一. for 语句
###
for ITEM in range(10):
code
###
>>> range(5)
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
>>> range(10)
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
>>>
>>> range(1,10)
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
>>> range(1,11)
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
>>> range(1,11,2)
[1, 3, 5, 7, 9]
>>> range(2,11,2)
[2, 4, 6, 8, 10]
range(stop): 0 ~ stop-1
range(start,stop): start ~ stop-1
range(start,stop,step): start ~ stop
例:求2到101之间所有偶数的和

求输入任意数的阶乘

break、continue、exit
break:跳出整个循环,不会再循环后面的内容
continue:跳出本次循环,continue后面的代码不再执行,但是循环依然继续
exit():结束程序的运行



练习
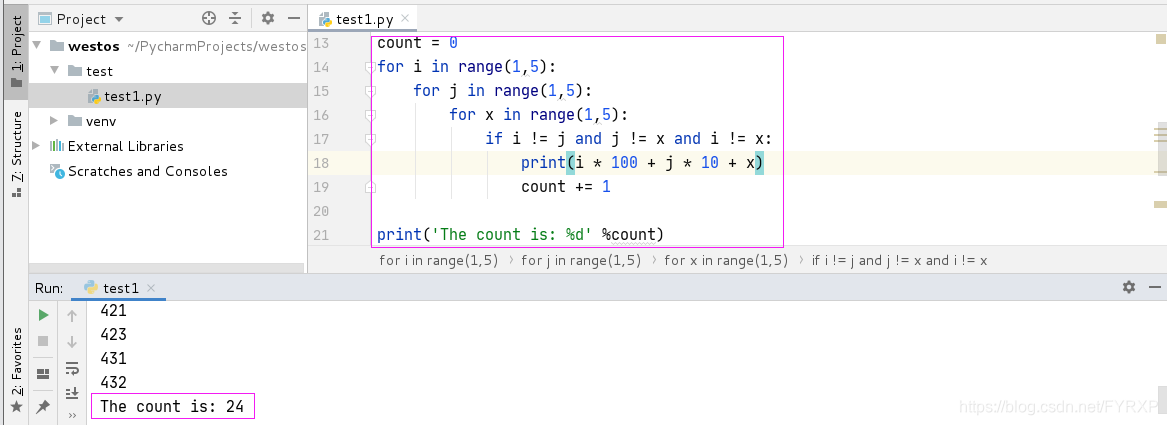
有1,2,3,4四个数字
求这四个数字能生成多少个互不相同且无重复数字的三位数(不能含有122,
133这种)
用户登陆程序需求:
1. 输入用户名和密码;
2. 判断用户名和密码是否正确? (name='root', passwd='westos')
3. 为了防止暴力破解, 登陆仅有三次机会, 如果超过三次机会,
报错提示;
for i in range(3):
name = input('UserName:')
passwd = input('Password:')
if name == 'root' and passwd == 'westos':
print('Login success')
break
else:
print('Login failed')
print('%d chance last' %(2 - i))
else:
print('Please try later!')
实现命令行式程序
import os
for i in range(1000):
cmd = input('[kiosk@python test]$ ')
if cmd:
if cmd == 'exit':
print('logout')
break
else:
print('run %s' %(cmd))
os.system(cmd)
else:
continue
二. while 语句
while 条件:
条件满足时,做的事情1
