本文字数:18059;估计阅读时间:46 分钟
作者:Raufs Dunamalijevs
本文在公众号【ClickHouseInc】首发

要点总结
我们为 ClickHouse 引入了 QBit,这是一种将浮点数按位面(bit plane)方式存储的新列类型。通过它,你可以在执行向量搜索时灵活选择读取的位数,实现召回率与查询性能之间的动态权衡,而无需修改原始数据。
向量搜索如今应用广泛。它支撑着音乐推荐系统、大语言模型中的检索增强生成(Retrieval-Augmented Generation,RAG)等场景——通过检索外部知识来提升回答质量,甚至在一定程度上,搜索引擎如 Google 也采用了向量搜索。尽管已有不少专为高效向量搜索打造的数据库系统,但它们通常不擅长处理结构化数据。因此,很多用户更愿意在常规数据库上使用具备一定向量能力的扩展,而不是迁移到专用的向量数据库。
ClickHouse 早已支持暴力向量搜索。最近,我们新增了近似最近邻(Approximate Nearest Neighbour,ANN)算法的支持,包括目前主流的 HNSW,用于加速向量检索。同时,我们重新设计了量化方案,推出了全新数据类型:QBit。
各种向量搜索方法都有各自的参数配置,用来在召回率、准确性和性能之间做出权衡。这些参数通常需要在使用前就设定好,一旦选错,往往会浪费大量时间和计算资源,而且后续调整代价也很高。
而有了 QBit,就无需在一开始做出艰难决定。你可以在查询阶段自由调整精度与速度的平衡,边试边找出最适合你场景的方案。
向量搜索简介
先说基本原理。向量搜索的目标,是从数据集中找出与某个目标文档(无论是文本、图片、音乐等)最相似的项。第一步是将所有数据项通过嵌入模型转换成高维向量(由浮点数构成的数组)。这些嵌入向量能够表达数据的语义。接着,我们通过比较向量之间的距离,判断它们在含义上的相似程度。
举个简单例子。假设我们有一组代表水果和动物的嵌入向量,你猜猜看——哪一个最接近柠檬?🍋
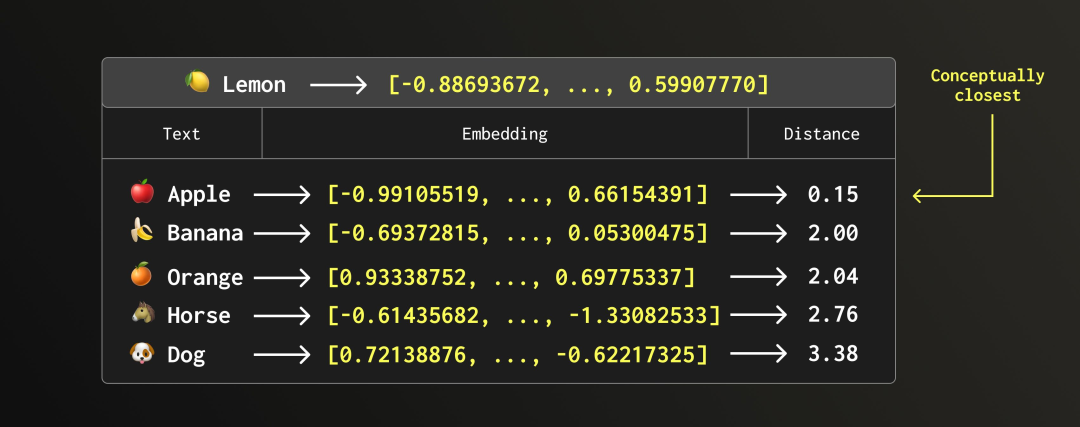
可能是苹果?这个例子听起来或许有些简单粗暴。毕竟,从概念上讲,柠檬更接近橙子,或者也许是香蕉——它们都是黄色的。但这确实是一个真实的例子,使用的是维度为 5 的小型向量进行的暴力搜索。
CREATE TABLE fruit_animal
ENGINE = MergeTree
ORDER BY word
AS SELECT *
FROM VALUES(
'word String, vec Array(Float64)',
('apple', [-0.99105519, 1.28887844, -0.43526649, -0.98520696, 0.66154391]),
('banana', [-0.69372815, 0.25587061, -0.88226235, -2.54593015, 0.05300475]),
('orange', [0.93338752, 2.06571317, -0.54612565, -1.51625717, 0.69775337]),
('dog', [0.72138876, 1.55757105, 2.10953259, -0.33961248, -0.62217325]),
('horse', [-0.61435682, 0.48542571, 1.21091247, -0.62530446, -1.33082533])
);SELECT word, L2Distance(
vec, [-0.88693672, 1.31532824, -0.51182908, -0.99652702, 0.59907770]
) AS distance
FROM fruit_animal
ORDER BY distance
LIMIT 5; ┌─word───┬────────────distance─┐
1. │ apple │ 0.14639757188169716 │
2. │ banana │ 1.9989613690076786 │
3. │ orange │ 2.039041552613732 │
4. │ horse │ 2.7555776805484813 │
5. │ dog │ 3.382295083120104 │
└────────┴─────────────────────┘当使用更高维度的向量时,可以表达更复杂的语义关系,检索结果也会更加丰富。不过,至少我们都能认同,把马和狗排在相似度列表的最后,还是挺符合直觉的。
近似最近邻(Approximate Nearest Neighbours,ANN)
精确向量搜索的确强大,但它速度慢、成本高。很多实际应用其实并不要求百分百精确。例如,听完 Eminem 的歌之后,系统推荐 Snoop Dogg 或 Tupac 是可以接受的。但如果下一首推荐是完全风格不搭的,就说明哪里出问题了。
这也是为什么会出现近似最近邻(ANN)技术。它允许我们牺牲一点准确性,换取更快、更低成本的检索速度。目前最常用的两种 ANN 方法是量化(quantisation)和 HNSW。
我们稍后会简单介绍这两种方法,并说明 QBit 在这个方案中扮演什么角色。
量化(Quantisation)
假设我们当前存储的向量类型是 Float64,而我们对其性能不太满意。此时一个自然的问题就是:如果将这些数据转为更小的类型,效果会怎样?
