We walk through the start process of an Activity. During the journey, we will see important structure representing Activity, Process, Stack and Task. The detailed information regarding stack and task were described in Android developer website. I will only focus on the key method which is related to starting activity. Trivia logic will be skipped.
Phase 1: Create Data Structure For Target Activity
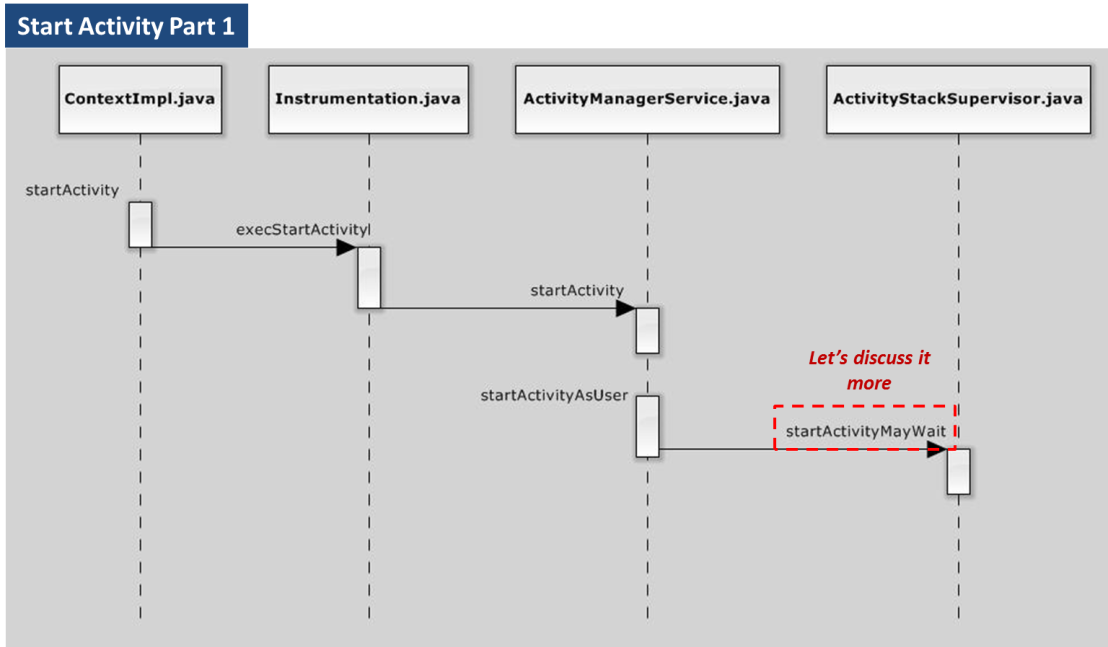
Let’s see the code flow below.
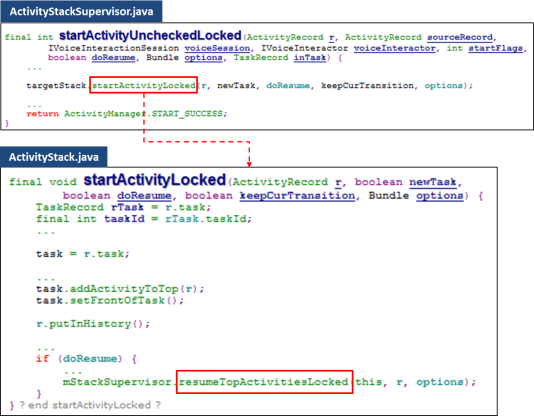
According to above sequence chart, the first important method which is worthy to be discussed is “startActivityMayWait“. The main task of it is collecting the target activity information via package manager then maintain the information by ActivityInfo.java. ActivityInfo is then utilized in next phase.
