构造注入
- 导入所需要的包
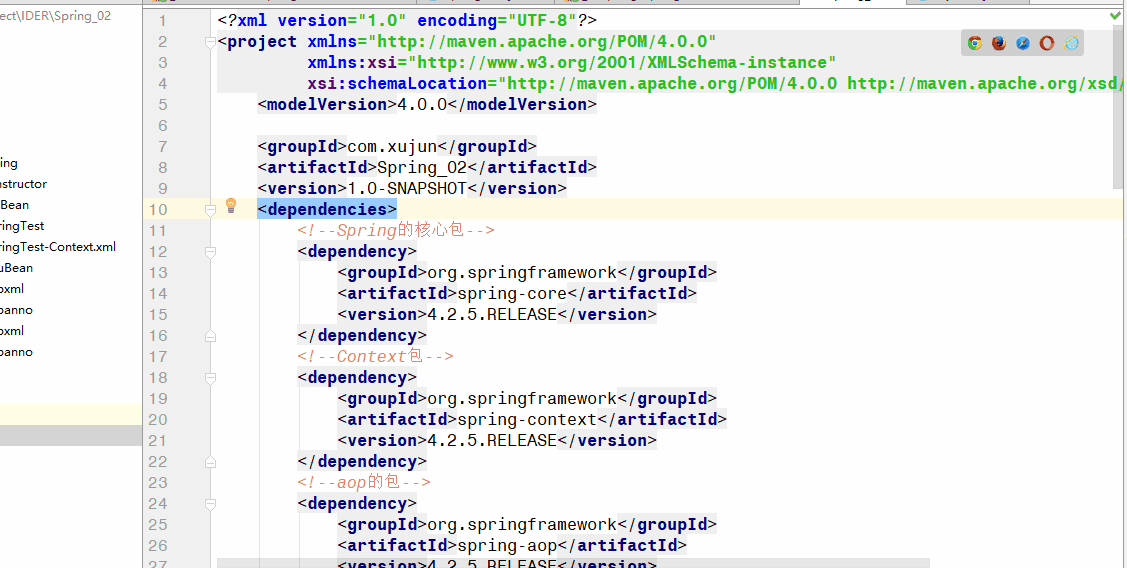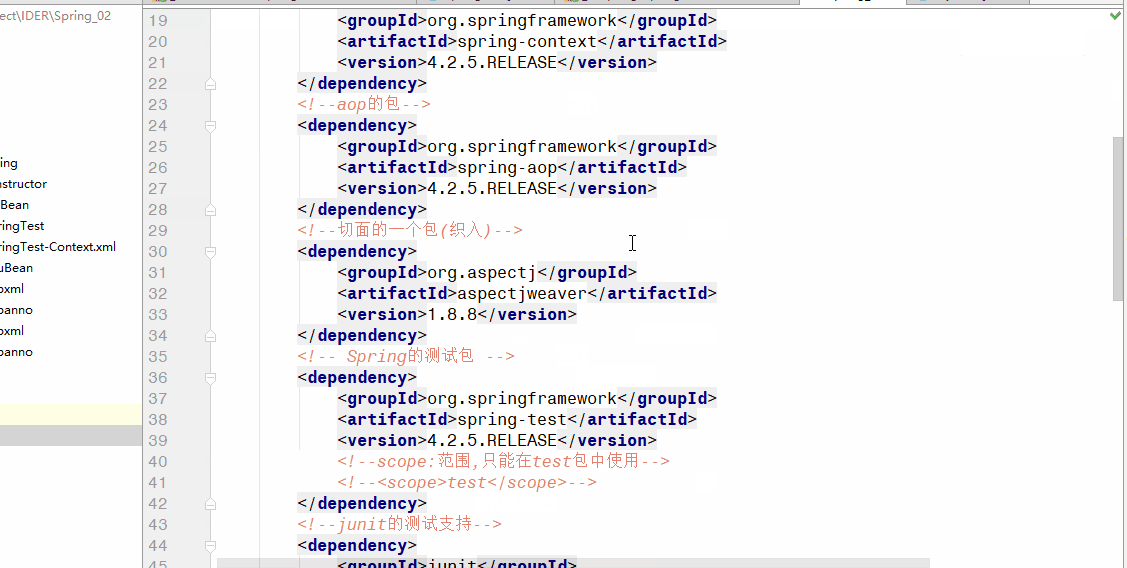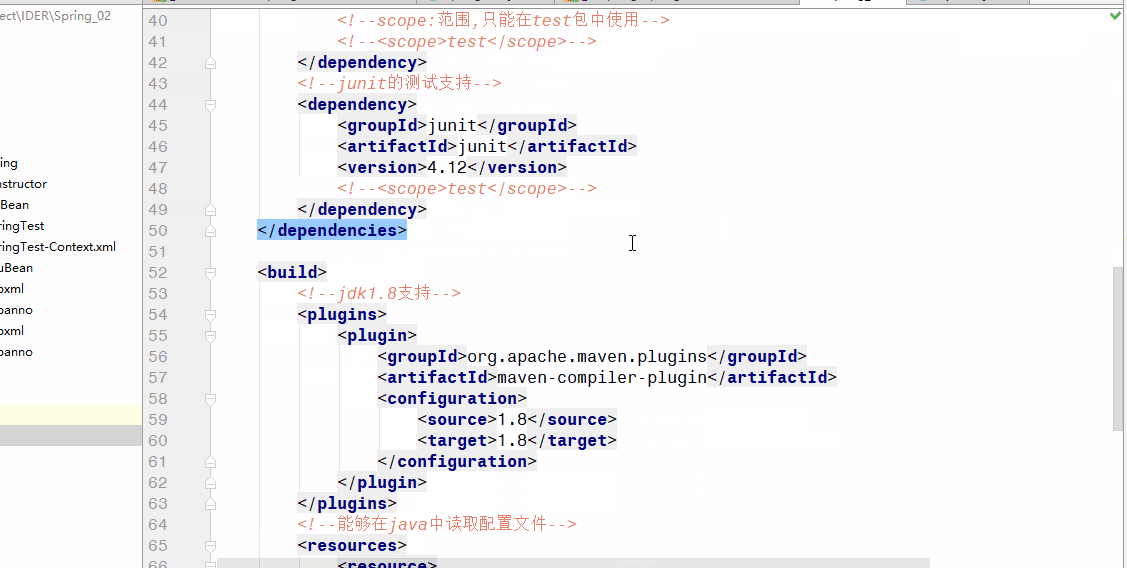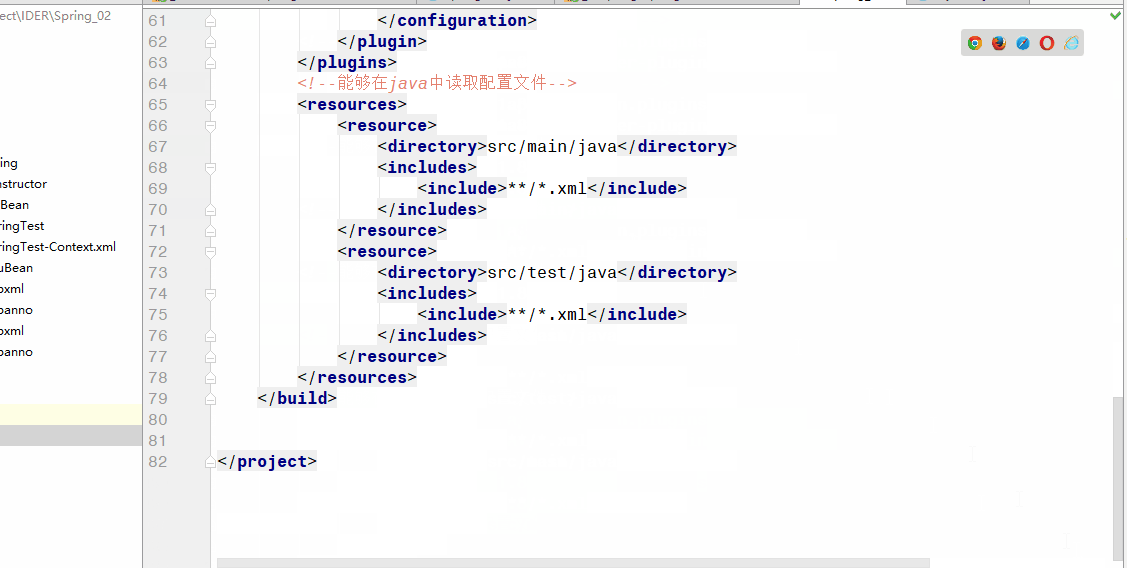
<dependencies>
<!--Spring的核心包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-core</artifactId>
<version>4.2.5.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!--Context包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>4.2.5.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!--aop的包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId>
