今天和大家聊聊分类任务中常用且重要的XGBoost算法。

XGBoost
作为一种集成学习模型,它的核心是将多棵“弱”决策树组合成强预测器:不同于随机森林的并行训练与结果平均,XGBoost采用“提升”策略——树按顺序逐棵构建,每棵新树的目标都是修正前序所有树的预测误差。从直观上看,新树会去拟合当前模型的残差(严格来说是损失函数的梯度),通过这种迭代方式,持续将模型预测方向往降低损失的方向推进,最终实现精准的类别输出。
另外,我还整理了XGBOOST相关资料,需要的话可以免费分享给你
➔➔➔➔点击查看原文,获取更多机器学习干货和资料!![]() https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/0qHc6r7GReHofHkAhCNo5A
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/0qHc6r7GReHofHkAhCNo5A
XGBoost基础详解
1. XGBoost的核心原理
XGBoost(Extreme Gradient Boosting)是一种优化的梯度提升树算法,其核心思想是通过迭代地训练弱学习器(通常是CART树)并将它们组合起来,形成一个强大的预测模型。 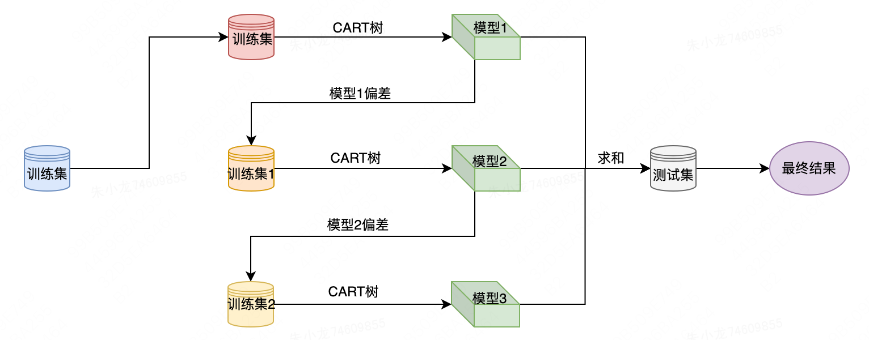
1.1 目标函数
XGBoost的目标函数由损失函数和正则化项组成:
其中:
-
是损失函数,衡量预测值与真实值之间的差异
-
是正则化项,控制模型复杂度,防止过拟合
-
是树的数量
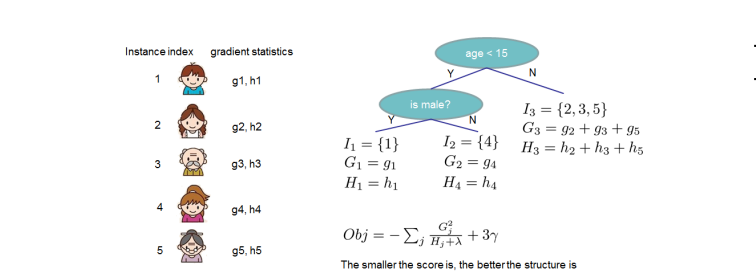
1.2 梯度提升过程
XGBoost采用加法模型,最终预测值是所有树的预测结果之和:
其中是第t轮的预测值,是第t棵树的预测结果。
每次迭代都训练一棵新树来拟合当前模型的残差(即负梯度),这就是梯度提升的核心思想。
1.3 正则化
XGBoost引入了两种主要的正则化项:
其中:
-
是树的叶子节点数量
-
是第j个叶子节点的权重
-
和是正则化参数
这些正则化项有助于控制树的复杂度,提高模型的泛化能力。
2. XGBoost的优势
-
高效性:XGBoost采用了并行计算、近似算法和缓存优化等技术,大大提高了训练速度
-
灵活性:支持多种目标函数,可用于分类、回归和排序等任务
-
鲁棒性:内置处理缺失值的机制,对异常值不敏感
-
可扩展性:能够处理大规模数据集
XGBoost入门项目:鸢尾花分类(完整代码、结果图和论文扫码即可免费领取)
下面我们将通过一个简单的鸢尾花分类项目来实践XGBoost的使用。
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split, GridSearchCV