数据越小,表示它所占的空间越小,而更小的数据体积也意味着距离计算可以更快完成。在 ClickHouse 的向量化查询执行引擎中,处理器每轮操作可以装入更多数值,直接提升整体吞吐量。同时,磁盘读取的数据减少,也能有效降低 I/O 压力。这种通过压缩数据精度来提升性能的技术,就是所谓的量化。
进行量化时,需要决定具体的存储方式。主要有两种方案:
-
保留一份量化后的副本,与原始列共存;
-
或者在数据写入时直接类型转换,完全替代原始值。
第一种方式虽然会使数据量翻倍,但更安全,因为你随时可以回退到原始的高精度数据。而第二种方式节省了空间和 I/O,但一旦使用,就无法还原。如果后来发现量化精度不足,导致搜索结果偏差,就没有补救办法了。
分层可导航小世界(HNSW):向量索引的主流方案
在向量搜索中,许多数据结构被设计用来避免对所有候选项进行遍历,我们通常称这些结构为“索引”。在所有方案中,HNSW(Hierarchical Navigable Small World)被广泛认为是当前最优之一。
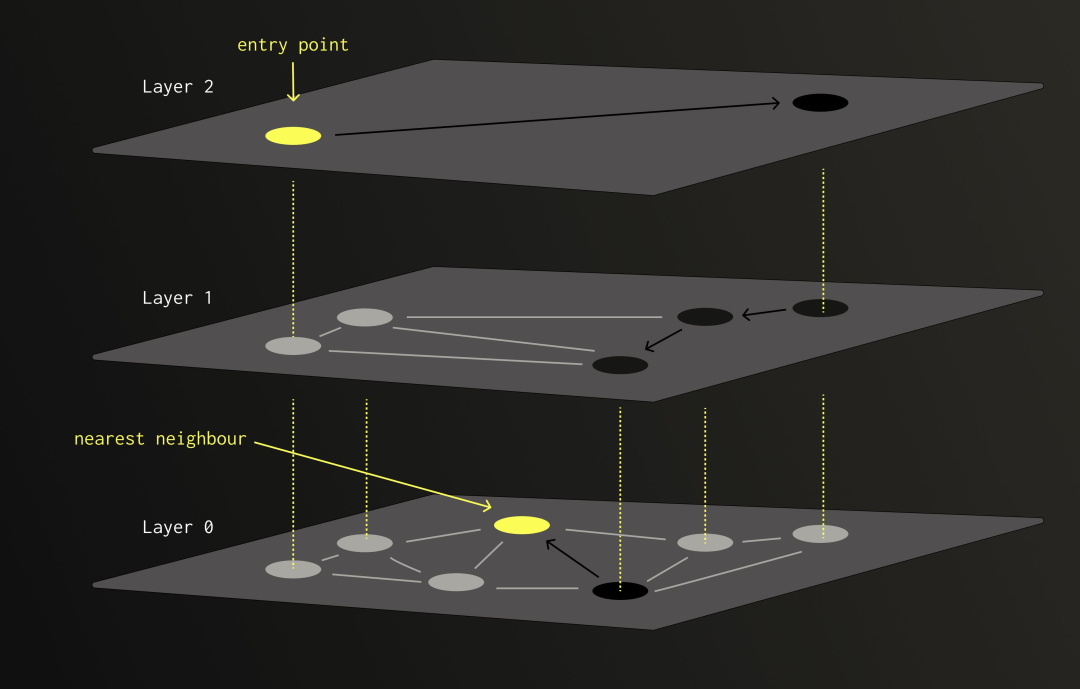
HNSW 的结构由多层节点(即向量)组成。每个节点会被随机分配到一个或多个层,层级越高,被选中的概率越低,且呈指数级下降。
搜索过程从最高层的某个节点开始,然后采用“贪婪搜索”策略,持续向当前距离目标最近的邻居移动。当无法再找到更接近的节点时,就会向下进入下一层(密度更高的层级),继续执行相同的过程。上层节点之间的连接可以加速跳跃,避免陷入局部最优,而底层则提供了更精细的局部匹配能力。
正是由于这种层级设计,HNSW 在面对大规模数据时,可以将搜索复杂度降低到对数级,远远优于暴力搜索或基于量化的线性扫描方法。
不过,这种结构的主要瓶颈在于内存。ClickHouse 采用的是 `usearch` 实现的 HNSW,它完全驻留于内存,并且不支持分片。因此,数据集越大,内存需求就越高。虽然在构建索引前对数据进行量化可以一定程度上减小内存占用,但包括量化精度在内的许多参数都必须预先设定,而这种“刚性”正是 QBit 想要解决的问题。
QBit:位级别可调精度的向量存储
QBit 是一种新型的数据结构,它能够存储 BFloat16、Float32 和 Float64 类型的数据,其原理是利用浮点数的位级编码方式进行拆分。与传统做法不同,QBit 不再将每个浮点数作为整体进行存储,而是将它们按位拆分成多个“比特平面”——也就是说,把所有数的第 1 位收集成一列,第 2 位收集成另一列,以此类推。
在执行向量搜索时,ClickHouse 可以按需读取相应的子列(subcolumns),只重建用户指定精度所需的数据部分。
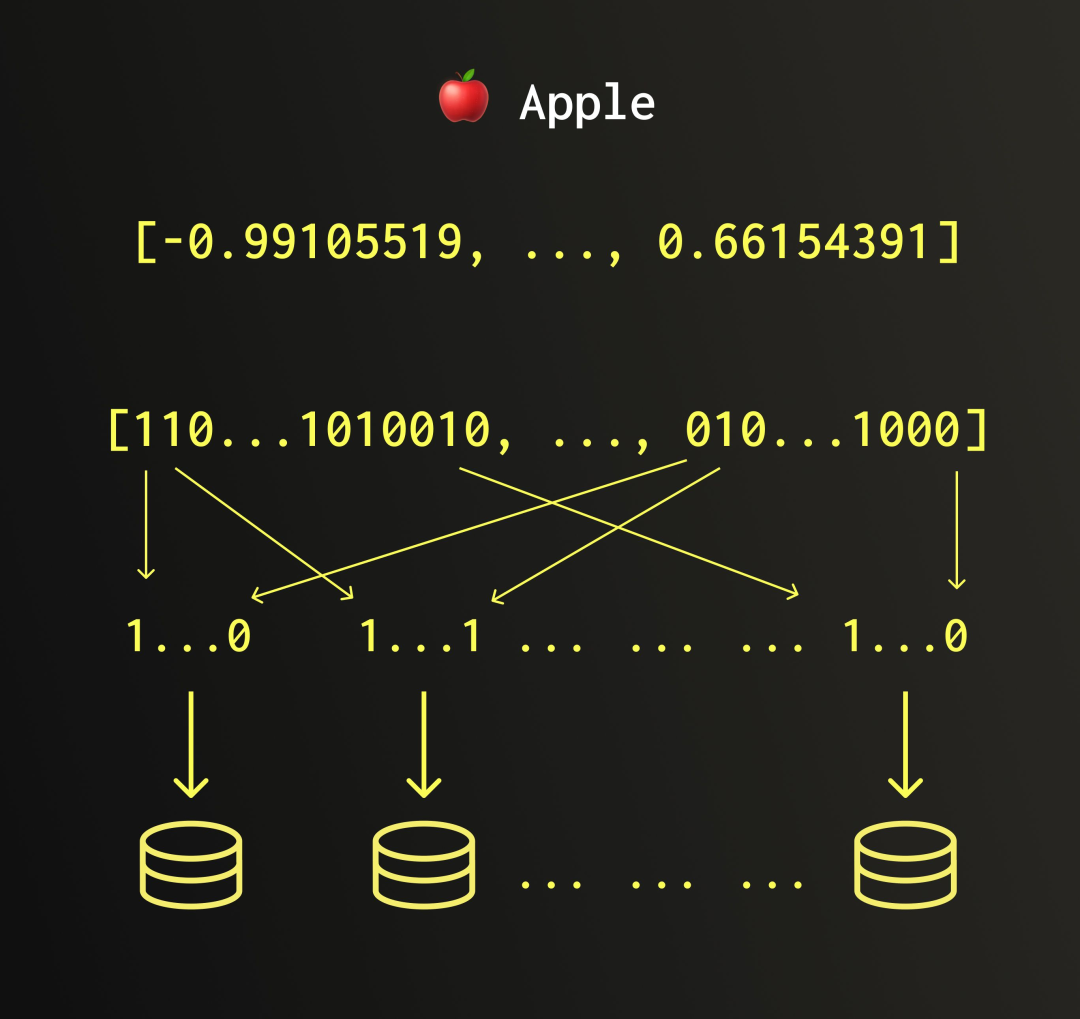
这一方法解决了传统量化方案中的几个核心问题。它无需额外存储一份量化副本,也不必担心因压缩过度而导致数据失真。同时,相比 HNSW 的内存索引结构,QBit 直接操作存储中的数据,显著缓解了内存瓶颈问题。
更重要的是,QBit 不要求用户在查询之前就做出关于精度或性能的决定。你可以在每次查询时自由调整精度,实现准确性与查询速度之间的动态权衡。
当然,虽然 QBit 能显著加速向量搜索,其本质仍是 O(n) 级别的全量扫描。换句话说:如果你的数据集足够小,能够让 HNSW 索引完整驻留于内存中,那么 HNSW 仍然是速度最快的选择。
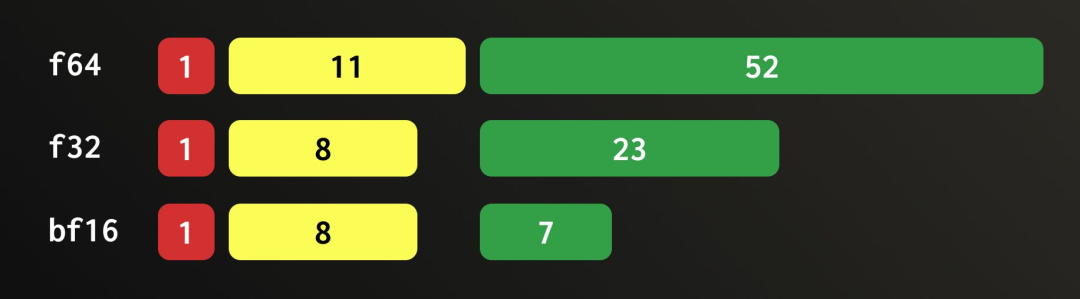
