看了resnet的论文,然后手动用tf.nn模块搭建了resnet34。虽然比较累与笨,但是还是方便了我的理解。

这里说说我的理解,残差网络主要是为了防止退化,因此会将特征跳动到下一个以防衰退。
实线部分就是将前面的model与卷积后的model直接相加,形状不变的。
而后面的虚线怎么理解呢?虚线是因为前面的model和后面的model不一样的shape。这里论文中说可以通过填充0来解决,好处是降低网络复杂度,但是这样效果可能一般。第二种方法就是线性投影,其实就是进行一次卷积,这里线性要保证不要加激活函数,加上bias可以。因为model的size大小也变,因此用1x1的卷积核,个数和后面的model要一样,然后stride是2就行了。
大概是这样:
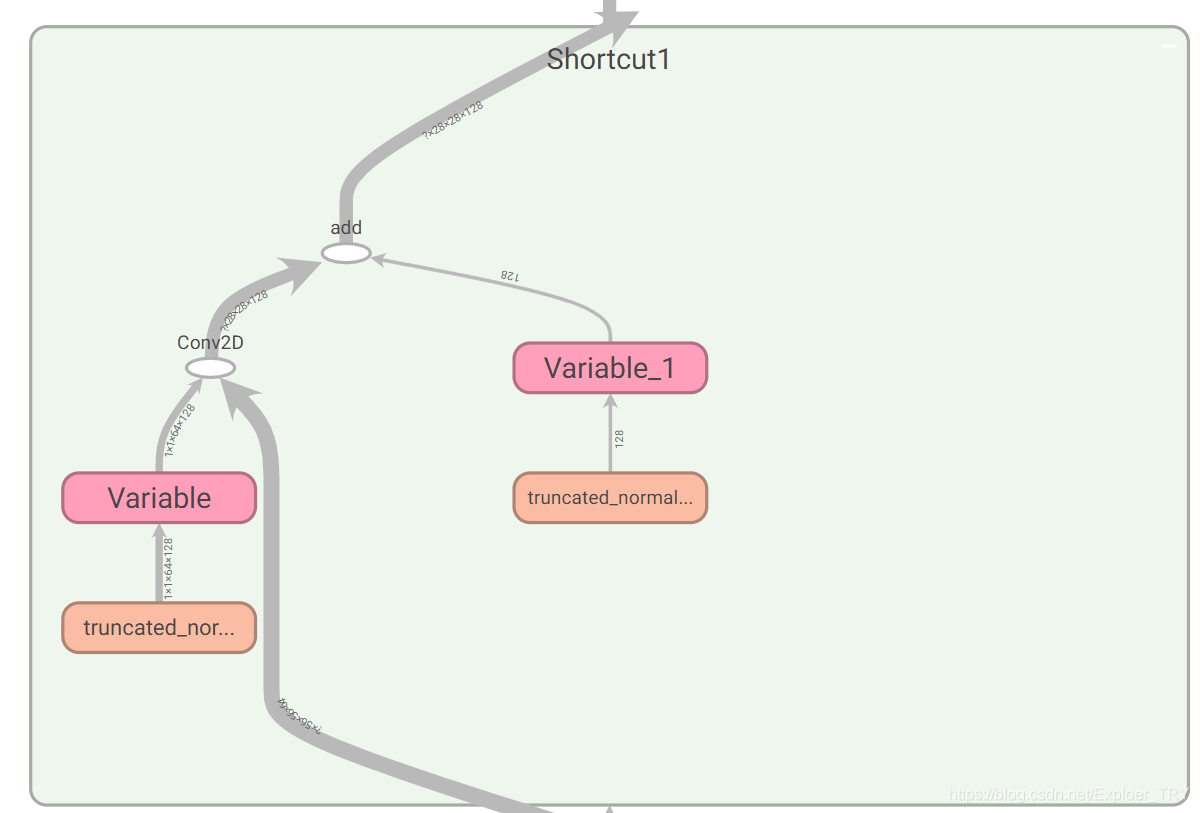
然后附上具体的实现demo(后面还有一个版本):
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Mon April 15 2019
@author: Ruoyu Chen
The Resnet34 networks
"""
import tensorflow as tf
BATCH_SIZE = 10
def weight_variable(shape, name=None):
initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape, stddev=0.1)
return tf.Variable(initial, name)
def bias_variable(shape, name=None):
initial = tf.constant(0.1, shape=shape)
return tf.Variable(initial, name)
def conv2d(input, filter, strides, padding="SAME", name=None):
# filters with shape [filter_height * filter_width * in_channels, output_channels]
# Must have strides[0] = strides[3] =1
# For the most common case of the same horizontal and vertices strides, strides = [1, stride, stride, 1]
'''
Args:
input: A Tensor. Must be one of the following types: float32, float64.
