Spring Cloud 2.2.2 源码之三十五@RefreshScope详解一
RefreshScope注解类实例化基本流程

@RefreshScope作用
主要声明一个类的对象的作用域和刷新相关,既不是单例也不是原型,而且是会进行动态代理的。@Scope("refresh")表示他是跟refresh的作用域相关。
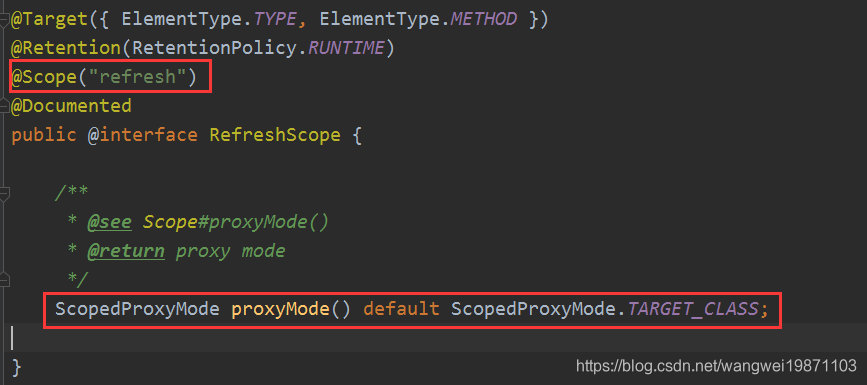
生命周期跟RefreshScope相关。
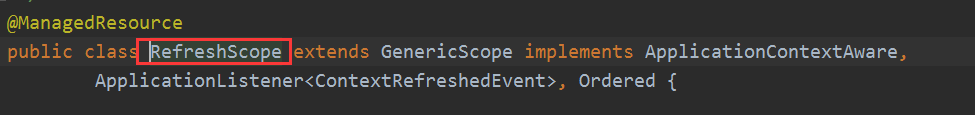
@Scope回顾这个的作用
如果我们这样写,这个类会被扫描进容器,我们来看看扫描的时候是怎么做的。
ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner的doScan
扫描的时候会进行scope的解析和设置,然后进行代理的设置。
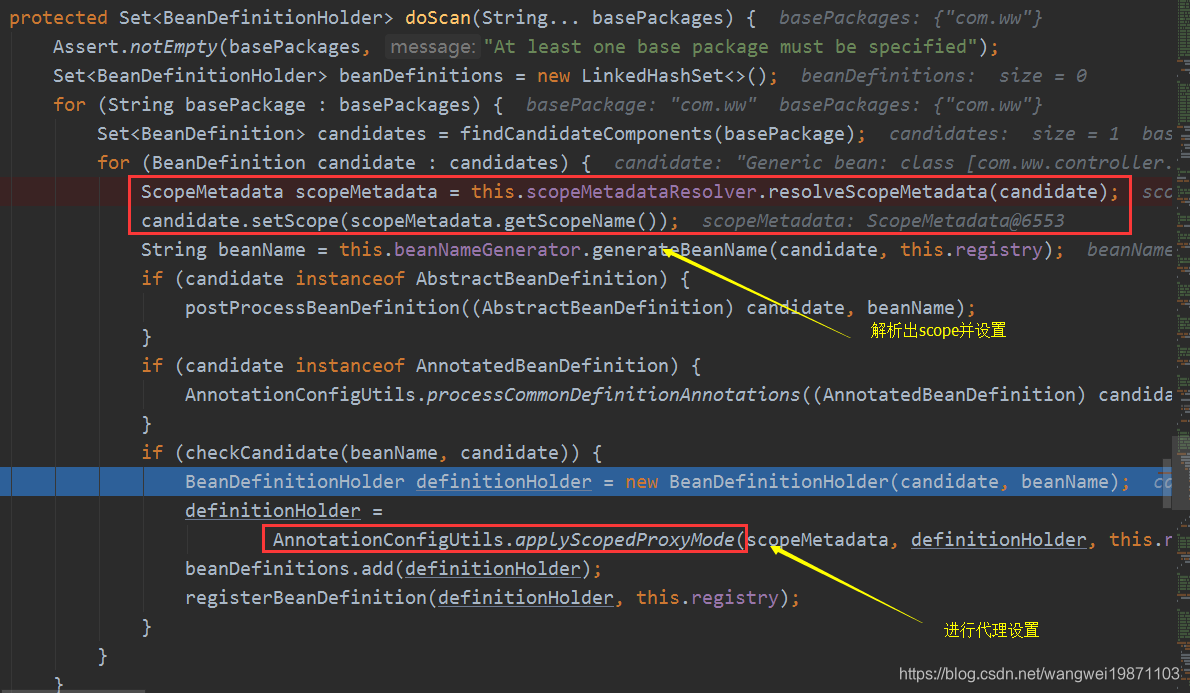
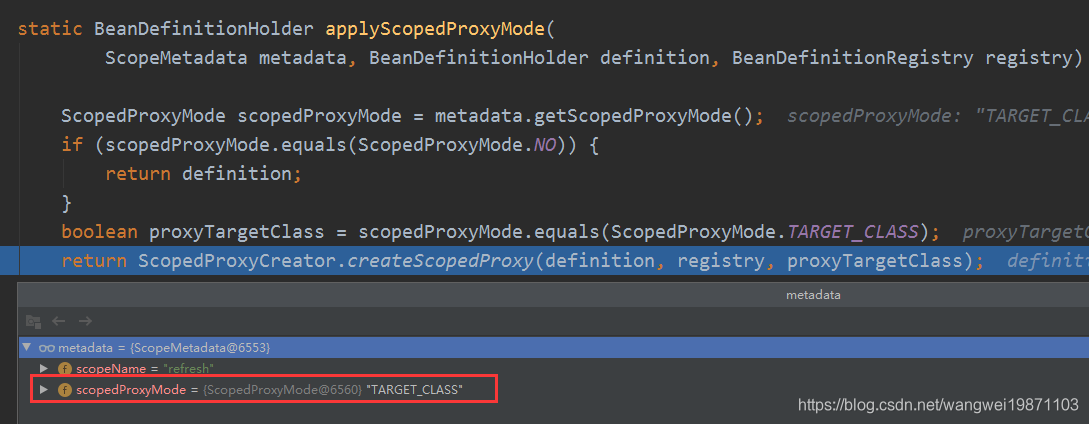
AnnotationConfigUtils的applyScopedProxyMode
因为前面RefreshScope注解设置了代理目标这个属性,所以这里会进行Scoped代理设置。
ScopedProxyUtils的createScopedProxy
创建一个代理bean定义来包装,并且设置好属性,然后注册到容器里,这里注意被代理对象的beanName被改成scopedTarget.xxx了,而代理对象的名字才是被代理对象原来的名字。
public static BeanDefinitionHolder createScopedProxy(BeanDefinitionHolder definition,
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, boolean proxyTargetClass) {
//原bean名字
String originalBeanName = definition.getBeanName();
//原bean定义
BeanDefinition targetDefinition = definition.getBeanDefinition();
//代理bean名字,加了scopedTarget.前缀
String targetBeanName = getTargetBeanName(originalBeanName);
//创建代理bean定义,类型是ScopedProxyFactoryBean
RootBeanDefinition proxyDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(ScopedProxyFactoryBean.class);
//设置装饰的bean定义,把原bean定义放进去
proxyDefinition.setDecoratedDefinition(new BeanDefinitionHolder(targetDefinition, targetBeanName));
//设置原bean定义
proxyDefinition.setOriginatingBeanDefinition(targetDefinition);
proxyDefinition.setSource(definition.getSource());
proxyDefinition.setRole(targetDefinition.getRole());
//添加属性
proxyDefinition.getPropertyValues().add("targetBeanName", targetBeanName);
if (proxyTargetClass) {
targetDefinition.setAttribute(AutoProxyUtils.PRESERVE_TARGET_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE, Boolean.TRUE);
// ScopedProxyFactoryBean's "proxyTargetClass" default is TRUE, so we don't need to set it explicitly here.