| Category | Brute-force | HNSW | QBit |
| Precision | Perfect | Great | Flexible |
| Speed | Slow | Fast | Flexible |
| Others | Quantized: more space or irreversible precision | Index has to fit in memory and has to be built | Still O(#records) |
QBit 深入解析
让我们回到前面的那个熟悉的例子,不过这次我们将从 QBit 的角度重新审视它。
CREATE TABLE fruit_animal
(
word String,
vec QBit(Float64, 5)
)
ENGINE = MergeTree
ORDER BY word;
INSERT INTO fruit_animal VALUES
('apple', [...]),
('banana', [...]),
('orange', [...]),
('dog', [...]),
('horse', [...]);我们现在可以执行这样一个查询:
SELECT
word,
L2DistanceTransposed(vec, [...], 16) AS distance
FROM fruit_animal
ORDER BY distance; ┌─word───┬────────────distance─┐
1. │ apple │ 0.14639757188169716 │
2. │ banana │ 1.998961369007679 │
3. │ orange │ 2.039041552613732 │
4. │ cat │ 2.752802631487914 │
5. │ horse │ 2.7555776805484813 │
6. │ dog │ 3.382295083120104 │
└────────┴─────────────────────┘QBit 的使用可以拆分为两个核心部分:
-
数据类型本身的定义与数据写入过程;
-
向量之间的距离计算。
我们将分别详细介绍这两个方面。
数据类型
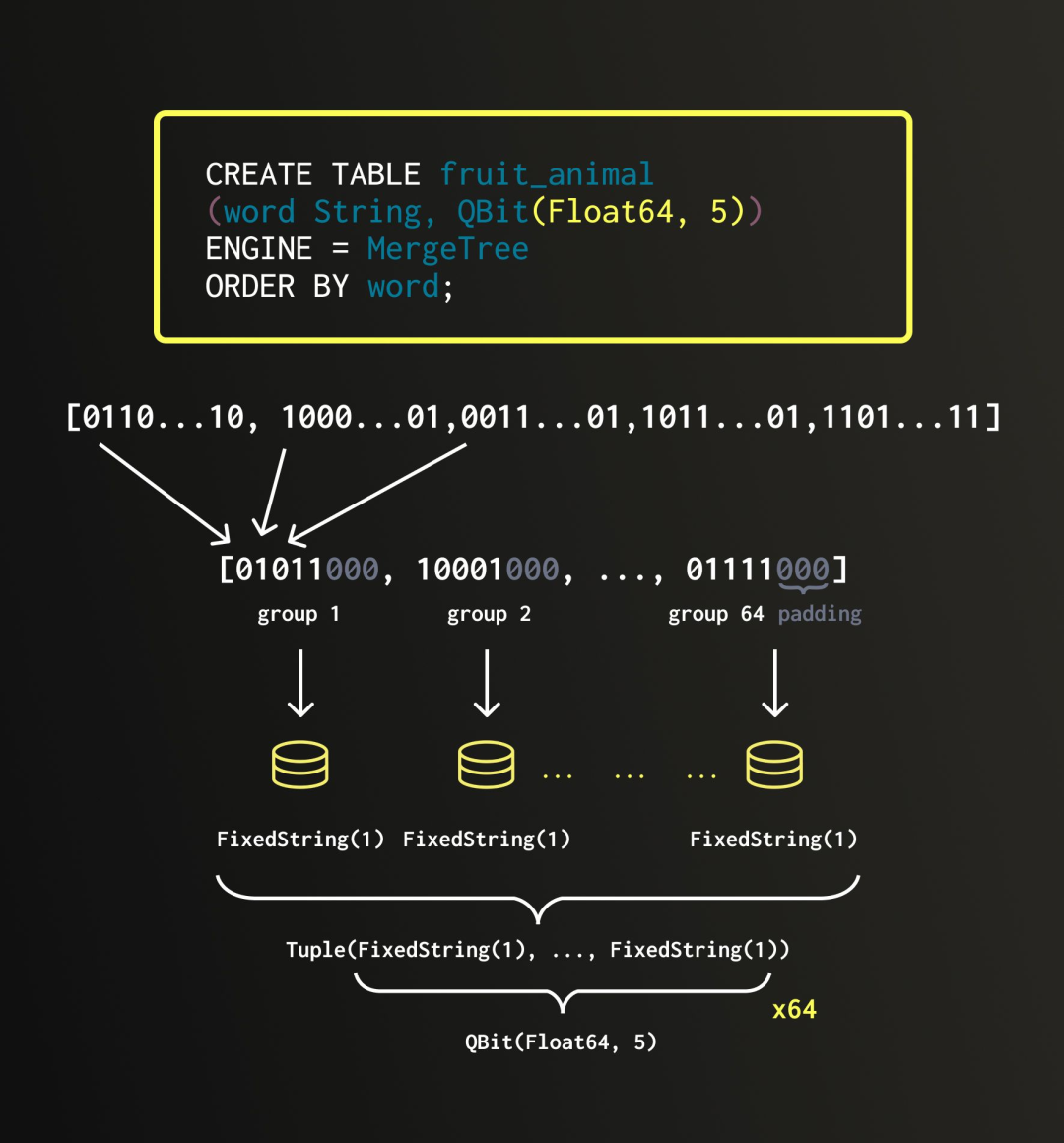
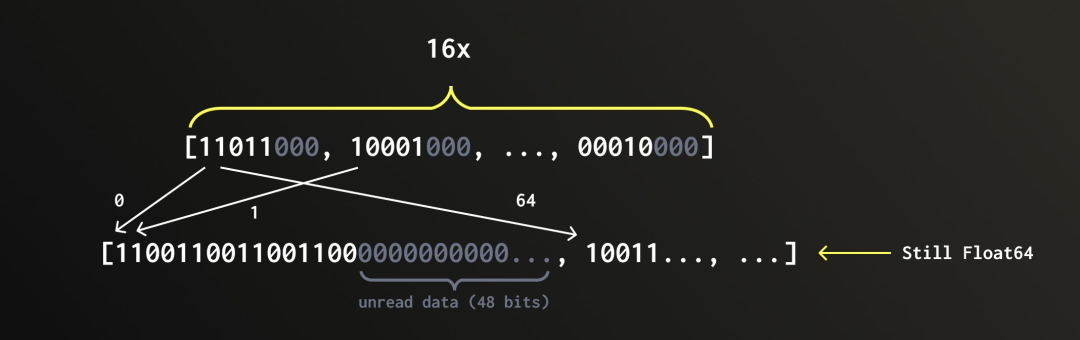
当数据写入 QBit 列时,会先进行一次转置操作:所有向量中第 1 位比特被提取出来排列成一组,第 2 位比特构成另一组,以此类推。我们把这些按位划分的集合称为“组”。
每个组会单独存储在一个 FixedString(N) 类型的列中。所谓 FixedString(N),指的是定长 N 字节的字符串,在内存中连续排列,且组与组之间没有任何分隔符。所有组最终会被组合成一个 Tuple,这就是 QBit 的核心数据结构。
举个例子,如果我们一开始是一个包含 8 个 Float64 元素的向量,那么每组会包含 8 个比特。由于每个 Float64 占 64 位,总共会生成 64 个组,每组对应一个比特位。也就是说,QBit(Float64, 8) 的内部结构就是一个包含 64 个 FixedString(1) 列的 Tuple。
