本章内容包括:
- if语句
- if else语句
- 逻辑运算符:&&、||和!
- cctype字符函数库
- 条件运算符:?:
- switch语句
- continue语句和break语句
- 读取数字的循环
- 基本文件的输入和输出
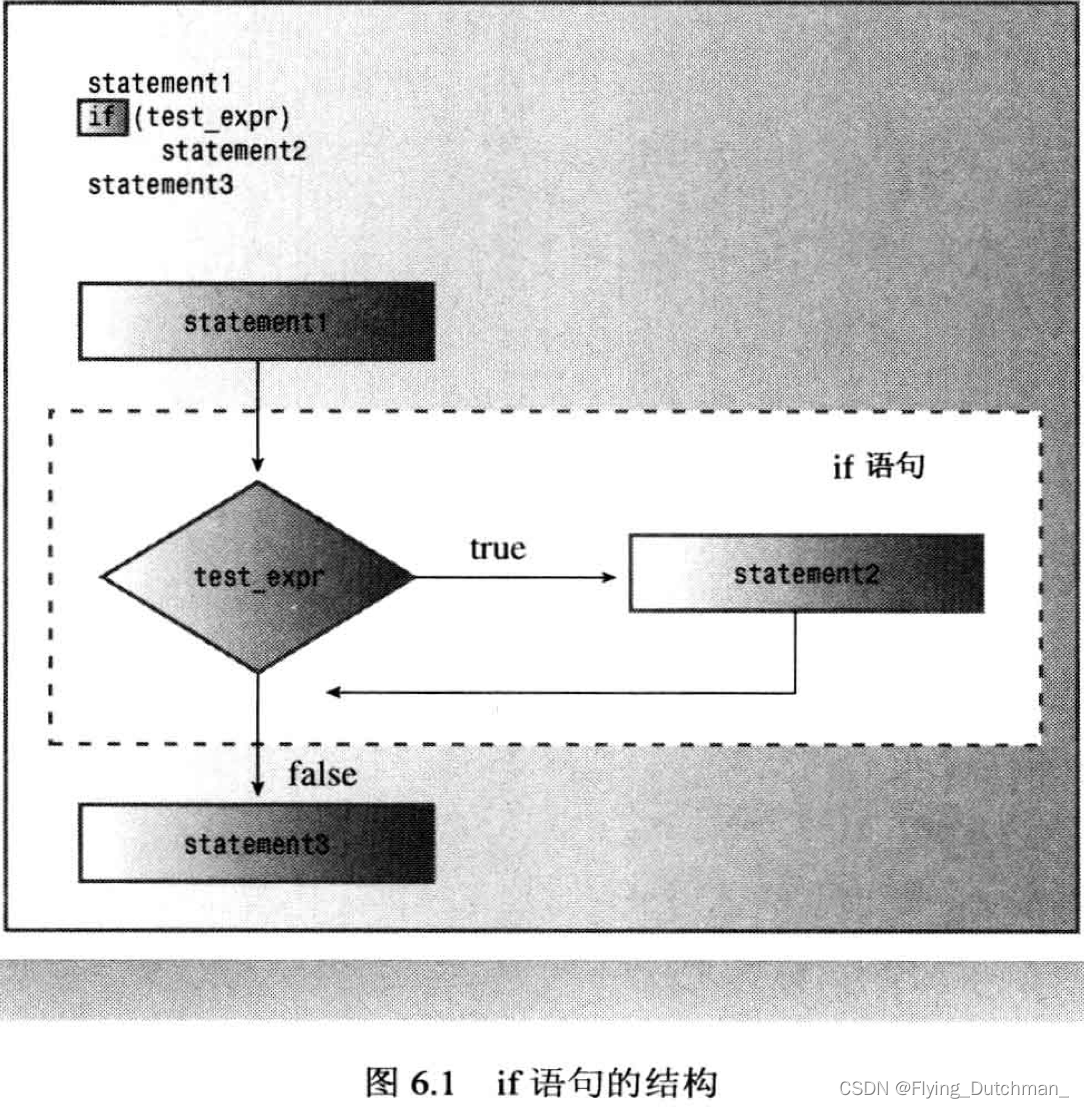
if 语句
- if有两种格式:if和if else
//if 语法和while相似:
if (test_condition)
statement- 如果测试条件为true,程序执行statement语句,后者可以是一条语句也可以是语句块{}。
- 如果测试条件为false,程序跳过statement语句
- if测试条件被强制转换为bool值,0为false,非0为true
//程序清单6.1
//有多少字符和空格
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(void)
{
char ch;
int total = 0;
int spaces = 0;
cin.get(ch);
while (ch != '.')