<version>4.2.5.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!--切面的一个包(织入)-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.8.8</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring的测试包 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>4.2.5.RELEASE</version>
<!--scope:范围,只能在test包中使用-->
<!--<scope>test</scope>-->
</dependency>
<!--junit的测试支持-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<!--<scope>test</scope>-->
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<!--jdk1.8支持-->
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
<!--能够在java中读取配置文件-->
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/java</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
</resource>
<resource>
<directory>src/test/java</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
</resource>
</resources>
</build
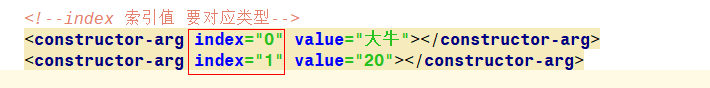
2.构造注入的方式
方式一:通过名称注入 
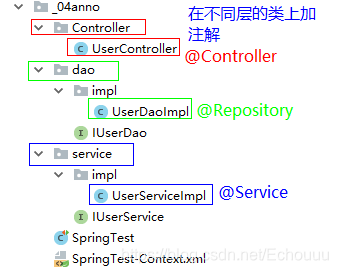
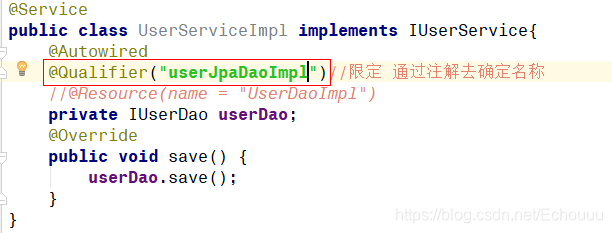
3.如果一个接口下面有多个实现
在不同的实现类注解上加上名称
eg:@Repository(“userJpaDaoImpl”),调用的时候加上注解 @Qualifier(“对应的名称”) 来注入不同的实现类;
@Resource 可以实现这个功能,并且不需要加@Autowired
Spring中的AOP
AOP是面向切面编程,AOP可以用于事务管理,日志管理,性能监测等地方。
1.导入相应的包,详见文章开头
