
Java集合是一种特别有用的工具类,可用于存储数量不等的对象,并可以实现常用的数据结构
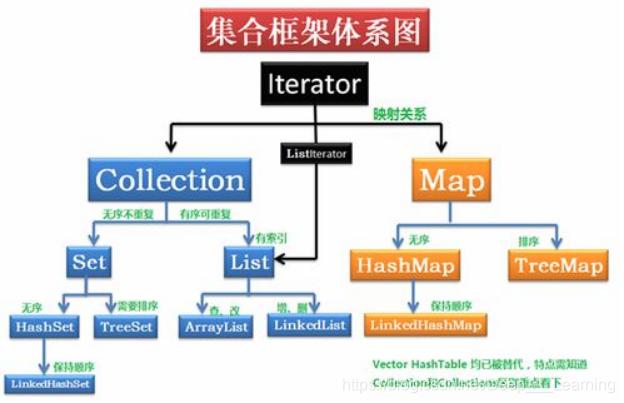
Set
Set集合不允许包含相同的元素,如果把两个相同的元素加入到同一个Set集合中,则add()方法返回false,且新元素不会被加入
HashSet
HashSet按Hash算法来存储集合中的元素,因此具有很好的存取和查找性能
其特点如下:
- 不能保证元素的排列顺序,顺序可能与添加顺序不同,顺序也有可能发生变化
- HashSet不是同步的,如果有多个线程同时访问一个HashSet,必须通过代码来保证其同步
- 集合元素值可以是null
TreeSet
TreeSet可以确保集合元素处于排序状态
TreeSet采用红黑树的数据结构来存储集合元素,并且它支持两种排序方法:自然排序和定制排序
注意:如果希望TreeSet能正常运作,TreeSet只能添加同一种类型的对象
List
List代表一个元素有序、可重复的集合,集合中每个元素都有对应的顺序索引
package day6;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class ArrayListTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
arrayList.add("Java");
arrayList.add("C++");
arrayList.add("C");
arrayList.add("Python");
arrayList.add("Go");
arrayList.add("JavaScript");
// 排序
arrayList.sort(new Comparator<String>() {
@Override
public int compare(String o1, String o2) {
return o1.compareTo(o2);
}
});
System.out.println(arrayList);
Iterator<String> iterator = arrayList.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
System.out.println("==========");
}
}
}
[C, C++, Go, Java, JavaScript, Python]
C
==========
C++
==========
Go
==========
Java
==========
JavaScript
==========
Python
==========
Process finished with exit code 0
Queue
Queue用于模拟队列这种数据结构,队列通常是指 ” 先进先出(FIFO)“的容器
PriorityQueue
PriorityQueue不允许插入null元素,它还需要对队列元素进行排序,它有两种排序方法:自然排序和定制排序
package day6;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class PriorityQueueTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PriorityQueue<Integer> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>();
// 添加元素
priorityQueue.add(6);
priorityQueue.add(-3);
priorityQueue.add(30);
priorityQueue.add(20);
priorityQueue.add(0);
// 输出队列
System.out.println(priorityQueue);
// 删除第一个元素
System.out.println(priorityQueue.poll());
System.out.println(priorityQueue);
}
}
[-3, 0, 30, 20, 6]
-3
[0, 6, 30, 20]
Process finished with exit code 0
package day6;
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ArrayDequeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
ArrayDeque<Integer> stack = new ArrayDeque<>();
while (n != 0) {
stack.push(n % 2);
n /= 2;
}
System.out.println("==========");
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
System.out.print(stack.pop());
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("==========");
}
}
10
==========
1010
==========
Process finished with exit code 0
Map
Map用于保存具有映射关系的数据
package day6;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class HashMapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String, Integer> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put("a", 1);
hashMap.put("b", 2);
hashMap.put("c", 3);
hashMap.put("d", 4);
hashMap.put("e", 5);
System.out.println(hashMap.containsKey("a"));
System.out.println(hashMap.containsValue(2));
for (String key : hashMap.keySet()) {
System.out.println(key + ": " + hashMap.get(key));
}
hashMap.remove("c");
System.out.println(hashMap);
}
}
true
true
a: 1