}
else {
proxyDefinition.getPropertyValues().add("proxyTargetClass", Boolean.FALSE);
}
// Copy autowire settings from original bean definition.
proxyDefinition.setAutowireCandidate(targetDefinition.isAutowireCandidate());
proxyDefinition.setPrimary(targetDefinition.isPrimary());
if (targetDefinition instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
proxyDefinition.copyQualifiersFrom((AbstractBeanDefinition) targetDefinition);
}
// The target bean should be ignored in favor of the scoped proxy.
targetDefinition.setAutowireCandidate(false);
targetDefinition.setPrimary(false);
// 注册原bean定义,名字是scopedTarget.XXX
registry.registerBeanDefinition(targetBeanName, targetDefinition);
// Return the scoped proxy definition as primary bean definition
// (potentially an inner bean).
return new BeanDefinitionHolder(proxyDefinition, originalBeanName, definition.getAliases());
}
注册被代理对象bean定义:
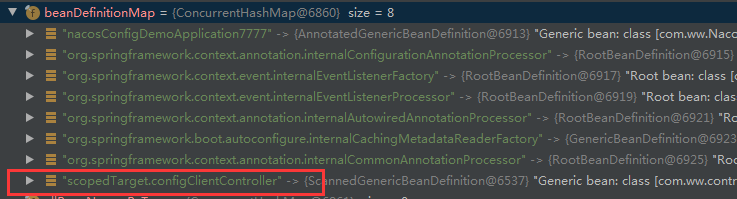
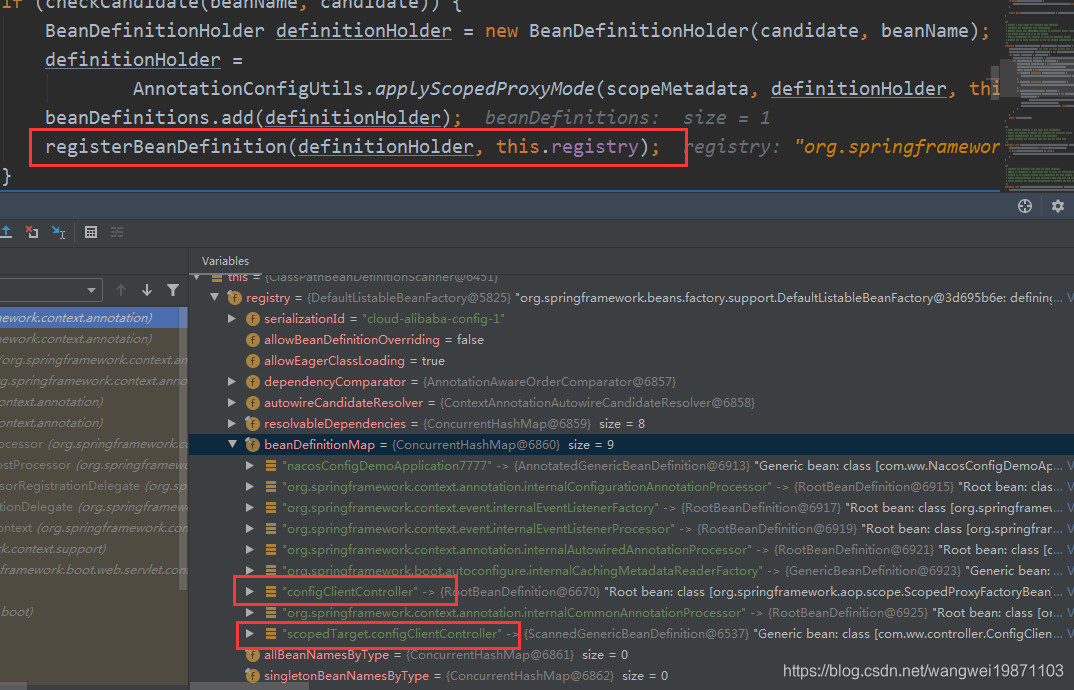
但是外面最后还有一次注册,是注册代理对象的bean定义,名字没变,其实就是多了一个代理的,configClientXXX是代理对象,scopedTarget.configClientXXX是被代理对象:
下篇继续说后面怎么实例化。
好了,今天就到这里了,希望对学习理解有帮助,大神看见勿喷,仅为自己的学习理解,能力有限,请多包涵





 本文深入解析SpringCloud中@RefreshScope注解的实现原理,详细阐述其在类实例化过程中的作用及生命周期,包括ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner的doScan、AnnotationConfigUtils的applyScopedProxyMode及ScopedProxyUtils的createScopedProxy等关键步骤。
本文深入解析SpringCloud中@RefreshScope注解的实现原理,详细阐述其在类实例化过程中的作用及生命周期,包括ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner的doScan、AnnotationConfigUtils的applyScopedProxyMode及ScopedProxyUtils的createScopedProxy等关键步骤。
















 6718
6718

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