filter: A Tensor. Must have the same type as input.
strides: A list of ints. 1-D of length 4. The stride of the sliding window for each dimension of input.
padding: A string from: "SAME", "VALID". The type of padding algorithm to use.
use_cudnn_on_gpu: An optional bool. Defaults to True.
name: A name for the operation (optional).
'''
return tf.nn.conv2d(input, filter, strides, padding="SAME", name=name) # padding="SAME"用零填充边界
def Resnet34(input):
'''参考论文: '''
# input_size:(224,224,3)
with tf.name_scope("Conv1"):
with tf.name_scope("Variable"):
kernel_1 = weight_variable([7, 7, 3, 64], name='kernel_1')
bias_1 = weight_variable([64], name='bias_1')
with tf.name_scope("Convolution"):
layer_1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(input, kernel_1, strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], name='conv_layer_1') + bias_1, name='layer_1')
with tf.name_scope("Maxpool_1"):
Maxpool_1 = tf.nn.max_pool(layer_1, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding="SAME",name='maxpool_1') # size = (7,7,832)
with tf.name_scope("Block1"):
with tf.name_scope("Conv2"):
with tf.name_scope("Variable"):
kernel_2 = weight_variable([3, 3, 64, 64], name='kernel_2')
bias_2 = weight_variable([64], name='bias_2')
with tf.name_scope("Convolution"):
layer_2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(Maxpool_1, kernel_2, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], name='conv_layer_2') + bias_2,name='layer_2')
with tf.name_scope("Conv3"):
with tf.name_scope("Variable"):
kernel_3 = weight_variable([3, 3, 64, 64], name='kernel_3')
bias_3 = weight_variable([64], name='bias_3')
with tf.name_scope("Convolution"):
layer_3 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(layer_2 , kernel_3, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], name='conv_layer_3') + bias_3,name='layer_3')
with tf.name_scope("Res1"):
Res1 = layer_3 + Maxpool_1
with tf.name_scope("Block2"):
with tf.name_scope("Conv4"):
with tf.name_scope("Variable"):
kernel_4 = weight_variable([3, 3, 64, 64], name='kernel_4')
bias_4 = weight_variable([64], name='bias_4')
with tf.name_scope("Convolution"):
layer_4 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(Res1, kernel_4, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], name='conv_layer_4') + bias_4,name='layer_4')
with tf.name_scope("Conv5"):
with tf.name_scope("Variable"):
kernel_5 = weight_variable([3, 3, 64, 64], name='kernel_5')
bias_5 = weight_variable([64], name='bias_5')
with tf.name_scope("Convolution"):
layer_5 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(layer_4 , kernel_5, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], name='conv_layer_5') + bias_5,name='layer_5')
with tf.name_scope("Res2"):
Res2 = layer_5 + Res1
with tf.name_scope("Block3"):
with tf.name_scope("Conv6"):
with tf.name_scope("Variable"):
kernel_6 = weight_variable([3, 3, 64, 64], name='kernel_6')
bias_6 = weight_variable([64], name='bias_6')
with tf.name_scope("Convolution"):
layer_6 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(Res2, kernel_6, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], name='conv_layer_6') + bias_6, name='layer_6')
with tf.name_scope("Conv7"):
with tf.name_scope("Variable"):
kernel_7 = weight_variable([3, 3, 64, 64], name='kernel_7')
bias_7 = weight_variable([64], name='bias_7')
with tf.name_scope("Convolution"):
layer_7 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(layer_6 , kernel_7, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], name='conv_layer_7') + bias_7,name='layer_7')
with tf.name_scope("Res3"):
Res3 = layer_7 + Res2
with tf.name_scope("Block4"):
with tf.name_scope("Conv8"):
with tf.name_scope("Variable"):
kernel_8 = weight_variable([3, 3, 64, 128], name='kernel_8')
bias_8 = weight_variable([128], name='bias_8')
with tf.name_scope("Convolution"):
layer_8 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(Res3, kernel_8, strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], name='conv_layer_8') + bias_8, name='layer_8')