如果原始向量长度不能被 8 整除,QBit 会自动补齐数据,使其对齐到 8 的整数倍。这是因为 FixedString 类型只能处理完整字节对齐的数据。例如,上图中的向量包含 5 个 Float64 元素,那么系统会在末尾补上 3 个零元素,使其扩展为 8 个 Float64,进而转置为包含 64 个 FixedString(1) 的 Tuple。类似地,如果一开始是 76 个 BFloat16 元素,也会补齐到 80 个,再转置为一个包含 16 个 FixedString(10) 的 Tuple。
距离计算
SELECT
word,
L2DistanceTransposed(vec, [...], 16) AS distance
FROM fruit_animal
ORDER BY distance;输入输出优化
在进行距离计算前,系统首先需要从磁盘中读取数据,并将其从按位分组的形式还原为完整的向量结构。由于 QBit 是按照精度将浮点数进行比特转置存储的,ClickHouse 可以只读取用于达到所需精度的高位比特平面,而跳过剩余部分。
比如在上面的查询中,我们设定的精度为 16 位。由于 Float64 总共有 64 位,只需读取前 16 个比特平面,即可重建数值的高精度部分,从而节省了约 75% 的读取数据量。

读取完成后,系统根据这些高位比特构造出数值的上半部分,而未读取的低位部分则会自动填充为零。
计算性能优化
或许你会好奇,是否可以通过将数据转换为更小的类型(如 Float32 或 BFloat16)来直接去除未使用的低位部分?理论上确实可行,但如果在每一行数据上都显式进行类型转换,计算开销会非常高。一种更高效的做法是:只对参考向量(即用来与 QBit 中所有向量进行比对的那个向量)进行类型转换,然后在处理 QBit 数据时,逻辑上“视作”它本身就是一个更低精度的结构。也就是说,虽然底层数据结构没有改变,但我们可以在比特层面忽略某些列。这种方法的前提是:QBit 的位布局必须与低精度浮点类型的结构一致。但需要注意,这并非总是成立。
我们先来看一个理想场景:如果原始数据为 Float32,且查询使用的精度在 16 位或以下,那么情况会相对简单。BFloat16 是 Float32 的截断版本,它保留了相同的符号位与 8 位指数部分,但仅保留 23 位尾数中的高 7 位。因此,从 QBit 中读取前 16 个比特平面,刚好可以重建出与 BFloat16 相匹配的结构。在这种情况下,我们可以安全地将参考向量转换为 BFloat16,并将 QBit 数据当作是从一开始就以 BFloat16 格式存储的进行处理。
但如果原始数据是 Float64,事情就没那么简单了。Float64 拥有 11 位指数和 52 位尾数,它并不是简单地将 Float32 扩展一倍那么简单,它的整体结构以及指数偏移规则都与 Float32 完全不同。将 Float64 向下转换为 Float32 需要遵循 IEEE-754 标准,每个数值都要舍入为 Float32 可表示的最接近值。这种舍入运算本身计算开销很大,无法通过简单的按位切片或重排列来模拟。
即使将精度限制为 16 位或更低,从 Float64 转换为 BFloat16 的过程本质上也等价于先将其转换为 Float32,再进一步截断成 BFloat16。这意味着,在处理 Float64 数据时,想通过位级操作来“伪装”为低精度数据几乎是不可行的。
向量化实现
向量化简介
