TreeMap是基于红黑树的实现的K-V集合。支持排序。也是线程不安全的集合。
文章目录
前言
TreeMap是红黑树结构。Entry<K,V>节点是一个静态内部类。定义了红黑树的数据结构。红黑书本质上是平衡二叉树。二叉树在极端的情况下会从树结构变为线性结构。因此红黑树作为平衡二叉树的一种实现,在这里得到了应用。红黑树主要通过旋转和变色的方式调节自身平衡。也就是说TreeMap在put的过程中先不考虑是否平衡,而是按照二叉树的规则插入的。即:左节点<父节点<右节点。最后才调整整个树的结构达到平衡。
static final class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
K key;
V value;
//左节点
Entry<K,V> left;
//右节点
Entry<K,V> right;
//父节点
Entry<K,V> parent;
//默认黑色
boolean color = BLACK;
/**
* 节点的构造器
*/
Entry(K key, V value, Entry<K,V> parent) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.parent = parent;
}
}
一、构造器
//默认的构造器。使用Key的自然排序的方式创建集合
public TreeMap() {
comparator = null;
}
//传入一个比较器,可以自定义排序方式去创建集合
public TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) {
this.comparator = comparator;
}
//传入Map集合。使用key自然排序的方式添加
public TreeMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
comparator = null;
putAll(m);
}
//构造一个包含相同映射并使用与指定排序映射相同顺序的新树映射。也就是传入的是SortedMap的实例
public TreeMap(SortedMap<K, ? extends V> m) {
comparator = m.comparator();
try {
buildFromSorted(m.size(), m.entrySet().iterator(), null, null);
} catch (java.io.IOException | ClassNotFoundException cannotHappen) {
}
}
二、 属性
private final Comparator<? super K> comparator;
//根结点
private transient Entry<K,V> root;
/**
* TreeMap集合的长度
*/
private transient int size = 0;
/**
* 集合修改的次数
*/
private transient int modCount = 0;
1.put 添加数据
代码如下:
public V put(K key, V value) {
//获取根结点
Entry<K,V> t = root;
//根结点为空,那么直接插入的节点就是根结点
if (t == null) {
//这里使用了比较器,但是没有返回值,因为返回也不需要。
compare(key, key);
root = new Entry<>(key, value, null);
size = 1;
modCount++;
return null;
}
int cmp;
Entry<K,V> parent;
// 获取比较器。这里的比较器根据创建TreeMap的时候可以指定,不指定就是空,使用自然排序的方式
Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
if (cpr != null) {
do {
//从根结点开始循环,获取父节点
parent = t;
cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
//cmp<0,就表示当前节点在父节点左侧,反之右侧
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
//否则就修改
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
else {
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
do {
parent = t;
cmp = k.compareTo(t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
//上面的while循环获取到直接父类以后,这里构建节点,直接插入。
Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent);
if (cmp < 0)
parent.left = e;
else
parent.right = e;
