前言
这几天刷到了二叉树和图,正好复习下这里面的一些知识。
关于二叉树的题,大部分都不难,只要好好掌握了层次遍历。中序遍历以及递归,就能够应付绝大部分类型的题,哪怕是面试手撕,也能够很轻松的做出来,其次就是善于利用队列和栈,做题时卡住的时候,要多往这两个方向来思考。
 这是我声明的树结构,代码如下,
这是我声明的树结构,代码如下,
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(1);
root->left = new TreeNode(2);
root->right = new TreeNode(3);
root->left->left = new TreeNode(4);
root->left->right = new TreeNode(5);
root->right->right = new TreeNode(8);
root->right->right->left = new TreeNode(6);
root->right->right->right = new TreeNode(7);
root->left->right->right = new TreeNode(9);
记得释放内存,
void Solution::deleteTree(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) {
return; // 如果当前节点为空,直接返回
}
// 先递归释放左子树
deleteTree(root->left);
// 然后递归释放右子树
deleteTree(root->right);
// 释放当前节点
delete root;
}
一、前中序遍历
前中序遍历主要是递归,递归的思想很重要,建议大家在做题的时候可以把结果打印出来,
vector<int> Solution::HelperpreorderTraversal(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& result) {
//vector<int>& result 这里一定要用引用传递,不然不会更新参数,第一次做的时候检查一半天
if (root == nullptr) {
return result; // 确保 root 不为空
}
result.push_back(root->val);
vector<int> left = HelperpreorderTraversal(root->left, result);
//cout << "left中的值为" << left << endl;
//result.push_back(root->val); 放在这里时即为中序遍历。
vector<int> right = HelperpreorderTraversal(root->right, result);
//cout << "right中的值为" << right <<endl;
cout << "result中的值为:" << result << endl;
return result;
}
首先检查root是否为空,然后不为空就一直先遍历左子树然后把节点加入到result结果中,下图给出了打印结果

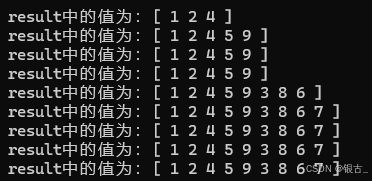
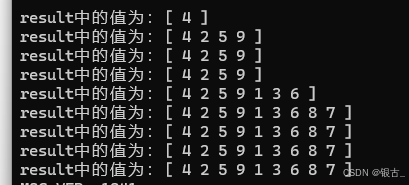
既然前序遍历写出来了,那中序遍历就很简单了,也是用递归在上面代码中,将result.push_back(root->val);
放在中间即可,下面是中序遍历打印的result\

第二种是采用迭代的方法,这里以中序遍历为例,主要是用一个栈来存储遍历的节点,只要左子树不为空,就一直向左遍历并将其入栈,以上面构建的树为例,在栈中的存储为stack = { 1 , 2 , 4}
当4入栈后退出内层循环,让current等于栈顶元素,此时 current = 4 ,然后4出栈,stackj = { 1,2},再将current 的值加入result中,current = 2, stack ={1},开始遍历右子树依次循环往复
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root){
vector<int> result;
stack<TreeNode*> stack;
TreeNode* current = root;
while (current != nullptr || !stack.empty()) {
while (current != nullptr) {
stack.push(current);
current = current->left;
}
current = stack.top();
stack.pop();
result.push_back(current->val);
current = current->right;
