04-树5 Root of AVL Tree (25 分)
An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. In an AVL tree, the heights of the two child subtrees of any node differ by at most one; if at any time they differ by more than one, rebalancing is done to restore this property. Figures 1-4 illustrate the rotation rules.
大意:AVL树是一个自我平衡的二叉树。在AVL树中,任何节点的两个子子树的高度最多相差一个;若他们相差超过一个时,重新平衡来保持这个特性。图1-4说明了旋转规则。
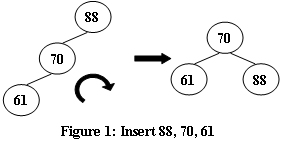
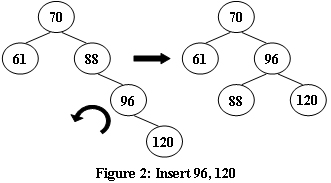


Now given a sequence of insertions, you are supposed to tell the root of the resulting AVL tree.
大意:现在给定一个插入序列,你需要知道生成的AVL树的根。
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤20) which is the total number of keys to be inserted. Then N distinct integer keys are given in the next line. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
大意:每一输入包含一个测试样例。每一个样例,第一个是一个正整数N(≤20) ,表示插入的键值的总数,接下是N个不同的整数键值,所有的数字用一个空格分开。
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the root of the resulting AVL tree in one line.
大意:每一个测试样例,输出AVL树的根。
Sample Input 1:
5
88 70 61 96 120
Sample Output 1:
70
Sample Input 2:
7
88 70 61 96 120 90 65
Sample Output 2:
88
解题思路:这是基础的AVL操作,LL、LR、RR、RL。Talking is cheap, show me the code.?
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <list>
#include <queue>
#include <set>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <map> //STL 映射容器
#include <memory>
#include <cstdio> //定义输入/输出函数
#include <cstdlib> //定义杂项函数及内存分配函数
#include <cstring>
#define maxn 100
using namespace std;
typedef struct AVLNode * Position;
typedef Position AVLTree ;
typedef int ElementType;
struct AVLNode{
ElementType Data;
AVLTree Left,Right;
int Height;
};
int Max(int a,int b){
return a>b?a:b;
}
int GetHeight(AVLTree T){
if(!T) return -1;
else return Max(GetHeight(T->Left),GetHeight(T->Right))+1;
}
AVLTree SingleLeftRotation(AVLTree A){
/*注意:A必须有一个左子节点B*/
/*将A与B做左单旋,更新A与B的高度,返回新的根节点B*/
/*顺时针旋转*/
AVLTree B=A->Left;
A->Left=B->Right;/*B的右子树接到A的左子树上*/
B->Right=A;/*A接到B的右子树上*/
A->Height = Max( GetHeight(A->Left) , GetHeight(A->Right) ) + 1;
B->Height = Max( GetHeight(B->Left) , GetHeight(B->Right) ) + 1;
return B;
}
AVLTree SingleRightRotation(AVLTree A){
/*注意:A必须有一个右子节点B*/
/*将A与B做右单旋,更新A与B的高度,返回新的根节点B*/
/*逆时针旋转*/
AVLTree B=A->Right;
A->Right=B->Left;/*B的左子树接到A的右子树上*/
B->Left=A;/*A接到B的左子树上*/
A->Height = Max( GetHeight(A->Left) , GetHeight(A->Right) ) + 1;
B->Height = Max( GetHeight(B->Left) , GetHeight(B->Right) ) + 1;
return B;
}
AVLTree DoubleLeftRightRotation(AVLTree A){
/*注意:A必须有一个左子节点B,且B必须有一个右子节点C*/
/*将A、B与C做两次单旋,返回新的根节点C*/
/*将B与C做右单旋,C被返回(逆时针旋转BC)*/
A->Left=SingleRightRotation(A->Left);
/*将A与C做左单旋,C被返回(顺时针旋转AC)*/
return SingleLeftRotation(A);
}
AVLTree DoubleRightLeftRotation(AVLTree A){
/*注意:A必须有一个右子节点B,且B必须有一个左子节点C*/
/*将A、B与C做两次单旋,返回新的根节点C*/
/*将B与C做左单旋,C被返回(顺时针旋转BC)*/
A->Right=SingleLeftRotation(A->Right);
/*将A与C做右单旋,C被返回(逆时针旋转AC)*/
return SingleRightRotation(A);
}
AVLTree Insert(AVLTree T,ElementType X){
/*将X插入AVL树中,并返回调整后的AVL树*/
if(!T){/*若插入空树,则新建包含一个节点的AVL树*/
T=(AVLTree)malloc(sizeof(struct AVLNode));
T->Data=X;
T->Height=0;
T->Left=T->Right=NULL;
}/*if(插入空树)结束*/
else if( X < T->Data ){
/*插入T的左子树*/
T->Left=Insert(T->Left,X);
/*如果需要左旋*/
if(GetHeight(T->Left) - GetHeight(T->Right)==2){
if(X < T->Left->Data){
T=SingleLeftRotation(T);/*左单旋*/
}
else{
T=DoubleLeftRightRotation(T);/*左-右双旋*/
}
}
}/*else if(插入左子树)结束*/
else if(X > T->Data){
/*插入T的右子树*/
T->Right=Insert(T->Right,X);
/*若需要右旋*/
if(GetHeight(T->Left) - GetHeight(T->Right)==-2){
if(X > T->Right->Data){
T=SingleRightRotation(T);/*右单旋*/
}
else{
T=DoubleRightLeftRotation(T);/*右-左双旋*/
}
}
}/*else if(插入右子树)结束*/
/*else X==T->Data,表示X已经存在则无需插入*/
/*最后别忘记更新树高*/
T->Height=Max(GetHeight(T->Left),GetHeight(T->Right))+1;
return T;
}
int main()
{
int N,i,X;
AVLTree T=NULL;
scanf("%d",&N);
for(i=0;i<N;i++){
scanf("%d",&X);
T=Insert(T,X);
}
printf("%d\n",T->Data);
return 0;
}







 本文详细介绍了AVL树的插入操作及其自我平衡过程,包括四种旋转规则:LL、LR、RR、RL,通过具体实例展示了如何维持AVL树的高度平衡特性。
本文详细介绍了AVL树的插入操作及其自我平衡过程,包括四种旋转规则:LL、LR、RR、RL,通过具体实例展示了如何维持AVL树的高度平衡特性。
















 2451
2451

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








