📝 面试求职: 「面试试题小程序」 ,内容涵盖 测试基础、Linux操作系统、MySQL数据库、Web功能测试、接口测试、APPium移动端测试、Python知识、Selenium自动化测试相关、性能测试、性能测试、计算机网络知识、Jmeter、HR面试,命中率杠杠的。(大家刷起来…)
📝 职场经验干货:
1. 分析需求
首先,明确你需要测试的几个关键方面:
WebSocket连接:模拟客户端与服务器通过WebSocket保持长连接。
Redis交互:如果需要直接操作Redis(例如检查队列状态),可以在Locust脚本中集成redis-py库。
心跳机制:模拟客户端定期发送心跳包以维持会话活跃。
2. 准备工作
确保你已经安装了必要的Python库:
pip install locust websockets redis3. 编写Locust脚本
以下是一个示例脚本,演示了如何在Locust中集成WebSocket、Redis以及实现心跳机制。
WebSocket客户端处理
import websocket
import time
from locust import User, task, between, events
class WebSocketClient:
def __init__(self, host):
self.host = host
self.ws = None
def connect(self):
self.ws = websocket.create_connection(self.host)
return "Connected"
def send(self, message):
start_time = time.time()
try:
self.ws.send(message)
response = self.ws.recv()
total_time = int((time.time() - start_time) * 1000)
events.request_success.fire(request_type="WebSocket", name="send", response_time=total_time, response_length=len(response))
return response
except Exception as e:
total_time = int((time.time() - start_time) * 1000)
events.request_failure.fire(request_type="WebSocket", name="send", response_time=total_time, exception=e)
def heartbeat(self):
"""模拟发送心跳"""
while True:
time.sleep(30) # 心跳间隔时间
self.send("heartbeat")
def disconnect(self):
if self.ws:
self.ws.close()Redis客户端处理
import redis
class RedisClient:
def __init__(self, host='localhost', port=6379, db=0):
self.client = redis.StrictRedis(host=host, port=port, db=db, decode_responses=True)
def check_queue_status(self, queue_name):
return self.client.llen(queue_name)
用户类定义
class HospitalQueueUser(User):
abstract = True
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super(HospitalQueueUser, self).__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.ws_client = WebSocketClient("ws://your_websocket_server")
self.redis_client = RedisClient()
@task(1)
def ws_task(self):
response = self.ws_client.send("register_patient")
print(f"Received: {response}")
@task(2)
def check_queue(self):
status = self.redis_client.check_queue_status("patient_queue")
print(f"Queue status: {status}")
def on_start(self):
"""每个虚拟用户开始时调用"""
result = self.ws_client.connect()
print(result)
gevent.spawn(self.ws_client.heartbeat) # 启动心跳线程
def on_stop(self):
"""每个虚拟用户结束时调用"""
self.ws_client.disconnect()4. 运行测试
保存上述脚本后,在命令行中运行Locust:
locust -f your_locustfile.py然后,打开浏览器访问http://localhost:8089,输入要模拟的用户数和每秒启动的用户数,点击“Start swarming”按钮开始测试。
注意事项
资源管理:确保正确关闭WebSocket连接和Redis连接,避免资源泄露。
并发控制:根据实际情况调整并发用户数和心跳频率,避免给服务器带来过大的压力。
数据一致性:在测试过程中,注意观察Redis中的数据变化是否符合预期,以便验证系统的正确性。
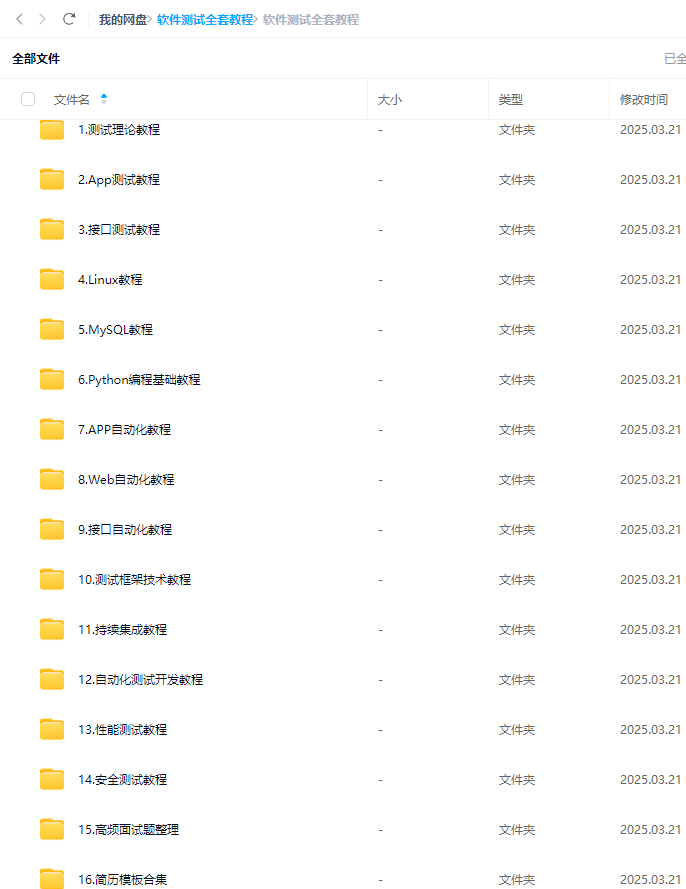
最后: 下方这份完整的软件测试视频教程已经整理上传完成,需要的朋友们可以自行领取【保证100%免费】
























 2148
2148

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