}
return result;
}
实战
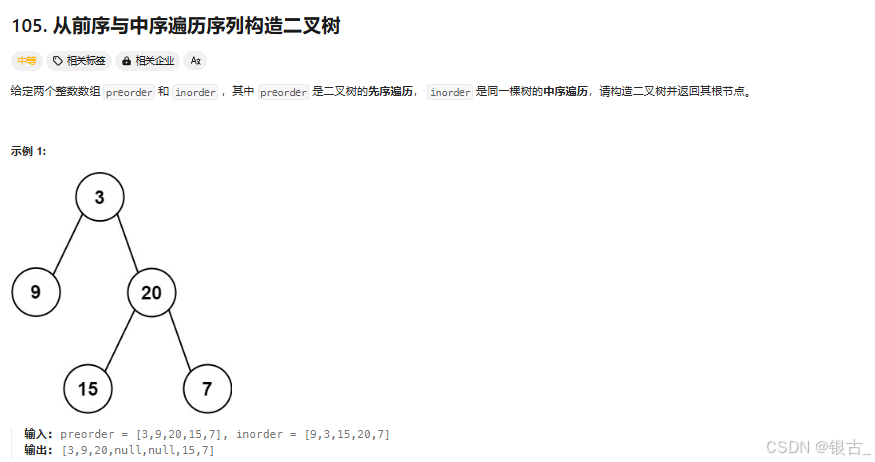
附上代码,
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) {
if (preorder.empty() || inorder.empty()) {
return nullptr;
}
// 前序遍历的第一个元素是树的根节点
int rootVal = preorder[0];
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootVal);
// 在中序遍历中找到根节点的位置
auto it = find(inorder.begin(), inorder.end(), rootVal);
int index = it - inorder.begin();
// 递归构建左子树和右子树
vector<int> leftPreorder(preorder.begin() + 1, preorder.begin() + 1 + index);
vector<int> rightPreorder(preorder.begin() + 1 + index, preorder.end());
vector<int> leftInorder(inorder.begin(), inorder.begin() + index);
vector<int> rightInorder(inorder.begin() + index + 1, inorder.end());
root->left = buildTree(leftPreorder, leftInorder);
root->right = buildTree(rightPreorder, rightInorder);
return root;
}
二、层次遍历
层次遍历我主要是利用了队列,用队列来存储每一行的元素,我这里用的是迭代的方法,我们遍历每一个元素,将其放入队列中,使用一个while循环,只要队列不为空,那么每次就出队一个元素,再将这个元素的左右子树入队,下面是一个经典的层次遍历实现。
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> result;
if (!root) {
return result;
}
queue<TreeNode*> Q;
Q.push(root); //将根节点先入队
while (!Q.empty()) {
vector<int> temp; //作为临时存储节点的temp
for (int i = Q.size(); i > 0; i--) {
TreeNode* current = Q.front();
Q.pop();
temp.push_back(current->val);
if (current->left) {
Q.push(current->left);
}
if (current->right) {
Q.push(current->right);
}
}
result.push_back(temp);
}
return result;
}
实战
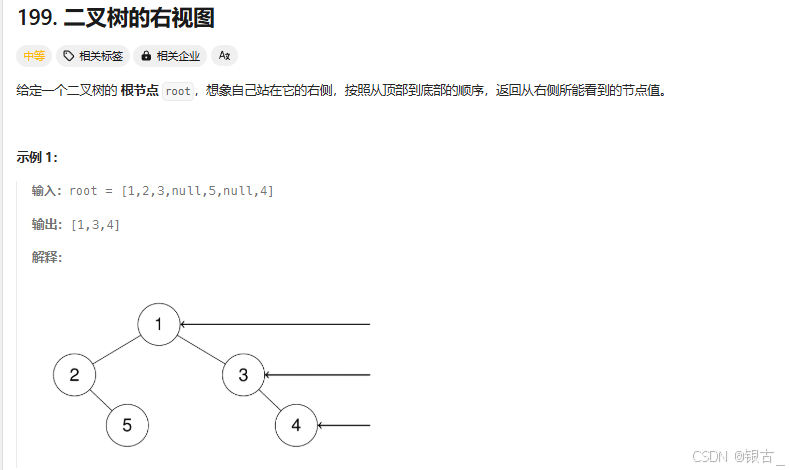
这道题其实就是让我们每次把层次遍历的第一个元素放到结果里就好了,难点在于怎样找出第一个元素,其实仔细想想,我们的临时数组temp就存储了每一行的元素,比如在对2 3 遍历时 temp = { 2 ,3},所以temp中最后一个元素就是我们要的元素,然后pushback就好啦~,当让如果我们把两个if条件换一下就可以要第0个元素了。
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> result;
if (!root) {
return result;
}
queue<TreeNode*> Q;
Q.push(root); //将根节点先入队
while (!Q.empty()) {
vector<int> temp; //作为临时存储节点的temp
for (int i = Q.size(); i > 0; i--) {
TreeNode* current = Q.front();
Q.pop();
temp.push_back(current->val);
if (current->left) {
Q.push(current->left);
}
if (current->right) {
Q.push(current->right);
}
}
int size = temp.size()-1; //我们只需要temp中最后一个元素
result.push_back(temp);
}
return result;
}
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