QBit 相较于传统量化列的核心性能差异,在于查询时需要将按位分组的数据重新还原为向量形式。这一过程的效率对于整体性能至关重要。ClickHouse 拥有原生支持向量化的查询引擎,因此我们完全可以借助这一优势来提升解码效率。你可以在这篇 [ClickHouse 博客文章] 中进一步了解向量化原理。
简单来说,向量化是利用 CPU 的 SIMD(单指令多数据)机制,在一条指令中并行处理多个数值。SIMD 指令集通常以“向量”为处理单元,每个向量由固定长度的多个元素组成,这些元素被称为“通道(lane)”。
目前主要有两种实现向量化算法的方式:
-
自动向量化(Auto-vectorisation):通过将算法编写得足够简单,使得编译器能够自动推导出 SIMD 指令。但由于现代编译器在这方面的能力仍然有限,这种方式通常要求系统整体架构围绕自动向量化而设计,实用性有限。
-
内建函数(Intrinsics):显式使用特定平台提供的内建函数,将代码直接映射为底层 CPU 指令。虽然这种方式与平台绑定,但可以实现精细化控制。
通用算法流程
由于用于将 QBit 反转置为向量的过程较为复杂,编译器难以自动向量化,因此我们选择使用内建函数手动实现。下面我们先介绍算法的基本原理,然后再说明它是如何与向量化机制结合的。
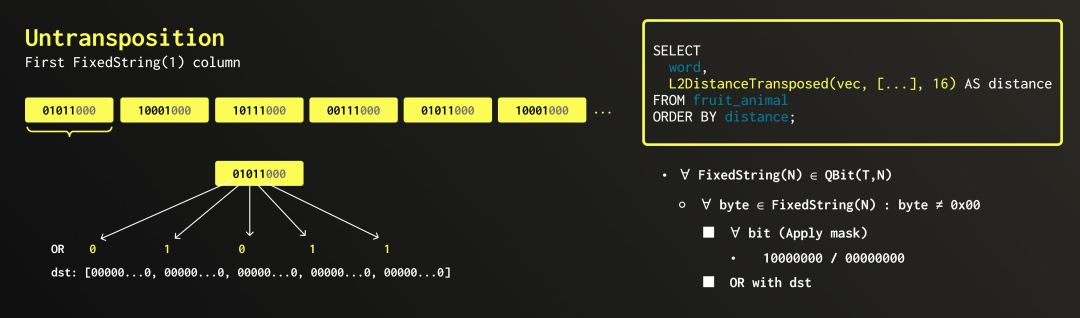



具体来说,我们会遍历 QBit 中的所有 FixedString 列(以 Float64 为例,共有 64 个)。对于每一列,我们逐字节扫描其内容,并在每个字节中逐位处理。
如果某个位为 0,我们就在目标向量的对应位置应用一个全零掩码;如果该位为 1,则根据其在字节中的位置应用不同的掩码。例如,第 1 位对应掩码 0b10000000,第 2 位为 0b01000000,以此类推。我们通过逻辑 OR 运算,将当前位合并到目标字节中。
向量化算法实现
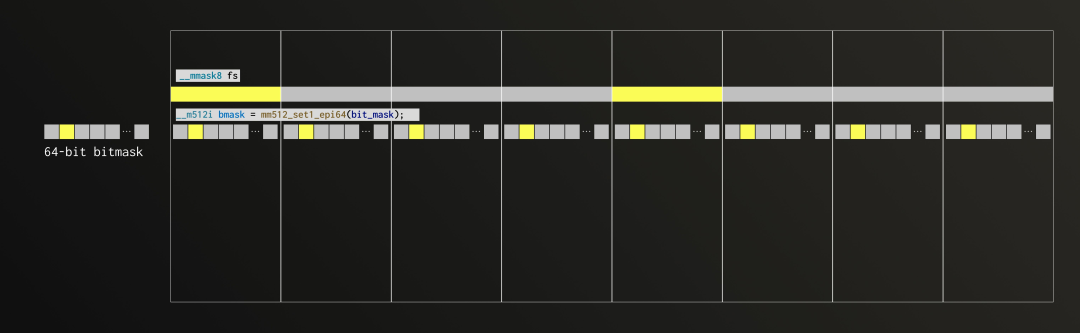
接下来我们使用 AVX-512 指令集(现代 CPU 广泛支持的 SIMD 扩展)来看如何实现前述算法中的第 2 次迭代(对应步骤 3 和 4)。在这个过程中,我们正对第二个 FixedString(1) 组进行解包,每个位都将填充进 8 个 Float64 向量的第 2 位中。

在 SIMD 模式下,更易于将数据理解为“通道”。AVX-512 每次操作的是一个 512 位的寄存器,相当于 8 个并行的 64 位通道。我们将固定字符串按通道映射进去,便于理解数据在寄存器中的分布方式。
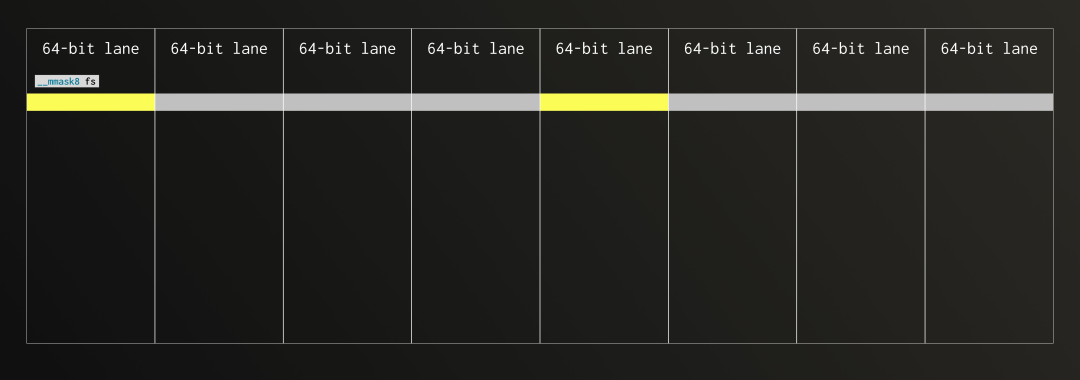
因为这次我们处理的是 Float64 的第 2 位,因此需要设置的掩码只包含第 2 位为 1。随后,我们将该掩码应用于全部通道。
目标寄存器(dst)中已经包含了上一轮解包后的中间结果,在本轮操作中,我们将把新的第 2 位数据继续合并进去,逐步构建完整的数值。

现在进入真正有趣的部分。如果掩码全为 1,我们可以直接将新解包的比特通过 OR 操作写入目标寄存器(这就是我们称为 upd 的情形);如果掩码全为 0,原有值将保持不变。在实际操作中,掩码的每一位决定是否更新对应的通道:为 1 则使用 upd 的值,为 0 则保留旧值。幸运的是,AVX-512 提供了一个专用内建函数,能够根据掩码位在 SIMD 通道中有条件地合并元素,从而在 upd 和 dst 之间自动选择。
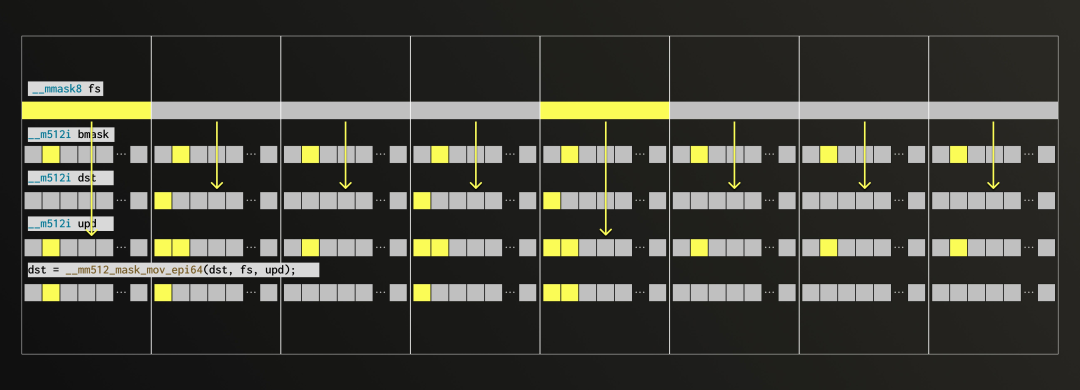
至此,我们成功在一次 SIMD 操作中解包了八个浮点数。
