参考链接
参考博客:http://colah.github.io/posts/2015-08-Understanding-LSTMs/
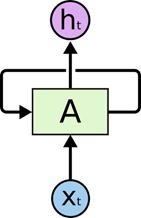
标准的循环神经网络(RNN)
- 模型图:
RNN包含一个循环,在上面的示例图中,神经网络的模块A,正在读取某个输入 X t X_t Xt,并输出一个值 h t h_t ht。循环可以使得信息从当前步传递到下一步。
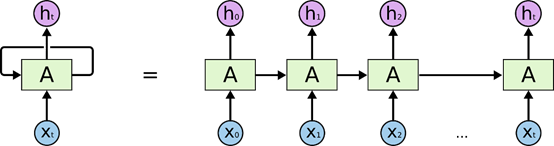
- 展开RNN:
链式的特征揭示了 RNN 本质上是与序列相关的。他们是对于这类数据的最自然的神经网络架构。
- RNN公式: h t = t a n h ( W ∗ [ h t − 1 , x t ] + b ) h_t=tanh(W*[h_{t-1},x_t ]+b) ht=tanh(W∗[ht−1,xt]+b)
LSTM 网络
- 长期依赖(Long-Term Dependencies)问题
RNN 的关键点之一就是他们可以用来连接先前的信息到当前的任务上。当相关的信息和预测位置之间的间隔是非常小的时候,RNN 可以学会使用先前的信息。但是当相关信息和当前预测位置之间的间隔变得较大时,RNN 会丧失学习到连接如此远的信息的能力。为了解决这个问题产生了LSTM 网络。 - Long Short Term Memory = LSTM是一种 特殊的RNN,可以学习长期依赖信息
- 所有 RNN 都具有一种重复神经网络模块的链式的形式。标准的 RNN如下:
LSTM 同样是这样的结构,但是重复的模块拥有一个不同的结构。
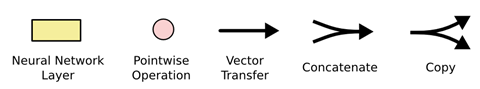
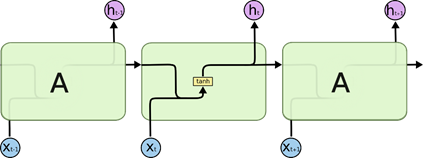 图中各种元素图标的含义:
图中各种元素图标的含义: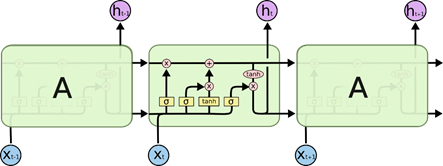
LSTM 的核心思想:
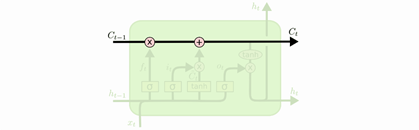
- LSTM 的关键就是每个单元的状态
C
t
C_t
Ct(长期的记忆),可以将其抽象如下:
LSTM有通过精心设计的称作为 “门” 的结构来去除或者增加信息到状态 C t C_t Ct中。门是一种让信息选择式通过的方法。他们包含一个 sigmoid 神经网络层和一个按位的乘法操作,如下图所示:
 Sigmoid层输出0到1之间的数值,描述每个部分有多少量可以通过。0代表“不许任何量通过”,1 就指“允许任意量通过”。LSTM 拥有三个门,来保护和控制单元状态 C t C_t Ct。
Sigmoid层输出0到1之间的数值,描述每个部分有多少量可以通过。0代表“不许任何量通过”,1 就指“允许任意量通过”。LSTM 拥有三个门,来保护和控制单元状态 C t C_t Ct。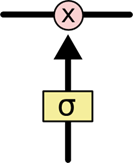
LSTM 的单元构成:
- LSTM 单元结构图如下:
其中最上面的那条线表示的是RNN的长期记忆的状态向量 C t C_t Ct, h t h_t ht是RNN单元的短期记忆状态向量, h t h_t ht同时也是当前单元的输出,输入为 x t x_t xt和 h t − 1 h_{t-1} ht−1。

