一.数据库约束
指定在列上的 , 是关系型数据库的一个重要功能 , 主要作用是 : 保证数据的完整性 , 或 数据的正确性
1.约束类型
|
约束类型 |
说明 |
|
NOT NULL |
指示某列不能存储 NULL 值 |
|
UNIQUE |
保证某列的每行必须有唯一值 |
|
DEFAULT |
规定没有给列赋值时的默认值 |
|
PRIMARY KEY (主键) |
NOT NULL 和 UNIQUE 的结合 ; 确保某列有唯一表示 , 有卒于更快速地找到表中的一个特定的记录 |
|
FOREIGN KEY (外键) |
保证一个表中的数据匹配到另一个表中的值的参照完整性 |
|
CHECK |
保证列中的值符合指定的条件 |
2.1 NULL 约束
作用 : 把某列定义为必填项
示例 :
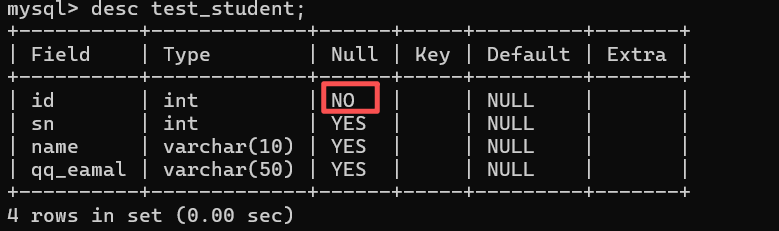
create table if not exists test_student(
id int not null, #not null 约束
sn int ,
name varchar(10),
qq_eamal varchar(50)
);
desc test_student;
注意 :
- 如果 : insert into test_student values(NULL,10088,'张三','10088@qq.com'); 插入了 NULL则会报错 :

- 只有非空列有值时才能正常写入 例如 : insert into test_student values(1,10023,'李四','10023@qq.com');
2.2 UNIQUE : 唯一约束
作用 : 指定某列的值在表中不能重复 (第二次插入相同的值就会报错 , NULL除外)
示例 :
drop table if exists test_student;#删除 test_student 表
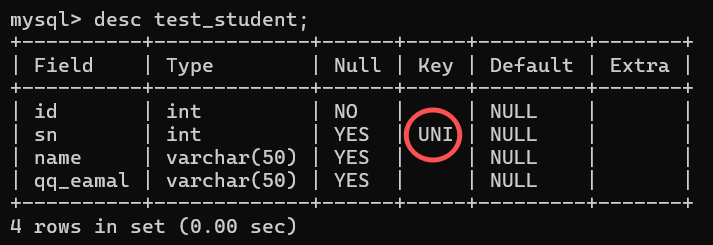
create table test_student(
id int not null, #not null 约束
sn int unique, #唯一约束
name varchar(50),
qq_eamal varchar(50)
); #创建表
desc test_student;#显示表结构
注意 :
- 第二次插入相同的值就会报错 : insert into test_student values(1,10023,'李四','10023@qq.com'),(2,10023,'张三','zhansan@qq.com');