with tf.name_scope("Conv9"):
with tf.name_scope("Variable"):
kernel_9 = weight_variable([3, 3, 128, 128], name='kernel_9')
bias_9 = weight_variable([128], name='bias_9')
with tf.name_scope("Convolution"):
layer_9 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(layer_8 , kernel_9, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], name='conv_layer_9') + bias_9,name='layer_9')
with tf.name_scope("Shortcut1"):
kernel_line_1 = weight_variable([1, 1, 64, 128], name='kernel_line_1')
bias_line_1 = weight_variable([128], name='bias_line_1')
layer_line_1 = conv2d(Res3 , kernel_line_1, strides=[1, 2, 2, 1]) + bias_line_1
with tf.name_scope("Res4"):
Res4 = layer_line_1 + layer_9
with tf.name_scope("Block5"):
with tf.name_scope("Conv10"):
with tf.name_scope("Variable"):
kernel_10 = weight_variable([3, 3, 128, 128], name='kernel_10')
bias_10 = weight_variable([128], name='bias_10')
with tf.name_scope("Convolution"):
layer_10 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(Res4, kernel_10, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], name='conv_layer_10') + bias_10, name='layer_10')
with tf.name_scope("Conv11"):
with tf.name_scope("Variable"):
kernel_11 = weight_variable([3, 3, 128, 128], name='kernel_11')
bias_11 = weight_variable([128], name='bias_11')
with tf.name_scope("Convolution"):
layer_11 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(layer_10 , kernel_11, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], name='conv_layer_11') + bias_11,name='layer_11')
with tf.name_scope("Res5"):
Res5 = Res4 + layer_11
with tf.name_scope("Block6"):
with tf.name_scope("Conv12"):
with tf.name_scope("Variable"):
kernel_12 = weight_variable([3, 3, 128, 128], name='kernel_12')
bias_12 = weight_variable([128], name='bias_12')
with tf.name_scope("Convolution"):
layer_12 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(Res5, kernel_12, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], name='conv_layer_12') + bias_12, name='layer_12')
with tf.name_scope("Conv13"):
with tf.name_scope("Variable"):
kernel_13 = weight_variable([3, 3, 128, 128], name='kernel_13')
bias_13 = weight_variable([128], name='bias_13')
with tf.name_scope("Convolution"):
layer_13 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(layer_12 , kernel_13, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], name='conv_layer_13') + bias_13,name='layer_13')
with tf.name_scope("Res6"):
Res6 = Res5 + layer_13
with tf.name_scope("Block7"):
with tf.name_scope("Conv14"):
with tf.name_scope("Variable"):
kernel_14 = weight_variable([3, 3, 128, 128], name='kernel_14')
bias_14 = weight_variable([128], name='bias_14')
with tf.name_scope("Convolution"):
layer_14 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(Res6, kernel_14, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], name='conv_layer_14') + bias_14, name='layer_14')
with tf.name_scope("Conv15"):
with tf.name_scope("Variable"):
kernel_15 = weight_variable([3, 3, 128, 128], name='kernel_15')
bias_15 = weight_variable([128], name='bias_15')
with tf.name_scope("Convolution"):
layer_15 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(layer_14 , kernel_15, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], name='conv_layer_15') + bias_15,name='layer_15')
with tf.name_scope("Res7"):
Res7 = Res6 + layer_15
with tf.name_scope("Block8"):
with tf.name_scope("Conv16"):
with tf.name_scope("Variable"):
kernel_16 = weight_variable([3, 3, 128, 256], name='kernel_16')
bias_16 = weight_variable([256], name='bias_16')
with tf.name_scope("Convolution"):
layer_16 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(Res7, kernel_16, strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], name='conv_layer_16') + bias_16, name='layer_16')
with tf.name_scope("Conv17"):
with tf.name_scope("Variable"):
kernel_17 = weight_variable([3, 3, 256, 256], name='kernel_17')
bias_17 = weight_variable([256], name='bias_17')