//插入完毕之后开始整体调整二叉树的平衡性。
fixAfterInsertion(e);
size++;
modCount++;
return null;
}
在看fixAfterInsertion(e)这个方法之前,我们先看几个辅助方法。
//获取p的父亲
private static <K,V> Entry<K,V> parentOf(Entry<K,V> p) {
return (p == null ? null: p.parent);
}
//获取p的左孩子
private static <K,V> Entry<K,V> leftOf(Entry<K,V> p) {
return (p == null) ? null: p.left;
}
//获取p的右孩子
private static <K,V> Entry<K,V> rightOf(Entry<K,V> p) {
return (p == null) ? null: p.right;
}
//判断p的颜色
private static <K,V> boolean colorOf(Entry<K,V> p) {
return (p == null ? BLACK : p.color);
}
//给p设置颜色
private static <K,V> void setColor(Entry<K,V> p, boolean c) {
if (p != null)
p.color = c;
}
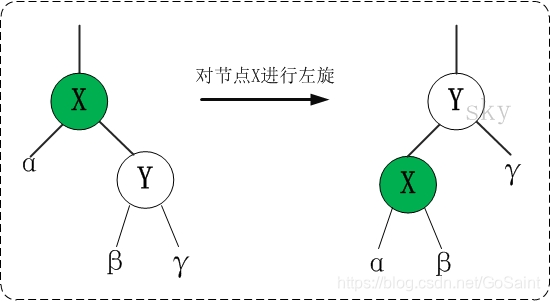
1 树的左旋
//左旋代码
private void rotateLeft(Entry<K,V> p) {
if(p!=null){
//获取p的右孩子y
Entry<K,V> r=p.right;
//将r的左节点赋值给p的右节点
p.right=r.left;
if(r.left!=null){
//将p设置为r左节点的父亲
r.left.parent=p;
}
//将p的父亲设置为r的父亲
r.parent=p.parent;
//p的父亲是空,那么p就是根节点
if(p.parent==null){
root=r;
}else if(p.parent.left==p){
//p原来是左节点,那么r也是左节点
p.parent.left = r;
}else{
p.parent.right= r;
}
r.left=p;
p.parent=r;
}
}
2 树的右旋
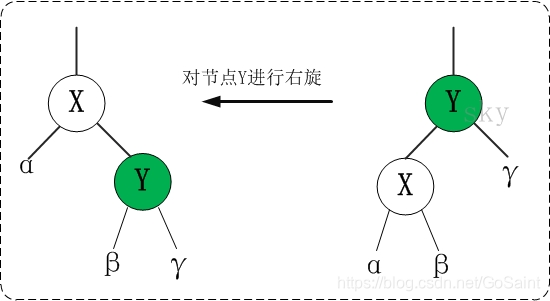
private void rotateRight(Entry<K,V> p) {
if (p != null) {
Entry<K,V> l = p.left;
p.left = l.right;
if (l.right != null) l.right.parent = p;
l.parent = p.parent;
if (p.parent == null)
root = l;
else if (p.parent.right == p)
p.parent.right = l;
else p.parent.left = l;
l.right = p;
p.parent = l;
}
}
3 红黑树平衡的调整
红黑树的特征:
(1) 每个节点或者是黑色,或者是红色。
(2) 根节点是黑色。
(3) 每个叶子节点是黑色。 [注意:这里叶子节点,是指为空的叶子节点!]
(4) 如果一个节点是红色的,则它的子节点必须是黑色的。
(5) 从一个节点到该节点的子孙节点的所有路径上包含相同数目的黑节点。
根据上面的5个原则,红黑树默认插入的节点都是红色。这样只会违背4,不会违背其他的规则。因此只需要对4做调整。
/**
* 插入节点之后的调整
*/
private void fixAfterInsertion(Entry<K, V> x) {
//首先将插入节点作为一个红的节点.
x.color = RED;
//红黑树的root节点是黑色节点。
/**
* 1 x!=null
* 2 x不是root节点,因为root节点是黑色节点
* 3 x的父节点也是红色节点
*/
while (x != null && x != root && x.parent.color == RED) {
/**
* 三种情况
* 1 当前节点的左叔叔节点==当前节点的父节点。也就是当前节点的父节点是左节点
* 2 当前节点的叔叔节点!=当前节点的父节点。也急速hi当前节点的父节点是右节点
*/
if (parentOf(x) == leftOf(parentOf(parentOf(x)))) {
//获取当前节点的右叔叔.也就是当前节点的叔叔。左叔叔就是父节点
Entry<K, V> y = rightOf(parentOf(parentOf(x)));
if(colorOf(y)==RED){
/* Case 1 当前节点的父节点是红色,且当前节点的祖父节点的另一个子节点(叔叔节点)也是红色。
(01) 将“父节点”设为黑色。
(02) 将“叔叔节点”设为黑色。
(03) 将“祖父节点”设为“红色”。
(04) 将“祖父节点”设为“当前节点”(红色节点);即,之后继续对“当前节点”进行操作。*/
setColor(parentOf(x),BLACK);