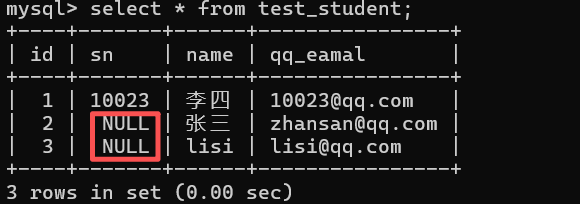
- 第二次插入相同的值是 NULL时 , 不会报错 : insert into test_student values (1,10023,'李四','10023@qq.com'), (2,null,'张三','zhansan@qq.com'), (3,null,'lisi','lisi@qq.com'); select * from test_student; #显示表内容
2.3 DEFAULT : 默认值约束
作用 : 指定插入数据时 , 如果被 DEFAULT 约束的列为 NULL , 则会使用默认值
示例 :
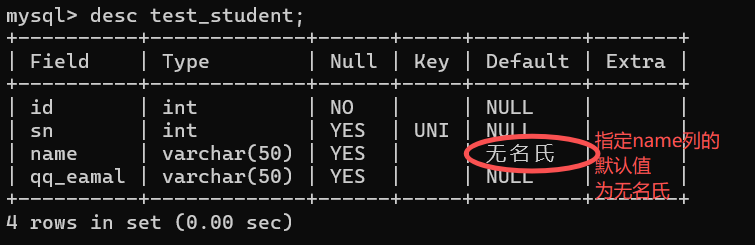
create table test_student(
id int not null, # NOT NULL 约束
sn int unique, # 唯一约束
name varchar(50) default '无名氏', # 默认值约束
qq_eamal varchar(50)
);
desc test_student;
注意 :
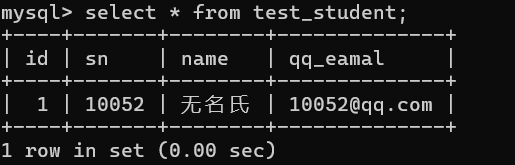
- 指定插入数据时 , 如果被 DEFAULT 约束的列为 NULL , 则会使用默认值 : insert into test_student (id,sn,qq_eamal) values(1,10052,'10052@qq.com');#没有插入 name 列
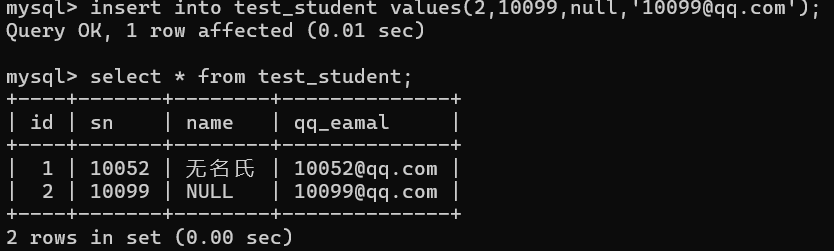
- 虽然指定默认值约束 , 但是 如果手动插入 NULL 时 , 结果仍为 NULL ; 即 : 用户插入优先级高于默认值值约束 insert into test_student values(2,10099,null,'10099@qq.com');
2.4 PRIMARY KEY : 主键约束
作用 : 确保每列有唯一标识 , 有助于更容易更快速地找到表中的一个特定记录
主键效果 : NOT NULL 和 UNIQUE 的结合 (把表中的某一列设置成 非空且唯一)
示例 :
drop table if exists test_student;
create table test_student(
id int not null primary key, #主键约束
sn int unique, #唯一约束
name varchar(50) default '无名氏', #默认值约束
qq_eamal varchar(50)
);
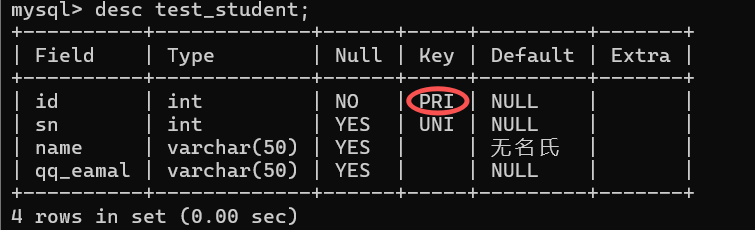
注意 :
- 主键约束的列 即是非空的 , 也是唯一的 , 写入数据时 NOT NULL 和 UNIQUE 两个约束同时生效
- 一个表中不允许有两个主键
- 一个主键可以同时包含多列(复合主键)
示例 :
drop table if exists test_student;
create table test_student(
id int ,
sn int unique, #唯一约束
name varchar(50) default '无名氏', #默认值约束
qq_eamal varchar(50),
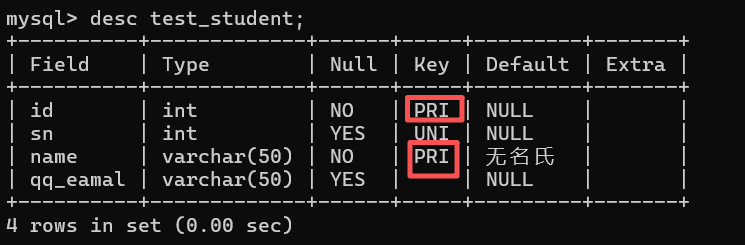
primary key(id,name) # 复合主键
);
desc test_student;
- 对于整数类型的主键 , 常搭配自增长 auto_increment 来使用 , 插入数据对应字段不给值时 , 使用最大值+1
这个计数器是独立于表中已有记录的,只保证 递增,不保证 连续 ; 只要有操作导致计数器跳过某个值,最终的id就会出现不连续
示例 :
drop table if exists test_student;
create table test_student(
