手把手带你了解使用Pandas的10个小技巧
Pandas是数据分析师,数据科学家必备的数据处理Python库,本文参照SQL语言,分享10个在实际应用中肯定会用到的小技巧。
1. select from table where f1=‘a’ and f2=‘b’
使用AND或OR从dataframe中提取子集:
# and
dfb = df.loc[(df.Week == week) & (df.Day == day)]
# or
dfb = df.loc[(df.Week == week)|(df.Day == day)]
2. select * from table where “a” in
从一个dataframe中选择一个包含在另外一个dataframe的数据,例如下面的SQL语句:
select * from table1 where field1 in (select field1 from table2)
例如,有一个名为“days”的dataframe,它包含以下值:
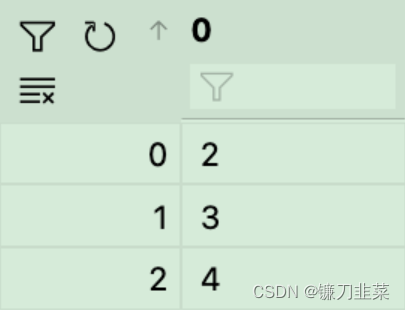
另一个dataframe是:
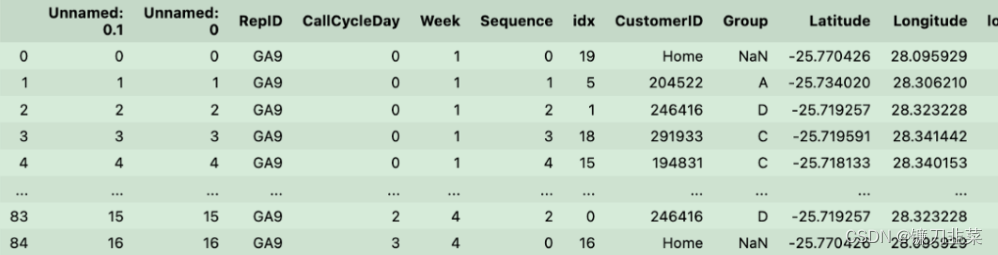
可以直接用下面的方式获取:
days = [0,1,2]
df[df(days)]
3. select * from table where “a” not in
还是使用上面的数据,使用~操作符就可以了:
days = [0,1,2]
df[~df(days)]
4. select sum(*) from table group by
分组统计和求和也是常见的操作,使用方式为:
df(by=['RepID','Week','CallCycleDay']).sum()
如果想保存结果或稍后使用它们并引用这些字段,请添加as_index=False:
df.groupby(by=['RepID','Week','CallCycleDay'], as_index=False).sum()
使用as_index= false,可以表的形式保存列.
5. 从一个表更另外一个表的字段
如果从一个dataframe中更改了一些值,现在想要更新另外一个dataframe,这个操作就很有用。
dfb = dfa[dfa.field1='somevalue'].copy()
dfb['field2'] = 'somevalue'
dfa.update(dfb)
这里的更新是通过索引匹配的。
6. 使用apply/lambda创建新字段
要创建了一个名为address的新字段,它是几个字段进行拼接的:
dfa['address'] = dfa.apply(lambda row: row['StreetName'] + ', ' +row['Suburb'] + ', ' + str(row['PostalCode']),axis=1)
7. 插入新行
插入新数据的最佳方法是使用concat。可以用pd. datafframe .from_records将新行转换为df:
newRow = row.copy()
newRow.CustomerID = str(newRow.CustomerID)+'-'+str(x)
newRow.duplicate = True
df = pd.concat([df,pd.DataFrame.from_records([newRow])])
8. 更改列的类型
可以使用astype函数将其快速更改列的数据类型:
df = pd.read_excel(customers_.xlsx')
df['Longitude'] = df['Longitude'].astype(str)
df['Latitude'] = df['Longitude'].astype(str)