setColor(y,BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)),RED);
x=parentOf(parentOf(x));
}else {
//叔叔为黑色
if(x==parentOf(x).right){
/*Case 2 当前节点的父节点是红色,叔叔节点是黑色,且当前节点是其父节点的右孩子
(01) 将“父节点”作为“新的当前节点”。
(02) 以“新的当前节点”为支点进行左旋。*/
x=parentOf(x);
rotateLeft(x);
}
/*
* Case 3 当前节点的父节点是红色,叔叔节点是黑色,且当前节点是其父节点的左孩子
(01) 将“父节点”设为“黑色”。
(02) 将“祖父节点”设为“红色”。
(03) 以“祖父节点”为支点进行右旋。*/
setColor(parentOf(x),BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)),RED);
rotateRight(parentOf(parentOf(x)));
}
} else {
//当前节点的父节点是右节点。叔叔节点是左结点
//1 获取叔叔也节点
Entry<K, V> y = leftOf(parentOf(parentOf(x)));
if(colorOf(y)==RED){
/* Case 1 当前节点的父节点是红色,且当前节点的祖父节点的另一个子节点(叔叔节点)也是红色。
(01) 将“父节点”设为黑色。
(02) 将“叔叔节点”设为黑色。
(03) 将“祖父节点”设为“红色”。
(04) 将“祖父节点”设为“当前节点”(红色节点);即,之后继续对“当前节点”进行操作。*/
setColor(parentOf(x),BLACK);
setColor(y,BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)),RED);
x=parentOf(parentOf(x));
}else {
//叔叔为黑色
if(x==parentOf(x).left){
/*Case 2 当前节点的父节点是红色,叔叔节点是黑色,且当前节点是其父节点的右孩子
(01) 将“父节点”作为“新的当前节点”。
(02) 以“新的当前节点”为支点进行右旋。*/
x=parentOf(x);
rotateRight(x);
}
/*
* Case 3 当前节点的父节点是红色,叔叔节点是黑色,且当前节点是其父节点的左孩子
(01) 将“父节点”设为“黑色”。
(02) 将“祖父节点”设为“红色”。
(03) 以“祖父节点”为支点进行左旋。*/
setColor(parentOf(x),BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)),RED);
rotateLeft(parentOf(parentOf(x)));
}
}
}
}
2.get 获取数据
public V get(Object key) {
Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key);
return (p==null ? null : p.value);
}
get数据。内部调用getEntry(key)方法!
final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {
// 如果比较器不为空,那么
if (comparator != null)
return getEntryUsingComparator(key);
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
Entry<K,V> p = root;
//这里循环节点。从root开始,直到节点的key和传递的key相等,直接返回
while (p != null) {
int cmp = k.compareTo(p.key);
if (cmp < 0)
p = p.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
p = p.right;
else
return p;
}
return null;
}
//获取节点。使用比较器。根据比较器的规则比较
final Entry<K,V> getEntryUsingComparator(Object key) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
K k = (K) key;
Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
if (cpr != null) {
Entry<K,V> p = root;
while (p != null) {
int cmp = cpr.compare(k, p.key);
if (cmp < 0)
p = p.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
p = p.right;
else
return p;
}
}
return null;
}