{
if (ch == ' ')
++spaces;
++toatl:
cin.get(ch);
}
cout << spaces << " spaces, " << total << " characters total in sentense\n";
return 0;
}if else 语句
- if语句让程序决定是否执行特定的语句或语句块
- if else 让程序决定执行两条语句或语句块中的哪一条
if (test_condition)
statement1
else
statement2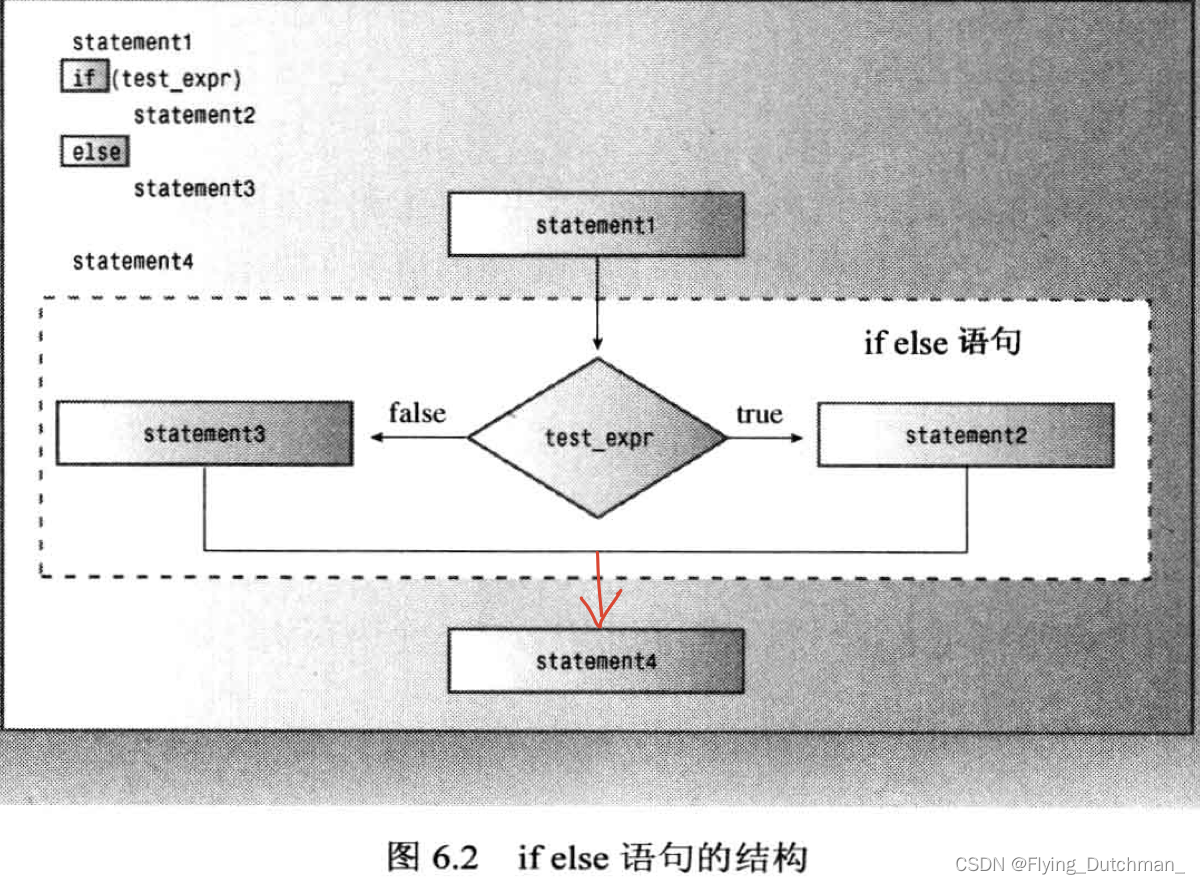
//程序清单6.2
//字符++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(void)
{
char ch;
cout << "Type,and I shall repeat.\n";
cin.get(ch)
while(ch != '.')
