LDF
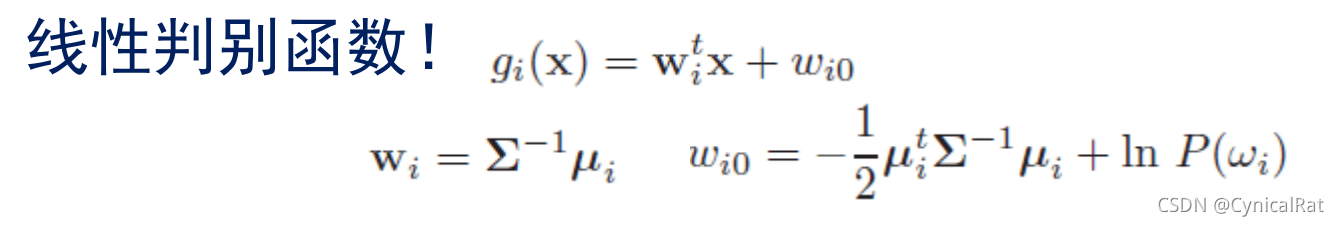 QDF
QDF
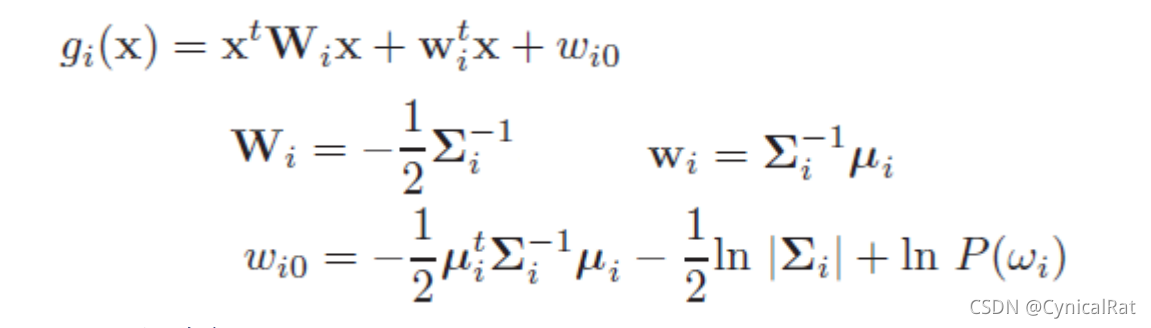
python实现
import numpy as np
# import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import math
import tensorflow as tf
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split, cross_val_score, GridSearchCV # 划分数据 交叉验证 网格搜索
class LDFandQDF():
# 计算判别函数系数
def train(self, x_train, y_train, classA, classB):
"""X为训练数据集,y为训练label"""
X1 = np.array([x_train[i] for i in range(len(x_train)) if y_train[i] == classA]) # 找出标签为classA的数据
X2 = np.array([x_train[i] for i in range(len(x_train)) if y_train[i] == classB]) # 找出标签为classB的数据
# 计算先验概率
Pw1 = len(X1) / (len(X1) + len(X2))
Pw2 = len(X2) / (len(X1) + len(X2))
# 求均值
mju1 = np.mean(X1, axis=0) # mju是ndarray类型
mju2 = np.mean(X2, axis=0)
# 求协方差
covX1 = np.cov(X1.T)
covX2 = np.cov(X2.T)
# 协方差行列式
cov1_det = np.linalg.det(covX1)
cov2_det = np.linalg.det(covX2)
# 协方差的逆
if cov1_det == 0: # 第一类
# 协方差矩阵不可逆,使用伪逆
invX1 = np.linalg.pinv(covX1)
else:
# 协方差矩阵可逆
invX1 = np.linalg.inv(covX1)
if cov2_det == 0: # 第二类
# 协方差矩阵不可逆,使用伪逆
invX2 = np.linalg.pinv(covX2)
else:
# 协方差矩阵可逆
invX2 = np.linalg.inv(covX1)
# 记录类别
self.classa = classA
self.classb = classB
# 记录计算结果
self.Pw1 = Pw1 # 先验概率
self.Pw2 = Pw2
self.mju1 = mju1 # 第一类classA 均值
# self.covX1 = covX1 # 协方差
self.inv_covX1 = invX1 # 协方差的逆
self.cov1_det = cov1_det # 协方差行列式
self.mju2 = mju2 # 第二类classB
# self.covX2 = covX2
self.inv_covX2 = invX2
self.cov2_det = cov2_det
# 进行预测
def predict(self, method):
self.method = method
predict_class = []
W1 = -(1 / 2) * self.inv_covX1
W2 = -(1 / 2) * self.inv_covX2
w1 = np.dot(self.inv_covX1, self.mju1)
w2 = np.dot(self.inv_covX2, self.mju2)
if method == 'QDF':
if self.cov1_det == 0: # 行列式为0,协方差不满秩,无法求对数,把对数项忽略
w10 = -(1 / 2) * np.dot(np.dot(self.mju1.T, self.inv_covX1), self.mju1) + math.log(self.Pw1)
else: # 协方差矩阵满秩,正常
w10 = -(1 / 2) * np.dot(np.dot(self.mju1.T, self.inv_covX1), self.mju1) - (1 / 2) * math.log(
self.cov1_det) + math.log(self.Pw1)
if self.cov2_det == 0:
w20 = -(1 / 2) * np.dot(np.dot(self.mju2.T, self.inv_covX2), self.mju2) + math.log(self.Pw2)
else:
w20 = -(1 / 2) * np.dot(np.dot(self.mju2.T, self.inv_covX2), self.mju2) - (1 / 2) * math.log(
self.cov2_det) + math.log(self.Pw2)
for i in range(len(self.x_test_)):
g1x = np.dot(np.dot(self.x_test_[i].T, W1), self.x_test_[i]) + np.dot(w1.T, self.x_test_[i]) + w10
g2x = np.dot(np.dot(self.x_test_[i].T, W2), self.x_test_[i]) + np.dot(w2.T, self.x_test_[i]) + w20
if (g1x - g2x) > 0:
predict_class.append(self.classa)
else:
predict_class.append(self.classb)
if method == 'LDF':