id int not null primary key auto_increment, #主键约束
sn int unique, #唯一约束
name varchar(50) default '无名氏', #默认值约束
qq_eamal varchar(50)
);
desc test_student;
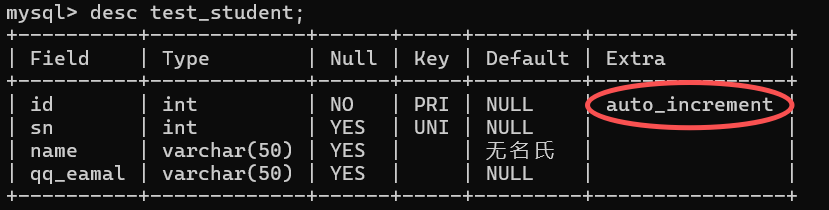
insert into test_student values(1,56645,'ifoasj','56645@qq.com'),(null,65465,'saodji','65465@qq.com');#插入的 id 为 NULL
此处插入的 NULL 并不是说把 NULL 写入数据库 , 而是让数据库去帮我们处理
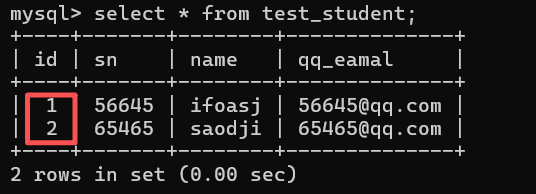
insert into test_student (sn,name,qq_eamal) values(98562,'芝士粉','98562@qq.com');#未插入 id
2.5 FOREIGN KEY : 外键约束
作用 : 外键用于关联其他表的 主键 或 唯一键
语法 : foreign key (列名1) references 主表(列名2)
列名1 : 表示当前表中哪个字段要与主键建立的外键关系
列名2 : 主列中的主键
示例 :
drop table if exists test_student;
create table test_student(
id int not null primary key auto_increment, #主键约束
sn int unique, #唯一约束
name varchar(50) default '无名氏', #默认值约束
qq_eamal varchar(50)
);#主表
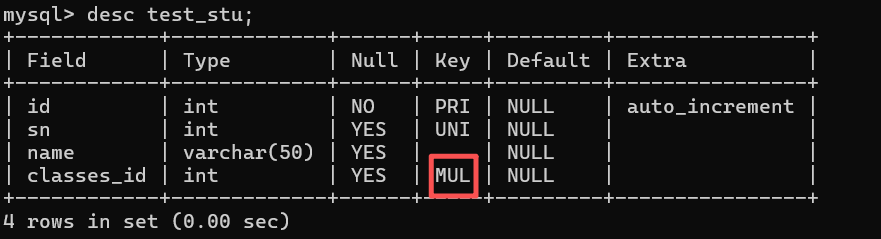
create table test_stu(
id int primary key auto_increment,
sn int unique,
name varchar(50),
classes_id int,
foreign key(classes_id) references test_student(id) # 创建外键
);#子表
desc test_student;
注意 :
- 删除主表中的数据时 , 如果子表中存在对主表的依赖时 , 如果直接删除主表中的信息会报一个主外键关系的错误
insert into test_student values(1,56645,'ifoasj','56645@qq.com'),(null,65465,'saodji','65465@qq.com'); #为主表添加
insert into test_stu values(1,56645,'语文',1),(2,65465,'数学',2);#为子表添加元素
错误示例 : delete from test_student where id = 1;

如果要删除主表中的记录 , 子表中不能有对该条记录的依赖 ; 即 : 要先删除子表中的记录 , 再去删除主表中的记录:
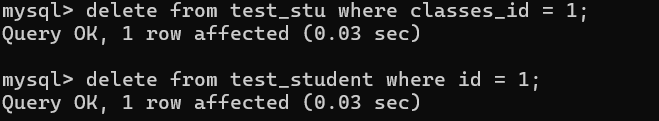
delete from test_stu where classes_id = 1;
delete from test_student where id = 1;
2.6 CHECK 约束
示例 :
create table test_user(
id int ,
name varchar(50),
sex varchar(10),
check (sex = '男' or sex = '女')#该字段允许的值
);
注意 : 只在 MySQL 8.0+生效





















 990
990

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