当数据准备就绪后,我们就可以进行距离计算了。为此,我们采用了 SimSimd —— 一款高性能向量距离计算库,几乎能在所有主流硬件平台上运行。
性能基准测试
我们在 HackerNews 数据集上进行了性能测试,该数据集包含约 2900 万条以 Float32 嵌入表示的评论。我们测量了新评论向量在数据集中进行向量搜索的查询速度,并使用其中 10 条新评论来评估召回率。
召回率的定义是:在检索结果中前 k 个条目中,真实最近邻的覆盖比例(这里 k = 20)。Granularity 表示我们读取了多少个位组。
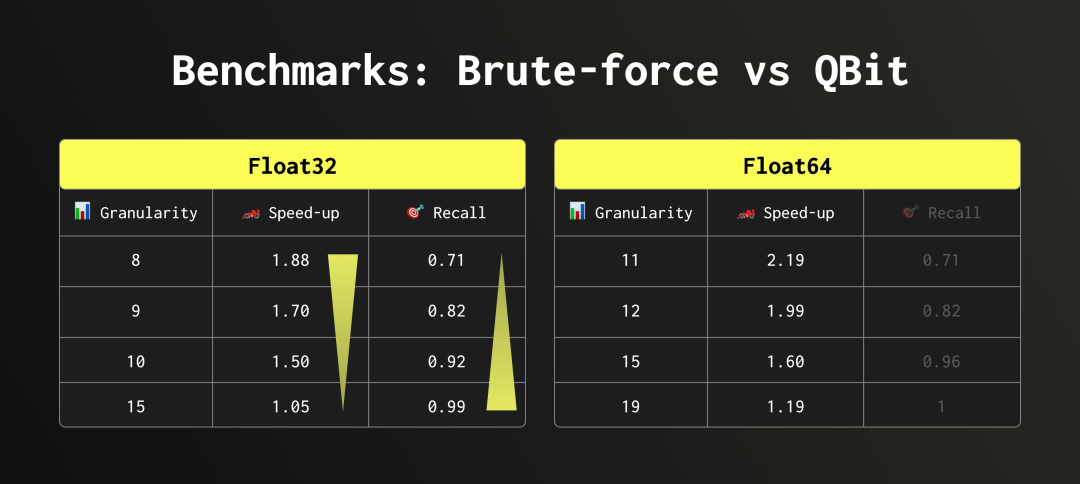
测试结果显示,在保持较高召回率的同时,我们实现了近 2 倍的查询加速。更重要的是,用户现在可以根据业务需求,在查询过程中灵活调整精度与速度之间的平衡。
需要注意的是,Float64 的召回率结果可能略显乐观:因为这些嵌入向量实际上是由 Float32 升级而来的,其低位部分并不包含有效信息。因此即便移除它们,对召回影响也有限。但无论是哪种类型,性能加速的结果都是完全可靠的。
不过说实话,基准测试确实太乏味了。我们不妨用点真实数据来看看效果。
Fun: 实战实验 - 知识库语义搜索
我们选择了 DBpedia 数据集,下载后创建表格并添加一个 QBit 列。该数据集包含 100 万条 Wikipedia 文章,每条都由一个 Float32 向量表示。
set allow_experimental_qbit_type = 1;
ALTER TABLE dbpedia ADD COLUMN qbit QBit(Float32, 1536);
ALTER TABLE dbpedia UPDATE qbit = vector WHERE 1;我们接着进行一次暴力向量搜索。目标是查找与以下五个“太空”主题最相关的概念:Moon、Apollo 11、Space Shuttle、Astronaut、Rocket。换个说法:
对于每个关键词,检索语义上最接近的前 1000 条记录。最终结果中包含至少同时出现在三个关键词检索结果中的条目,并按照匹配词条数量及与最近一个概念的最小距离排序(排除原始条目本身)。
完整查询已发布在 Pastila 上(因为篇幅较长)。下面是运行结果:
Row 1:
──────
title: Apollo program
text: The Apollo program, also known as Project Apollo, was the third United States human spaceflight program carried out by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), which accomplished landing the first humans on the Moon from 1969 to 1972. First conceived during Dwight D. Eisenhower's administration as a three-man spacecraft to follow the one-man Project Mercury which put the first Americans in space, Apollo was later dedicated to President John F.