with tf.name_scope("Convolution"):
layer_17 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(layer_16 , kernel_17, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], name='conv_layer_17') + bias_17,name='layer_17')
with tf.name_scope("Shortcut2"):
kernel_line_2 = weight_variable([1, 1, 128, 256], name='kernel_line_2')
bias_line_2 = weight_variable([256], name='bias_line_2')
layer_line_2 = conv2d(Res7 , kernel_line_2, strides=[1, 2, 2, 1]) + bias_line_2
with tf.name_scope("Res8"):
Res8 = layer_line_2 + layer_17
with tf.name_scope("Block9"):
with tf.name_scope("Conv18"):
with tf.name_scope("Variable"):
kernel_18 = weight_variable([3, 3, 256, 256], name='kernel_18')
bias_18 = weight_variable([256], name='bias_18')
with tf.name_scope("Convolution"):
layer_18 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(Res8, kernel_18, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], name='conv_layer_18') + bias_18, name='layer_18')
with tf.name_scope("Conv19"):
with tf.name_scope("Variable"):
kernel_19 = weight_variable([3, 3, 256, 256], name='kernel_19')
bias_19 = weight_variable([256], name='bias_19')
with tf.name_scope("Convolution"):
layer_19 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(layer_18 , kernel_19, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], name='conv_layer_19') + bias_19,name='layer_19')
with tf.name_scope("Res9"):
Res9 = Res8 + layer_19
with tf.name_scope("Block10"):
with tf.name_scope("Conv20"):
with tf.name_scope("Variable"):
kernel_20 = weight_variable([3, 3, 256, 256], name='kernel_20')
bias_20 = weight_variable([256], name='bias_20')
with tf.name_scope("Convolution"):
layer_20 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(Res9, kernel_20, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], name='conv_layer_20') + bias_20, name='layer_20')
with tf.name_scope("Conv21"):
with tf.name_scope("Variable"):
kernel_21 = weight_variable([3, 3, 256, 256], name='kernel_21')
bias_21 = weight_variable([256], name='bias_21')
with tf.name_scope("Convolution"):
layer_21 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(layer_20 , kernel_21, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], name='conv_layer_21') + bias_21,name='layer_21')
with tf.name_scope("Res10"):
Res10 = Res9 + layer_21
with tf.name_scope("Block11"):
with tf.name_scope("Conv22"):
with tf.name_scope("Variable"):
kernel_22 = weight_variable([3, 3, 256, 256], name='kernel_22')
bias_22 = weight_variable([256], name='bias_22')
with tf.name_scope("Convolution"):
layer_22 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(Res10, kernel_22, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], name='conv_layer_22') + bias_22, name='layer_22')
with tf.name_scope("Conv23"):
with tf.name_scope("Variable"):
kernel_23 = weight_variable([3, 3, 256, 256], name='kernel_23')
bias_23 = weight_variable([256], name='bias_23')
with tf.name_scope("Convolution"):
layer_23 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(layer_22 , kernel_23, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], name='conv_layer_23') + bias_23,name='layer_23')
with tf.name_scope("Res11"):
Res11 = Res10 + layer_23
with tf.name_scope("Block12"):
with tf.name_scope("Conv24"):
with tf.name_scope("Variable"):
kernel_24 = weight_variable([3, 3, 256, 256], name='kernel_24')
bias_24 = weight_variable([256], name='bias_24')
with tf.name_scope("Convolution"):
layer_24 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(Res11, kernel_24, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], name='conv_layer_24') + bias_24, name='layer_24')
with tf.name_scope("Conv25"):
with tf.name_scope("Variable"):
kernel_25 = weight_variable([3, 3, 256, 256], name='kernel_25')
bias_25 = weight_variable([256], name='bias_25')
with tf.name_scope("Convolution"):
layer_25 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(layer_24 , kernel_25, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], name='conv_layer_25') + bias_25,name='layer_25')
