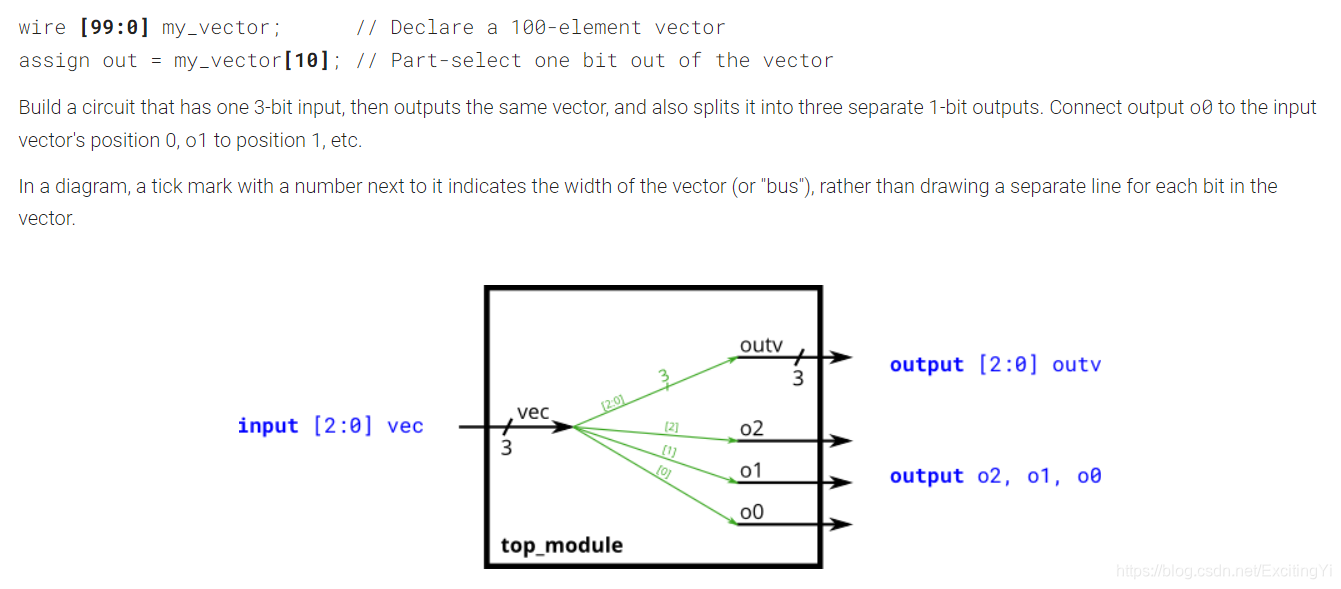
module top_module (
input wire [2:0] vec,
output wire [2:0] outv,
output wire o2,
output wire o1,
output wire o0 ); // Module body starts after module declaration
assign outv = vec;
assign o0 = vec[0];
assign o1 = vec[1];
assign o2 = vec[2];
endmodule
Declaring Vectors
Vectors must be declared:
type [upper:lower] vector_name;
e.g.

Implict Nets:
The unpacked dimensions are declared after the name.