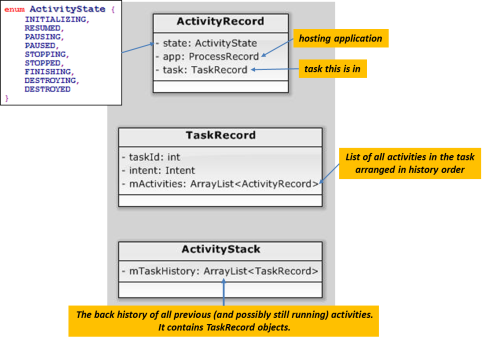
In continued phases, activity managed classes are adopted. Theses classes include ActivityRecord, TaskRecord and ActivityStack (see here for concept). The class dependency is as below figure.
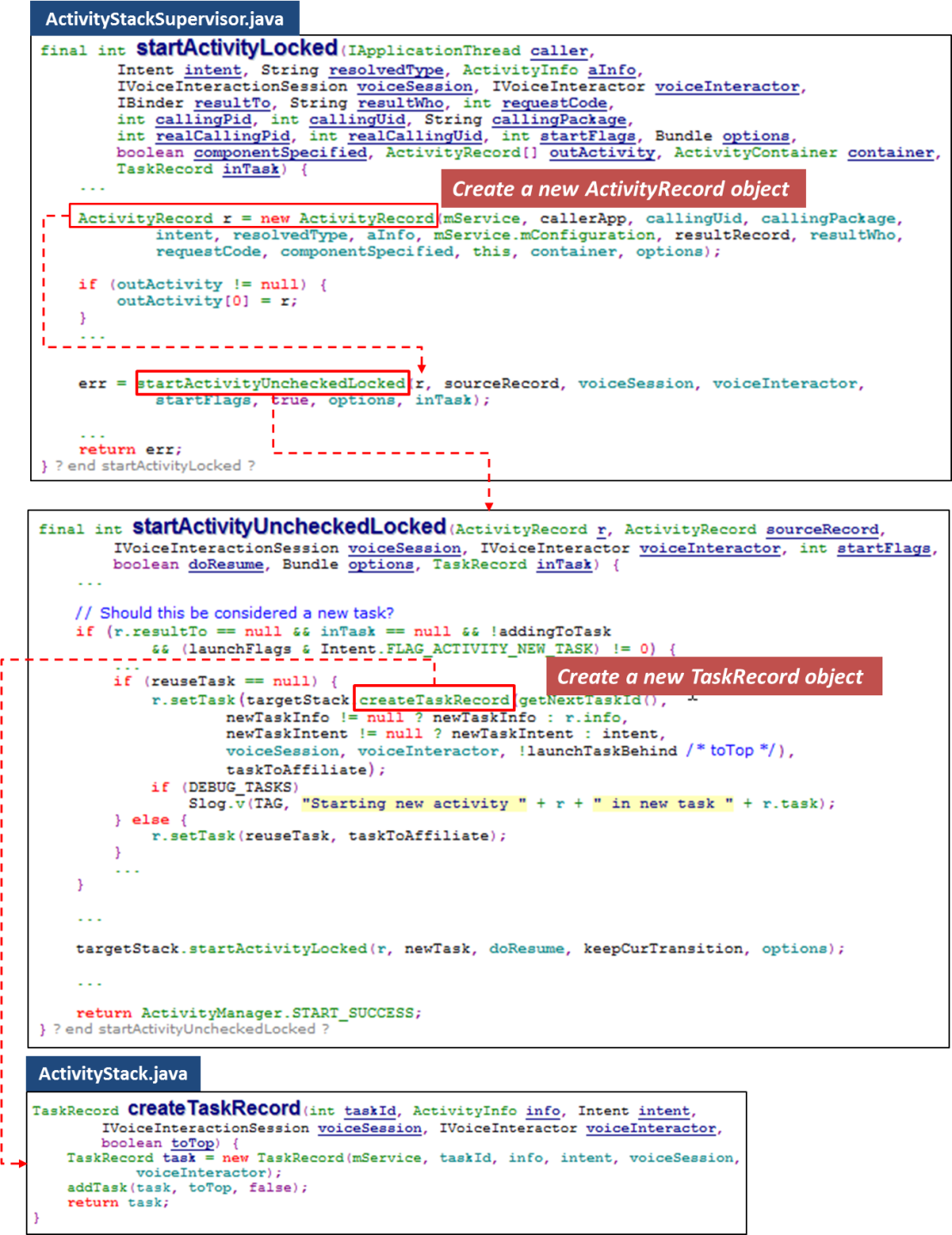
Let’s continue the code flow. Now, two major objects managing activity are created.
