Lecture 10 | State registers
NAND

| a | b | c |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
Signals and Waveforms
Clock

Grouping
 ### Circuit Delay
### Circuit Delay
 ## Circuits with State(e.g. register) 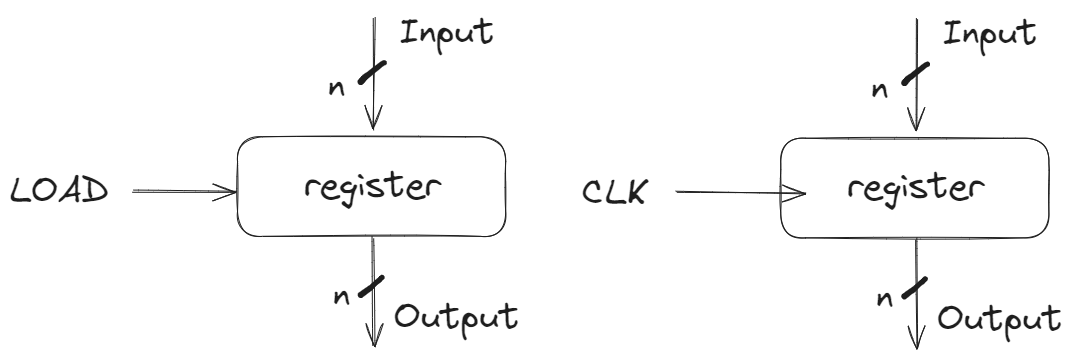 ## Accumulator ```c S = 0; for(i = 0; i < n; i ++) S = S + Xi; ``` 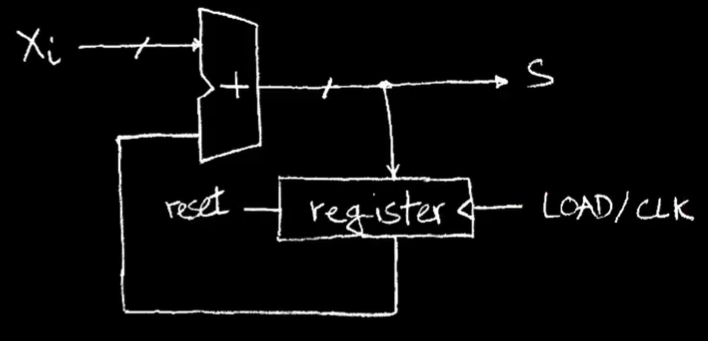 Register is used to hold up the transfer of data to adder. When reset line is asserted or goes one, the register will be reset. 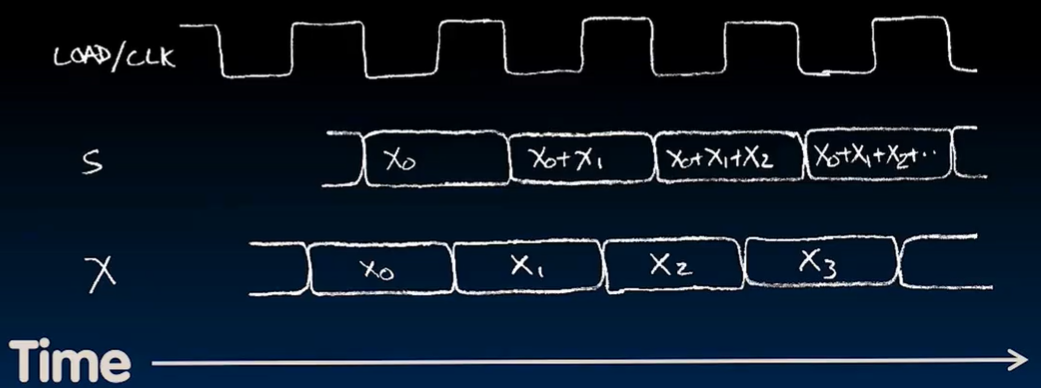 ### Register Details Flip-flops  一个 n 位寄存器实际上是 n 个 1 位触发器。 D input is **Data**, Q is **output** 这些也叫做 D-type Flip-Flop #### 上升沿触发(rising edge-triggered) 当它从 0 变为 1 时,就会触发。 On the rising edge of the clock, the input d is sampled and transferred to the output. At all other times, the input d is ignored.
## Circuits with State(e.g. register)  ## Accumulator ```c S = 0; for(i = 0; i < n; i ++) S = S + Xi; ```  Register is used to hold up the transfer of data to adder. When reset line is asserted or goes one, the register will be reset.  ### Register Details Flip-flops  一个 n 位寄存器实际上是 n 个 1 位触发器。 D input is **Data**, Q is **output** 这些也叫做 D-type Flip-Flop #### 上升沿触发(rising edge-triggered) 当它从 0 变为 1 时,就会触发。 On the rising edge of the clock, the input d is sampled and transferred to the output. At all other times, the input d is ignored.
  q 中刚开始的阴影部分代表可能是 1 也可能是 0。红色部分是因为存在一定延迟。 #### Example(more detail)  ### Accumulator Revisited 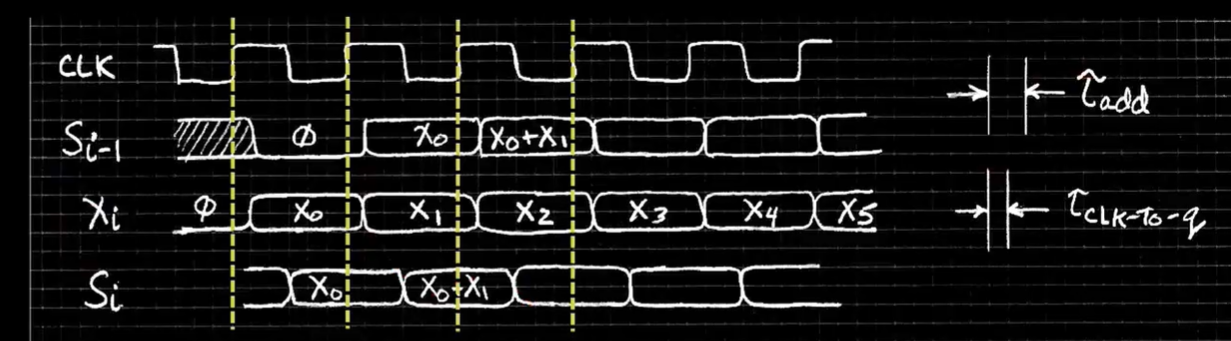
 q 中刚开始的阴影部分代表可能是 1 也可能是 0。红色部分是因为存在一定延迟。 #### Example(more detail)  ### Accumulator Revisited 


