一、事务传播机制(Propagation)
1.Spring 定义了7中事务传播机制
目录
1. 拦截器: TransactionInterceptor
2. 事务管理器:PlatformTransactionManager
3. 事务逻辑执行:TransactionAspectSupport#invokeWithinTransaction
3. 回滚核心逻辑(DataSourceTransactionManager)
spring版本说明: 6.2.7
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class, propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW) 配置.
| 传播行为类型 | 说明 |
| REQUIRED (默认) | 存在事务则加入,不存在则创建新事务 |
| REQUIRES_NEW | 始终创建新事务,挂起当前事务(若存在) |
| SUPPORTS | 存在事务则加入,不存在则以非事务运行 |
| MANDATORY | 必须存在事务,否则抛出IllegalTransactionStateException |
| NOT_SUPPORTED | 以非事务方式执行,挂起当前事务(若存在) |
| NEVER | 必须在非事务环境下执行,否则抛出异常 |
| NESTED | 嵌套事务(基于保存点),外层回滚会导致内层回滚,内层回滚不影响外层 |
二、 实现类和调研流程
1. 拦截器: TransactionInterceptor
public class TransactionInterceptor extends TransactionAspectSupport implements MethodInterceptor, Serializable{
}
主要方法:
TransactionInterceptor#invoke
@Override
@Nullable
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
// Work out the target class: may be {@code null}.
// The TransactionAttributeSource should be passed the target class
// as well as the method, which may be from an interface.
Class<?> targetClass = (invocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(invocation.getThis()) : null);
// Adapt to TransactionAspectSupport's invokeWithinTransaction...
return invokeWithinTransaction(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass, invocation::proceed);
}2. 事务管理器:PlatformTransactionManager
public interface PlatformTransactionManager extends TransactionManager {
TransactionStatus getTransaction(@Nullable TransactionDefinition definition) throws TransactionException;
void commit(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException;
void rollback(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException;
}3. 事务逻辑执行:TransactionAspectSupport#invokeWithinTransaction
protected Object invokeWithinTransaction(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass,
final InvocationCallback invocation) throws Throwable {
// If the transaction attribute is null, the method is non-transactional.
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
final TransactionAttribute txAttr = (tas != null ? tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) : null);
final TransactionManager tm = determineTransactionManager(txAttr, targetClass);
if (this.reactiveAdapterRegistry != null && tm instanceof ReactiveTransactionManager rtm) {
boolean isSuspendingFunction = KotlinDetector.isSuspendingFunction(method);
boolean hasSuspendingFlowReturnType = isSuspendingFunction &&
COROUTINES_FLOW_CLASS_NAME.equals(new MethodParameter(method, -1).getParameterType().getName());
ReactiveTransactionSupport txSupport = this.transactionSupportCache.computeIfAbsent(method, key -> {
Class<?> reactiveType =
(isSuspendingFunction ? (hasSuspendingFlowReturnType ? Flux.class : Mono.class) : method.getReturnType());
ReactiveAdapter adapter = this.reactiveAdapterRegistry.getAdapter(reactiveType);
if (adapter == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot apply reactive transaction to non-reactive return type [" +
method.getReturnType() + "] with specified transaction manager: " + tm);
}
return new ReactiveTransactionSupport(adapter);
});
return txSupport.invokeWithinTransaction(method, targetClass, invocation, txAttr, rtm);
}
PlatformTransactionManager ptm = asPlatformTransactionManager(tm);
final String joinpointIdentification = methodIdentification(method, targetClass, txAttr);
if (txAttr == null || !(ptm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager cpptm)) {
// Standard transaction demarcation with getTransaction and commit/rollback calls.
TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(ptm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);
Object retVal;
try {
// This is an around advice: Invoke the next interceptor in the chain.
// This will normally result in a target object being invoked.
retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// target invocation exception
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex);
throw ex;
}
finally {
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
if (retVal != null && txAttr != null) {
TransactionStatus status = txInfo.getTransactionStatus();
if (status != null) {
if (retVal instanceof Future<?> future && future.isDone()) {
try {
future.get();
}
catch (ExecutionException ex) {
Throwable cause = ex.getCause();
Assert.state(cause != null, "Cause must not be null");
if (txAttr.rollbackOn(cause)) {
status.setRollbackOnly();
}
}
catch (InterruptedException ex) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
else if (vavrPresent && VavrDelegate.isVavrTry(retVal)) {
// Set rollback-only in case of Vavr failure matching our rollback rules...