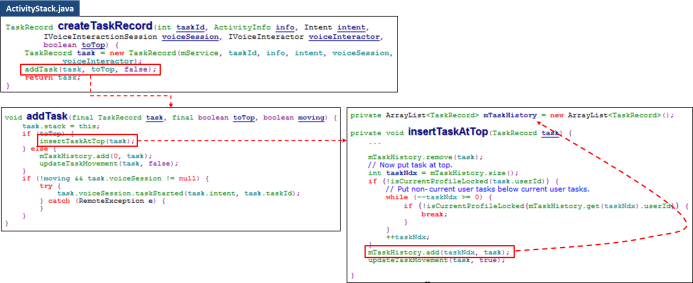
A new created task was then put at the top of stack. Refer to following code snippet.
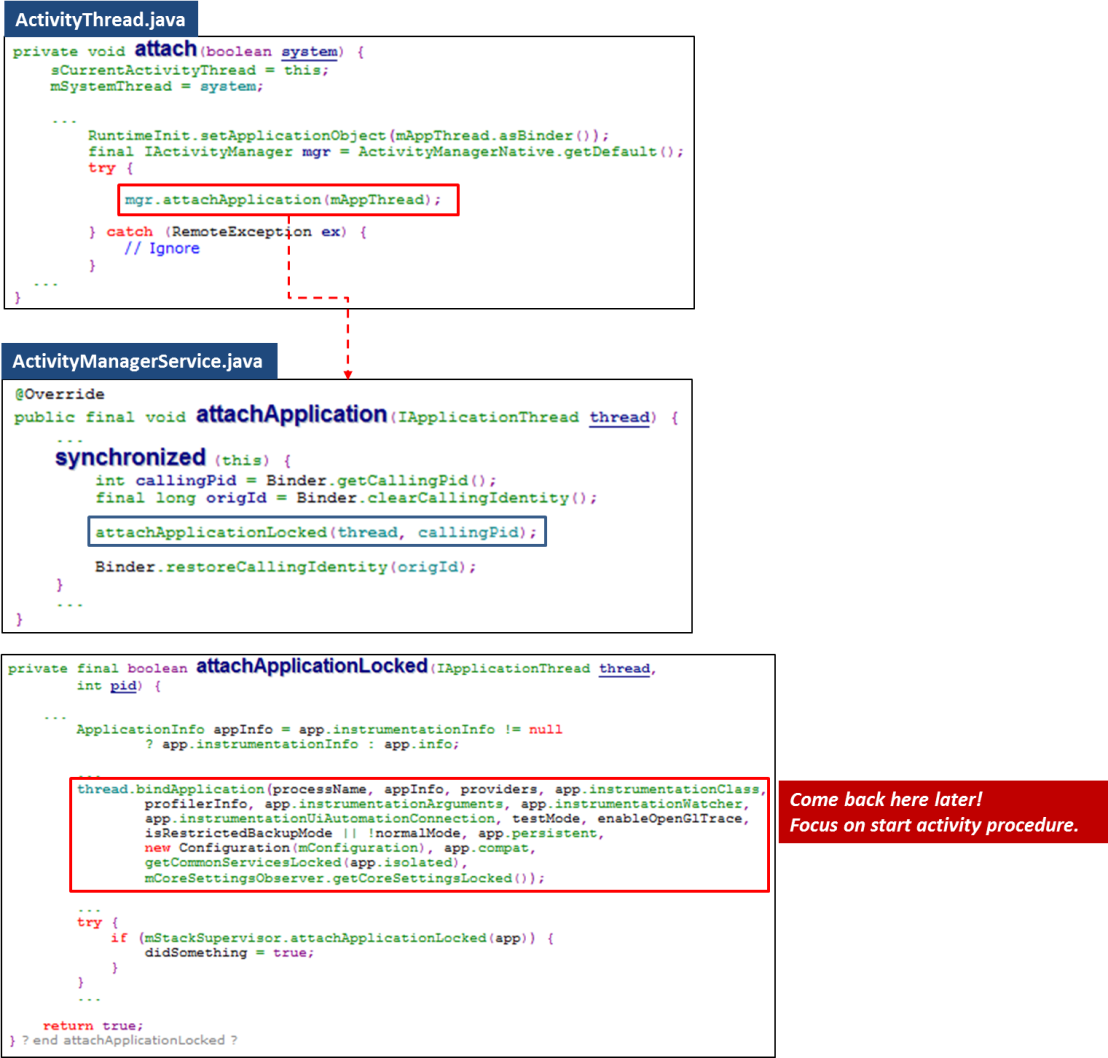
Phase 2: Create Process
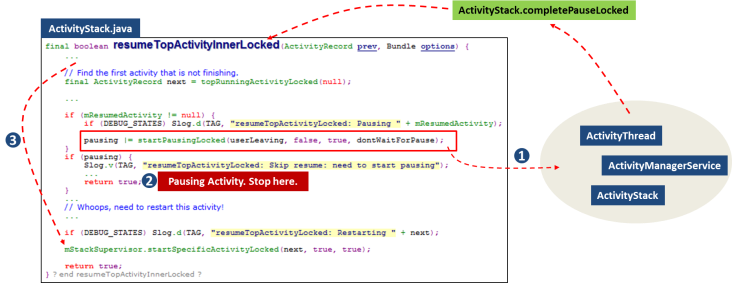
In phase 1, we collected information for Activity and created vessels (ActivityRecord and TaskRecord) for it. Next step is to try to “resume" the activity to show. Before resuming target activity, current activity who launched target activity should be put into ground. Yes, it should enter “paused" state. Let’s see how it works.
resumeTopActivitiesLocked is the main entry point to phase 2. I summarize two major tasks in resumeTopActivitiesLocked method in below figure. We don’t discuss the activity pausing flow here. I left it to We focus on starting activity.
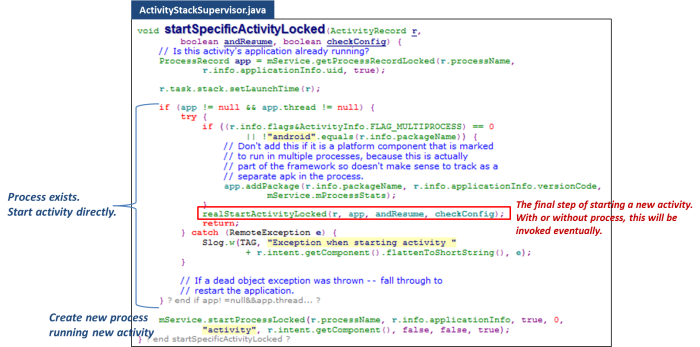
While starting a new activity, system will try to find an existed process or just create a new one.
