我们常常在事务注解中,定义rollbackFor 为事务定义异常的类型。
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class) public Result<Boolean> updateArticle(Long articleId, ArticleCreateRequest request) // TODO code. }Spring(6.2.7)
一、实现逻辑类(RuleBasedTransactionAttribute)
1. 异常回滚入口: RuleBasedTransactionAttribute#rollbackOn
public class RuleBasedTransactionAttribute extends DefaultTransactionAttribute implements Serializable {
@Override
public boolean rollbackOn(Throwable ex) {
RollbackRuleAttribute winner = null;
int deepest = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
// 1. 检查是否有显式配置的回滚规则
if (this.rollbackRules != null) {
for (RollbackRuleAttribute rule : this.rollbackRules) {
int depth = rule.getDepth(ex);
// 2. 检查异常是否匹配回滚规则
if (depth >= 0 && depth < deepest) {
deepest = depth;
winner = rule; // 匹配则回滚
}
}
}
// User superclass behavior (rollback on unchecked) if no rule matches.
if (winner == null) {
// 3. 没有匹配规则时使用默认行为
return super.rollbackOn(ex);
}
return !(winner instanceof NoRollbackRuleAttribute);
}
}
2. 回滚规则解析: RollbackRuleAttribute#getDepth
public class RollbackRuleAttribute implements Serializable{
public int getDepth(Throwable exception) {
// 递归调用
return getDepth(exception.getClass(), 0);
}
private int getDepth(Class<?> exceptionType, int depth) {
if (this.exceptionType != null) {
// 1. 检查当前异常类是否匹配规则
if (this.exceptionType.equals(exceptionType)) {
// Found it!
return depth;
}
}
// 2. 根据名称匹配
else if (exceptionType.getName().contains(this.exceptionPattern)) {
// Found it!
return depth;
}
// If we've gone as far as we can go and haven't found it...
// 3. 递归检查父类 (RuntimeException->Exception->Throwable)
if (exceptionType == Throwable.class) {
// 没有找到.
return -1;
}
// 递归
return getDepth(exceptionType.getSuperclass(), depth + 1);
}
}
3. 默认回滚规则: DefaultTransactionAttribute#rollbackOn
public class DefaultTransactionAttribute extends DefaultTransactionDefinition implements TransactionAttribute {
@Override
public boolean rollbackOn(Throwable ex) {
return (ex instanceof RuntimeException || ex instanceof Error);
}
}
4. rollback 调用流程图解
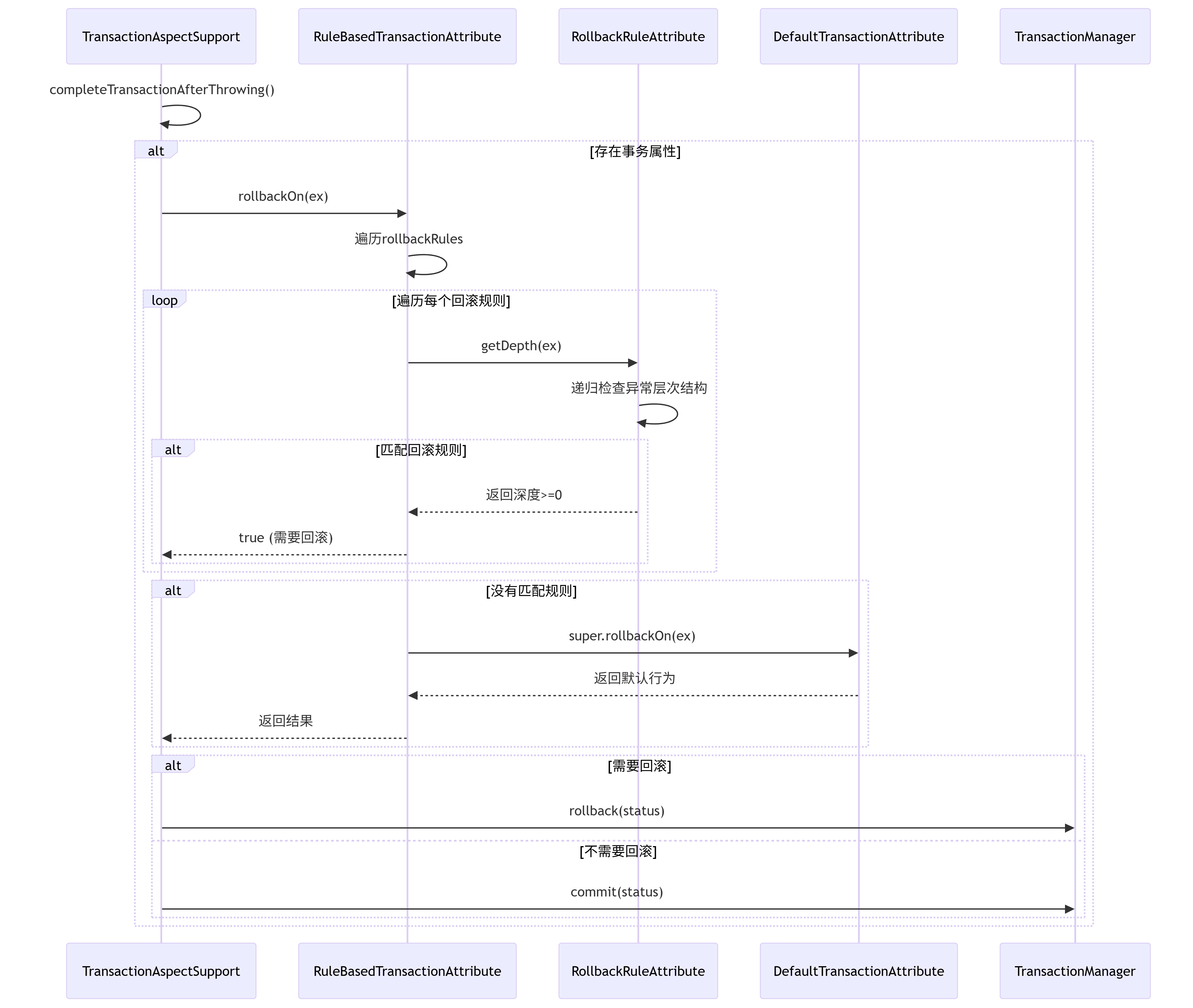
二、具体代码实现逻辑
1. 事务属性解析(注解 --->规则)
SpringTransactionAnnotationParser#parseTransactionAnnotation
public class SpringTransactionAnnotationParser implements TransactionAnnotationParser, Serializable {
protected TransactionAttribute parseTransactionAnnotation(AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
RuleBasedTransactionAttribute rbta = new RuleBasedTransactionAttribute();
Propagation propagation = attributes.getEnum("propagation");
rbta.setPropagationBehavior(propagation.value());
Isolation isolation = attributes.getEnum("isolation");
rbta.setIsolationLevel(isolation.value());
rbta.setTimeout(attributes.getNumber("timeout").intValue());
String timeoutString = attributes.getString("timeoutString");
