Android Application Launch Part 2
There are three distinct phases of process launch :- Process Creation
- Binding Application
- Launching Activity / Starting Service / Invoking intent receiver ...
Process Creation
-
ActivityManagerService creates a new process by invoking
startProcessLocked() method which sends arguments to
Zygote process over the socket connection.
Zygote forks itself and calls
ZygoteInit.main() which then instantiates
ActivityThread object and finally returns pid of newly created process.
ActivityThread then starts the message loop by calling
Looper.prepareLoop() and
Looper.loop() subsequently.
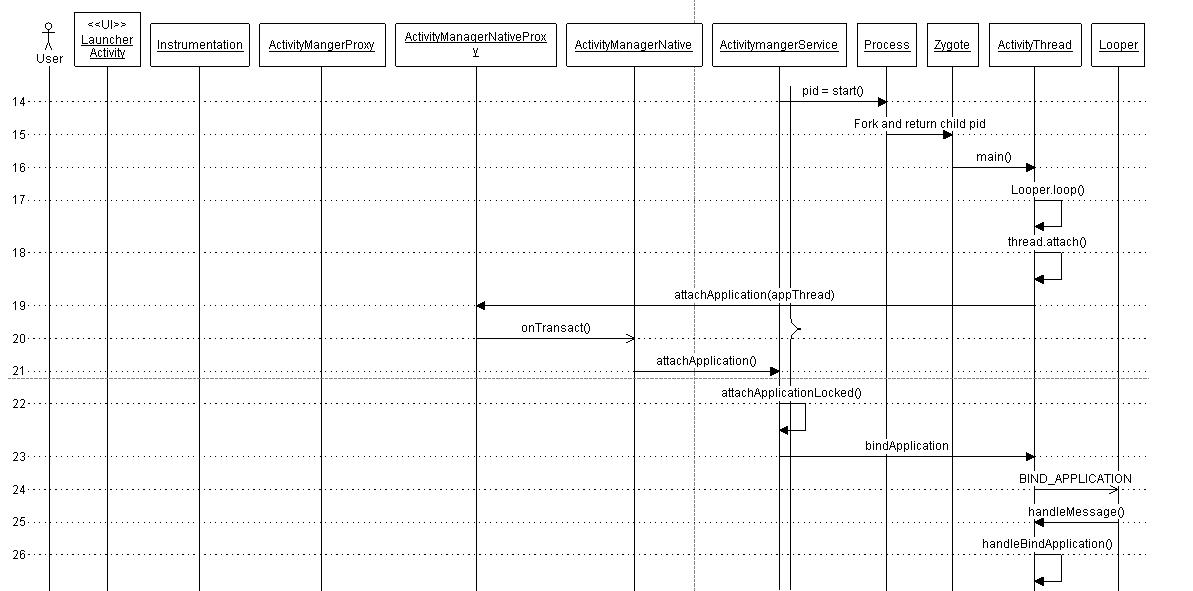
Application Binding -
The next step is to attach the process to the specific application. This is done by calling bindApplication on the thread object. This method sends
BIND_APPLICATION message to the message queue. This message is retrieved by the handler object which then invokes
handleMessage() method to trigger the message specific action -
handleBindApplication(). This method invokes
makeApplication() method which loads app specific classes into memory.
This call sequence is depicted in following figure.
Activity Launch -
After the previous step, the system contains the process responsible for the application with application classes loaded in process's private memory. The call sequence to launch an activity is common between a newly created process and an existing process. The actual process of launching starts in
realStartActivity() method which calls
sheduleLaunchActivity() on the application thread object. This method sends
LAUNCH_ACTIVITY message to the message queue. The message is handled by
handleLaunchActivity() method as shown below.
Assuming that user clicks on Video Browser application. the call sequence to launch the activity is as shown in the figure.
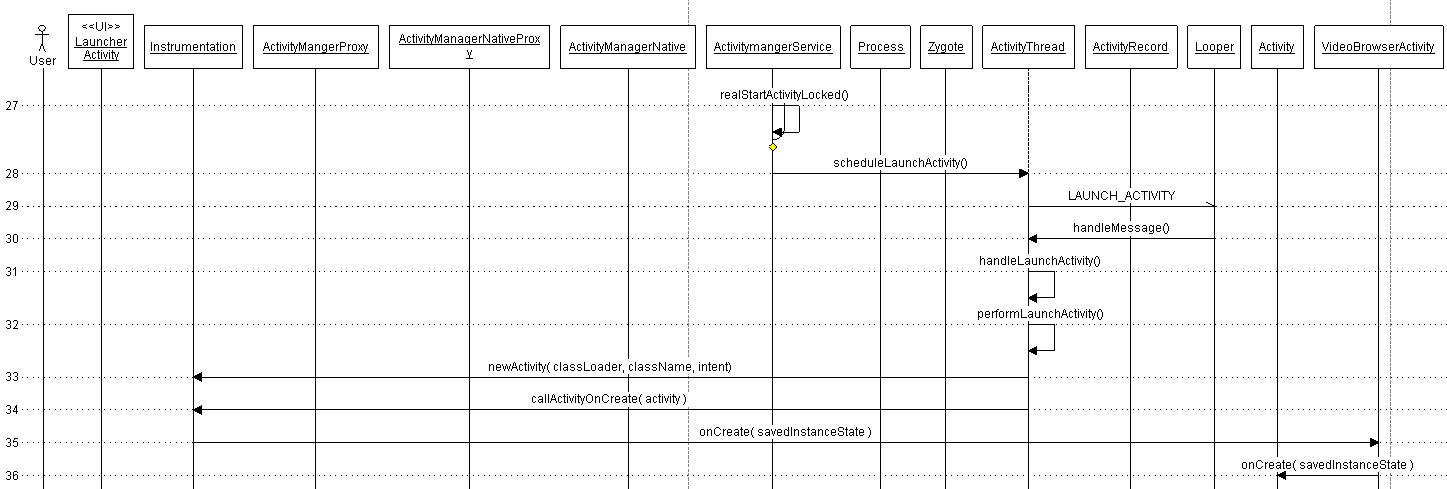
The Activity starts its managed lifecycle with onCreate() method call. The activity comes to foreground with onRestart() call and starts interacting with the user with onStart() call.





 本文详细介绍了Android应用程序从进程创建到活动启动的整个过程。包括ActivityManagerService如何通过调用startProcessLocked()来创建进程,Zygote进程的fork机制及ActivityThread的初始化过程;然后解释了如何通过bindApplication绑定应用程序并加载特定的应用程序类;最后,通过realStartActivity()方法触发活动启动,并展示了从onCreate()到onStart()的活动生命周期。
本文详细介绍了Android应用程序从进程创建到活动启动的整个过程。包括ActivityManagerService如何通过调用startProcessLocked()来创建进程,Zygote进程的fork机制及ActivityThread的初始化过程;然后解释了如何通过bindApplication绑定应用程序并加载特定的应用程序类;最后,通过realStartActivity()方法触发活动启动,并展示了从onCreate()到onStart()的活动生命周期。
















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