with tf.name_scope("Res12"):
Res12 = Res11 + layer_25
with tf.name_scope("Block13"):
with tf.name_scope("Conv26"):
with tf.name_scope("Variable"):
kernel_26 = weight_variable([3, 3, 256, 256], name='kernel_26')
bias_26 = weight_variable([256], name='bias_26')
with tf.name_scope("Convolution"):
layer_26 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(Res12, kernel_26, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], name='conv_layer_26') + bias_26, name='layer_26')
with tf.name_scope("Conv27"):
with tf.name_scope("Variable"):
kernel_27 = weight_variable([3, 3, 256, 256], name='kernel_27')
bias_27 = weight_variable([256], name='bias_27')
with tf.name_scope("Convolution"):
layer_27 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(layer_26 , kernel_27, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], name='conv_layer_27') + bias_27,name='layer_27')
with tf.name_scope("Res13"):
Res13 = Res12 + layer_27
with tf.name_scope("Block14"):
with tf.name_scope("Conv28"):
with tf.name_scope("Variable"):
kernel_28 = weight_variable([3, 3, 256, 512], name='kernel_28')
bias_28 = weight_variable([512], name='bias_28')
with tf.name_scope("Convolution"):
layer_28 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(Res13, kernel_28, strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], name='conv_layer_28') + bias_28, name='layer_28')
with tf.name_scope("Conv29"):
with tf.name_scope("Variable"):
kernel_29 = weight_variable([3, 3, 512, 512], name='kernel_29')
bias_29 = weight_variable([512], name='bias_29')
with tf.name_scope("Convolution"):
layer_29 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(layer_28 , kernel_29, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], name='conv_layer_29') + bias_29,name='layer_29')
with tf.name_scope("Shortcut3"):
kernel_line_3 = weight_variable([1, 1, 256, 512], name='kernel_line_3')
bias_line_3 = weight_variable([512], name='bias_line_3')
layer_line_3 = conv2d(Res13 , kernel_line_3, strides=[1, 2, 2, 1]) + bias_line_3
with tf.name_scope("Res14"):
Res14 = layer_line_3 + layer_29
with tf.name_scope("Block15"):
with tf.name_scope("Conv30"):
with tf.name_scope("Variable"):
kernel_30 = weight_variable([3, 3, 512, 512], name='kernel_30')
bias_30 = weight_variable([512], name='bias_30')
with tf.name_scope("Convolution"):
layer_30 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(Res14, kernel_30, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], name='conv_layer_30') + bias_30, name='layer_30')
with tf.name_scope("Conv31"):
with tf.name_scope("Variable"):
kernel_31 = weight_variable([3, 3, 512, 512], name='kernel_31')
bias_31 = weight_variable([512], name='bias_31')
with tf.name_scope("Convolution"):
layer_31 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(layer_30 , kernel_31, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], name='conv_layer_31') + bias_31,name='layer_31')
with tf.name_scope("Res15"):
Res15 = Res14 + layer_31
with tf.name_scope("Block16"):
with tf.name_scope("Conv32"):
with tf.name_scope("Variable"):
kernel_32 = weight_variable([3, 3, 512, 512], name='kernel_32')
bias_32 = weight_variable([512], name='bias_32')
with tf.name_scope("Convolution"):
layer_32 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(Res15, kernel_32, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], name='conv_layer_32') + bias_32, name='layer_32')
with tf.name_scope("Conv33"):
with tf.name_scope("Variable"):
kernel_33 = weight_variable([3, 3, 512, 512], name='kernel_33')
bias_33 = weight_variable([512], name='bias_33')
with tf.name_scope("Convolution"):
layer_33 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(layer_32 , kernel_33, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], name='conv_layer_33') + bias_33,name='layer_33')
with tf.name_scope("Res16"):
Res16 = Res15 + layer_33
with tf.name_scope("Avg_Pool"):
