大家好,我是 同学小张,+v: jasper_8017 一起交流,持续学习AI大模型应用实战案例,持续分享,欢迎大家点赞+关注,订阅我的大模型专栏,共同学习和进步。
现在订阅专栏,+微信私信我 返3元,即将涨价!
前面我们一直在用立方体作为例子,太枯燥了。立方体的顶点是固定的,我们手动就可以写出来。但是现实中,立方体是不够的,需要更加复杂的物体渲染。这些物体的顶点如何得到呢?
可以通过模型加载的方式实现顶点属性的获取。我们以 assimp 模型加载器为例,讲解如何加载模型,并获取顶点属性。
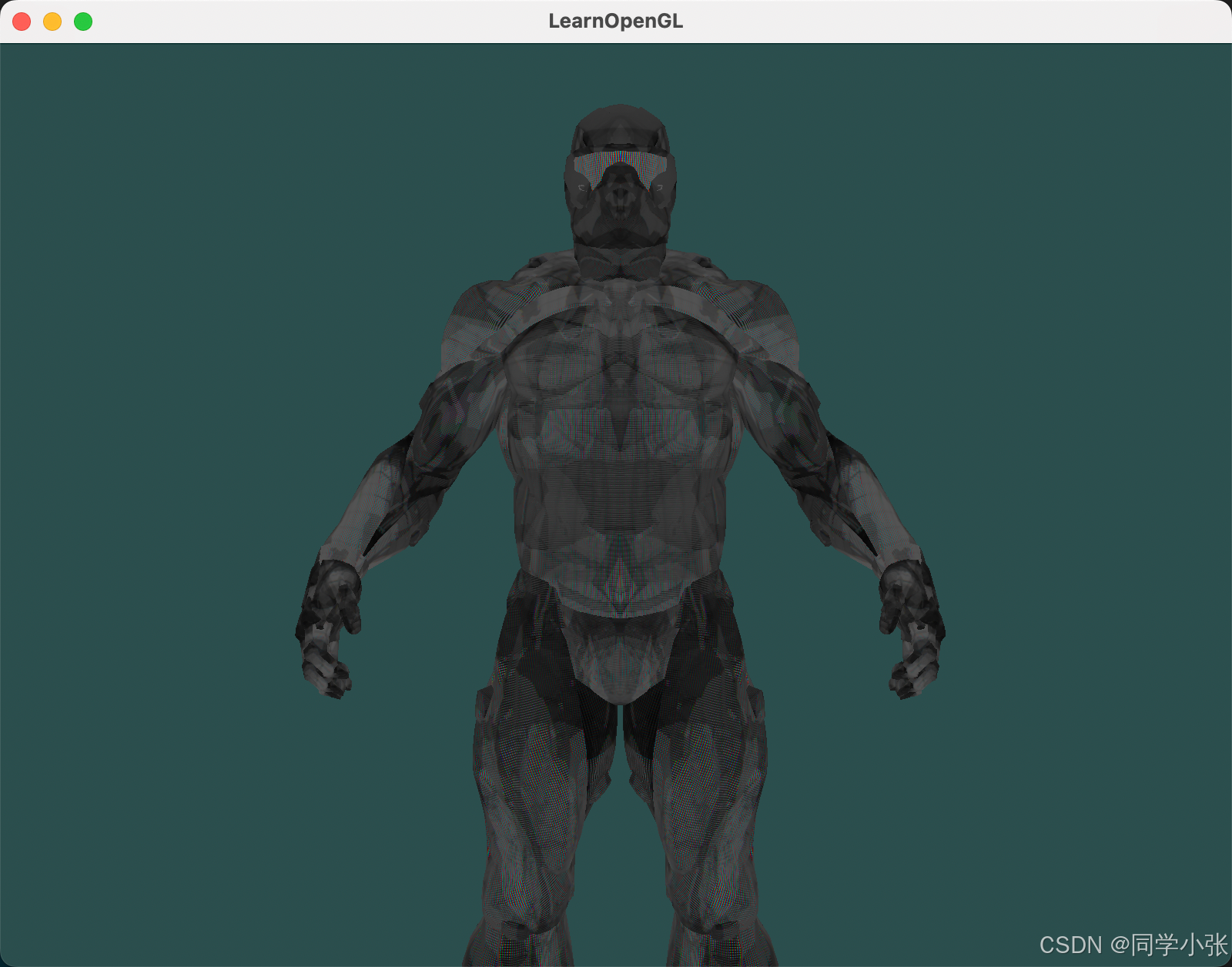
先来看下最终效果:
文章目录
1. Assimp 模型加载介绍
Assimp,全称为Open Asset Import Library。Assimp可以导入几十种不同格式的模型文件(同样也可以导出部分模型格式)。只要Assimp加载完了模型文件,我们就可以从Assimp上获取所有我们需要的模型数据。Assimp把不同的模型文件都转换为一个统一的数据结构,所有无论我们导入何种格式的模型文件,都可以用同一个方式去访问我们需要的模型数据。
当导入一个模型文件时,即Assimp加载一整个包含所有模型和场景数据的模型文件到一个scene对象时,Assimp会为这个模型文件中的所有场景节点、模型节点都生成一个具有对应关系的数据结构,且将这些场景中的各种元素与模型数据对应起来。下图展示了一个简化的Assimp生成的模型文件数据结构:
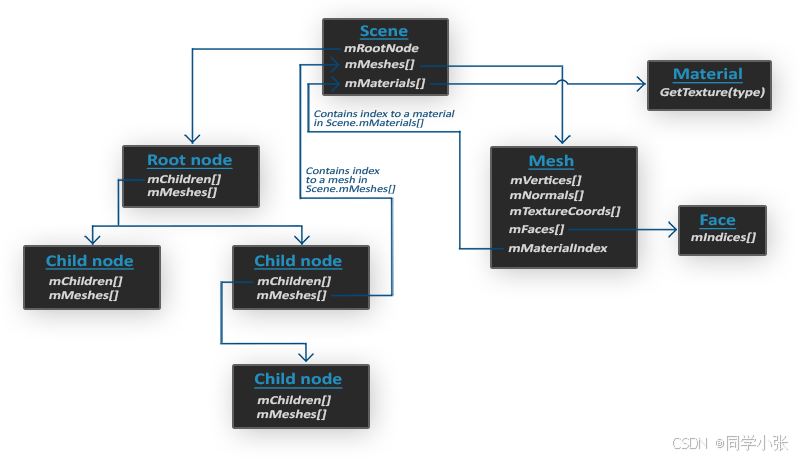
- 所有的模型、场景数据都包含在scene对象中,如所有的材质和Mesh。同样,场景的根节点引用也包含在这个scene对象中
- 场景的根节点可能也会包含很多子节点和一个指向保存模型点云数据mMeshes[]的索引集合。根节点上的mMeshes[]里保存了实际了Mesh对象,而每个子节点上的mMesshes[]都只是指向根节点中的mMeshes[]的一个指针
- 一个Mesh对象本身包含渲染所需的所有相关数据,比如顶点位置、法线向量、纹理坐标、面片及物体的材质
- 一个Mesh会包含多个面片。一个Face(面片)表示渲染中的一个最基本的形状单位,即图元(基本图元有点、线、三角面片、矩形面片)。一个面片记录了一个图元的顶点索引,通过这个索引,可以在mMeshes[]中寻找到对应的顶点位置数据。顶点数据和索引分开存放,可以便于我们使用缓存(VBO、NBO、TBO、IBO)来高速渲染物体。
- 一个Mesh还会包含一个Material(材质)对象用于指定物体的一些材质属性。如颜色、纹理贴图(漫反射贴图、高光贴图等)
所以我们要做的第一件事,就是加载一个模型文件为scene对象,然后获取每个节点对应的Mesh对象(我们需要递归搜索每个节点的子节点来获取所有的节点),并处理每个Mesh对象对应的顶点数据、索引以及它的材质属性。最终我们得到一个只包含我们需要的数据的Mesh集合。
2. Assimp 库安装
我们采用源码编译的方式安装 Assimp 库。步骤如下:
(1) 下载 Assimp 源码
git clone https://github.com/assimp/assimp.git
(2) 通过 CMake 编译 Assimp
cd assimp
cmake CMakeLists.txt -DASSIMP_BUILD_ASSIMP_TOOLS=ON
cmake --build .
编译完成后,在 bin 文件夹下会生成 assimp 工具和库。
3. 使用 Assimp 加载模型
3.1 网格(Mesh)
一个网格是我们在OpenGL中绘制物体的最小单位。一个模型通常有多个网格组成。
那么网格应该有哪些属性呢?
思考我们前面的教程,给立方体顶点时,我们至少需要顶点坐标、法线、纹理坐标。
另外,一个网格也应该包含一个绘制用的纹理贴图,还有绘制数据的索引。
3.1.1 顶点数据结构
首先,定义一个顶点数据结构:
struct Vertex
