import torch
num_class = 5
N = 3
tensor = torch.randint(0, num_class, [N])
print(tensor)
one_hot = torch.zeros(N, num_class).long()
one_hot.scatter_(dim=1,index=tensor.unsqueeze(dim=1),src=torch.ones(N, num_class).long())
print(one_hot)
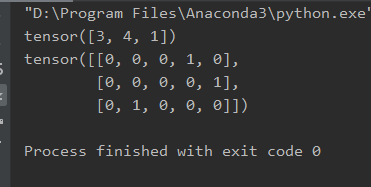
 本文介绍如何使用PyTorch实现One-Hot编码,包括初始化张量、使用scatter_函数进行转换的过程。One-Hot编码是机器学习中常用的预处理手段,将类别变量转换为二进制向量。
本文介绍如何使用PyTorch实现One-Hot编码,包括初始化张量、使用scatter_函数进行转换的过程。One-Hot编码是机器学习中常用的预处理手段,将类别变量转换为二进制向量。
import torch
num_class = 5
N = 3
tensor = torch.randint(0, num_class, [N])
print(tensor)
one_hot = torch.zeros(N, num_class).long()
one_hot.scatter_(dim=1,index=tensor.unsqueeze(dim=1),src=torch.ones(N, num_class).long())
print(one_hot)

您可能感兴趣的与本文相关的镜像

PyTorch 2.7
PyTorch 是一个开源的 Python 机器学习库,基于 Torch 库,底层由 C++ 实现,应用于人工智能领域,如计算机视觉和自然语言处理
 6021
6021
 2197
2197

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?