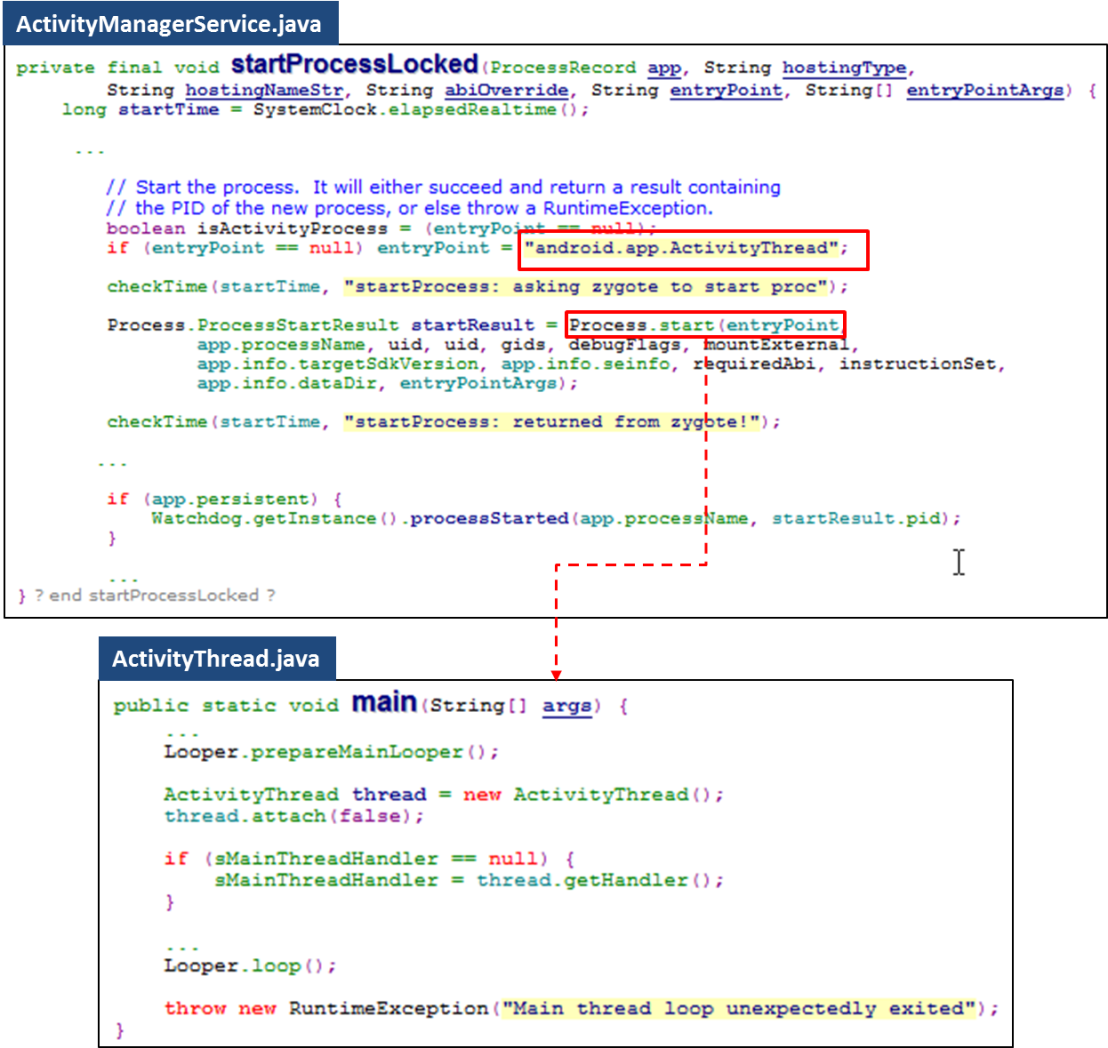
Now, system creates a new process. The newly created process is only a vessel. It is not related to the target activity yet.
Following code snippet indicates an important method of “bindApplication“. We skip it here. Focus on start activity flow.
Phase 3: Activity Ready to GO
In this phase, an Activity object is created and ready to GO.
Summary
It’s a very long journey to walk through the activity start process. I don’t plan to end here. I will discuss details of bindApplication and performLaunchActivity in next article.





 本文详细解析了Android中Activity的启动过程,从创建目标Activity的数据结构到创建进程,最后到Activity准备就绪的状态转变。文章重点介绍了关键方法的使用及Activity、Task和Stack等重要概念。
本文详细解析了Android中Activity的启动过程,从创建目标Activity的数据结构到创建进程,最后到Activity准备就绪的状态转变。文章重点介绍了关键方法的使用及Activity、Task和Stack等重要概念。




















 757
757

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








