一.JDBC简介
取自百度百科:
JDBC(Java DataBase Connectivity,java数据库连接)是一种用于执行SQL语句的Java API,可以为多种关系数据库提供统一访问,它由一组用Java语言编写的类和接口组成。JDBC提供了一种基准,据此可以构建更高级的工具和接口,使数据库开发人员能够编写数据库应用程序。
二.操作前准备工作
下载jdbc对应的jar包,并导入eclipse中,导入操作如下:
新建文件夹lib,将jar包粘贴至此,右键–Build Path-Add to Build Path


Referenced Libraries出现jar包,导入成功。
三. JDBC操作
JDBC基本操作CRUD
CRUD含义:
- create:添加数据
- retrieve:查询数据
- update:修改数据
- delete:删除数据
首先建立好数据库,可通过cmd控制台创建,也可通过其他如Mysql-font端或其他创建。
cmd创建操作:https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/Double____C/article/details/88287031
1.获取数据库连接
在操作前需与数据库建立连接
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/students", "root", "root");
2.数据查询
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import com.mysql.jdbc.PreparedStatement;
public class retrieveDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
// 数据库连接
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/students", "root", "root");
// 查询操作
String sql = "select * from students";
ps = (PreparedStatement) conn.prepareStatement(sql);
rs = ps.executeQuery();
while (rs.next()) {
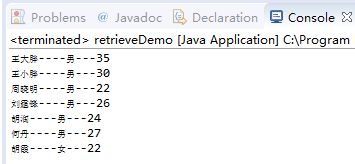
System.out.println(rs.getString("name") + "----" + rs.getString("sex") + "---" + rs.getInt("age"));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//关闭数据库连接
try {
if(rs != null)
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
rs = null;
}
try {
if(ps != null)
ps.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
ps = null;
}
try {
if(conn != null)
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
conn = null;
}
}
}
}
控制台输出如下: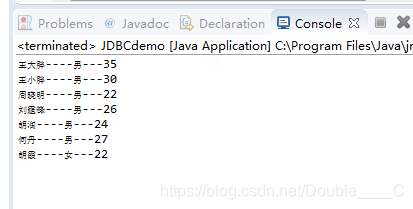
3.数据添加
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import com.mysql.jdbc.PreparedStatement;
public class JDBCdemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
try {
// 数据库连接
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/students", "root", "root");
// 添加操作
String sql = "insert into students (name, sex, age) values (?,?,?)";
ps = (PreparedStatement) conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setString(1, "何仙姑");
ps.setString(2, "女");
ps.setInt(3, 28);
int i = ps.executeUpdate();
if (i > 0) {
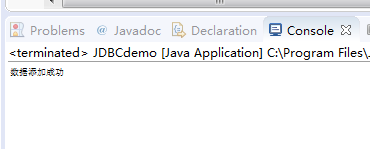
System.out.println("数据添加成功");
} else {
System.out.println("数据添加失败");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 关闭数据库连接
try {
if(ps != null)
ps.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
ps = null;
}
try {
if(conn != null)
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
conn = null;
}
}
}
}
控制台输出如下:
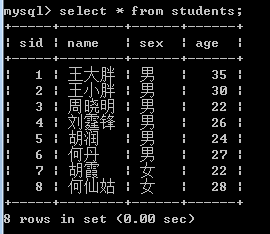
表查询结果如下:
4.数据删除
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import com.mysql.jdbc.PreparedStatement;
public class deleteDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
try {
// 数据库连接
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/students", "root", "root");
// 添加操作
String sql = "delete from students where name=?";
ps = (PreparedStatement) conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setString(1, "何仙姑");
int i = ps.executeUpdate();
if (i > 0) {
System.out.println("数据删除成功");
} else {
System.out.println("数据删除失败");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 关闭数据库连接
try {
if (ps != null)
ps.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
ps = null;
}
try {
if (conn != null)
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
conn = null;
}
}
}
}
控制台输出如下:
5.数据查找
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import com.mysql.jdbc.PreparedStatement;
public class updateDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
try {
// 数据库连接
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/students", "root", "root");
// 添加操作
String sql = "update students set age = ? where name = ?";
ps = (PreparedStatement) conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setInt(1, 24);
ps.setString(2, "王大胖");
int i = ps.executeUpdate();
if (i > 0) {
System.out.println("数据更新成功");
} else {
System.out.println("数据更新失败");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 关闭数据库连接
try {
if (ps != null)
ps.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
ps = null;
}
try {
if (conn != null)
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
conn = null;
}
}
}
}
查询后结果如下:
四.流程总结
1.连接数据库,创建connection对象;
2.通过connection对象,传入sql语句,获得PreparedStatement对象;
3.使用PreparedStatement对象执行executeUpdate(增删改操作)和executeQuery(查询操作);
4.输出结果;
5.关闭各对象资源。
五.其他
CRUD操作较多重复代码,可新建JDBCUtil.class,封装CRUD操作及数据库连接操作,便于操作





 本文介绍了JDBC的基本操作,包括CRUD(创建、读取、更新、删除)数据库记录的步骤。首先讲解了JDBC的概念,接着阐述了准备工作,如下载JDBC驱动并导入到开发环境。然后详细描述了如何进行数据查询、添加、更新和删除,总结了JDBC操作数据库的一般流程,并建议将重复代码封装到工具类以提高效率。
本文介绍了JDBC的基本操作,包括CRUD(创建、读取、更新、删除)数据库记录的步骤。首先讲解了JDBC的概念,接着阐述了准备工作,如下载JDBC驱动并导入到开发环境。然后详细描述了如何进行数据查询、添加、更新和删除,总结了JDBC操作数据库的一般流程,并建议将重复代码封装到工具类以提高效率。
















 1527
1527

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