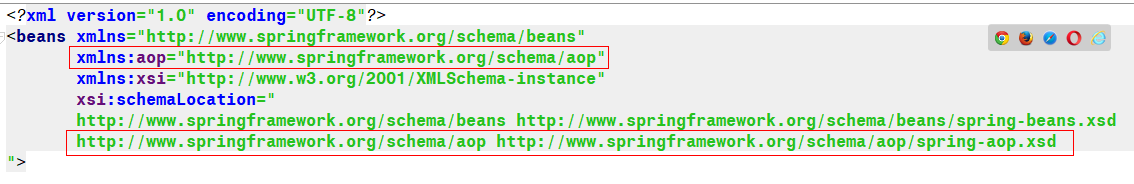
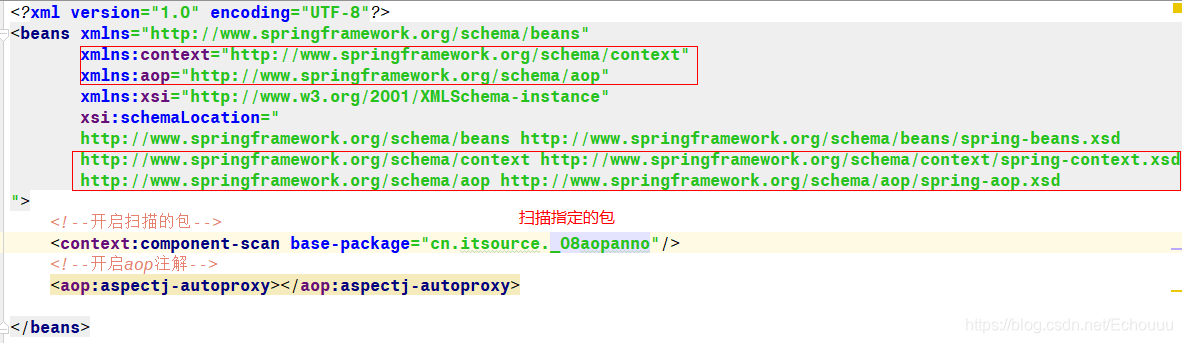
2.在配置文件中添加aop命名空间
3.准备一个service层接口
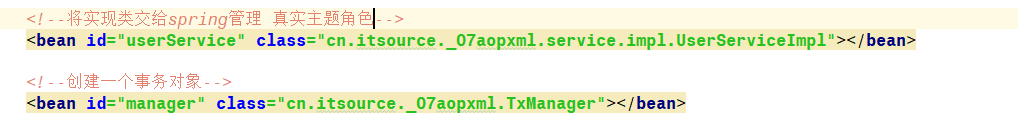
>4.实现类
>5.模拟事务管理器
6.配置
Spring AOP三要素
- 何时:在那个类中的哪个方法
- 何地:切点 在方法执行的之前还是之后
- 做了什么事情:执行事务管理器中的对应方法
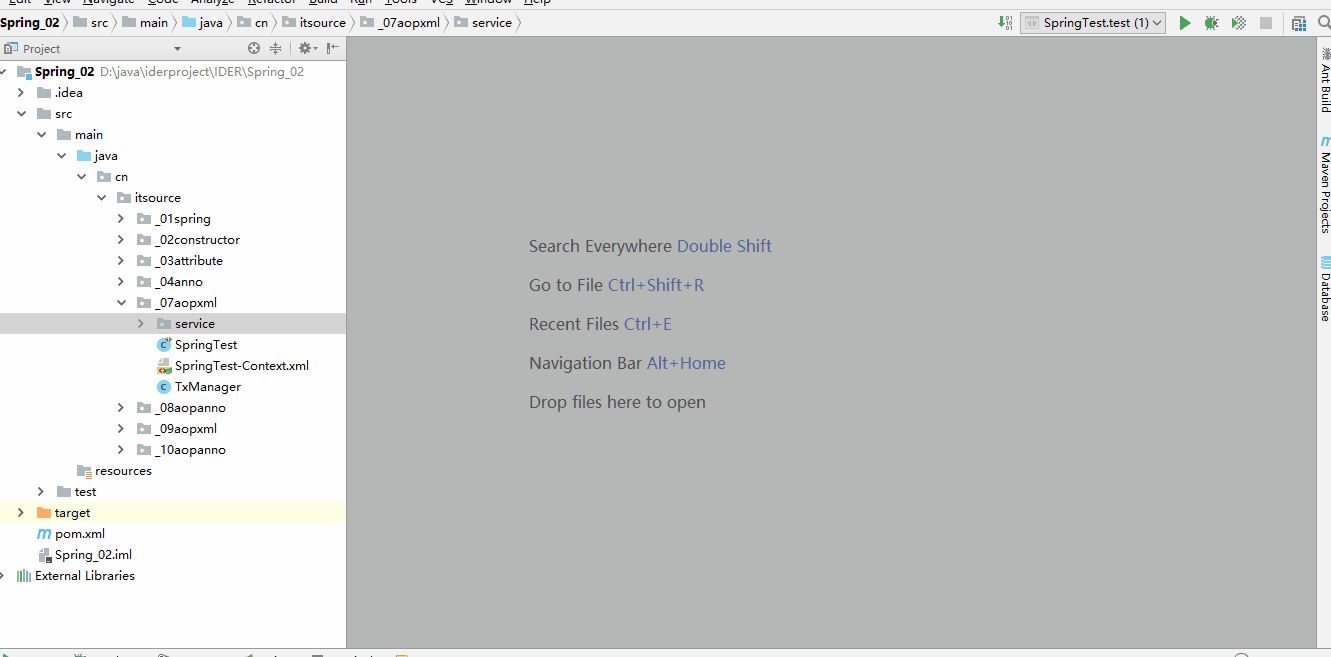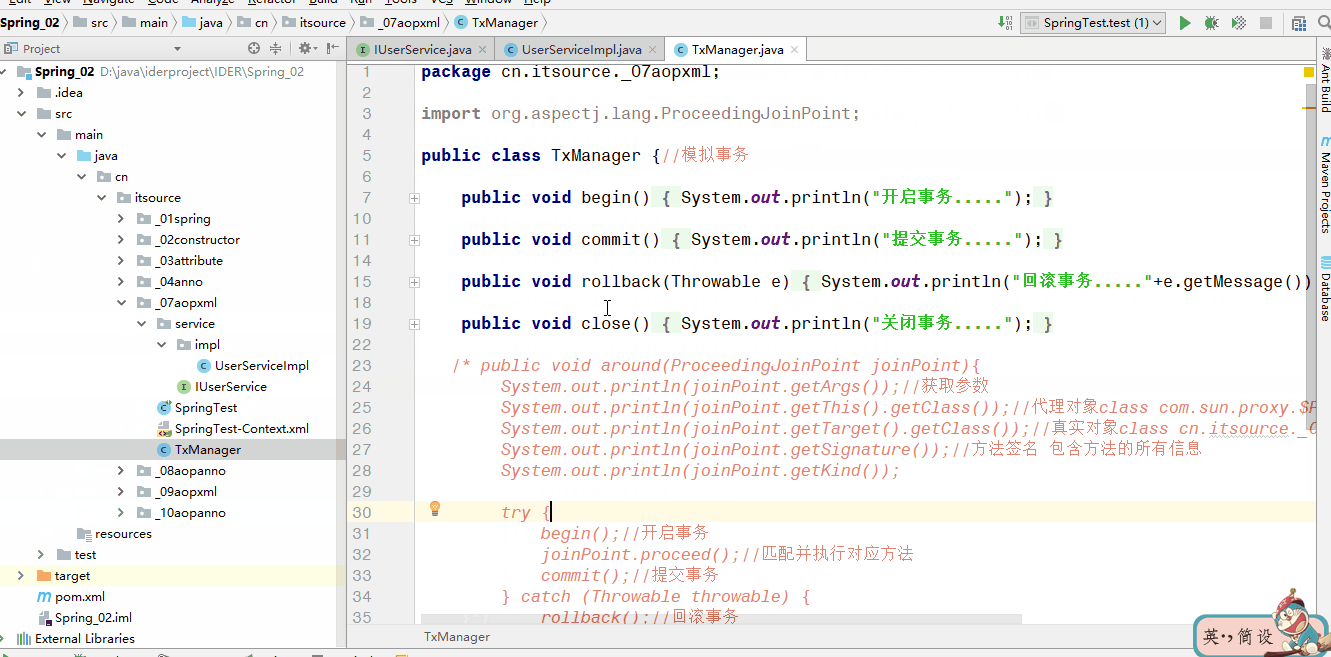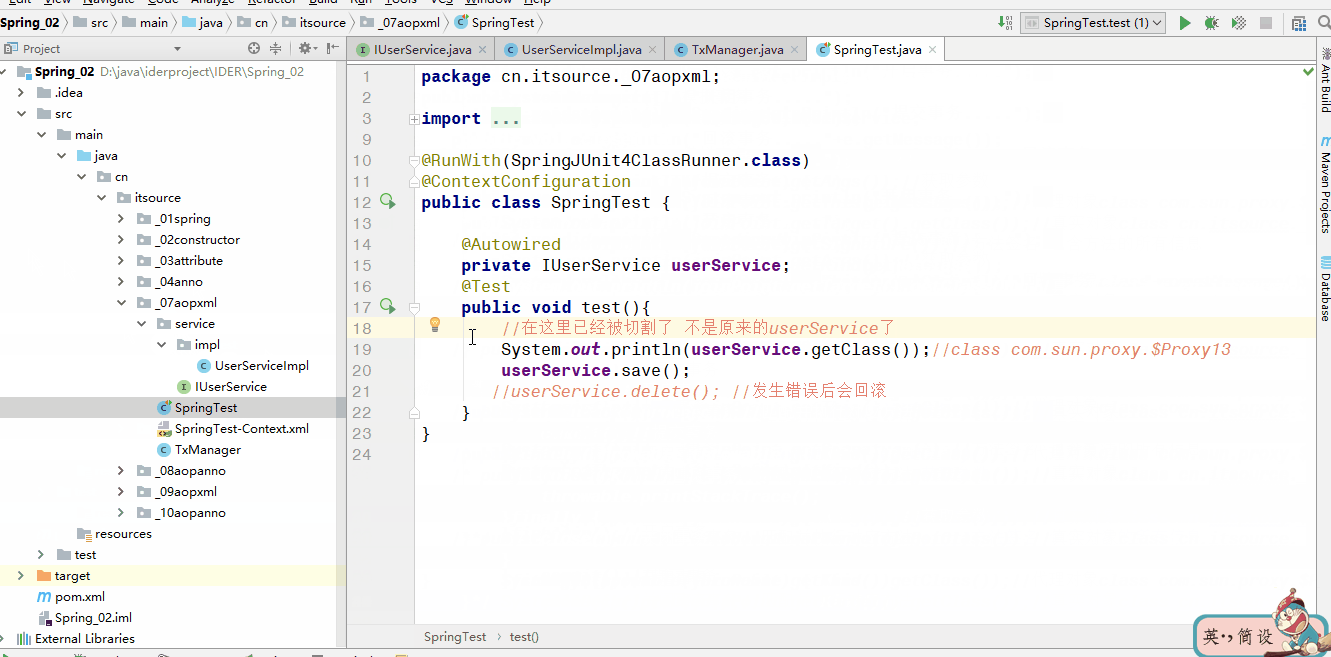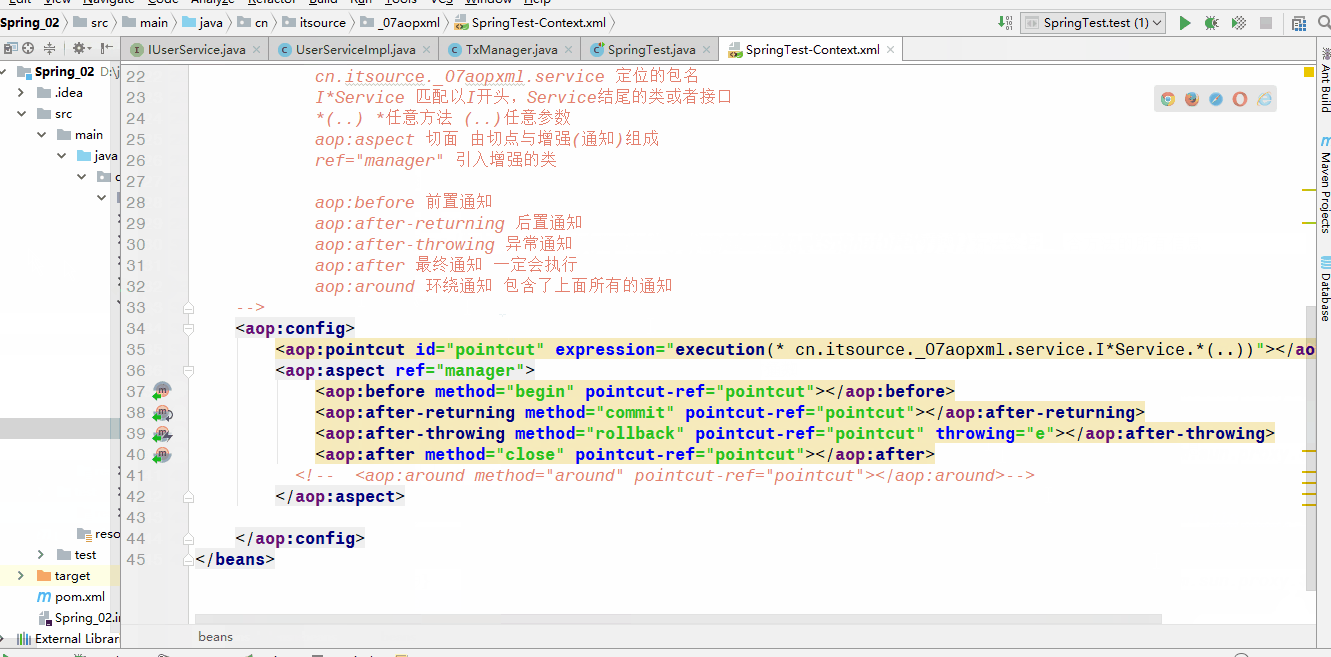
aop:pointcut 切点
id 切点名称(任意取)
expression 表达式 定位到对应的方法,只要定位到接口,它对应的实现也能找到
* 任意返回值
cn.itsource._07aopxml.service 定位的包名
I*Service 匹配以I开头,Service结尾的类或者接口