{
glm::vec3 Position;
glm::vec3 Normal;
glm::vec2 TexCoords;
};
3.1.2 纹理数据结构
然后,定义一个纹理数据结构:
struct Texture
{
unsigned int id;
std::string type; // 储存纹理的id和它的类型,比如diffuse纹理或者specular纹理。
};
3.1.3 网格类定义
(1)首先,网格类需要包含顶点数据、索引数据和纹理数据。
std::vector<Vertex> vertices;
std::vector<unsigned int> indices;
std::vector<Texture> textures;
(2)如何得到这些数据呢?
通过加载模型,创建每个Mesh实例时,可以将该Mesh的顶点数据、索引数据和纹理数据传递进来。
Mesh::Mesh(std::vector<Vertex> vertices, std::vector<unsigned int> indices, std::vector<Texture> textures)
{
this->vertices = vertices;
this->indices = indices;
this->textures = textures;
// process vertices
setupMesh();
}
(3)有了顶点数据,按之前的步骤,我们需要将顶点数据上传到着色器中,可以将这个操作封装到 setupMesh 函数中。不多在实现 setupMesh 函数之前,我们需要先定义 VAO、VBO、EBO。
unsigned int _VAO, _VBO, _EBO;
(4)实现 setupMesh 函数:
void Mesh::setupMesh()
{
glGenVertexArrays(1, &_VAO);
glGenBuffers(1, &_VBO);
glGenBuffers(1, &_EBO);
glBindVertexArray(_VAO);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, _VBO);
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vertices.size() * sizeof(Vertex), &vertices[0], GL_STATIC_DRAW);
glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, _EBO);
glBufferData(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, indices.size() * sizeof(unsigned int), &indices[0], GL_STATIC_DRAW);
// 设置顶点坐标指针
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, sizeof(Vertex), (GLvoid*)0);
// 设置法线指针
glEnableVertexAttribArray(1);
glVertexAttribPointer(1, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, sizeof(Vertex), (GLvoid*)offsetof(Vertex, Normal));
// 设置顶点的纹理坐标
glEnableVertexAttribArr




 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章



















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