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, classification_report, confusion_matrix, roc_curve, auc
from sklearn.preprocessing import label_binarize
import xgboost as xgb
import os
# 设置中文字体(服务器环境可能不需要,但保持兼容性)
plt.rcParams["font.family"] = ["Arial", "Helvetica", "sans-serif"]
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 解决负号显示问题
# 创建结果目录
result_dir = "xgboost_iris_results"
os.makedirs(result_dir, exist_ok=True)
# 加载数据集
iris = load_iris()
X = iris.data
y = iris.target
feature_names = iris.feature_names
class_names = iris.target_names
# 数据探索
print("数据集形状:", X.shape)
print("类别分布:", np.bincount(y))
# 数据框展示前5行
df = pd.DataFrame(X, columns=feature_names)
df['species'] = [class_names[i] for i in y]
print("\n数据集前5行:")
print(df.head())
# 数据可视化 - 特征分布图
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
for i, feature in enumerate(feature_names):
plt.subplot(2, 2, i+1)
for species in class_names:
plt.hist(df[df['species'] == species][feature],
label=species, alpha=0.7, bins=15)
plt.xlabel(feature)
plt.ylabel('Frequency')
plt.legend()
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig(f"{result_dir}/feature_distributions.png", dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight')
plt.close()
# 数据可视化 - 特征相关性热图
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
corr = df.drop('species', axis=1).corr()
sns.heatmap(corr, annot=True, cmap='coolwarm', fmt=".2f", linewidths=0.5)
plt.title('Correlation Matrix of Features')
plt.savefig(f"{result_dir}/feature_correlation.png", dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight')
plt.close()
# 划分训练集和测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=42, stratify=y
)
# 初始化XGBoost分类器
xgb_model = xgb.XGBClassifier(
objective='multi:softmax', # 多分类问题
num_class=3, # 类别数量
random_state=42
)
# 训练模型
xgb_model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 预测
y_pred = xgb_model.predict(X_test)
y_proba = xgb_model.predict_proba(X_test)
# 评估模型
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
print(f"\n模型准确率: {accuracy:.4f}")
print("\n分类报告:")
print(classification_report(y_test, y_pred, target_names=class_names))
# 混淆矩阵可视化
cm = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
sns.heatmap(cm, annot=True, fmt='d', cmap='Blues',
xticklabels=class_names,
yticklabels=class_names)
plt.xlabel('Predicted')
plt.ylabel('True')
plt.title('Confusion Matrix')