*(…) *任意方法 (…)任意参数
aop:aspect 切面 由切点与增强(通知)组成
ref=“manager” 引入增强的类
aop:before 前置通知
aop:after-returning 后置通知
aop:after-throwing 异常通知
aop:after 最终通知 一定会执行
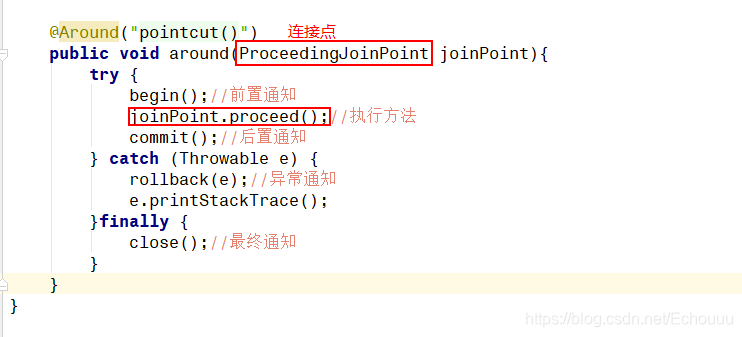
aop:around 环绕通知 包含了上面所有的通知- 环绕通知
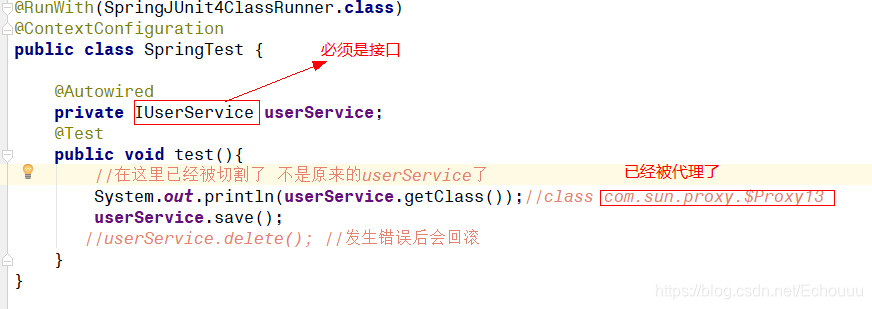
测试
查看一下这个对象是否已经被代理
声明必需是接口
测试一下有异常与没有异常的区别
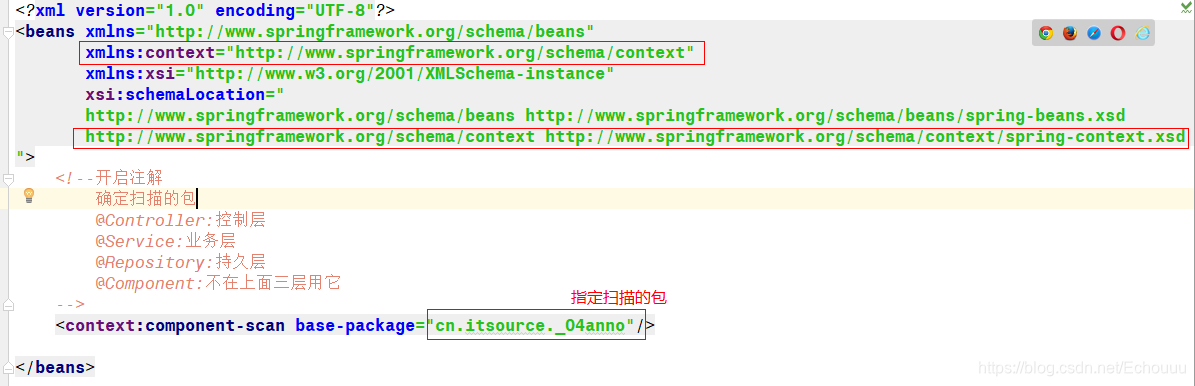
注解实现AOP
1.配置扫描包和aop注解支持
2.在事务管理器中加注解
>3.环绕通知
配置了环绕通知,就不能使用其他通知的注解
代理模式
- 代理模式
代理对象可以在客户端和目标对象之间起到中介的作用,比如房屋中介,车站代理点等起到中间连接作用的对象;- 代理模式分为静态和动态
- Spring中使用动态代理
1.JDK动态代理需要代理的类有接口
2 CGLIB不需要有接口
- 准备一个事务管理器,接口,实现类
- 测试