2. Build a combinational circuit that splits an input half-word (16 bits, [15:0] ) into lower [7:0] and upper [15:8] bytes.
`default_nettype none // Disable implicit nets. Reduces some types of bugs.
module top_module(
input wire [15:0] in,
output wire [7:0] out_hi,
output wire [7:0] out_lo );
assign out_hi = in[15:8];
assign out_lo = in[7:0];
endmodule
-
A 32-bit vector can be viewed as containing 4 bytes (bits [31:24], [23:16], etc.). Build a circuit that will reverse the byte ordering of the 4-byte word.
AaaaaaaaBbbbbbbbCcccccccDddddddd => DdddddddCcccccccBbbbbbbbAaaaaaaa
module top_module(
input [31:0] in,
output [31:0] out );//
assign out[7:0] = in[31:24];
assign out[15:8] = in[23:16];
assign out[23:16] = in[15:8];
assign out[31:24] = in[7:0];
// assign out[31:24] = ...;
endmodule
- Bitwise vs. Logical Operators
module top_module(
input [2:0] a,
input [2:0] b,
output [2:0] out_or_bitwise,
output out_or_logical,
output [5:0] out_not
);
assign out_or_bitwise = a | b; //bitwise or
assign out_or_logical = a || b; //logical or
assign out_not[5:3] = ~b; //bitwise not
assign out_not[2:0] = ~a;
endmodule
-
Build a combinational circuit with four inputs, in[3:0].
There are 3 outputs:
out_and: output of a 4-input AND gate.
out_or: output of a 4-input OR gate.
out_xor: output of a 4-input XOR gate.
module top_module(
input [3:0] in,
output out_and,
output out_or,
output out_xor
);
assign out_and = in[0] & in[1] & in[2] & in[3];
assign out_or = in[0] | in[1] | in[2] | in[3];
assign out_xor = in[0] ^ in[1] ^ in[2] ^ in[3];
endmodule
Concatenation operator:
Part selection was used to select portions of a vector. The concatenation operator {a,b,c} is used to create larger vectors by concatenating smaller portions of a vector together.
{3'b111, 3'b000} => 6'b111000
{1'b1, 1'b0, 3'b101} => 5'b10101
{4'ha, 4'd10} => 8'b10101010 // 4'ha and 4'd10 are both 4'b1010 in binary
Concatenation needs to know the width of every component (or how would you know the length of the result?). Thus, {1, 2, 3} is illegal and results in the error message: unsized constants are not allowed in concatenations.
The concatenation operator can be used on both the left and right sides of assignments.
input [15:0] in;
output [23:0] out;
assign {out[7:0], out[15:8]} = in; // Swap two bytes. Right side and left side are both 16-bit vectors.
assign out[15:0] = {in[7:0], in[15:8]}; // This is the same thing.
assign out = {in[7:0], in[15:8]}; // This is different. The 16-bit vector on the right is extended to
// match the 24-bit vector on the left, so out[23:16] are zero.
// In the first two examples, out[23:16] are not assigned.
- Given several input vectors, concatenate them together then split them up into several output vectors. There are six 5-bit input vectors: a, b, c, d, e, and f, for a total of 30 bits of input. There are four 8-bit output vectors: w, x, y, and z, for 32 bits of output. The output should be a concatenation of the input vectors followed by two 1 bits:
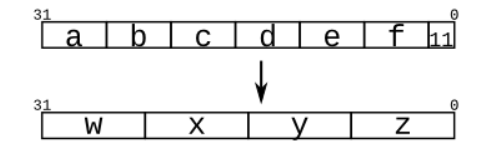
module top_module (
input [4:0] a, b, c, d, e, f,
output [7:0] w, x, y, z );//
assign {w,x,y,z} = {a,b,c,d,e,f,2'b11};
endmodule
repeat:
The concatenation operator allowed concatenating together vectors to form a larger vector. But sometimes you want the same thing concatenated together many times, and it is still tedious to do something like assign a = {b,b,b,b,b,b};. The replication operator allows repeating a vector and concatenating them together:
{num{vector}},This replicates vector by num times. num must be a constant. Both sets of braces are required.
Examples:
{5{1'b1}} // 5'b11111 (or 5'd31 or 5'h1f)
{2{a,b,c}} // The same as {a,b,c,a,b,c}
{3'd5, {2{3'd6}}} // 9'b101_110_110. It's a concatenation of 101 with
// the second vector, which is two copies of 3'b110.
sign extending:
One common place to see a replication operator is when sign-extending a smaller number to a larger one, while preserving its signed value. This is done by replicating the sign bit (the most significant bit) of the smaller number to the left. For example, sign-extending 4'b0101 (5) to 8 bits results in 8'b00000101 (5), while sign-extending 4'b1101 (-3) to 8 bits results in 8'b11111101 (-3).
- Build a circuit that sign-extends an 8-bit number to 32 bits. This requires a concatenation of 24 copies of the sign bit (i.e., replicate bit[7] 24 times) followed by the 8-bit number itself.
module top_module (
input [7:0] in,
output [31:0] out );//
assign out = {{24{in[7]}},in};
endmodule
module top_module (
input a, b, c, d, e,
output [24:0] out );//
assign out = {~{5{a}}^{a,b,c,d,e},~{5{b}}^{a,b,c,d,e},~{5{c}}^{a,b,c,d,e},~{5{d}}^{a,b,c,d,e},~{5{e}}^{a,b,c,d,e}};
endmodule




 这篇博客介绍了Verilog语言中的一些基本操作,包括向量声明、非隐式网络、位操作(如按位或、逻辑或、按位非)以及字节交换。通过具体的模块实例展示了如何将16位输入拆分为高低字节,以及如何将32位字节的顺序反转。此外,还展示了如何使用位连接操作符进行位级拼接和复制,以及如何实现4输入的与、或、异或门。最后,给出了一个将8位数扩展为32位并保持其符号的电路设计。
这篇博客介绍了Verilog语言中的一些基本操作,包括向量声明、非隐式网络、位操作(如按位或、逻辑或、按位非)以及字节交换。通过具体的模块实例展示了如何将16位输入拆分为高低字节,以及如何将32位字节的顺序反转。此外,还展示了如何使用位连接操作符进行位级拼接和复制,以及如何实现4输入的与、或、异或门。最后,给出了一个将8位数扩展为32位并保持其符号的电路设计。

















 2846
2846

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