{
if (ch == '\n')
cout << ch;
else
cout << ++ch;
cin.get(ch);
}
return 0;
}格式化if else语句
- if else 如果需要多条语句,就需要大括号{}括起来,组成语句块
if else if else结构
//程序清单
//猜数字
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int Fave = 27;
int main(void)
{
int n;
cout << "Enter a number (1-100) to find my favorite number: ";
do
{
cin >> n;
if (n < Fave)
cout << "Too low -- guess again: ";
else if (n > Fave)
cout << "Too high -- guess again: ";
else
cout << Fave << " is my favorite!\n";
}while (n != Fave);
return 0;
}
逻辑表达式
- OR(||)或、AND(&&)与、NOT(!)非
逻辑OR运算符:|| (有真为真,全假为假)
- ||的优先级比关系运算符低
- 但建议加括号,以防忘记,阅读直观
- 5 >3 || 5 > 10 ——> (5 >3) || (5 > 10)
//程序清单6.4
//不分大小写
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(void)
{
cout << "Reformat hard disk, continue? <y/n>: ";
char ch;
cin >> ch;
if (ch == y || ch == Y)
cout << "Warned!\a\a\n";
else if (ch == n || ch == N)
cout << "Wise choice...bye\n";
else
{
cout << "That wasn't a y or n! Input again: ";
cin >> ch;
}
return 0;
}逻辑AND运算符:&& (有假为假,全真为真)
- &&的优先级比关系运算符低
- 但建议加括号,以防忘记,阅读直观
- 5 >3 && 5 > 10 ——> (5 >3) && (5 > 10)
//程序清单6.5
//由于两种不同原因结束while循环
#include <iostream>
const int ArSize = 6;
using namespace std;
int main(void)
{
float naaq[ArSize];
cout << "Enter the NAAQs, program terminates when make " << ArSize;
cout << " entries or enter a negative value.\n";
int i = 0;
float temp;
cout << "First value: ";
cin >> temp;
while (i < ArSize && temp >= 0)