public class ProxyTest {
@Test
public void testProxy(){
//创建真实主题角色对象
IUserService userService = new UserServiceImpl();
//创建事务对象
TxManager txManager = new TxManager();
/*
* Foo f = (Foo) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
* Foo.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[] { Foo.class },
handler);
newProxyInstance:创建代理对象
参数一 ClassLoader loader :传入类加载器(随便找一个给它就可以)
参数二 Class<?>[] interfaces:抽象主题角色(就是接口对应的类)
userService.getClass().getInterfaces()
参数三 InvocationHandler h:处理器(由我们自己实现)
**/
IUserService proxy =(IUserService) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
ProxyTest.class.getClassLoader(),
userService.getClass().getInterfaces(),
new InvocationHandler() {
/**
* @param proxy : 代理对象(不用它)
* @param method : 执行方法
* @param args : 执行方法的参数
*/
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
//通过反射执行方法
Object invoke = null;
try {
txManager.begin();//前置通知
invoke = method.invoke(userService, args);
txManager.commit();//后置通知
} catch (Exception e) {
txManager.rollback();//异常通知
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
txManager.close();//最终通知
}
return invoke;
}
}
);
proxy.sava();
}
}





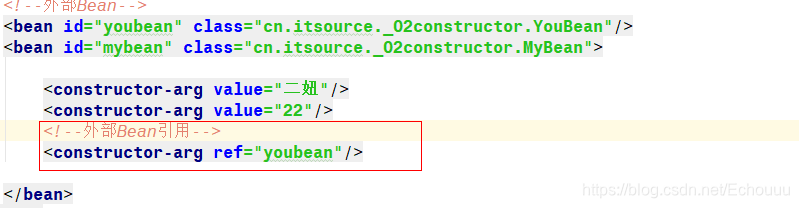
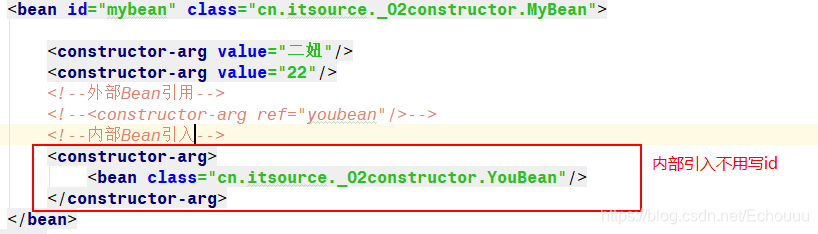
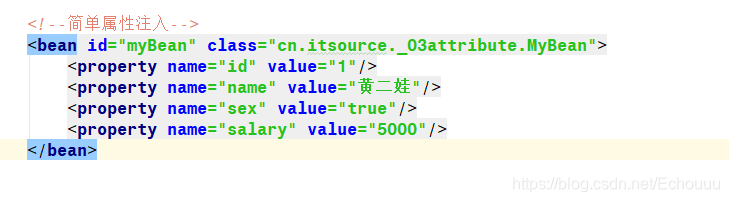
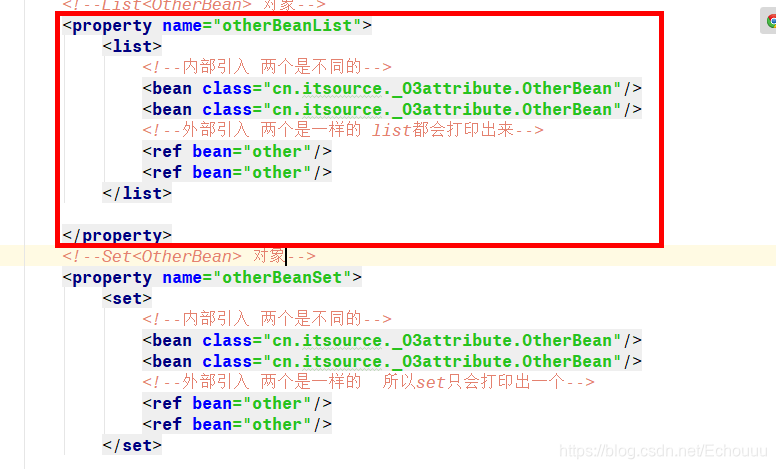
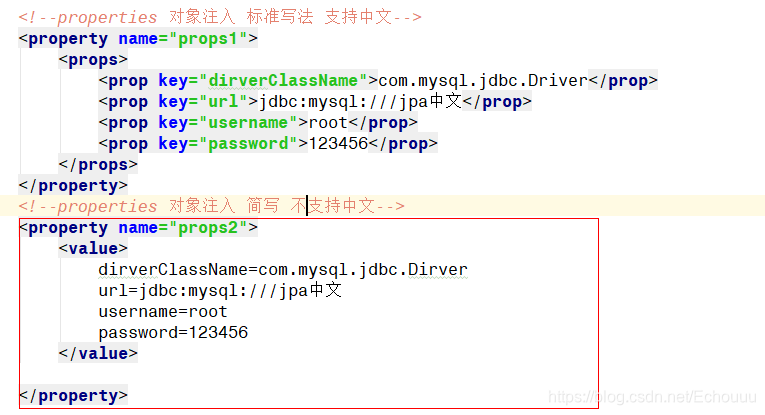
 本文详细介绍了Spring框架中的构造注入方法,包括通过名称、索引值、类型注入及外部和内部Bean引入等方式。同时深入探讨了面向切面编程(AOP)在Spring中的应用,涵盖事务管理、日志记录等功能,解析了Xml版和注解版AOP的配置步骤,以及动态代理模式在Spring中的实现。
本文详细介绍了Spring框架中的构造注入方法,包括通过名称、索引值、类型注入及外部和内部Bean引入等方式。同时深入探讨了面向切面编程(AOP)在Spring中的应用,涵盖事务管理、日志记录等功能,解析了Xml版和注解版AOP的配置步骤,以及动态代理模式在Spring中的实现。




















 1004
1004

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