retVal = VavrDelegate.evaluateTryFailure(retVal, txAttr, status);
}
}
}
commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo);
return retVal;
}
else {
Object result;
final ThrowableHolder throwableHolder = new ThrowableHolder();
// It's a CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager: pass a TransactionCallback in.
try {
result = cpptm.execute(txAttr, status -> {
TransactionInfo txInfo = prepareTransactionInfo(ptm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status);
try {
Object retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
if (retVal != null && vavrPresent && VavrDelegate.isVavrTry(retVal)) {
// Set rollback-only in case of Vavr failure matching our rollback rules...
retVal = VavrDelegate.evaluateTryFailure(retVal, txAttr, status);
}
return retVal;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (txAttr.rollbackOn(ex)) {
// A RuntimeException: will lead to a rollback.
if (ex instanceof RuntimeException runtimeException) {
throw runtimeException;
}
else {
throw new ThrowableHolderException(ex);
}
}
else {
// A normal return value: will lead to a commit.
throwableHolder.throwable = ex;
return null;
}
}
finally {
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
});
}
catch (ThrowableHolderException ex) {
throw ex.getCause();
}
catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", throwableHolder.throwable);
ex2.initApplicationException(throwableHolder.throwable);
}
throw ex2;
}
catch (Throwable ex2) {
if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", throwableHolder.throwable);
}
throw ex2;
}
// Check result state: It might indicate a Throwable to rethrow.
if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
throw throwableHolder.throwable;
}
return result;
}
}三、异常回滚实现原理
1. 回滚条件判断
TransactionAspectSupport#completeTransactionAfterThrowing
protected void completeTransactionAfterThrowing(@Nullable TransactionInfo txInfo, Throwable ex) {
if (txInfo != null && txInfo.getTransactionStatus() != null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Completing transaction for [" + txInfo.getJoinpointIdentification() +
"] after exception: " + ex);
}
if (txInfo.transactionAttribute != null && txInfo.transactionAttribute.rollbackOn(ex)) {
try {
txInfo.getTransactionManager().rollback(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
}
catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by rollback exception", ex);
ex2.initApplicationException(ex);
throw ex2;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by rollback exception", ex);