Assert.isTrue(!StringUtils.hasText(timeoutString) || rbta.getTimeout() < 0,
"Specify 'timeout' or 'timeoutString', not both");
rbta.setTimeoutString(timeoutString);
rbta.setReadOnly(attributes.getBoolean("readOnly"));
rbta.setQualifier(attributes.getString("value"));
rbta.setLabels(Set.of(attributes.getStringArray("label")));
List<RollbackRuleAttribute> rollbackRules = new ArrayList<>();
// 解析 rollbackFor 配置
for (Class<?> rbRule : attributes.getClassArray("rollbackFor")) {
rollbackRules.add(new RollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule));
}
for (String rbRule : attributes.getStringArray("rollbackForClassName")) {
rollbackRules.add(new RollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule));
}
// 解析 noRollbackFor 配置
for (Class<?> rbRule : attributes.getClassArray("noRollbackFor")) {
rollbackRules.add(new NoRollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule));
}
for (String rbRule : attributes.getStringArray("noRollbackForClassName")) {
rollbackRules.add(new NoRollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule));
}
rbta.setRollbackRules(rollbackRules);
return rbta;
}
}
2. 异常处理核心
TransactionAspectSupport#completeTransactionAfterThrowing
protected void completeTransactionAfterThrowing(@Nullable TransactionInfo txInfo, Throwable ex) {
if (txInfo != null && txInfo.getTransactionStatus() != null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Completing transaction for [" + txInfo.getJoinpointIdentification() +
"] after exception: " + ex);
}
// 检查是否需要回滚
if (txInfo.transactionAttribute != null && txInfo.transactionAttribute.rollbackOn(ex)) {
try {
// 执行回滚
txInfo.getTransactionManager().rollback(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
}
catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
// 记录日志并处理回滚失败
logger.error("Application exception overridden by rollback exception", ex);
ex2.initApplicationException(ex);
throw ex2;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by rollback exception", ex);
throw ex2;
}
}
else {
// We don't roll back on this exception.
// Will still roll back if TransactionStatus.isRollbackOnly() is true.
try {
// 提交事务(即使有异常)
txInfo.getTransactionManager().commit(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
}
catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", ex);
ex2.initApplicationException(ex);
throw ex2;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", ex);
throw ex2;
}
}
}
}
3. 回滚规则匹配:递归调用,异常继承
RollbackRuleAttribute#getDepth
private int getDepth(Class<?> exceptionType, int depth) {
if (this.exceptionType != null) {
if (this.exceptionType.equals(exceptionType)) {
// Found it!
return depth;
}
}
else if (exceptionType.getName().contains(this.exceptionPattern)) {
// Found it!
return depth;
}
// If we've gone as far as we can go and haven't found it...
