0.5 * r2 * d * sin(ang2);
}
int main()
{
int t, icase = 1;
scanf("%d", &t);
while (t--)
{
double r, R, ans = 0;
point p1, p2;
scanf("%lf%lf", &r, &R);
scanf("%lf%lf", &p1.x, &p1.y);
scanf("%lf%lf", &p2.x, &p2.y);
double d = sqrt((p1.x - p2.x) * (p1.x - p2.x) + (p1.y - p2.y) * (p1.y - p2.y));
printf("Case #%d: ", icase++);
if (d >= (2 * R))
{
printf("0.000000\n");
continue;
}
ans = calc_area(p1, p2, R, R);
if (d >= (R + r))
{
printf("%f\n", ans);
continue;
}
ans -= 2 * calc_area(p1, p2, R, r);
if (d >= (2 * r))
{
printf("%f\n", ans);
continue;
}
ans += calc_area(p1, p2, r, r);
printf("%f\n", ans);
}
return 0;
}





















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