throw ex2;
}
}
else {
// We don't roll back on this exception.
// Will still roll back if TransactionStatus.isRollbackOnly() is true.
try {
txInfo.getTransactionManager().commit(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
}
catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", ex);
ex2.initApplicationException(ex);
throw ex2;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", ex);
throw ex2;
}
}
}
}2. 回滚规则
-
默认规则:回滚
RuntimeException和Error -
DefaultTransactionAttribute#rollbackOn
-
@Override public boolean rollbackOn(Throwable ex) { return (ex instanceof RuntimeException || ex instanceof Error); } -
自定义规则:通过
@Transactional注解配置: -
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class, propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED) public boolean executeCompensation(String transactionId, String errorMessage) { }
3. 回滚核心逻辑(DataSourceTransactionManager)
DataSourceTransactionManager#doRollback
protected void doRollback(DefaultTransactionStatus status) {
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject)status.getTransaction();
Connection con = txObject.getConnectionHolder().getConnection();
if (status.isDebug()) {
this.logger.debug("Rolling back JDBC transaction on Connection [" + String.valueOf(con) + "]");
}
try {
con.rollback();
} catch (SQLException ex) {
throw this.translateException("JDBC rollback", ex);
}
}四、事务传播机制图解(REQUIRES_NEW)
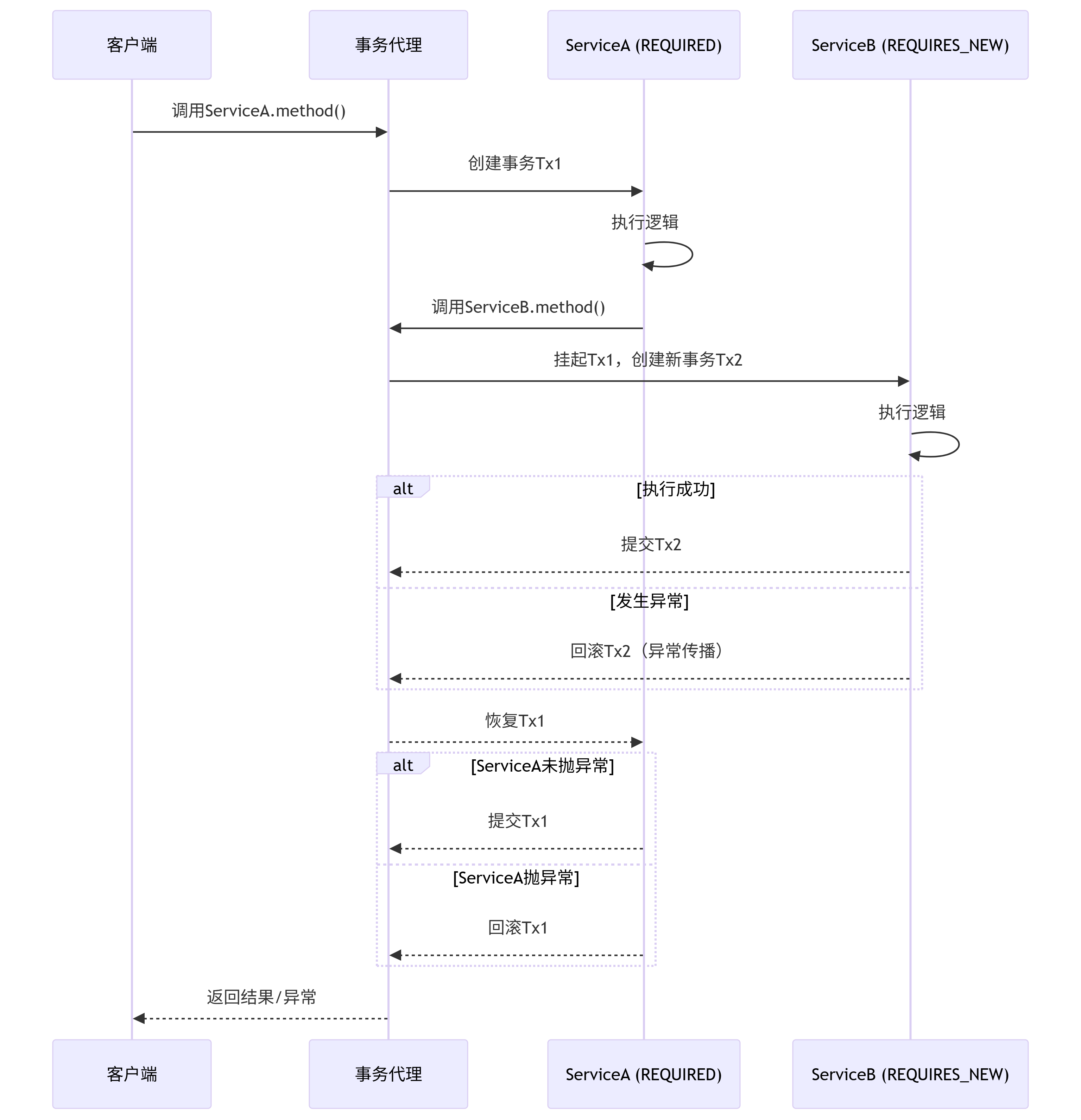
序列图
五、代码栗子
@Service
public class OrderService {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
// 外层事务(默认REQUIRED)
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void placeOrder(Order order) {
saveOrder(order); // 保存订单
try {
userService.updateUser(order.getUserId()); // 调用内层事务
} catch (Exception e) {
// 处理异常(内层事务回滚不影响外层)
}
}
}
@Service
public class UserService {
// 内层事务(始终新事务)
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
public void updateUser(Long userId) {
updateUserStats(userId); // 更新用户统计
if (someErrorCondition) {
throw new BusinessException("业务异常"); // 触发回滚
}
}
}六、回顾
-
传播机制调用:
-
通过
TransactionInterceptor拦截@Transactional方法 -
由
PlatformTransactionManager根据传播行为管理事务边界
-
-
异常回滚:
-
默认回滚
RuntimeException和Error -
可通过
rollbackFor/noRollbackFor自定义 -
最终由事务管理器调用JDBC/JPA的rollback()
-
-
事务嵌套:
-
REQUIRES_NEW会挂起当前事务并创建独立事务 -
NESTED使用保存点实现部分回滚
-
重要提示:事务生效需满足:
方法必须是
public调用必须来自代理对象(类内部调用不生效)
异常需抛出到事务拦截器(被catch的异常不会触发回滚)
但对于跨库调用的事务来说,那就要使用分布式事务了,如Seata(AT,TCC), RocketMQ 本地消息表机制来实现了。





















 2195
2195

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