num_concepts_matched: 4
min_distance: 0.82420665
avg_distance: 1.0207901149988174
Row 2:
──────
title: Apollo 8
text: Apollo 8, the second human spaceflight mission in the United States Apollo space program, was launched on December 21, 1968, and became the first manned spacecraft to leave Earth orbit, reach the Earth's Moon, orbit it and return safely to Earth.
num_concepts_matched: 4
min_distance: 0.8285278
avg_distance: 1.0357224345207214
Row 3:
──────
title: Lunar Orbiter 1
text: The Lunar Orbiter 1 robotic (unmanned) spacecraft, part of the Lunar Orbiter Program, was the first American spacecraft to orbit the Moon. It was designed primarily to photograph smooth areas of the lunar surface for selection and verification of safe landing sites for the Surveyor and Apollo missions. It was also equipped to collect selenodetic, radiation intensity, and micrometeoroid impact data.The spacecraft was placed in an Earth parking orbit on August 10, 1966 at 19:31 (UTC).
num_concepts_matched: 4
min_distance: 0.94581836
avg_distance: 1.0584313124418259
Row 4:
──────
title: Apollo (spacecraft)
text: The Apollo spacecraft was composed of three parts designed to accomplish the American Apollo program's goal of landing astronauts on the Moon by the end of the 1960s and returning them safely to Earth. The expendable (single-use) spacecraft consisted of a combined Command/Service Module (CSM) and a Lunar Module (LM).
num_concepts_matched: 4
min_distance: 0.9643517
avg_distance: 1.0367188602685928
Row 5:
──────
title: Surveyor 1
text: Surveyor 1 was the first lunar soft-lander in the unmanned Surveyor program of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA, United States). This lunar soft-lander gathered data about the lunar surface that would be needed for the manned Apollo Moon landings that began in 1969.
num_concepts_matched: 4
min_distance: 0.9738264
avg_distance: 1.0988530814647675
Row 6:
──────
title: Spaceflight
text: Spaceflight (also written space flight) is ballistic flight into or through outer space. Spaceflight can occur with spacecraft with or without humans on board. Examples of human spaceflight include the Russian Soyuz program, the U.S. Space shuttle program, as well as the ongoing International Space Station. Examples of unmanned spaceflight include space probes that leave Earth orbit, as well as satellites in orbit around Earth, such as communications satellites.
num_concepts_matched: 4
min_distance: 0.9831049
avg_distance: 1.060678943991661
Row 7:
──────
title: Skylab
text: Skylab was a space station launched and operated by NASA and was the United States' first space station. Skylab orbited the Earth from 1973 to 1979, and included a workshop, a solar observatory, and other systems. It was launched unmanned by a modified Saturn V rocket, with a weight of 169,950 pounds (77 t). Three manned missions to the station, conducted between 1973 and 1974 using the Apollo Command/Service Module (CSM) atop the smaller Saturn IB, each delivered a three-astronaut crew.
num_concepts_matched: 4
min_distance: 0.99155205
avg_distance: 1.0769911855459213
Row 8:
──────
title: Orbital spaceflight
text: An orbital spaceflight (or orbital flight) is a spaceflight in which a spacecraft is placed on a trajectory where it could remain in space for at least one orbit. To do this around the Earth, it must be on a free trajectory which has an altitude at perigee (altitude at closest approach) above 100 kilometers (62 mi) (this is, by at least one convention, the boundary of space). To remain in orbit at this altitude requires an orbital speed of ~7.8 km/s.
num_concepts_matched: 4
min_distance: 1.0075209
avg_distance: 1.085978478193283
Row 9:
───────
title: Dragon (spacecraft)
text: Dragon is a partially reusable spacecraft developed by SpaceX, an American private space transportation company based in Hawthorne, California. Dragon is launched into space by the SpaceX Falcon 9 two-stage-to-orbit launch vehicle, and SpaceX is developing a crewed version called the Dragon V2.During its maiden flight in December 2010, Dragon became the first commercially built and operated spacecraft to be recovered successfully from orbit.
num_concepts_matched: 4
min_distance: 1.0222818
avg_distance: 1.0942841172218323
Row 10:
───────
title: Space capsule
text: A space capsule is an often manned spacecraft which has a simple shape for the main section, without any wings or other features to create lift during atmospheric reentry.Capsules have been used in most of the manned space programs to date, including the world's first manned spacecraft Vostok and Mercury, as well as in later Soviet Voskhod, Soyuz, Zond/L1, L3, TKS, US Gemini, Apollo Command Module, Chinese Shenzhou and US, Russian and Indian manned spacecraft currently being developed.
