A Knight's Journey
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K | |
| Total Submissions: 35837 | Accepted: 12216 |
Description
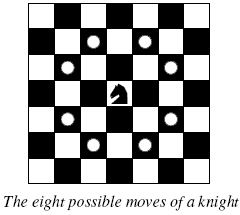 Background
BackgroundThe knight is getting bored of seeing the same black and white squares again and again and has decided to make a journey
around the world. Whenever a knight moves, it is two squares in one direction and one square perpendicular to this. The world of a knight is the chessboard he is living on. Our knight lives on a chessboard that has a smaller area than a regular 8 * 8 board, but it is still rectangular. Can you help this adventurous knight to make travel plans?
Problem
Find a path such that the knight visits every square once. The knight can start and end on any square of the board.
Input
The input begins with a positive integer n in the first line. The following lines contain n test cases. Each test case consists of a single line with two positive integers p and q, such that 1 <= p * q <= 26. This represents a
p * q chessboard, where p describes how many different square numbers 1, . . . , p exist, q describes how many different square letters exist. These are the first q letters of the Latin alphabet: A, . . .
Output
The output for every scenario begins with a line containing "Scenario #i:", where i is the number of the scenario starting at 1. Then print a single line containing the lexicographically first path that visits all squares of the
chessboard with knight moves followed by an empty line. The path should be given on a single line by concatenating the names of the visited squares. Each square name consists of a capital letter followed by a number.
If no such path exist, you should output impossible on a single line.
If no such path exist, you should output impossible on a single line.
Sample Input
3 1 1 2 3 4 3
Sample Output
Scenario #1: A1 Scenario #2: impossible Scenario #3:A1B3C1A2B4C2A3B1C3A4B2C4
测试数据:
3 7Scenario #3:A1B3D2F1G3E2G1F3E1G2E3C2A3B1C3A2C1D3B2D1F2 3 8Scenario #4:A1B3C1A2C3D1B2D3E1G2E3C2A3B1D2F1H2F3G1E2G3H1F2H3 题目大意:
人走“日”字型,判断能不能走完全部的方格,若能并输出走的顺序。
思路:就是一个深搜。不过个人认为有个难点:如何记录下所有经过的路径,并DFS返回时该怎么处理。
#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <map> #include<algorithm> #include<math.h> using namespace std; int vis[80][80]; int tx[80],ty[80]; int n,m; int cx[]= {-1,1,-2,2,-2,2,-1,1}; int cy[]= {-2,-2,-1,-1,1,1,2,2};//此顺次是固定的从下道上,从左到右的次序,并且是对称的 int bj; void dfs(int s1,int s2,int ans) { tx[ans]=s1;//一定是刚进DFS就存下坐标,否则在return后最后一个路径下标就没法存起来 ty[ans]=s2; if(ans==n*m)//搜索完成的标志 { bj=1; return ; } for(int i=0; i<8; i++) { int x=cx[i]+s1; int y=cy[i]+s2; if(x>=1&&y>=1&&x<=n&&y<=m&&!vis[x][y]&&!bj)//注意不要扔掉!bj,如果查找完毕后函数饭回的话,没有此句依然会进行 { vis[x][y]=1; dfs(x,y,ans+1); vis[x][y]=0; } } } int main() { int cla; scanf("%d",&cla); for(int gr=1; gr<=cla; gr++) { bj=0; memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis)); memset(tx,0,sizeof(tx)); memset(ty,0,sizeof(ty)); printf("Scenario #%d:\n",gr); scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); vis[1][1]=1; dfs(1,1,1);//便收索边进行步数的计算 if(bj) { for(int i=1; i<=n*m; i++) { printf("%c%d",ty[i]-1+'A',tx[i]); } } else printf("impossible"); printf("\n"); if(gr!=cla) printf("\n"); } return 0; }





















 964
964

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