3.ceilingEntry(K key)、ceilingKey(K key)
| 返回值 | 函数名称 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
| Map.Entry<K,V> | ceilingEntry(K key) | 返回大于或者等于key的节点 |
| K | ceilingKey(K key) | 返回大于或者等于key的值 |
public Map.Entry<K,V> ceilingEntry(K key) {
return exportEntry(getCeilingEntry(key));
}
public K ceilingKey(K key) {
return keyOrNull(getCeilingEntry(key));
}
//两个函数都是调用了getCeilingEntry(key)这个方法。
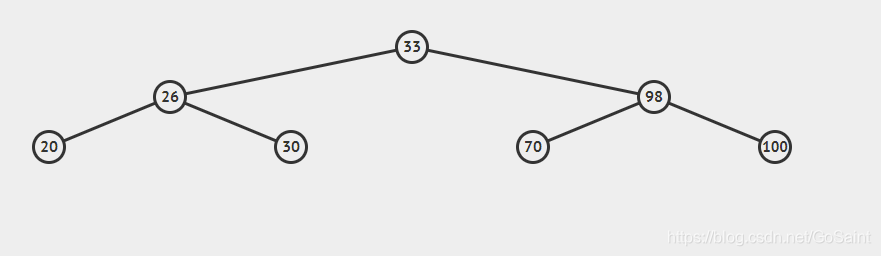
/**
* 11 12 5 22 7 17 33 45 49 以插入如左边数据开始
*/
final Entry<K,V> getCeilingEntry(K key) {
//① 第一次,获取root节点p=17
Entry<K,V> p = root;
while (p != null) {
//① 传入的18>17.因此cmp>0
//② 传入的18<33 因此cmp<0
//③ 传入的18<22 因此cmp<0
int cmp = compare(key, p.key);
if (cmp < 0) {
//② 由于33>18。cmp<0,所以此时只能寻找33的左边,如果为空,就直接返回
//③ 由于22>18。cmp<0,所以此时只能寻找22的左边,此时为空,直接返回。
if (p.left != null)
//② 33的left==22。索引p=22
p = p.left;
else
return p;
} else if (cmp > 0) {
//① p.right=33
if (p.right != null) {
//① 所以此时p=33
p = p.right;
} else {
//这里的逻辑是大于49才会进入该节点。
//获取父节点
Entry<K,V> parent = p.parent;
//获取当前节点
Entry<K,V> ch = p;
//循环里面是不断获取父节点和父节点的右节点,直到parent==null。返回
while (parent != null && ch == parent.right) {
ch = parent;
parent = parent.parent;
}
return parent;
}
} else
return p;
}
return null;
}
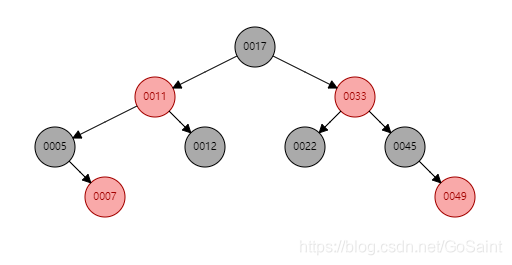
总结:传入的key不断和树的节点比较。大于节点,则在树的右边寻找,小于节点,则在树的左边寻找。等于则直接返回。大于树的最大节点,返回null.
4.clear()
//将root置为空
public void clear() {
modCount++;
size = 0;
root = null;
}
5.containsKey(Object key)
//判断是否包含key值。调用getEntry(key)来实现
public boolean containsKey(Object key) {
return getEntry(key) != null;
}
final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {
// Offload comparator-based version for sake of performance
if (comparator != null)
return getEntryUsingComparator(key);
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
Entry<K,V> p = root;
//这里循环查找。返回cmp=1的数据
while (p != null) {
int cmp = k.compareTo(p.key);
if (cmp < 0)
p = p.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
p = p.right;
else
return p;
}
return null;
}
6.containsValue(Object value)
//判断是否包含某个值
public boolean containsValue(Object value) {
for (Entry<K,V> e = getFirstEntry(); e != null; e = successor(e))
if (valEquals(value, e.value))
return true;
return false;
}
//使用了for循环。getFirstEntry()为获取第一个结点。
//此代码块可知,获取的是树的左边的最后一个子结点。对于二叉树而言,中序遍历和后序遍历都可以。
final Entry<K,V> getFirstEntry() {