w10 = -(1 / 2) * np.dot(np.dot(self.mju1.T, self.inv_covX1), self.mju1) + math.log(self.Pw1)
w20 = -(1 / 2) * np.dot(np.dot(self.mju2.T, self.inv_covX2), self.mju2) + math.log(self.Pw2)
for i in range(len(self.x_test_)):
g1x = np.dot(w1.T, self.x_test_[i]) + w10
g2x = np.dot(w2.T, self.x_test_[i]) + w20
if (g1x - g2x) > 0:
predict_class.append(self.classa)
else:
predict_class.append(self.classb)
return predict_class
def split_test_data(self, xtest, ytest):
x_test_ = np.array(
[xtest[i] for i in range(len(xtest)) if (ytest[i] == self.classa or ytest[i] == self.classb)])
y_test_ = np.array(
[ytest[i] for i in range(len(ytest)) if (ytest[i] == self.classa or ytest[i] == self.classb)])
self.x_test_ = x_test_
self.y_test_ = y_test_
# 计算判别函数分类精度
def analysis_accuracy(self, y_predict):
count = 0
nums = len(self.y_test_)
for i in range(nums):
if y_predict[i] == self.y_test_[i]:
count += 1
precise = count / nums
# 显示信息
print("Function type:", self.method)
print("classes:", self.classa, self.classb)
print("Numbers of test samples:", nums)
print("Numbers of predict correct samples:", count)
print("Test precise:", precise)
return precise
# 挑出对应类别的测试集
if '__main__' == __name__:
# 产生分类数据
mnist = tf.keras.datasets.mnist
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data() # 读取mnist数据集,已经划分好了训练集和测试集
y_train = y_train.astype(np.uint8) # 将标签转换成整数
x_train_new = x_train.reshape(len(x_train), -1) # 将数据集和测试集的图像像素展开,变成784维特征
x_test_new = x_test.reshape(len(x_test), -1)
# #PCA降维,但是结果不是很理想,本以为会大幅改善LDF的分类性能,但是没啥用
#
# features = np.append(x_train_new, x_test_new, axis=0)
# labels = np.append(y_train, y_test, axis=0)
#
# features_ = StandardScaler().fit_transform(features)
#
# pca = PCA(n_components=0.95, whiten=True)
# features_pca = pca.fit_transform(features_)
#
# x_train_pca, x_test_pca, y_train_pca, y_test_pca = train_test_split(features_pca, labels, test_size=0.2, )
#
# print(features_pca.shape)
# print(x_train_pca.shape, y_train_pca.shape)
# ldfqdf = LDFandQDF() # 调用上面写的类
# ldfqdf.train(x_train_pca, y_train_pca, 0, 5)
# ldfqdf.split_test_data(x_test_pca, y_test_pca)
#
# predic_result1 = ldfqdf.predict('LDF')
# ldfqdf.analysis_accuracy(predic_result1)
#
# predic_result2 = ldfqdf.predict('QDF')
# ldfqdf.analysis_accuracy(predic_result2)
# 不降维,用原数据直接算
ldfqdf = LDFandQDF() # 调用上面写的类
ldfqdf.train(x_train_new, y_train, 1, 9)
ldfqdf.split_test_data(x_test_new, y_test)
predic_result1 = ldfqdf.predict('LDF')
ldfqdf.analysis_accuracy(predic_result1)
predic_result2 = ldfqdf.predict('QDF')
ldfqdf.analysis_accuracy(predic_result2)

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