avg_pool = tf.nn.avg_pool(Res16, ksize=[1, 7, 7, 1], strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding="VALID",name='Avg')
with tf.name_scope('Reshape_line'):
line = tf.reshape(avg_pool, [-1, 512], name = 'line')
with tf.name_scope('fully_connected_layer'):
with tf.name_scope("Variable"):
fc_34 = weight_variable([512, 1000], name='fc_34')
bias_34 = bias_variable([1000], name='bias_34')
with tf.name_scope("Layer"):
layer_34 = tf.matmul(line, fc_34, name='layer_34') + bias_34
with tf.name_scope('Output'):
output = tf.nn.softmax(layer_34, name = 'softmax')
return output
def backward(datasets, label, test_data, test_label):
with tf.name_scope('Input_data'):
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 224, 224, 3], name="Input")
Y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1], name='Estimation')
LEARNING_RATE_BASE = 0.00001 # 最初学习率
LEARNING_RATE_DECAY = 0.99 # 学习率的衰减率
LEARNING_RATE_STEP = 1000 # 喂入多少轮BATCH-SIZE以后,更新一次学习率。一般为总样本数量/BATCH_SIZE
gloabl_steps = tf.Variable(0, trainable=False) # 计数器,用来记录运行了几轮的BATCH_SIZE,初始为0,设置为不可训练
learning_rate = tf.train.exponential_decay(LEARNING_RATE_BASE, gloabl_steps, LEARNING_RATE_STEP,
LEARNING_RATE_DECAY, staircase=True)
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, name="keep_prob")
y = VGG16(X)
global_step = tf.Variable(0, trainable=False)
with tf.name_scope('Accuracy'):
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y, 1), tf.argmax(Y_, 1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, "float"))
with tf.name_scope('loss'):
loss_mse = tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(Y_ * tf.log(y), reduction_indices=[1]))
tf.summary.scalar('loss', loss)
with tf.name_scope('train'):
train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(0.001).minimize(loss_mse)
saver = tf.train.Saver()
with tf.Session() as sess:
init_op = tf.global_variables_initializer()
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter("./logs", sess.graph)
sess.run(init_op)
# 训练模型。
STEPS = 500001
min_loss = 1
for i in range(STEPS):
start = (i * BATCH_SIZE) % len(datasets)
end = start + BATCH_SIZE
if i % 100 == 0:
run_options = tf.RunOptions(trace_level=tf.RunOptions.FULL_TRACE)
run_metadata = tf.RunMetadata()
summary_str, step, _ = sess.run([merged, gloabl_steps, train_step],
feed_dict={X: datasets[start:end], Y_: label[start:end], keep_prob:1.0},
options=run_options, run_metadata=run_metadata)
writer.add_summary(summary_str, i)
writer.add_run_metadata(run_metadata, 'step%d' % (i))
test_accuracy = accuracy.eval(feed_dict={X: test_data, Y_: test_label, keep_prob: 1.0})
print("After %d training step(s), accuracy is %g" % (i, test_accuracy))
saver.save(sess, './logs/variable', global_step=i)
else:
summary_str, step, _ = sess.run([merged, gloabl_steps, train_step],
feed_dict={X: datasets[start:end], Y_: label[start:end]})
writer.add_summary(summary_str, i)
def main():
with tf.name_scope('Input_data'):
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 224, 224, 3], name="Input")
y = Resnet34(X)
sess = tf.Session()
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter("./logs", sess.graph)
writer.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
通过运行该demo可以获得event文件,然后打开tensorboard就可以看到具体的流程了。
tensorboard --logdir logs
graph如图所示(图片可能比较糊,双击打开就是清晰的大图):

其他的Resnet结构也可以类似推导过来。
方法2,主要是resnet—v2的实现:
import tensorflow as tf
def weight_variable(shape, name=None):
initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape,mean = 0.0, stddev=0.01)
return tf.Variable(initial, name)
def bias_variable(shape, name=None):
initial = tf.constant(0.1, shape=shape)
return tf.Variable(initial, name)
def conv2d(input, filter, strides=[1,1,1,1], padding="SAME", name=None):
# filters with shape [filter_height * filter_width * in_channels, output_channels]
# Must have strides[0] = strides[3] =1
# For the most common case of the same horizontal and vertices strides, strides = [1, stride, stride, 1]
'''
Args:
input: A Tensor. Must be one of the following types: float32, float64.