{
naaq[i] = temp;
++i;
if (i < Arsize)
{
cout << "Next value: ";
cin >> temp;
}
}
if (i == 0)
cout << "No data.";
else
{
cout << "Enter your NAAQ: ";
float you;
cin >> you;
int count = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)
if (naaq[i] > you)
++count;
cout << count << " new age than you do.\n";
return 0;
}用&&来设置取值范围(优秀、良好、及格、不及格)
//程序清单6.6
//评级
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const char * qualify[4] = {"pefect.\n", "good.\n", "not bad.\n", "bad.\n"};
int main (void)
{
int index;
float score;
cout << "Enter your score: ";
cin >> score;
if ((score > 90) && (score <= 100))
index = 0;
else if ((score > 70) && (score <= 90))
index = 1;
else if ((score > 60) && (score <= 70))
index = 2;
else
index = 3;
cout << score << "' is " << qualify[index] << endl;
return 0;
}
逻辑NOT运算符:!(真假取反)
- if (!(x > 5))等同于if(x <= 5)
//程序清单6.7
//提醒输入超出范围
#include <iostream>
#include <climits>
using namespace std;
bool is_int(double);
int main(void)
{
double num;
cout << "Enter an integer value: ";
cin >> num;
while(!is_int(num))
{
cout << "Out of range --try again: ";
cin >> num;
}
int val = int (num);
cout << "You enter the integer: " << val << endl;
return 0;
}
bool is_int(double x)
{
if ((x <= INT_MAX) && (x >= INT_MIN))
return true;
else
return false;
}- 将可能的int值作为double来取,double取值范围更大,取值合适后在强制类型转换
- !运算符优先级高于所有关系运算符和算数运算符
!(x >5)
!x >5- AND优先级高于OR
age > 30 && age < 45 || weight > 300