9. 删除列
使用drop可以删除列
def cleanColumns(df):
for col in df.columns:
if col[0:7] == "Unnamed":
df.drop(col, inplace=True, axis=1)
return df
10. 地图上标注点
这个可能是最没用的技巧,但是很好玩。首先要有一些经纬度数据:
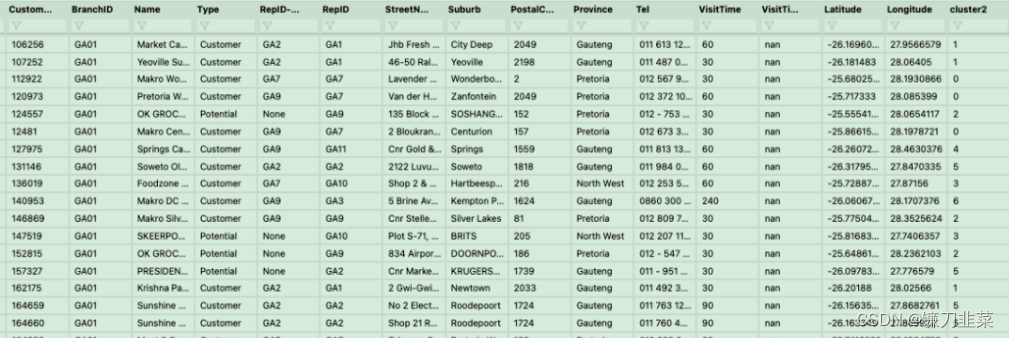
根据经纬度把它在地图上进行标注:
df_clustercentroids = pd.read_csv(centroidFile)
lst_elements = sorted(list(dfm.cluster2.unique()))
lst_colors = ['#%06X' % np.random.randint(0, 0xFFFFFF) for i in range(len(lst_elements))]
dfm["color"] = dfm["cluster2"]
dfm["color"] = dfm["color"].apply(lambda x:lst_colors[lst_elements.index(x)])
m = folium.Map(location=[dfm.iloc[0].Latitude,dfm.iloc[0].Longitude], zoom_start = 9)
for index, row in dfm.iterrows():
folium.CircleMarker(location=[float(row['Latitude']), float(row['Longitude'])],radius=4,popup=str(row['RepID']) + '|' +str(row.CustomerID),color=row['color'],fill=True,fill_color=row['color']).add_to(m)
for index, row in df_clustercentroids.iterrows():
folium.Marker(location=[float(row['Latitude']), float(row['Longitude'])],popup=str(index) + '|#=' +str(dfm.loc[dfm.cluster2==index].groupby(['cluster2'])['CustomerID'].count().iloc[0]),icon=folium.Icon(color='black',icon_color=lst_colors[index]),tooltip=str(index) + '|#=' +str(dfm.loc[dfm.cluster2==index].groupby(['cluster2'])['CustomerID'].count().iloc[0])).add_to(m)
m
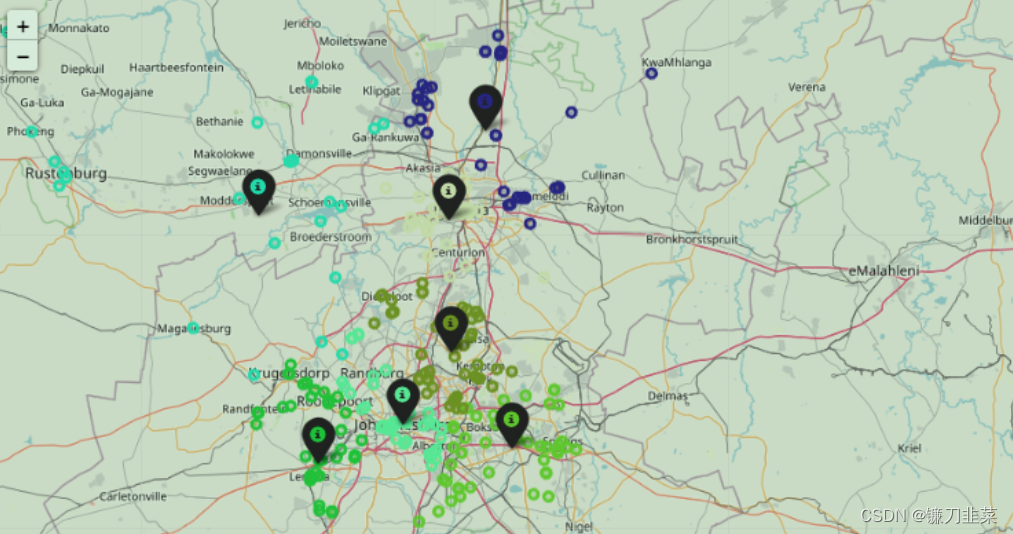
结果如下:





 本文介绍了使用Pandas库进行数据处理的10个关键技巧,包括根据条件筛选数据帧、合并数据、创建新字段、更改列类型、删除列以及在地图上标注点等,旨在帮助数据分析师和数据科学家提升工作效率。
本文介绍了使用Pandas库进行数据处理的10个关键技巧,包括根据条件筛选数据帧、合并数据、创建新字段、更改列类型、删除列以及在地图上标注点等,旨在帮助数据分析师和数据科学家提升工作效率。

















 1904
1904

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