Entry<K,V> p = root;
if (p != null)
while (p.left != null)
p = p.left;
return p;
}
//下面二叉树执行上面的for循环,遍历顺序是11-> 22-> 33-> 34 ->45.由此可知TreeMap使用的是中序遍历。上面的代码可以记忆,用来遍历二叉树
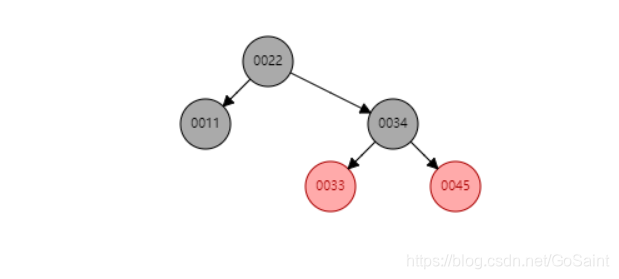
7.descendingKeySet() 获取key的降序集合
实例代码如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeMap<Integer, Integer> t = new TreeMap<>();
t.put(22, 22);
t.put(34, 34);
t.put(11, 11);
t.put(77, 77);
t.put(33, 33);
t.put(45, 45);
t.containsValue(45);
NavigableSet<Integer> integers = t.descendingKeySet();
Iterator<Integer> iterator = integers.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Integer next = iterator.next();
System.out.println(next);
}
}
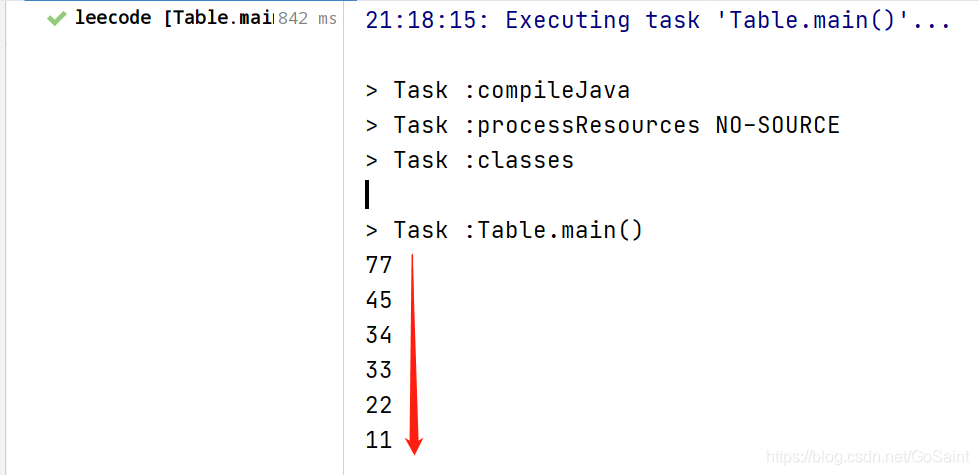
实例代码如下:
//获取key降序的集合
public NavigableSet<K> descendingKeySet() {
return descendingMap().navigableKeySet();
}
8.descendingMap() 获取TreeMap的降序集合
实例代码如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeMap<Integer, Integer> t = new TreeMap<>();
t.put(22, 22);
t.put(34, 34);
t.put(11, 11);
t.put(77, 77);
t.put(33, 33);
t.put(45, 45);
NavigableMap<Integer, Integer> descendingMap = t.descendingMap();
for (Map.Entry<Integer,Integer> m: descendingMap.entrySet()){
System.out.println("key=="+m.getKey()+" value=="+m.getValue());
}
}
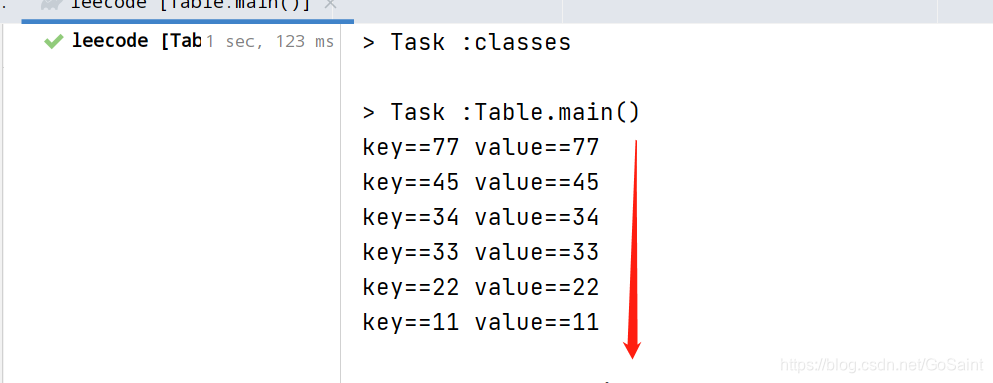
//获取TreeMap降序集合
public NavigableMap<K, V> descendingMap() {
NavigableMap<K, V> km = descendingMap;
return (km != null) ? km :
(descendingMap = new DescendingSubMap<>(this,
true, null, true,
true, null, true));
}
9 .entrySet() 获取集合的Set形式
//默认升序排列
public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() {
EntrySet es = entrySet;
return (es != null) ? es : (entrySet = new EntrySet());
}
10 .firstEntry() 获取第一个结点
//调用getFirstEntry()方法,默认是左边的最小值
public Map.Entry<K,V> firstEntry() {
return exportEntry(getFirstEntry());
}
11 .firstEntry() 获取第一个结点的key
//调用getFirstEntry()获取第一个结点,然后调用key()方法获取key
public K firstKey() {
return key(getFirstEntry());
}
//直接获取key.为e.key
static <K> K key(Entry<K,?> e) {
if (e==null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return e.key;
}
总结
1 TreeMap的数据结构是红黑树。由于继承了NavigableMap,因此可以排序。默认使用的是key自然排序,可以在构建TreeMap的时候指定排序方式。2 TreeMap的插入先根据二叉树的原则,然后调整平衡
3 TreeMap线程不安全。可以使用ConcurrentHashMap





















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