//等同于
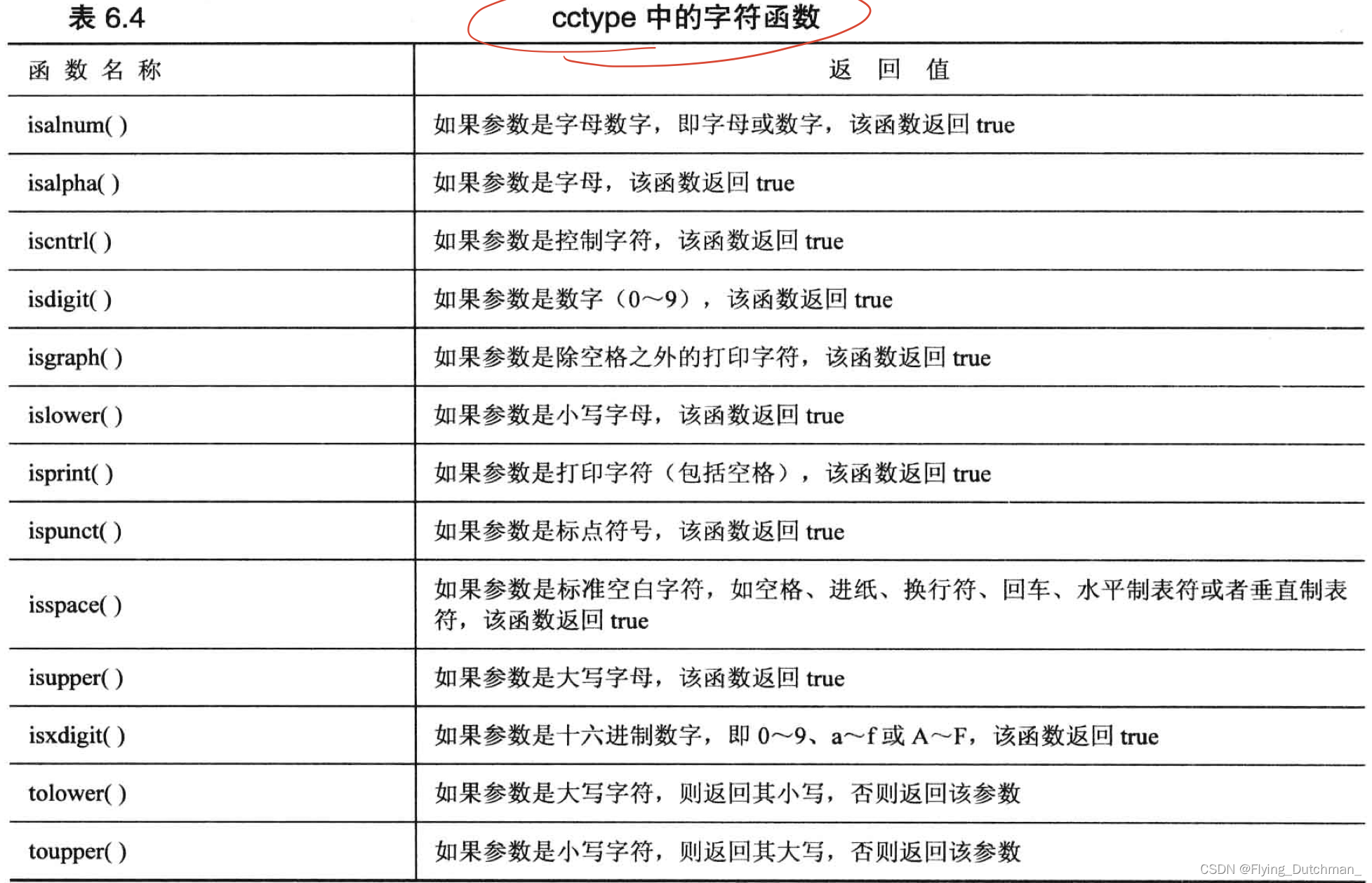
((age > 30) && (age < 45)) || (weight > 300)字符函数库cctype
- 简化诸如确定字符是否为大写、数字、标点符号等工作
//程序清单6.8
#include <iostream>
#include <cctype>
using namespace std;
int main(void)
{
cout << "Enter text to analysis, and @ to terminate.\n";
char ch;
int whitespaces = 0;
int digits = 0;
int chars = 0;
int punct = 0;
int others = 0;
cin.get(ch);
while(ch != '@')
{
if (isalpha(ch))
chars++;
else if (isspace(ch))
whitespace++;
else if (isdigit(ch))
digits++;
else if (ispunct(ch))
punct++;
else
others++;
cin.get(ch);
cout << "letters: " << chars << endl;
cout << "whitespace: " << whitespace << endl;
cout << "punctuations: " << punct << endl;
cout << "others: " << others << endl;
return 0;
}?:运算符(两者取其一)
- expression1 ?expression2 :expression3
- expression1为真,条件表达式值为expression2,否则,条件表达式值为expression3
(5 > 3) ? 10 : 12 //(5 > 3) 为真,表达式值为10
(3 == 9) ? 25 : 18 //(3 == 9)为假,表达式值为18//程序清单6.9
//两个数比大小
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(void)
{
int a, b;
cout << "Enter two integers: ";
cin >> a >> b;
int c = (a > b) ? a : b;
cout << "The larger of " << a << " and " << b << " is " << c << endl;
return 0;
}- 它与下面的语句等效
int c;
if (a > b)
c = a;
else
c = b;- 条件运算符最适合与简单关系和简单表达式的值。
- 当代码变得复杂时,使用if else语句来表达可能更为清晰。
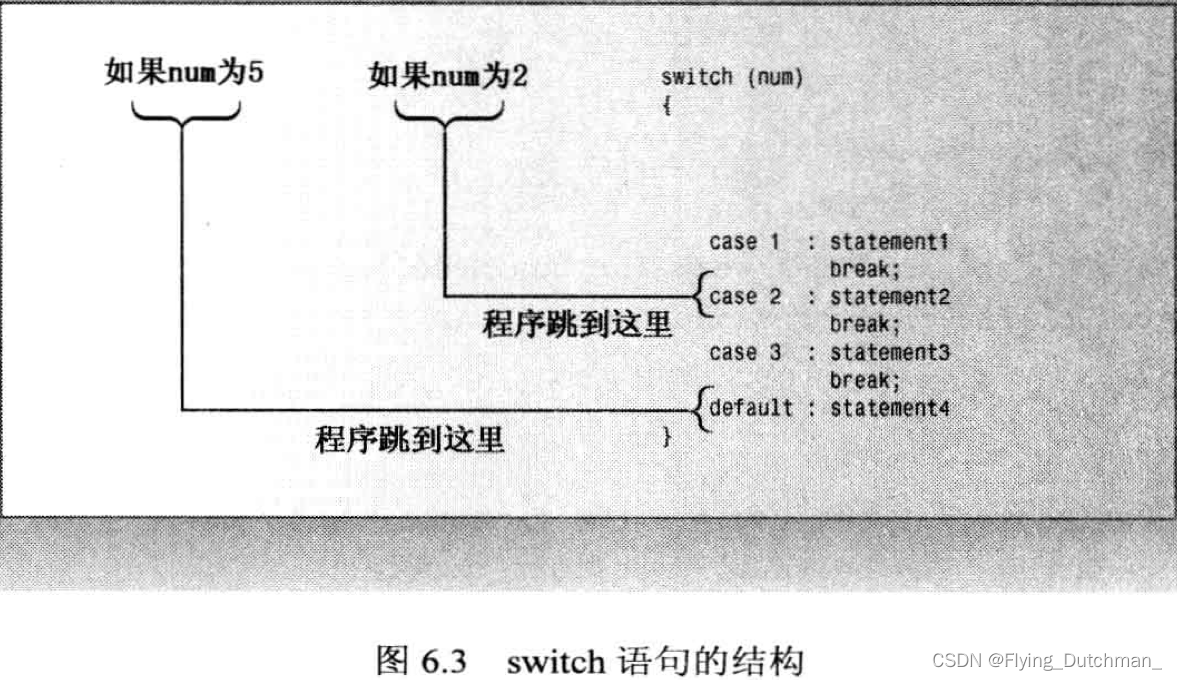
switch语句(多选一)
switch (integer_expression)
{
case label1 : statement(s)
case label2 : statement(s)
...
