【std::system_error】这个如何使用?
#include <cstdlib>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
std::system("ls -l >test.txt"); // execute the UNIX command "ls -l >test.txt"
std::cout << std::ifstream("test.txt").rdbuf();
}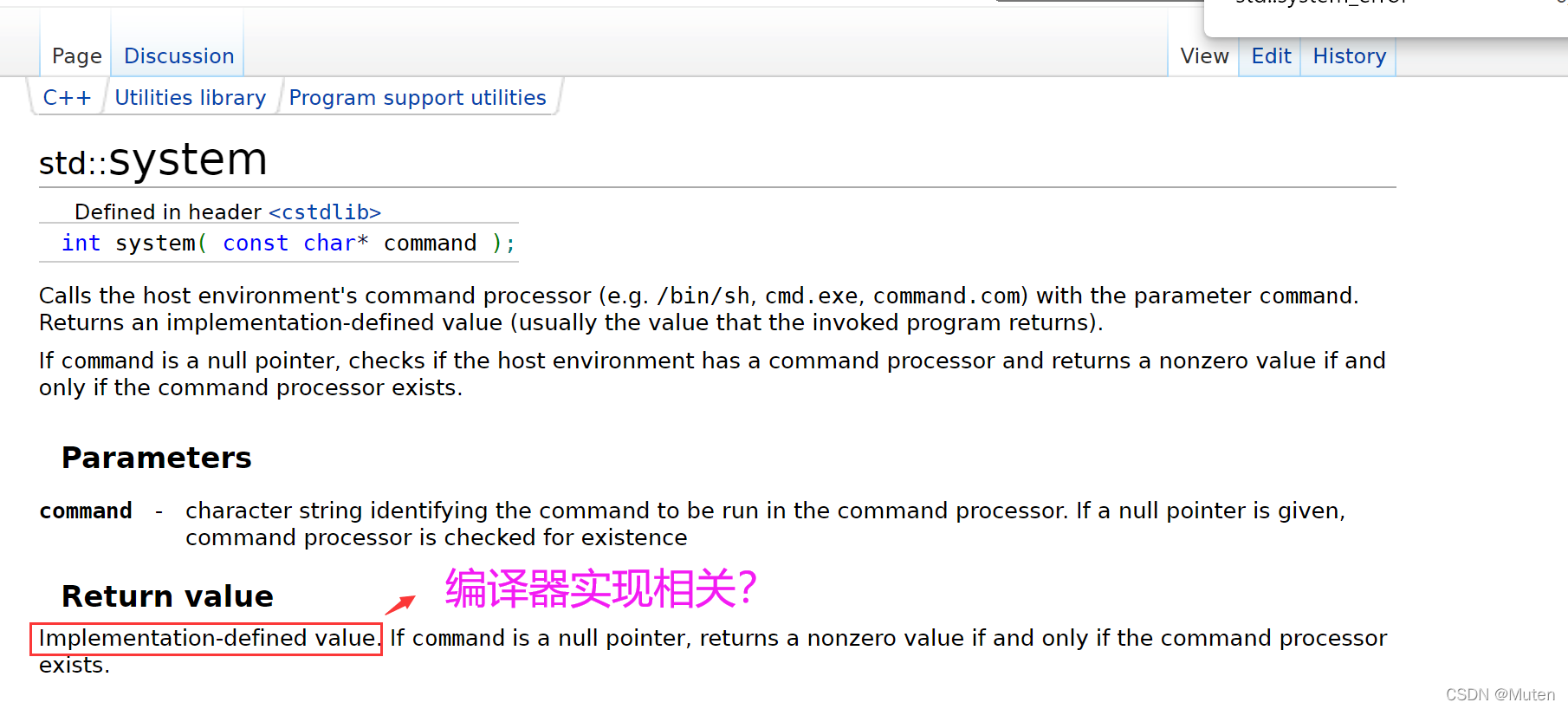
Implementation-defined value. If command is a null pointer, returns a nonzero value if and only if the command processor exists.#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main( void )
{
FILE *stream;
char buf[1024];
memset( buf, '\0', sizeof(buf) );//初始化buf
stream = popen( "ls -lrt" , "r" );
//将“ls -lrt”命令的输出 通过管道读取(“r”参数)到FILE* stream
fread( buf, sizeof(char), sizeof(buf), stream); //将刚刚FILE* stream的数据流读取到buf中
printf("buf=%s\n",buf);
pclose( stream );
return 0;
}





 本文详细解读了C语言中system()函数的用法,包括执行shell脚本、获取命令执行结果,并介绍了std::system_error的使用。通过实例演示了如何利用system函数执行ls命令并将输出保存到文件,以及探讨了其返回值的实现细节。
本文详细解读了C语言中system()函数的用法,包括执行shell脚本、获取命令执行结果,并介绍了std::system_error的使用。通过实例演示了如何利用system函数执行ls命令并将输出保存到文件,以及探讨了其返回值的实现细节。
















 1042
1042

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