条件满足时,做的事情2
......
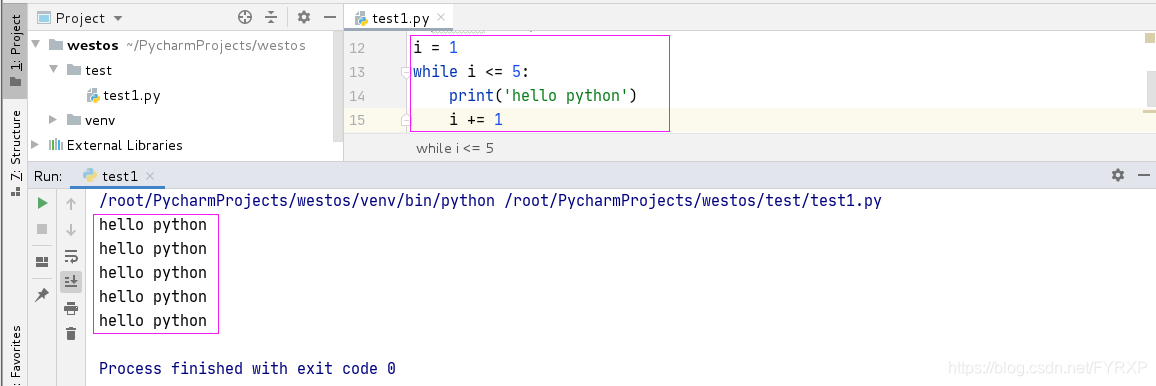
练习
计算:0~100之间所有数字的累积求和
python中的计数方法
常见的计数方法有两种,可以分为
自然计数法(从1开始) -- 更符合人类的习惯
程序计数法(从0开始) -- 几乎所有的程序语言都选择从0开始计数
因此,大家在编写程序时,应该尽量养成习惯:除非需求的特殊要求,否则>循环的计数从0开始
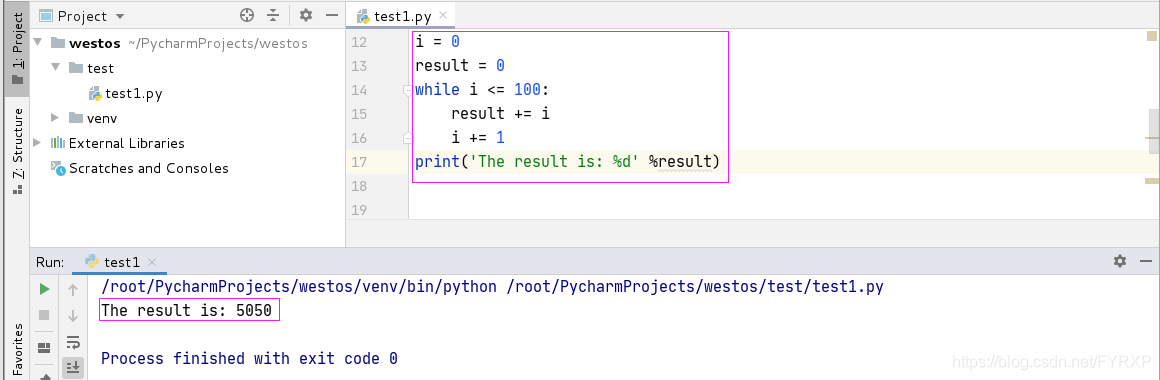
循环计算
在程序开发中,通常会遇到利用循环重复计算的需求(利用CPU的强大之处 完
成相应的复杂计算)
遇到这种情况:
1.在while上方定义一个变量,用于存放最终的计算结果
2.在循环体内部,每次循环都用最新的计算结果,更新之前定义的变量
用户登陆程序需求:
1. 输入用户名和密码;
2. 判断用户名和密码是否正确? (name='root', passwd='westos')
3. 为了防止暴力破解, 登陆仅有三次机会, 如果超过三次机会,
报错提示;
trycount = 0
while trycount < 3:
name = input('UserName:')
passwd = input('Password:')
if name == 'root' and passwd == 'westos':
print('Login success')
break
else:
print('Login failed')
print('%d chance last' %(2 - trycount))
trycount += 1
else:
print('Please try later!')
row = 1
while row <= 5:
col = 1
while col <= row:
print('*',end='')
col += 1
print('')
row += 1
猜数字游戏
1. 系统随机生成一个1~100的数字;
2. 用户总共有5次猜数字的机会;
3. 如果用户猜测的数字大于系统给出的数字,打印“too big”;
4. 如果用户猜测的数字小于系统给出的数字,打印"too small";
5. 如果用户猜测的数字等于系统给出的数字,打印"恭喜",并且退
出循环;
import random
trycount = 0
computer = random.randint(1,100)
print(computer)
while trycount < 5:
player = int(input('Num:'))
if player > computer:
print('too big')
trycount += 1
elif player < computer:
print('too small')
trycount += 1
else:
print('Congratulation!')
break