default : statement(s)
}
- integer_expression的值为4,则程序执行标签case 4
- integer_expression必须是结果为整数的表达式
- 标签必须是整数常量表达式(int、char或枚举量)
- integer_expression不与任何标签匹配,程序跳到default一行
- 程序执行完某个case不会停止,会继续往下执行,要停止必须使用break语句
//程序清单6.10
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void showmenu(void);
void report(void);
void comport(void);
int main(void)
{
showmenu();
int choice;
cin >> chioce;
while (choice != 5)
{
switch(choice)
{
case 1 : cout << "\a\n";
break;
case 2 : report();
break;
case 3 : cout << "Boss was in all day.\n";
break;
case 4 : comfort();
break;
default: cout << "That's not a choice.\n";
}
shormenu();
cin >> choice;
}
return 0;
}
void showmenu(void)
{
cout << "Enter 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5:\n";
"1) alarm 2) report\n";
"3) alibi 4) comfort\n";
"5) quit\n";
}
void report(void)
{
cout << "Sales up! Expenses down!\n";
}
void comfort(void)
{
cout << "Finest CEO!";
} //正是由于程序执行完某个case不会停止,会继续往下执行的特性
//可以为大小写提供相同语句
char choice;
cin >> chioce;
while (choice != 'Q' && choice != 'q')
{
switch(choice)
{
case 'a' :
case 'A' : cout << "\a\n";
break;
case 'r' :
case 'R' : report();
break;
case 'l' :
case 'L' : cout << "Boss was in all day.\n";
break;
case 'c' :
case 'C' : comfort();
break;
default: cout << "That's not a choice.\n";
}
shormenu();
cin >> choice;
}将枚举量用作标签
- 当switch语句将int值和枚举量标签进行比较时,将枚举量提升为int
- 在while循环测试条件中,也会将枚举量提升为int类型
//程序清单6.11
//switch语句和枚举
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