if (exceptionType == Throwable.class) {
return -1;
}
return getDepth(exceptionType.getSuperclass(), depth + 1);
}
4. 实际回滚操作:
AbstractPlatformTransactionManager#processRollback
public abstract class AbstractPlatformTransactionManager
implements PlatformTransactionManager, ConfigurableTransactionManager, Serializable {
private void processRollback(DefaultTransactionStatus status, boolean unexpected) {
try {
boolean unexpectedRollback = unexpected;
boolean rollbackListenerInvoked = false;
try {
triggerBeforeCompletion(status);
// 嵌套事务回滚处理
if (status.hasSavepoint()) {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Rolling back transaction to savepoint");
}
this.transactionExecutionListeners.forEach(listener -> listener.beforeRollback(status));
rollbackListenerInvoked = true;
status.rollbackToHeldSavepoint();
}
// 新事务回滚
else if (status.isNewTransaction()) {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Initiating transaction rollback");
}
this.transactionExecutionListeners.forEach(listener -> listener.beforeRollback(status));
rollbackListenerInvoked = true;
doRollback(status);
}
else {
// Participating in larger transaction
// 参与现有事务
if (status.hasTransaction()) {
if (status.isLocalRollbackOnly() || isGlobalRollbackOnParticipationFailure()) {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Participating transaction failed - marking existing transaction as rollback-only");
}
doSetRollbackOnly(status);
}
else {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Participating transaction failed - letting transaction originator decide on rollback");
}
}
}
else {
logger.debug("Should roll back transaction but cannot - no transaction available");
}
// Unexpected rollback only matters here if we're asked to fail early
if (!isFailEarlyOnGlobalRollbackOnly()) {
unexpectedRollback = false;
}
}
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_UNKNOWN);
if (rollbackListenerInvoked) {
this.transactionExecutionListeners.forEach(listener -> listener.afterRollback(status, ex));
}
throw ex;
}
triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_ROLLED_BACK);
if (rollbackListenerInvoked) {
this.transactionExecutionListeners.forEach(listener -> listener.afterRollback(status, null));
}
// Raise UnexpectedRollbackException if we had a global rollback-only marker
if (unexpectedRollback) {
throw new UnexpectedRollbackException(
"Transaction rolled back because it has been marked as rollback-only");
}
}
finally {
cleanupAfterCompletion(status);
}
}
}
三、rollbackFor = Exception.class 的特殊处理
当配置 @Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class) 时:
1、规则创建:
RollbackRuleAttribute rule = new RollbackRuleAttribute(Exception.class);
2、异常匹配:
- 任何
Exception的子类都会匹配(深度 >= 0) - 包括
SQLException、IOException等受检异常 - 也包括
RuntimeException及其子类
3、覆盖默认行为:
- 默认只回滚
RuntimeException和Error - 此配置覆盖了默认行为
4、与 noRollbackFor 交互:
@Transactional( rollbackFor = Exception.class, noRollbackFor = BusinessException.class )
BusinessException不会触发回滚。- 其他
Exception子类都会触发回滚
四、代码例子:
@Service
public class OrderService {
@Autowired
private OrderRepository orderRepository;
@Autowired
private PaymentService paymentService;
// 配置对所有Exception回滚
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void processOrder(Order order) throws PaymentException {
// 保存订单
orderRepository.save(order);
try {
// 支付操作(可能抛出受检异常)
paymentService.processPayment(order);
} catch (PaymentException ex) {
// 记录日志但继续处理
log.error("支付处理失败", ex);
}
// 发送通知(可能抛出IOException)
sendOrderConfirmation(order);
}
private void sendOrderConfirmation(Order order) throws IOException {
// 发送邮件或短信
if (someErrorCondition) {
throw new IOException("通知发送失败");
}
}
}
代码解析:
1.PaymentException 场景
- 匹配
rollbackFor = Exception.class→ 触发回滚 sendOrderConfirmation()抛出IOException- 支付失败 ->捕获异常 ->继续执行
2.数据库操作失败:
orderRepository.save()抛出DataAccessException(RuntimeException)- 匹配回滚规则-> 触发回滚
五、实现原理绘制
1、规则解析:
- Spring 在启动时解析
@Transactional注解 - 将
rollbackFor转换为RollbackRuleAttribute集合
2、异常匹配:
- 出现异常时,递归检查异常继承层次
- 深度 ≥ 0 表示匹配成功
3、回滚规则:
RuleBasedTransactionAttribute整合所有规则- 按顺序检查直到找到匹配规则
- 没有匹配时使用默认行为(RuntimeException|Error)
4、实际回滚:
- 根据事务状态决定回滚方式
- 新事务:完整回滚
- 嵌套事务:回滚到保存点
- 参与事务:标记为仅回滚
5、JDBC 实现:
- 最终调用
Connection.rollback() - 由具体事务管理器(如
DataSourceTransactionManager)实现
六、注意重要注意事项
1、Error 处理:
rollbackFor = Exception.class不包含 Error- Error 会触发回滚(默认行为)
- 如需包含 Error:
@Transactional(rollbackFor = {Exception.class, Error.class})
2、异常继承:
- Spring 5.2+ 支持接口异常匹配
- 例如:
class CustomException implements MyBusinessException - 配置
rollbackFor = MyBusinessException.class会匹配
3、性能考虑:
- 深度递归可能影响性能
- 避免过于宽泛的规则(如
rollbackFor = Throwable.class)(不建议 ×) - 精确指定需要回滚的异常类型
注意版本差异,spring 每个版本的实现都略有不同。






















 1498
1498

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