plt.savefig(f"{result_dir}/confusion_matrix.png", dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight')
plt.close()
# 特征重要性可视化
feature_importance = xgb_model.feature_importances_
sorted_idx = np.argsort(feature_importance)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.barh(range(len(sorted_idx)), feature_importance[sorted_idx], align='center')
plt.yticks(range(len(sorted_idx)), [feature_names[i] for i in sorted_idx])
plt.xlabel('Feature Importance')
plt.title('XGBoost Feature Importance')
plt.savefig(f"{result_dir}/feature_importance.png", dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight')
plt.close()
# 绘制ROC曲线(多类别的情况)
y_test_binarized = label_binarize(y_test, classes=[0, 1, 2])
n_classes = y_test_binarized.shape[1]
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
for i in range(n_classes):
fpr, tpr, _ = roc_curve(y_test_binarized[:, i], y_proba[:, i])
roc_auc = auc(fpr, tpr)
plt.plot(fpr, tpr, lw=2, label=f'ROC curve for {class_names[i]} (area = {roc_auc:.2f})')
plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], 'k--', lw=2)
plt.xlim([0.0, 1.0])
plt.ylim([0.0, 1.05])
plt.xlabel('False Positive Rate')
plt.ylabel('True Positive Rate')
plt.title('ROC Curves for Multi-class Classification')