enum {red, orange, yellow, green, blue, violet, indigo};
int main(void)
{
cout << "Enter color code (0-6): ";
int code;
cin >> code;
while ((code >= red) && (code <= indigo))
{
switch (code)
{
case red : cout << "Her lips were red.\n"; break;
case orange : cout << "Her hair were orange.\n"; break;
case yellow : cout << "Her shoes were yellow.\n"; break;
case green : cout << "Her nails were green.\n"; break;
case blue : cout << "Her sweatsuit were blue.\n"; break;
case violet : cout << "Her eyes were violet.\n"; break;
case indigo : cout << "Her mood were indigo.\n"; break;
}
cout << "Enter color code (0-6): ";
cin >> code;
}
cout << "Bye\n";
return 0;
}
switch和if else
- switch:选项过多
- if else:设计取值范围、浮点测试、两个变量比较
break和continue语句
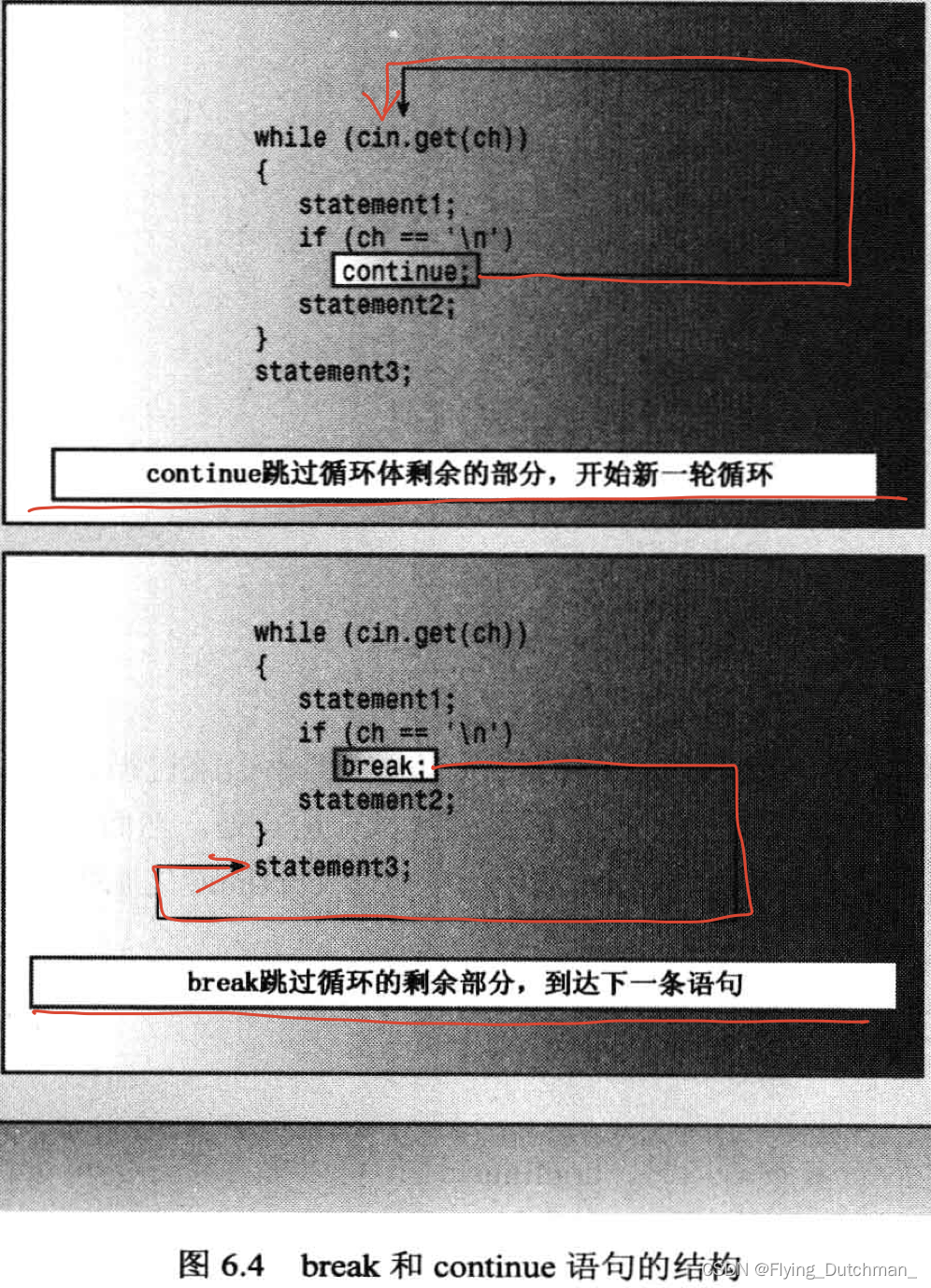
//程序清单6.12
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int ArSize = 80;
int main(void)
{
char line[ArSize];
int spaces = 0;
cout << "Enter a line of text:\n";
cin.getline(line, ArSize);
cout << "Complete line:\n" << line << endl;
cout << "line through first period:\n";
for (int i = 0; line[i] != '\0'; i++)
{
cout << line[i];
if (line[i] == '.')
break;
if (line[i] != ' ')
continue;
spaces++; //缩进是因为continue后的表达式会跳过
}
cout << endl << spaces << " spaces\n";
return 0;
}
- for循环中,continue语句使程序 直接跳到更新表达式处,然后跳到测试表达式处
- while循环中,continue使程序直接跳到测试表达式处,因此while循环中位于continue之后的更新表达式都将跳过
- 该程序可以不使用continue语句:
if (line[i] == ' ')
spaces++;读取数字的循环(要输入数字但是误输单词,怎么办?)