- Reset signal shown.
- Also, in practice X might not arrive to the adder at the same time as S i − 1 S_{i-1} Si−1
- S i S_i Si temporarily is wrong(底下阴影部分), but register always captures correct value.
- In good circuits, instability never happens around rising edge of clk.
| Clock(CLK) | steady square wave that synchronizes system |
| Setup Time | when the input must be stable before the rising edge of the CLK |
| Hold Time | when the input must be stable after the rising edge of the CLK |
| CLK-to-Q | Delay – how long it takes the output to change, measured from the rising edge of the CLK |
| Flip-flop | ont bit of state that samples every rising edge of the CLK |
| Register | several bits of state that samples on rising edge of CLK or on LOAD |
Finite State Machines(FSM) 有限状态机
 ### Example: 3 ones 
### Example: 3 ones 
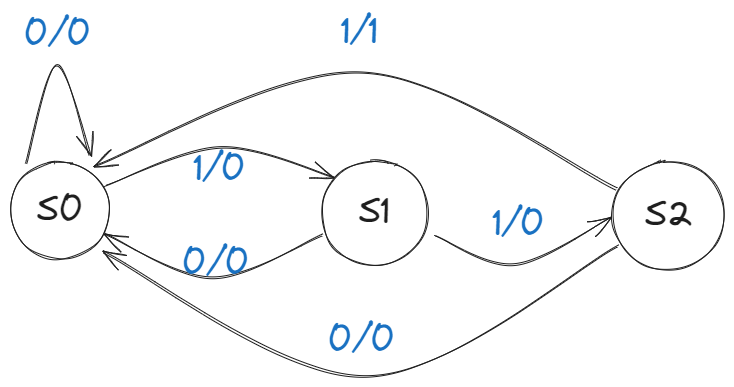 #### 流程如图:  #### Hardware Implementation of FSM
#### 流程如图:  #### Hardware Implementation of FSM

| PS | Input | NS | Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| 00 | 0 | 00 | 0 |
| 00 | 1 | 01 | 0 |
| 01 | 0 | 00 | 0 |
| 01 | 1 | 10 | 0 |
| 10 | 0 | 00 | 0 |
| 10 | 1 | 00 | 1 |

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