plt.legend(loc="lower right")
plt.savefig(f"{result_dir}/roc_curves.png", dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight')
plt.close()
# 超参数调优
param_grid = {
'max_depth': [3, 5, 7],
'learning_rate': [0.1, 0.01, 0.001],
'n_estimators': [100, 200, 300],
'subsample': [0.8, 1.0]
}
grid_search = GridSearchCV(
estimator=xgb_model,
param_grid=param_grid,
cv=5,
scoring='accuracy',
n_jobs=-1,
verbose=1
)
grid_search.fit(X_train, y_train)
print("\n最佳参数:", grid_search.best_params_)
print("最佳交叉验证准确率:", grid_search.best_score_)
# 使用最佳参数的模型
best_model = grid_search.best_estimator_
y_pred_best = best_model.predict(X_test)
print("\n调优后模型准确率:", accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred_best))
# 保存模型
import joblib
joblib.dump(best_model, f"{result_dir}/xgboost_iris_best_model.pkl")
print(f"\n最佳模型已保存至 {result_dir}/xgboost_iris_best_model.pkl")
项目解析
1. 项目概述
本项目使用XGBoost算法对经典的鸢尾花数据集进行分类。鸢尾花数据集包含3种不同类型的鸢尾花,每种类型有50个样本,每个样本有4个特征(花萼长度、花萼宽度、花瓣长度、花瓣宽度)。
2. 代码流程
-
数据加载与探索:加载鸢尾花数据集,查看数据基本信息和分布情况
-
数据可视化:绘制特征分布图和相关性热图,直观了解数据特征
-
数据集划分:将数据分为训练集(70%)和测试集(30%)
-
模型训练:使用XGBoost分类器进行训练
-
模型评估:计算准确率、生成分类报告、绘制混淆矩阵
-
特征重要性分析:查看各特征对分类结果的影响程度
-
超参数调优:使用网格搜索寻找最佳参数组合