会发生4种情况:
- n的值保持不变
- 不匹配的对象将被留在输入队列中
- cin对象中的一个错误标记被设置
- 对cin方法的调用将返回false(如果被转换为bool类型)
//程序清单6.13
//当用户输入的不是数字时,程序不再读取输入
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int Max = 5;
int main(void)
{
double fish[Max];
cout << "Enter fish's weight.\n";
cout << "Enter up to " << Max << " fish, <q> to terminate.\n";
cout << "fish #1: ";
int i;
while (i < Max && cin >> fish[i])
{
if (++i < Max)
cout << "fish #" << i+1 << ": ";
}
double total = 0.0;
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)
total += fish[i];
if (i == 0)
cout << "No fish.\n";
else
cout << "Average weight: " << total / i << endl;
cout << "Done.\n";
return 0;
}//程序清单6.14
//当用户输入的不是数字时,程序提示错误,让用户继续输入
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int Max = 5;
int main(void)
{
int golf[Max];
cout << "Enter golf scores.\n";
cout << "Enter " << Max << " rounds.\n";
int i;
for (i = 0; i < Max, i++)
{
cout << "round #" << i+1 < ": ";
while (!(cin >> golf[i])) //判断输入是否正确,如果错误,执行循环
{
cin.clear();
while (cin.get() != '\n')
continue;
cout << "Enter a number: ";
}
}
double total = 0.0;
for (i = 0; i < Max; i++)
total += golf[i];
cout << "Average score = " << total / Max << " in " << Max << " rounds.\n";
return 0;
}简单文件输入/输出
写入到文本文件中


//程序清单6.15
//写入文件
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream> //1、包含文本流
using namespace std;
int main(void)
{
char automobile[50];
int year;
double a_price;
double d_price;
ofstream outFile; //2、为类ofstream创建outFile对象
outFile.open("carinfo.txt"); //3、将outFile对象和carinfo.txt文件关联
cout << "Enter the make and model of automobile: ";
cin.getline(automobile, 50);
cout << "Enter the model year: ";
cin >> year;
cout << "Enter the original asking price: ";
cin >> a_price;
d_price = 0.913 * a_price;
cout << fixed; //用小数,不用科学计数
cout.precision(2); //保留小数点后两位
cout.setf(ios_base::showpoint); //小数点后为0也显示
cout << "Make and model: " << automobile << endl;
cout << "Year: " << year << endl;
cout << "Was asking $" << a_price << endl;
cout << "Now asking $" << d_price << endl;
//4、outFile和cin用法一模一样
outFile << fixed; //用小数,不用科学计数
outFile.precision(2); //保留小数点后两位
outFile.setf(ios_base::showpoint); //小数点后为0也显示
outFile << "Make and model: " << automobile << endl;
outFile << "Year: " << year << endl;
outFile << "Was asking $" << a_price << endl;
outFile << "Now asking $" << d_price << endl;
outFile.close(); //与outFile.open()成对
return 0;
}读取文本文件

//程序清单6.16
//读取文件
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream> //1、file I/O support
#include <cstdlib> //support for exit()
using namespace std;
const int SIZE = 60;
int main(void)
{
char filename[SIZE];
ifstream inFile; //2、为类ifstream创建对象inFile
cout << "Enter name of data file: ";
cin.getline(filename, SIZE);
inFile.open(filename); //3、将对象inFile与文件filename关联
if (!inFile.is_open()) //判断文件打开是否成功,若否执行循环
{
cout << "Could not open the file: " << filename << endl;
cout << "Terminating.\n";
exit(EXIT_FAILURE); //出错退出,正常用return
}
cout << "Sucess open the txt file.\n";
double value;
double sum = 0.0;
int count = 0;
inFile >> value;
while (inFile.good()) //读取成功且没到文件尾
{
++count;
sum += value;
inFile >> value;
}
if (inFile.eof()) //如果到文件尾
cout << "End of file reached.\n";
else if (inFile.fail()) //如果读取失败
cout << "Input terminated by data mismatch.\n";
else
cout << "Input terminated for unknown reason.\n";
if (count == 0)
cout << "No data processed.\n";
else
{
cout << "Items read: " << count << endl;
cout << "Sum: " << sum << endl;
cout << "Average: " << sum / count << endl;
}
inFile.close(); //与inFile.open()成对
return 0;
}





 本文详细介绍了C++中的条件控制结构,包括if、ifelse、逻辑运算符、switch语句,以及如何处理用户输入和文件输入输出。示例代码展示了如何使用这些结构进行条件判断和循环控制,同时讲解了字符函数库cctype的使用。
本文详细介绍了C++中的条件控制结构,包括if、ifelse、逻辑运算符、switch语句,以及如何处理用户输入和文件输入输出。示例代码展示了如何使用这些结构进行条件判断和循环控制,同时讲解了字符函数库cctype的使用。
















 5047
5047

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








