前言
@RefeshScope这个注解想必大家都用过,在微服务配置中心的场景下经常出现,它可以用来刷新Bean中的属性配置,那么它是如何做到的呢?让我们来一步步揭开它神秘的面纱。
RefreshScope介绍
就是说我们在修改了bean属性的时候项目不需要重新启动,就可以拿到最新的值。
我们先来看下@RefreshScope的接口
@Target({
ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Scope("refresh")
@Documented
public @interface RefreshScope {
/**
* @see Scope#proxyMode()
* @return proxy mode
*/
//创建基于类的代理(使用 CGLIB)
ScopedProxyMode proxyMode() default ScopedProxyMode.TARGET_CLASS;
}
可以看出其是一个复合注解,被标注了 @Scope(“refresh”),@RefreshScope 是scopeName="refresh"的 @Scope
我们来看下org.springframework.cloud.context.scope.refresh.RefreshScope类的关系图
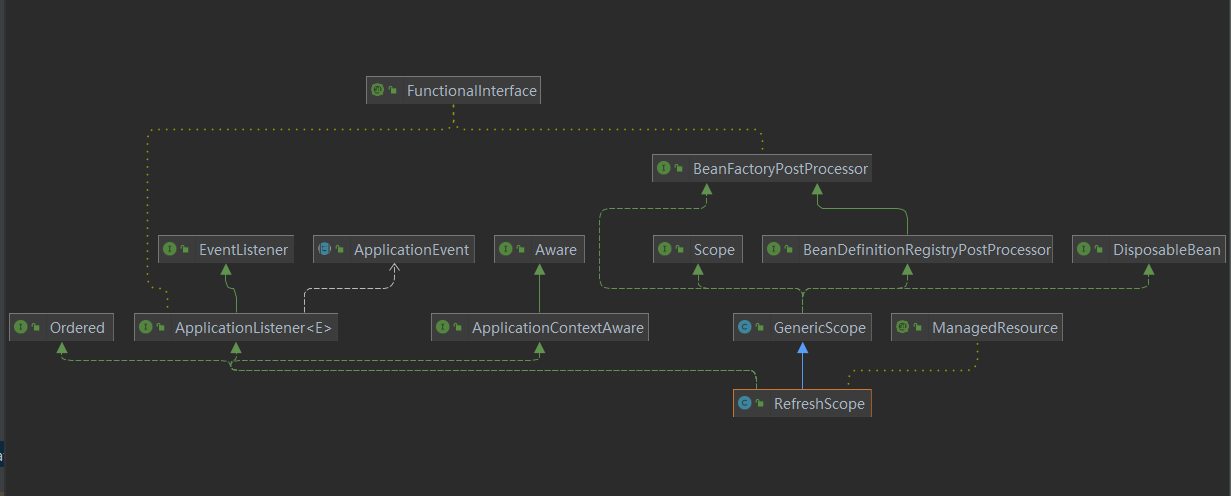
- Scope -> GenericScope -> RefreshScope
RefreshScope管理了Scope=Refresh的Bean的生命周期,提供了get(获取),refreshAll(刷新)、destory(销毁)等方法
源码解析
版本说明
<spring-boot.version>2.6.3</spring-boot.version>
<spring-cloud.version>2021.0.1</spring-cloud.version>
Bean创建过程
我们创建一个带@RefreshScope注解的类
@Data
@Component
@RefreshScope
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "test")
public class TestProperties {
private String name ;
}
启动项目进行debugger跟踪
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors
AbstractApplicationContext#invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法中
调用Bean Factory的后置处理器,从上面的类图中我们可以看到RefreshScope就是一个BeanFactoryPostProcessors
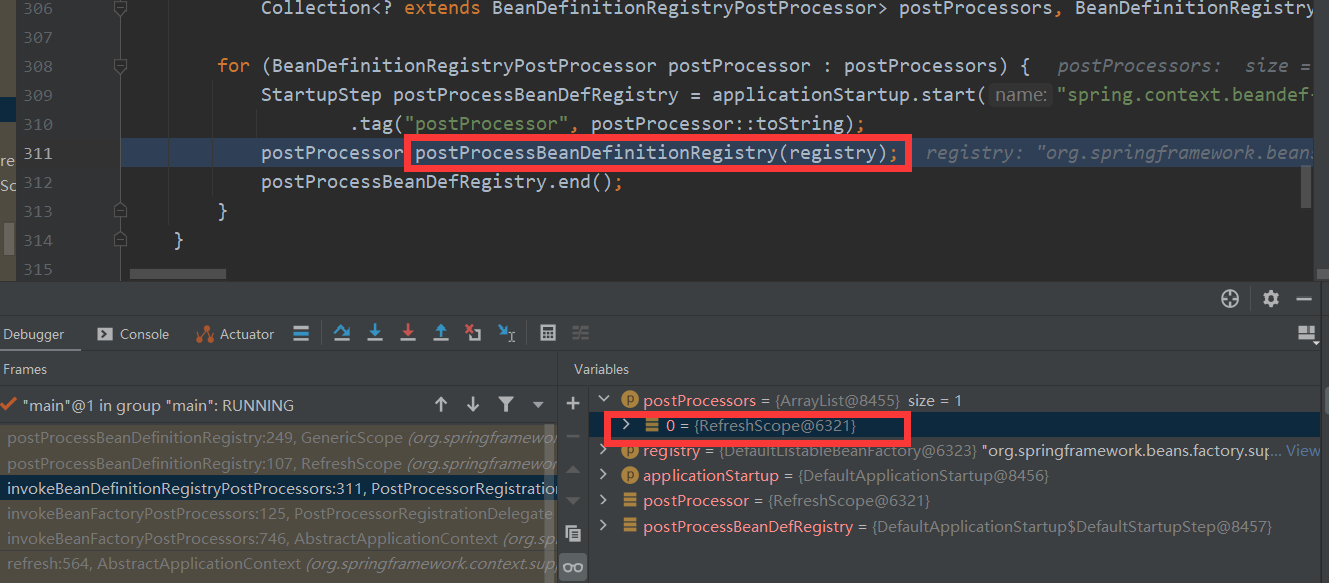
然后调用父类GenericScope的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法
该方法遍历所有的bean定义 如果当前的bean的scope为refresh,那么就把当前的bean设置为 LockedScopedProxyFactoryBean的代理对象。