- 忘记门:是决定会从
C
t
C_t
Ct中丢弃(遗忘)什么信息。该门会读取
h
t
−
1
h_{t-1}
ht−1和
x
t
x_t
xt,输出长度与
C
t
−
1
C_{t-1}
Ct−1一样的向量
f
t
f_t
ft,并且
f
t
f_t
ft中的值都在 0 到 1 之间,然后将
f
t
f_t
ft与
C
t
−
1
C_{t-1}
Ct−1逐点相乘。这样就可以看出
f
t
f_t
ft中的1 表示“完全保留”
C
t
−
1
C_{t-1}
Ct−1中对应的元素,0 表示“完全舍弃”
C
t
−
1
C_{t-1}
Ct−1中对应的元素。这相当于产生一个与状态
C
t
−
1
C_{t-1}
Ct−1相同大小筛子
f
t
f_t
ft去筛选
C
t
−
1
C_{t-1}
Ct−1中的信息。
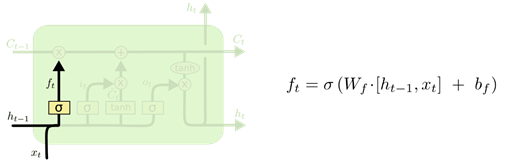
- 输入门:是确定当前输入
x
t
x_t
xt中什么样的信息要被存放到单元状态
C
t
−
1
C_{t-1}
Ct−1中去。这里包含三个部分:
- 第一部分:一个 t a n h tanh tanh层用于创建当前节点的新的信息向量 C t ⃗ \vec{C_t} Ct。
- 第二部分:sigmoid 层称 的 “输入门” ,相当于产生一个筛子
i
t
i_t
it用于与筛选当前节点产生的信息
C
t
⃗
\vec{C_t}
Ct那些应该加入到状态
C
t
−
1
C_{t-1}
Ct−1中。
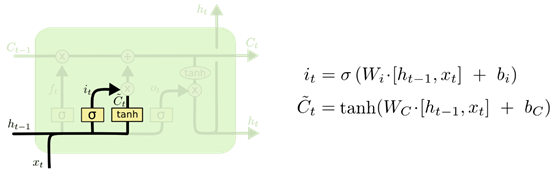
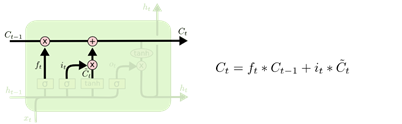
- 第三部分:将经过输出门筛选的当前节点的信息加入到状态
C
t
−
1
C_{t-1}
Ct−1中去产生新状态
C
t
C_t
Ct。
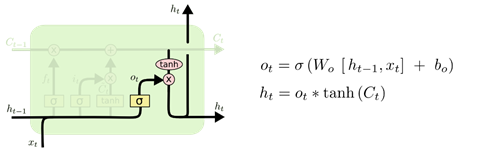
- 输出门:这一部分是用于产生当前节点的输出;这一部分由两个部分组成:
- 先由新状态 C t C_t Ct通过一个 t a n h tanh tanh层产生新状态 C t C_t Ct的总输出
- 输出门用于筛选总输出中的信息产生当前节点的输出。
LSTM 的变体
第一种:
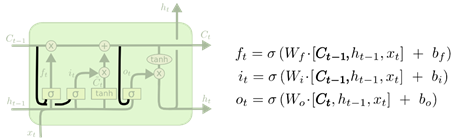
- 一种比较流行的 LSTM 变体,就是由 Gers & Schmidhuber (2000) 提出的,增加了 “peephole connection”。就是让门层也会接受状态的输入,如下图所示:
上面的图例中,我们增加了 peephole 到每个门上,但是许多论文会加入部分的 peephole 而非所有都加。
第二种:
另一个变体是通过使用coupled遗忘和输入门;它仅仅在遗忘的位置添加新的信息。
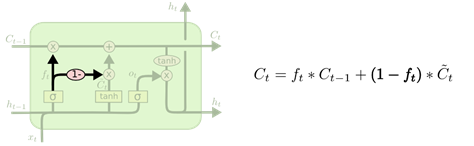
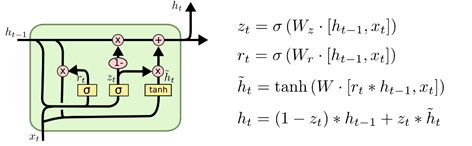
第三种:
另一个改动较大的变体是 Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU),这是由 Cho, et al. (2014) 提出。它将遗忘门和输入门合成了一个单一的 “更新门”。同样还混合了长记忆状态( C t C_t Ct)和短记忆状态( h t h_t ht),和其他一些改动。最终的模型比标准的 LSTM 模型要简单,也是非常流行的变体。





 本文介绍了循环神经网络(RNN)的基本概念及其在处理序列数据方面的应用,并深入探讨了长期依赖问题。针对这一问题,文章详细解释了长短期记忆(LSTM)网络的工作原理,包括其核心组件如遗忘门、输入门及输出门的作用机制。此外,还概述了几种LSTM的变体。
本文介绍了循环神经网络(RNN)的基本概念及其在处理序列数据方面的应用,并深入探讨了长期依赖问题。针对这一问题,文章详细解释了长短期记忆(LSTM)网络的工作原理,包括其核心组件如遗忘门、输入门及输出门的作用机制。此外,还概述了几种LSTM的变体。
















 1451
1451

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