filter: A Tensor. Must have the same type as input.
strides: A list of ints. 1-D of length 4. The stride of the sliding window for each dimension of input.
padding: A string from: "SAME", "VALID". The type of padding algorithm to use.
use_cudnn_on_gpu: An optional bool. Defaults to True.
name: A name for the operation (optional).
'''
return tf.nn.conv2d(input, filter, strides, padding=padding, name=name) # padding="SAME"用零填充边界
def max_pool_2x2(input, name):
return tf.nn.max_pool(input, ksize=[1,2,2,1], strides=[1,2,2,1], padding="SAME", name=name)
def Conv(input, name, filter_size, bias_size, stride, padding = 'SAME'):
with tf.name_scope(name):
with tf.name_scope('Variable'):
filters = weight_variable(filter_size, name='filter')
bias = weight_variable(bias_size, name='bias')
with tf.name_scope("Convolution"):
layer = conv2d(input, filters, strides=stride, padding = padding) + bias
return layer
def original_residual(block_input, name, block_num=2, size='SAME'):
'''
block_input: 代表输入的张量
block_num: 代表内部卷积次数
size: SAME代表输入张量形态不变,反之size缩小一半,channel扩大一倍
'''
with tf.name_scope(name):
net = block_input
channel = block_input.get_shape().as_list()[-1]
if size=='SAME':
for i in range(block_num):
net = Conv(net, name='conv'+str(i+1), filter_size=[3,3,channel,channel], bias_size=[channel], stride=[1,1,1,1])
if i != block_num-1:
net = tf.nn.relu(net)
net = tf.nn.relu(net + block_input)
elif size=='VALID':
net = tf.nn.relu(Conv(net, name='conv1', filter_size=[3,3,channel,2*channel], bias_size=[2*channel], stride=[1,2,2,1]))
for i in range(1, block_num):
net = Conv(net, name='conv'+str(i+1), filter_size=[3,3,2*channel,2*channel], bias_size=[2*channel], stride=[1,1,1,1])
if i != block_num-1:
net = tf.nn.relu(net)
block_input = Conv(block_input, name='shortcut', filter_size=[1,1,channel,2*channel], bias_size=[2*channel], stride=[1,2,2,1], padding = 'SAME')
net = tf.nn.relu(net+block_input)
return net
def proposed_residual(net, name, block_num=2, size='SAME', is_training=False):
'''
block_input: 代表输入的张量
block_num: 代表内部卷积次数
size: SAME代表输入张量形态不变,反之size缩小一半,channel扩大一倍
'''
block_input = net
channel = block_input.get_shape().as_list()[-1]
with tf.name_scope(name):
if size=='SAME':
for i in range(block_num):
net = tf.contrib.layers.batch_norm(net, is_training=is_training, scope=name+'_BN'+str(i))
net = tf.nn.relu(net,name = name+'_activation'+str(i))
net = tf.contrib.layers.conv2d(net,num_outputs=channel,kernel_size=(3,3),stride=(1,1),padding='SAME',activation_fn=None, scope=name+'_Conv'+str(i))
net = net + block_input
elif size=='VALID':
net = tf.contrib.layers.batch_norm(net, is_training=is_training, scope=name+'_BN0')
net = tf.nn.relu(net,name = name+'_activation0')
net = tf.contrib.layers.conv2d(net,num_outputs=channel*2,kernel_size=(3,3),stride=(2,2),padding='SAME',activation_fn=None, scope=name+'_Conv0')