三. string 语句
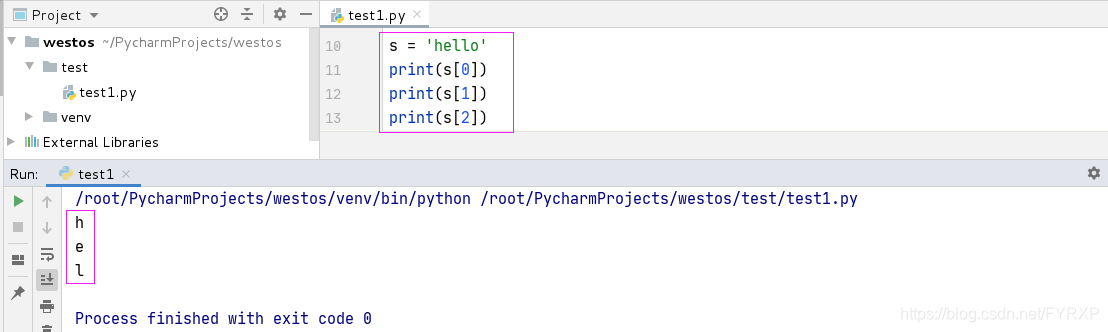
索引
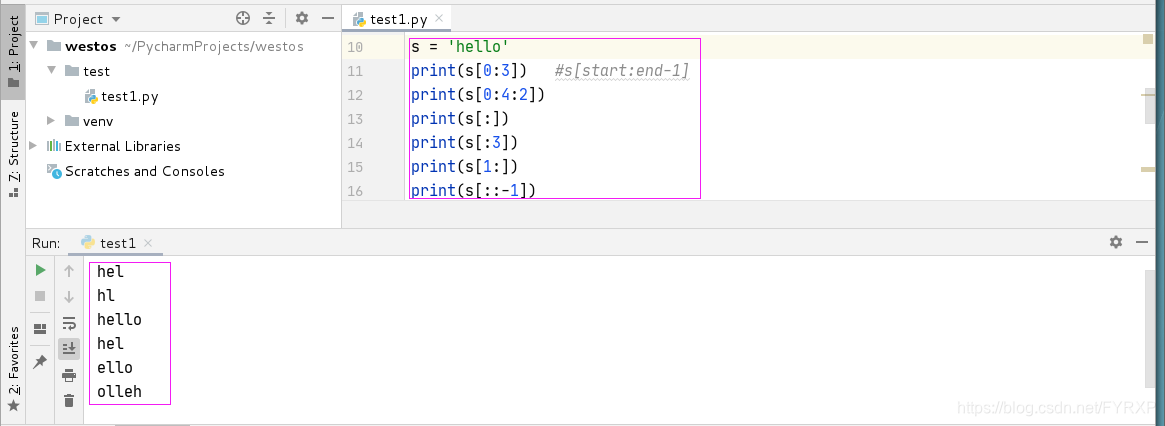
剪切cut
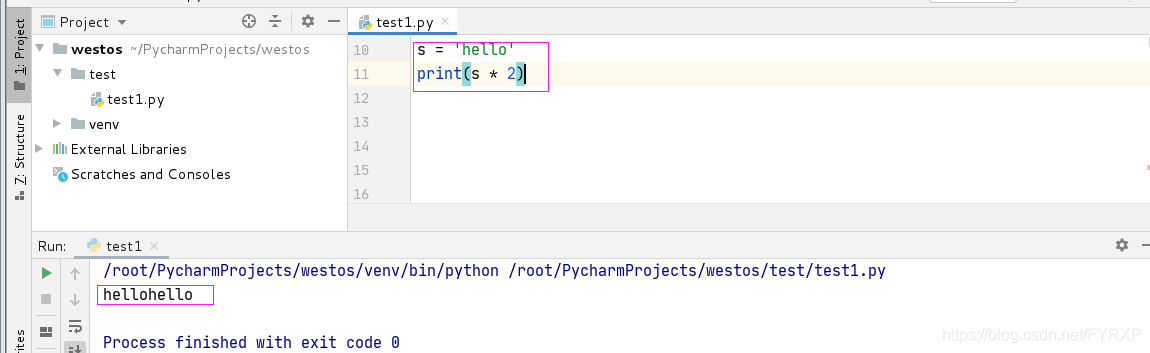
重复
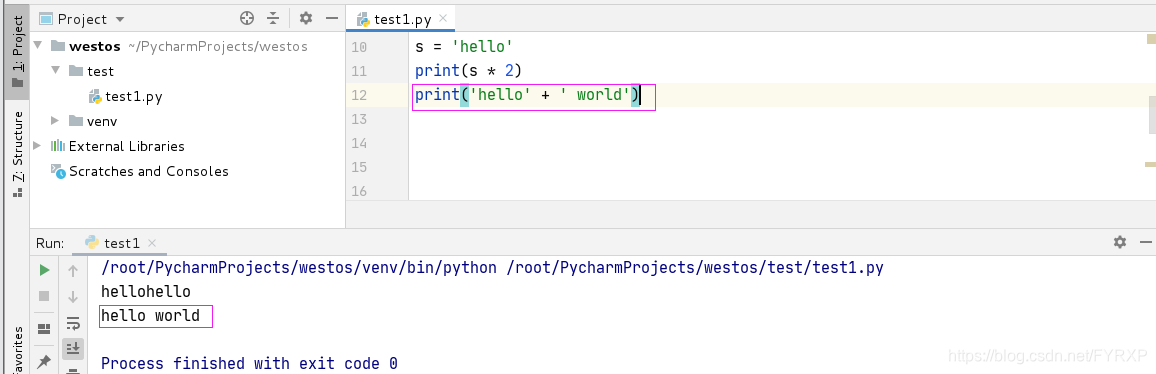
连接
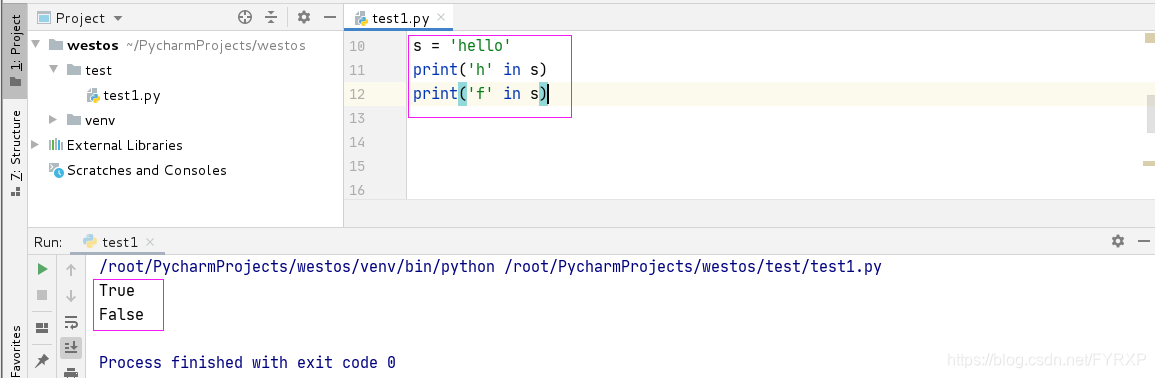
判断是否存在
练习
示例 1:
输入: 121
输出: true
示例 2:
输入: -121
输出: false
解释: 从左向右读, 为 -121 。 从右向左读, 为 121- 。因此它不
是一个回文数。
示例 3:
输入: 10
输出: false
解释: 从右向左读, 为 01 。因此它不是一个回文数。
num = input('Num:')
if num == num[::-1]:
print('ok')
else:
print('failed')
变量名是否合法:
1.变量名可以由字母,数字或者下划线组成
2.变量名只能以字母或者下划线开头
s = 'hello@'1.判断变量名的第一个元素是否为字母或者下划线 s[0]
2.如果第一个元素符合条件,判断除了第一个元素之外的其他元素s[1:]
while True:
s = input('Str:')
if a:
for i in x:
if b:
print('illegal')
break
else:
print('ok')
else:
print('illegal!')
 Python编程基础:循环、字符串与变量检查
Python编程基础:循环、字符串与变量检查





 这篇博客介绍了Python的基础语法,包括for循环的应用,如计算偶数和、阶乘及计数方法;while循环的使用,例如数字累积求和和用户登录程序;字符串操作,如索引、剪切、重复和连接,并提供了回文数判断的示例;最后讨论了变量名的合法性检查。
这篇博客介绍了Python的基础语法,包括for循环的应用,如计算偶数和、阶乘及计数方法;while循环的使用,例如数字累积求和和用户登录程序;字符串操作,如索引、剪切、重复和连接,并提供了回文数判断的示例;最后讨论了变量名的合法性检查。
















 3038
3038

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