-
模型保存:将优化后的模型保存,以便后续使用
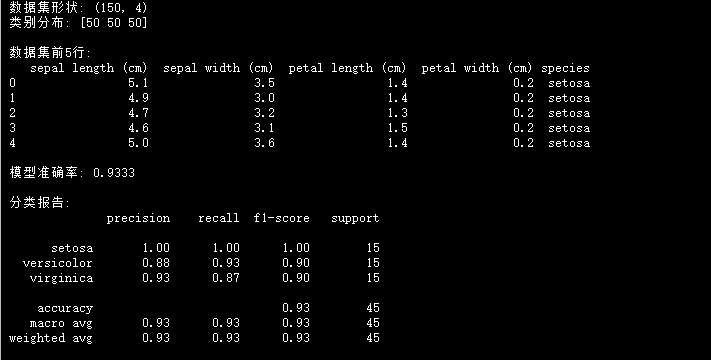
3. 结果解释
运行代码后,会在xgboost_iris_results目录下生成多种可视化结果:
-
特征分布图:展示每个特征在不同类别中的分布情况
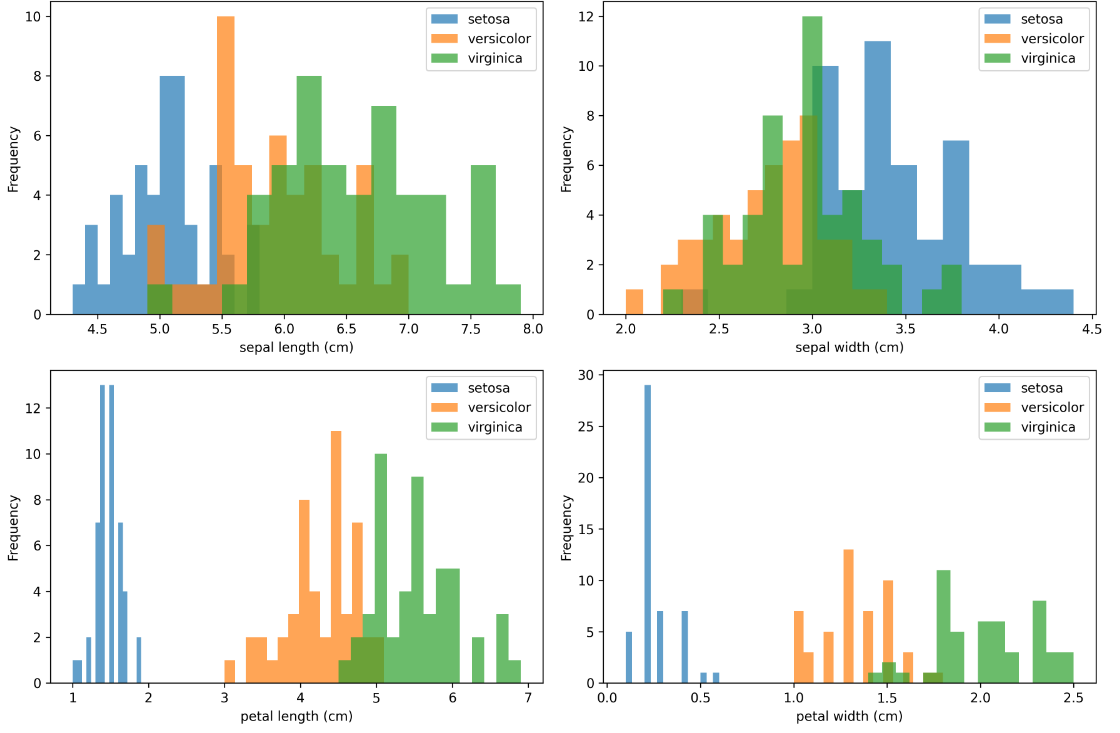
-
特征相关性热图:显示各特征之间的相关性强度
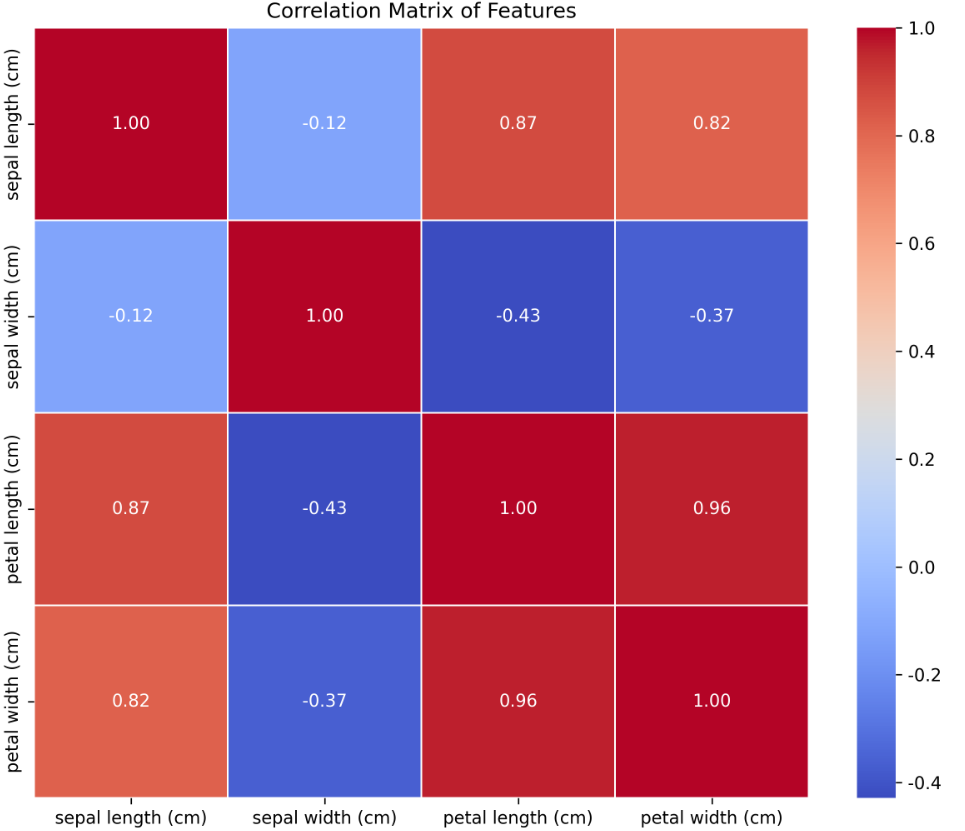
-
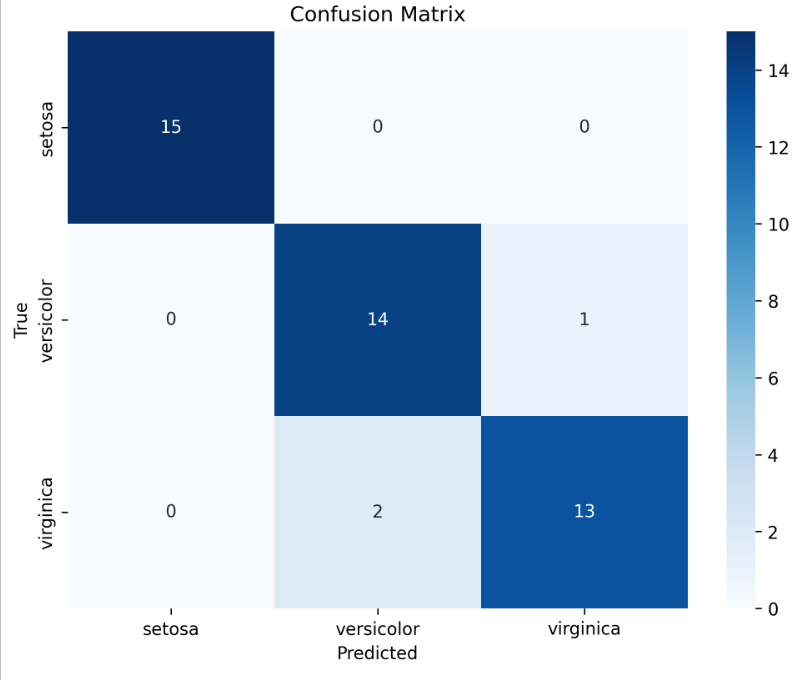
混淆矩阵:展示模型在测试集上的分类结果
-
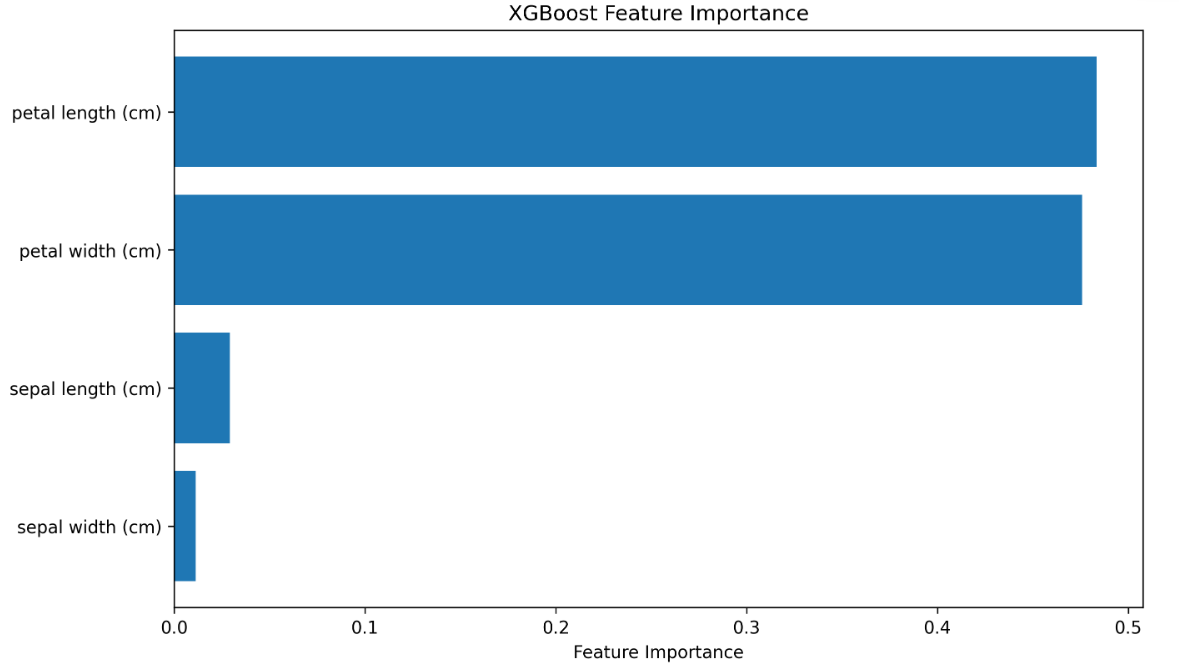
特征重要性图:显示每个特征对模型预测的贡献度
-
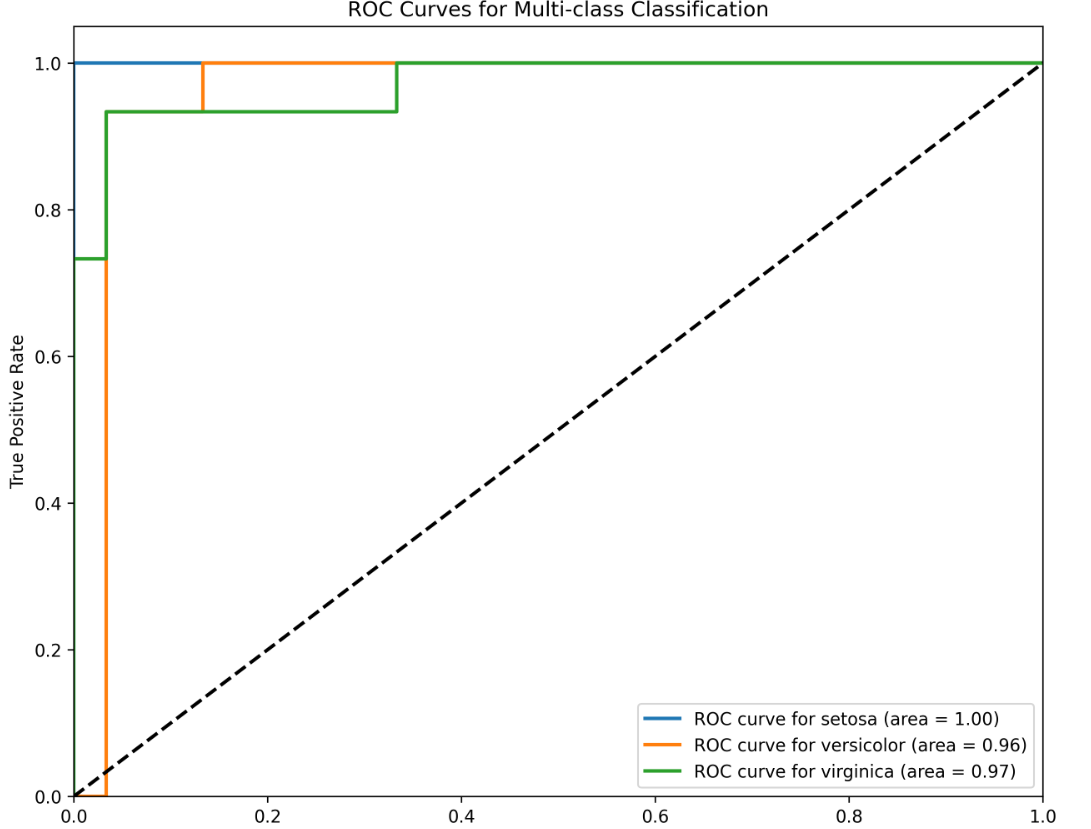
ROC曲线:评估模型在多类别分类任务中的性能
4. XGBoost参数说明
在本项目中,我们使用了XGBoost的一些重要参数:
-
objective='multi:softmax':指定多分类问题的目标函数 -
num_class=3:指定类别数量 -
max_depth:树的最大深度,控制过拟合 -
learning_rate:学习率,控制每棵树的贡献 -
n_estimators:树的数量 -
subsample:每棵树的样本采样比例
通过网格搜索,我们可以找到这些参数的最佳组合,进一步提高模型性能。
总结
XGBoost作为一种高效的集成学习算法,在分类和回归任务中都表现出色。它通过结合多个决策树的预测结果,能够捕捉数据中的复杂模式,同时通过正则化机制有效防止过拟合。
本入门项目展示了XGBoost在实际分类任务中的应用流程,包括数据探索、模型训练、评估和优化等步骤。通过这个项目,你可以掌握XGBoost的基本使用方法,并了解如何通过可视化手段分析模型性能和数据特征。
在实际应用中,XGBoost可以处理更复杂的数据集和任务,只需根据具体问题调整相应的参数和策略即可。
➔➔➔➔点击查看原文,获取更多机器学习干货和资料!![]() https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/0qHc6r7GReHofHkAhCNo5A
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/0qHc6r7GReHofHkAhCNo5A






















 10万+
10万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