num_concepts_matched: 4
min_distance: 1.0262821
avg_distance: 1.0882147550582886使用暴力搜索执行该查询,结果表现极佳(如 Apollo、Lunar Orbiter、Surveyor 等关键词条均被命中)。不过,资源开销也相当巨大:
共返回 10 条记录。耗时 1.157 秒,处理数据 1000 万行,32.76 GB(处理速度为 864 万行/秒,28.32 GB/秒)。
峰值内存使用达 6.05 GiB。
需要说明的是,这并非严格意义上的基准测试 —— 只是我在本地机器上执行的实际查询。接下来,我们尝试在 QBit 上以精度 5 运行相同的查询(即仅保留 1 位符号位和 4 位指数位,完全不保留尾数部分)。完整查询见 Pastila。
Row 1:
──────
title: Apollo 8
text: Apollo 8, the second human spaceflight mission in the United States Apollo space program, was launched on December 21, 1968, and became the first manned spacecraft to leave Earth orbit, reach the Earth's Moon, orbit it and return safely to Earth.
num_concepts_matched: 4
min_distance: 0.9924246668815613
avg_distance: 0.9929515272378922
Row 2:
──────
title: Apollo program
text: The Apollo program, also known as Project Apollo, was the third United States human spaceflight program carried out by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), which accomplished landing the first humans on the Moon from 1969 to 1972. First conceived during Dwight D. Eisenhower's administration as a three-man spacecraft to follow the one-man Project Mercury which put the first Americans in space, Apollo was later dedicated to President John F.
num_concepts_matched: 4
min_distance: 0.9924481511116028
avg_distance: 0.9929344654083252
Row 3:
──────
title: Apollo 5
text: Apollo 5 was the first unmanned flight of the Apollo Lunar Module (LM), which would later carry astronauts to the lunar surface. It lifted off on January 22, 1968, with a Saturn IB rocket on an Earth-orbital flight.
num_concepts_matched: 4
min_distance: 0.9925317764282227
avg_distance: 0.9930042922496796
Row 4:
──────
title: Apollo (spacecraft)
text: The Apollo spacecraft was composed of three parts designed to accomplish the American Apollo program's goal of landing astronauts on the Moon by the end of the 1960s and returning them safely to Earth. The expendable (single-use) spacecraft consisted of a combined Command/Service Module (CSM) and a Lunar Module (LM).
num_concepts_matched: 4
min_distance: 0.9926576018333435
avg_distance: 0.9928816854953766
Row 5:
──────
title: Lunar Orbiter 1
text: The Lunar Orbiter 1 robotic (unmanned) spacecraft, part of the Lunar Orbiter Program, was the first American spacecraft to orbit the Moon. It was designed primarily to photograph smooth areas of the lunar surface for selection and verification of safe landing sites for the Surveyor and Apollo missions. It was also equipped to collect selenodetic, radiation intensity, and micrometeoroid impact data.The spacecraft was placed in an Earth parking orbit on August 10, 1966 at 19:31 (UTC).
num_concepts_matched: 4
min_distance: 0.9926905632019043
avg_distance: 0.9929626882076263
Row 6:
──────
title: Spaceflight
text: Spaceflight (also written space flight) is ballistic flight into or through outer space. Spaceflight can occur with spacecraft with or without humans on board. Examples of human spaceflight include the Russian Soyuz program, the U.S. Space shuttle program, as well as the ongoing International Space Station. Examples of unmanned spaceflight include space probes that leave Earth orbit, as well as satellites in orbit around Earth, such as communications satellites.
num_concepts_matched: 4
min_distance: 0.9927355647087097
avg_distance: 0.992923766374588
Row 7:
──────
title: Surveyor 1
text: Surveyor 1 was the first lunar soft-lander in the unmanned Surveyor program of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA, United States). This lunar soft-lander gathered data about the lunar surface that would be needed for the manned Apollo Moon landings that began in 1969.
num_concepts_matched: 4
min_distance: 0.9927787184715271
avg_distance: 0.9931300282478333
Row 8:
──────
title: Orbital spaceflight
text: An orbital spaceflight (or orbital flight) is a spaceflight in which a spacecraft is placed on a trajectory where it could remain in space for at least one orbit. To do this around the Earth, it must be on a free trajectory which has an altitude at perigee (altitude at closest approach) above 100 kilometers (62 mi) (this is, by at least one convention, the boundary of space). To remain in orbit at this altitude requires an orbital speed of ~7.8 km/s.
num_concepts_matched: 4
min_distance: 0.9927811026573181
avg_distance: 0.9929587244987488
Row 9:
───────
title: DSE-Alpha
text: Deep Space Expedition Alpha (DSE-Alpha), is the name given to the mission proposed in 2005 to take the first space tourists to fly around the Moon. The mission is organized by Space Adventures Ltd., a commercial spaceflight company. The plans involve a modified Soyuz capsule docking with a booster rocket in Earth orbit which then sends the spacecraft on a free return circumlunar trajectory that circles around the Moon once.
num_concepts_matched: 4
min_distance: 0.9928749799728394
avg_distance: 0.9931814968585968
Row 10:
───────
title: Luna programme
text: The Luna programme (from the Russian word Луна "Luna" meaning "Moon"), occasionally called Lunik or Lunnik by western media, was a series of robotic spacecraft missions sent to the Moon by the Soviet Union between 1959 and 1976. Fifteen were successful, each designed as either an orbiter or lander, and accomplished many firsts in space exploration.
num_concepts_matched: 4
min_distance: 0.9929065704345703
avg_distance: 0.9930566549301147共返回 10 条记录。耗时 0.271 秒,处理数据 846 万行、4.54 GB(即 3119 万行/秒、16.75 GB/秒)。
峰值内存占用为 739.82 MiB。
结果如何?远超预期,令人惊喜。令人难以想象的是,即便将浮点数的整个尾数部分和一半的指数位都去除,它们依然能保留有意义的表达。QBit 的关键洞察在于:只要浮点数中保留对方向有显著影响的高位比特,向量搜索依然有效 —— 那些微不足道的低位完全可以忽略。
总结
我们构建了一种全新的数据类型 —— QBit,它允许用户控制用于距离计算的浮点数位数。这样一来,精度与性能的权衡可以在运行时灵活调整,无需提前配置。
在实际使用中,QBit 不仅降低了向量搜索的 I/O 和计算负担,同时也保持了极高的检索准确率。如实验证明,即使只使用 5 个比特,也足以实现高质量的语义检索 —— 甚至可以“飞向月球” 🚀
征稿启示
面向社区长期正文,文章内容包括但不限于关于 ClickHouse 的技术研究、项目实践和创新做法等。建议行文风格干货输出&图文并茂。质量合格的文章将会发布在本公众号,优秀者也有机会推荐到 ClickHouse 官网。请将文章稿件的 WORD 版本发邮件至:Tracy.Wang@clickhouse.com






















 720
720

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