@RefreshScope标注的类还有一个特点:会使用代理对象并进行延迟加载。我们来看一下postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法
@RefreshScope 注解的 bean,除了会生成一个beanName的 bean,同时会生成 scopedTarget.beanName的 bean
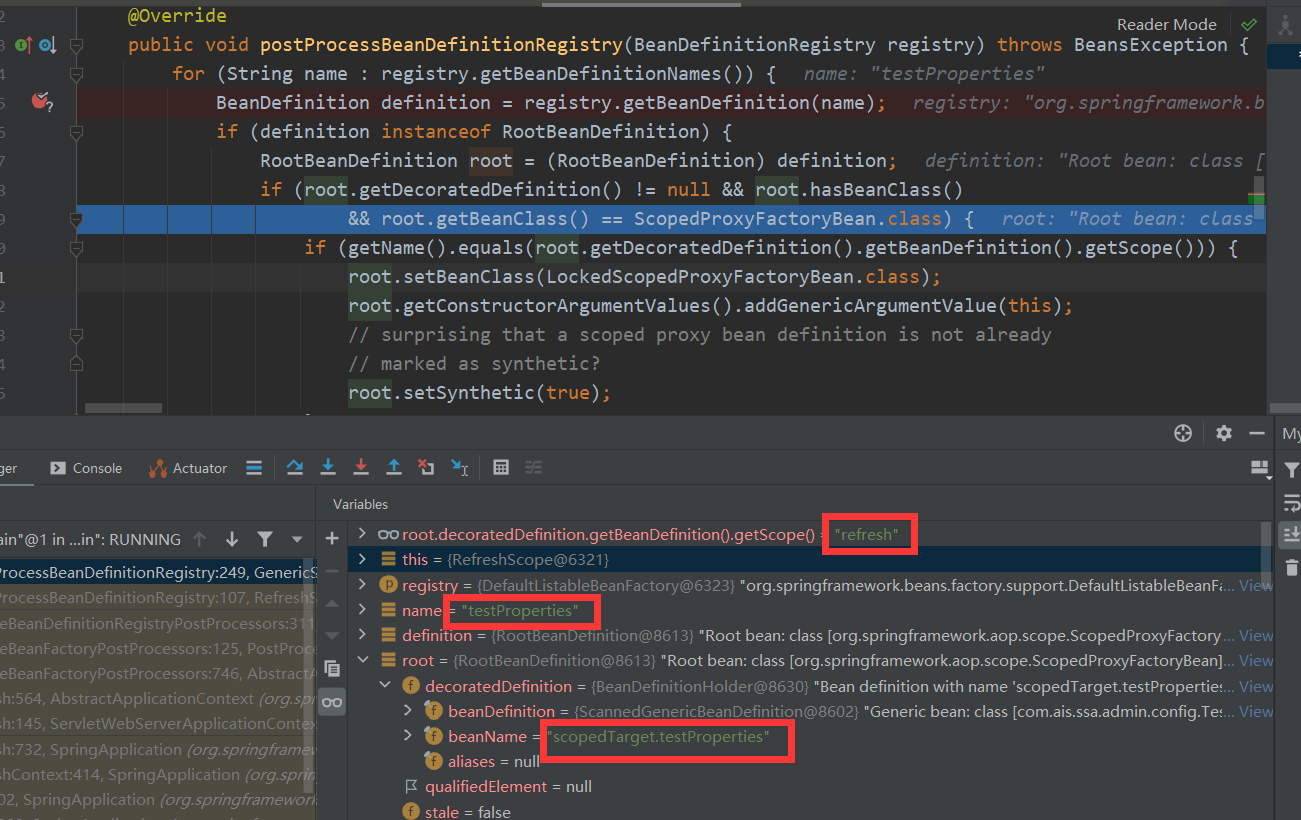
所以如果有@ConditionalOnSingleCandidate 注解的 bean,就不能在使用@RefreshScope的注解了。因为@ConditionalOnSingleCandidate全局只能有一个此类型的 bean
RefreshScope还会监听一个ContextRefreshedEvent,该事件会在ApplicationContext初始化或者refreshed时触发
ContextRefreshedEvent事件
AbstractApplicationContext#finishRefresh方法中
// 上下文刷新事件
publishEvent(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this));
我们来看一下RefreshScope中的代码:
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {
start(event);
}
public void start(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {
if (event.getApplicationContext() == this.context && this.eager && this.registry != null) {
eagerlyInitialize();
}
}
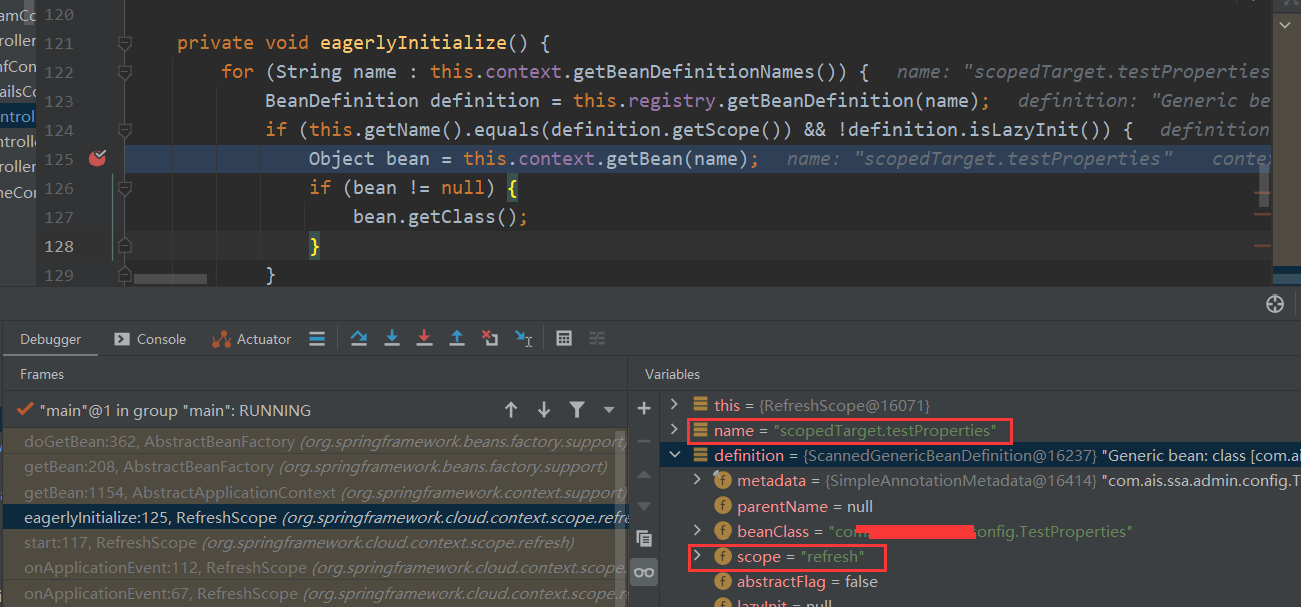
private void eagerlyInitialize() {
for (String name : this.context.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
BeanDefinition definition = this.registry.getBeanDefinition(name);
if (this.getName().equals(definition.getScope()) && !definition.isLazyInit()) {
Object bean = this.context.getBean(name);
if (bean != null) {
bean.getClass();
}
}
}
}
如果这个bean的scope = refresh的话就会去执行getBean方法,我们可以看到bean的名字为scopedTarget.testProperties这是一个被代理过的bean
doGetBean
上面的this.context.getBean(name)中会使用BeanFactory的doGetBean方法创建Bean,不同scope有不同的创建方式:
protected <T> T doGetBean(
String name, @Nullable Class<T> requiredType, @Nullable Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly)
throws BeansException {
String beanName = transformedBeanName(name);
Object beanInstance;
...
// 创建单例bean
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> {
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there
// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.
// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
}
});
beanInstance = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
// 创建原型bean
else if (mbd.isPrototype()) {
// It's a prototype -> create a new instance.
Object prototypeInstance = null;
try {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName)




 本文深入探讨了@RefreshScope在Spring Cloud中的作用,分析了Bean的创建过程,包括invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors、ContextRefreshedEvent事件和doGetBean。详细解释了动态刷新Bean配置变量值的机制,涉及RefreshEventListener、ContextRefresher和EnvironmentChangeEvent。文章总结了@RefreshScope如何实现配置的动态更新,并清理缓存以确保获取最新值。
本文深入探讨了@RefreshScope在Spring Cloud中的作用,分析了Bean的创建过程,包括invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors、ContextRefreshedEvent事件和doGetBean。详细解释了动态刷新Bean配置变量值的机制,涉及RefreshEventListener、ContextRefresher和EnvironmentChangeEvent。文章总结了@RefreshScope如何实现配置的动态更新,并清理缓存以确保获取最新值。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章


















 2912
2912

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