for i in range(1, block_num):
net = tf.contrib.layers.batch_norm(net, is_training=is_training, scope=name+'_BN'+str(i))
net = tf.nn.relu(net,name = name+'_activation'+str(i))
net = tf.contrib.layers.conv2d(net,num_outputs=channel*2,kernel_size=(3,3),stride=(1,1),padding='SAME',activation_fn=None, scope=name+'_Conv'+str(i))
block_input = tf.contrib.layers.conv2d(block_input,num_outputs=channel*2,kernel_size=(1,1),stride=(2,2),padding='SAME',activation_fn=None, scope=name+'_shortcut')
net = net + block_input
return net
def ResNet_v2(net, training=False):
net = tf.contrib.layers.conv2d(net,num_outputs=64,kernel_size=(5,5),stride=(2,2),padding='SAME',activation_fn=tf.nn.relu, scope='Conv1') # size = (75, 75)
net = proposed_residual(net, name='block1', block_num=2, size='SAME', is_training=training) # size = (75, 75)
net = proposed_residual(net, name='block2',block_num=2, size='SAME', is_training=training)
net = proposed_residual(net, name='block3',block_num=2, size='SAME', is_training=training)
net = proposed_residual(net, name='block4', block_num=2, size='VALID', is_training=training) # size = (38, 38)
net = proposed_residual(net, name='block5', block_num=2, size='SAME', is_training=training)
net = proposed_residual(net, name='block6', block_num=2, size='SAME', is_training=training)
net = proposed_residual(net, name='block7', block_num=2, size='SAME', is_training=training)
net = proposed_residual(net, name='block8', block_num=2, size='VALID', is_training=training) # size = (19, 19)
net = proposed_residual(net, name='block9', block_num=2, size='SAME', is_training=training)
net = proposed_residual(net, name='block10', block_num=2, size='SAME', is_training=training)
net = proposed_residual(net, name='block11', block_num=2, size='SAME', is_training=training)
net = proposed_residual(net, name='block12', block_num=2, size='SAME', is_training=training)
net = proposed_residual(net, name='block13', block_num=2, size='SAME', is_training=training)
net = proposed_residual(net, name='block14', block_num=2, size='VALID', is_training=training) # size = (10, 10)
net = proposed_residual(net, name='block15', block_num=2, size='SAME', is_training=training)
net = proposed_residual(net, name='block16', block_num=2, size='SAME', is_training=training)
net = tf.contrib.layers.avg_pool2d(net, kernel_size=(10,10), stride=(2,2),padding='VALID',scope='AVG')
net = tf.contrib.layers.flatten(net, scope='flatten')
net = tf.contrib.layers.fully_connected(net,num_outputs=60,activation_fn=None, scope='Layer')
return net








 本文详细解析了 ResNet34 的工作原理,包括如何防止模型退化及其实现技巧。通过 TensorFlow 模块手动搭建网络,并提供具体代码示例,深入探讨残差网络的设计与应用。
本文详细解析了 ResNet34 的工作原理,包括如何防止模型退化及其实现技巧。通过 TensorFlow 模块手动搭建网络,并提供具体代码示例,深入探讨残差网络的设计与应用。

















 2555
2555

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








