原理
模型表示:
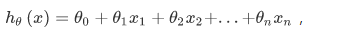
数据要进行缩放归一化
代价函数:
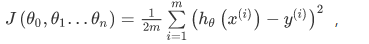
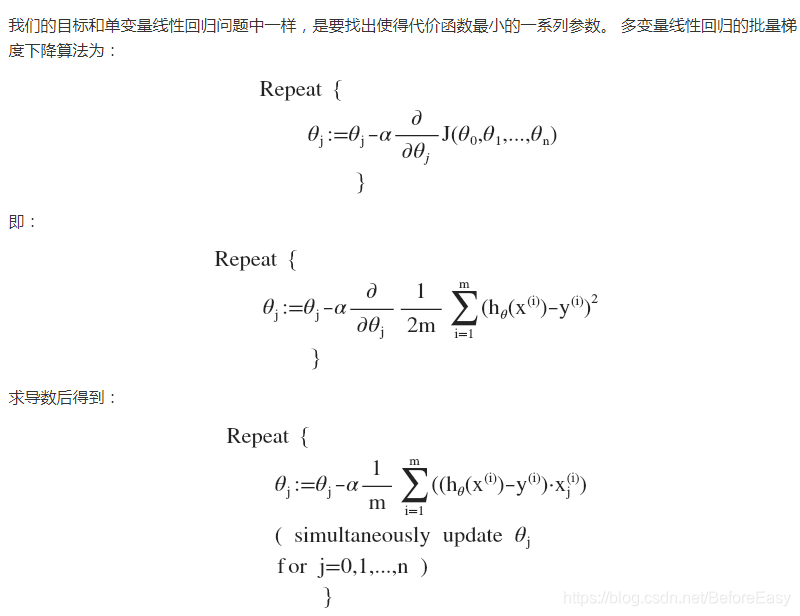
i表示第i个训练实例 j表示第j个特征
同时更新theta
用矩阵表示就是:
error = y_pred - y – shape(m,1)
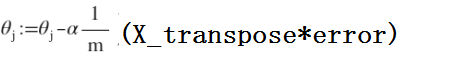
拆开用矩阵表示一下最后的求导更新过程:
假设训练数据规模m*n,m条训练数据,每条数据n个特征,所以有theta0 theta1 — thetan

代码如下:
准备数据:
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_california_housing
housing = fetch_california_housing()
m, n = housing.data.shape
#np.c_按colunm来组合array
housing_data_plus_bias = np.c_[np.ones((m, 1)), housing.data]
归一化
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
scaler = StandardScaler()
scaled_housing_data = scaler.fit_transform(housing.data)
scaled_housing_data_plus_bias = np.c_[np.ones((m, 1)), scaled_housing_data]
梯度下降:
n_epoches = 10000
learning_rate = 0.01
X = tf.constant(scaled_housing_data_plus_bias, dtype = tf.float32, name = 'X') # [m,n+1]
y = tf.constant(housing.target.reshape(-1,1),dtype=tf.float32,name='y')
theta = tf.Variable(tf.random_uniform([n + 1, 1], -1.0, 1.0, seed=42), name="theta") # [n+1,1]--shape
y_pred =tf.matmul(X,theta,name='predictions')
error = y_pred - y
mse = 1/2*tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(error),name = 'mse') # compute avarage
gradients = 1/m*tf.matmul(tf.transpose(X),error)
training_op = tf.assign(theta, theta-learning_rate*gradients)
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
for epoch in range(n_epoches):
if epoch % 100 == 0:
print("Epoch", epoch, "MSE =", mse.eval())
sess.run(training_op)
best_theta = theta.eval()
部分效果:
这里求gradients是在手推出线性回归的求导之后得到的,但是有的并不好求导,可以直接将gradients替换为:
gradients = tf.gradients(mse, [theta])[0]







 本文详细介绍了线性回归模型的原理与实现,重点讲解了如何使用梯度下降法进行参数优化。通过Python和TensorFlow实现了一个具体的线性回归模型,并展示了数据预处理、模型训练及评估的全过程。
本文详细介绍了线性回归模型的原理与实现,重点讲解了如何使用梯度下降法进行参数优化。通过Python和TensorFlow实现了一个具体的线性回归模型,并展示了数据预处理、模型训练及评估的全过程。

















 484
484

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