b: 2
c: 3
d: 4
e: 5
{a=1, b=2, d=4, e=5}
Process finished with exit code 0
使用Properties读写属性文件
package day6;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Properties;
public class PropertiesTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
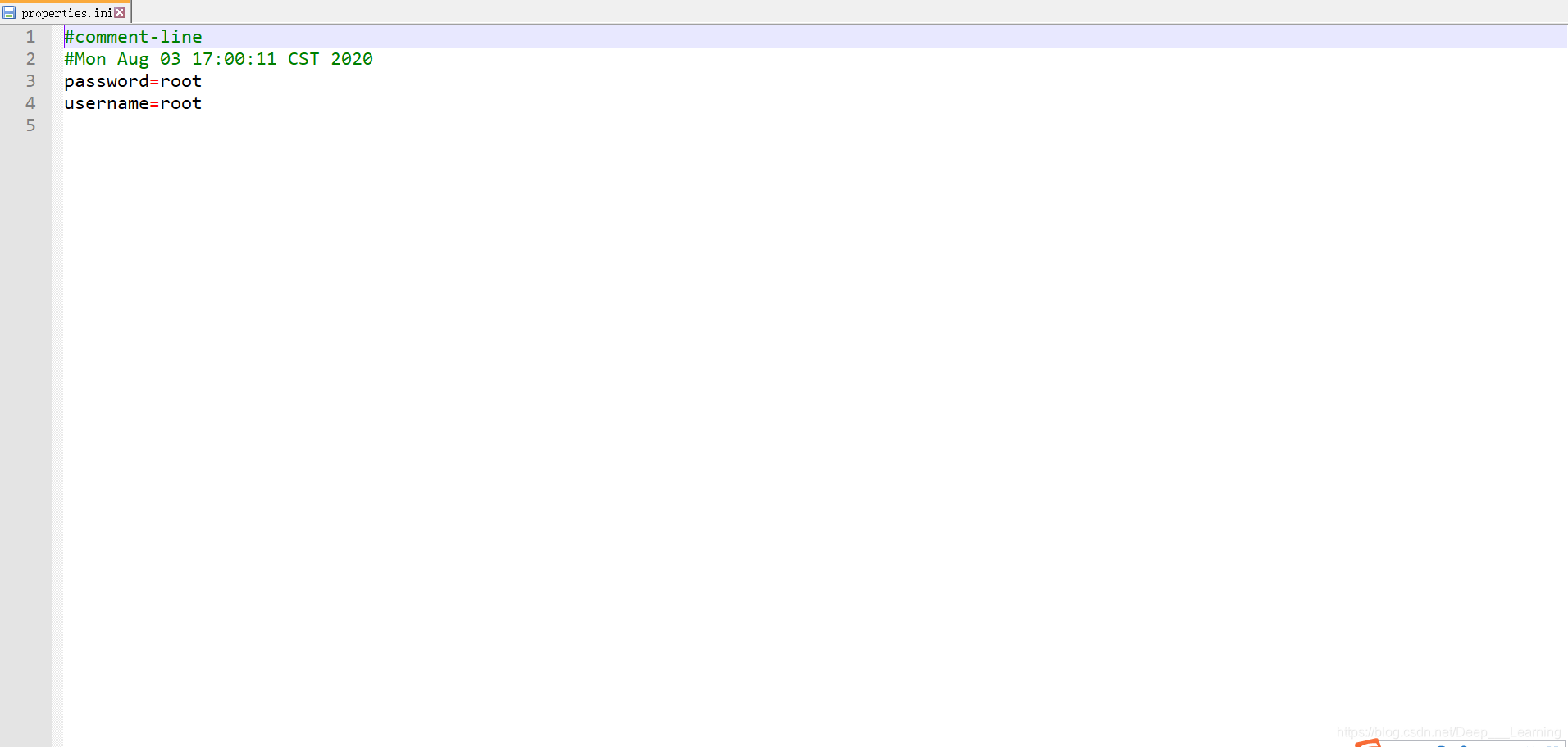
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("username", "root");
properties.setProperty("password", "root");
try {
properties.store(new FileOutputStream("properties.ini"), "comment-line");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Properties properties1 = new Properties();
try {
properties1.load(new FileInputStream("properties.ini"));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(properties1);
}
}
{password=root, username=root}
Process finished with exit code 0
package day6;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class TreeMapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeMap<String, Integer> treeMap = new TreeMap<>();
treeMap.put("a", 1);
treeMap.put("b", 2);
treeMap.put("d", 3);
treeMap.put("c", 34);
treeMap.put("z", 56);
treeMap.put("x", 89);
System.out.println(treeMap);
System.out.println(treeMap.lastKey());
System.out.println(treeMap.lowerEntry("c"));
System.out.println(treeMap.subMap("b", "x"));
}
}
{a=1, b=2, c=34, d=3, x=89, z=56}
z
b=2
{b=2, c=34, d=3}
Process finished with exit code 0
工具类:Collections
Collections提供了大量的方法对集合元素进行排序、查询和修改操作,还提供了将集合对象设置为不可变、对集合对象实现同步控制等方法
package day6;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
public class SortTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
arrayList.add(2);
arrayList.add(-2);
arrayList.add(3);
arrayList.add(0);
arrayList.add(-10);
arrayList.add(100);
System.out.println(arrayList);
Collections.sort(arrayList);
System.out.println(arrayList);
Collections.reverse(arrayList);
System.out.println(arrayList);
Collections.shuffle(arrayList);
System.out.println(arrayList);
}
}
[2, -2, 3, 0, -10, 100]
[-10, -2, 0, 2, 3, 100]
[100, 3, 2, 0, -2, -10]
[2, -2, -10, 0, 3, 100]
Process finished with exit code 0
package day6;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
public class SearchTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
arrayList.add(-1);
arrayList.add(2);
arrayList.add(-9);
arrayList.add(-10);
arrayList.add(19);
arrayList.add(100);
arrayList.add(0);
System.out.println(arrayList);
System.out.println(Collections.max(arrayList));
System.out.println(Collections.min(arrayList));
System.out.println(Collections.replaceAll(arrayList, 0, 1));
System.out.println(arrayList);
}
}
[-1, 2, -9, -10, 19, 100, 0]
100
-10
true
[-1, 2, -9, -10, 19, 100, 1]
Process finished with exit code 0





 本文深入探讨了Java集合框架的各种类型,包括Set、List、Queue、Map等,详细讲解了每种集合的特点、用法及其实现原理。通过具体示例演示了如何使用这些集合进行数据存储、排序、检索和管理。
本文深入探讨了Java集合框架的各种类型,包括Set、List、Queue、Map等,详细讲解了每种集合的特点、用法及其实现原理。通过具体示例演示了如何使用这些集合进行数据存储、排序、检索和管理。
















 1240
1240

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








