一,头指针链表的引入
1.回顾一下我们的头结点链表,当我们需要插入节点:
new_node->next=p->next,
p->next=new_node
2.当需要删除元素:
temp=p->next
p->next=temp->next
free(temp);
我们发现只要找到了前置节点,后面的插入、删除操作只需要按照固定的套路来就好,但由于头结点不存数据,当我们单个数据占据的内存很大时头结点就很占用空间,而这个空间我们又用不上就很浪费,所以才有头指针链表。头指针只存下个节点的地址而没有数据空间相比头结点链表就更节省空间,但是因为我们的插入、删除都需要先找到前置节点,当我们插入的位置在头指针和节点之间时就需要分情况讨论了,这就失去了逻辑完备性,而头结点链表面对这几种情况都只需要一种操作就能满足,因此头结点链表还是更受欢迎
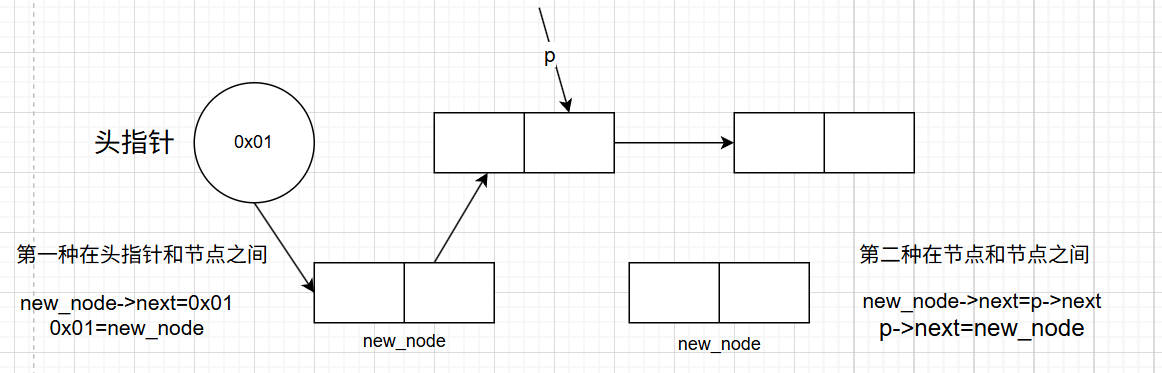
之前,在写插入函数遇到上图两种情况我们一般会用if语句分情况讨论,但现在我们介绍一种新的方法
3.引入dummy节点,放入栈
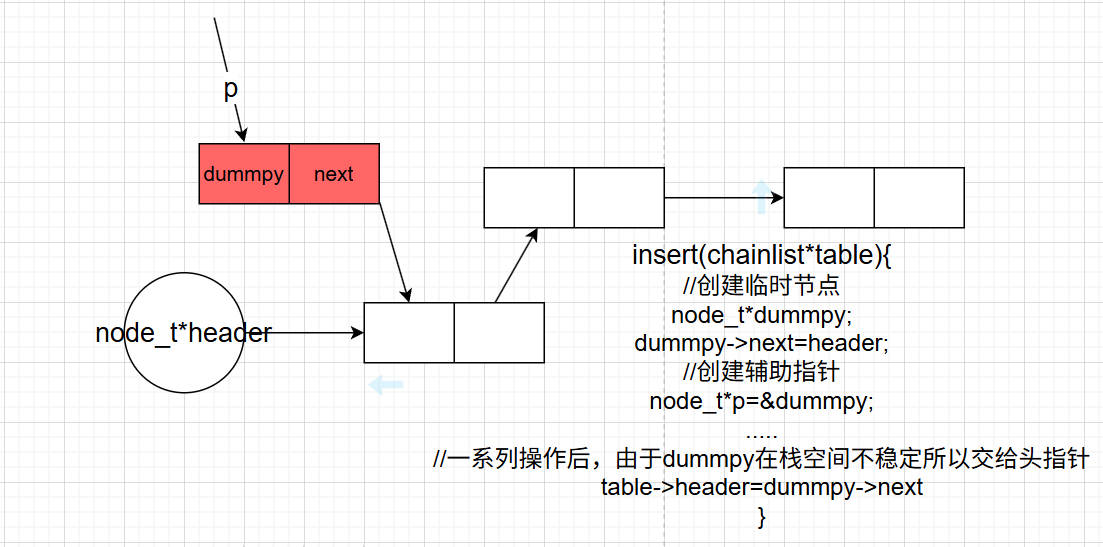
在相应函数中创建dummpy之后后面操作就和头节点链表的操作一样,只不过由于dummpy在栈空间,因此最后要把dummpy->next更新到header当中
二,代码实现
1.头文件中的接口
#include "common.h"
#ifndef CHAINLIST_H
#define CHAINLIST_H
typedef struct {
node_t* header;
int count;
}chainlist_t;
//初始化链表
void initchainlist(chainlist_t*table);
//插入元素
int insertchainlisthead(chainlist_t*table,Element_t val);
//任意位置插入
int insertchainlistpos(chainlist_t*table,int pos,Element_t val);
//删除元素
int deletechainlist(chainlist_t*table,Element_t val);
//销毁链表
void distorychainlist(chainlist_t*table);
//打印链表
void showchainlist(chainlist_t*table);
#endif //CHAINLIST_H
由于在这个工程中,带头指针的链表和带头结点的链表都需要定义节点结构体,因此我们还要一个common.h头文件将两个头文件中重复定义的成员提取出来
#ifndef COMMON_H
#define COMMON_H
typedef int Element_t;
typedef struct _node{
Element_t val;
struct _node*next;
}node_t;
#endif //COMMON_H
2.将头文件的接口一一实现
#include "chainlist.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void initchainlist(chainlist_t *table) {
if (table == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr,"table is null\n");
return;
}
table->header=NULL;
table->count=0;
}
int insertchainlisthead(chainlist_t *table, Element_t value) {
node_t dummpy;
dummpy.next=table->header;
node_t*p=&dummpy;
//1.为新节点分配空间
node_t*newnode=malloc(sizeof(node_t));
//2.判断分配是否成功
if (newnode==NULL) {
fprintf(stderr,"newnode malloc failed\n");
return -1;
}
//3.将新节点插入到表头
newnode->val=value;
newnode->next=dummpy.next;
dummpy.next=newnode;
//4.更新链表长度
table->count++;
table->header=dummpy.next;
return 0;
}
int insertchainlistpos(chainlist_t *table, int pos, Element_t value) {
node_t dummpy;
dummpy.next=table->header;
//判断pos是否合法
if (pos<0 || pos>table->count) {
fprintf(stderr,"pos is invalid\n");
return -1;
}
//1.定义指针p表示待插入的节点
node_t*p=&dummpy;
//2.找到待插入的位置
for (int i=0;i<pos;i++) {
p=p->next;
}
//3.为新节点分配空间
node_t*new_node=malloc(sizeof(node_t));
if (new_node==NULL) {
fprintf(stderr,"new_node malloc failed\n");
return -1;
}
new_node->val=value;
//4.将新节点插入到链表中
new_node->next=p->next;
p->next=new_node;
//5.更新链表长度
table->count++;
//6.将临时节点的next赋值给头指针
table->header=dummpy.next;
return 0;
}
int deletechainlist(chainlist_t *table, Element_t value) {
node_t dummpy;
dummpy.next=table->header;
node_t*p=&dummpy;
//1.找到待删除节点的位置
for(int i=0;i<table->count;i++) {
if (p->next->val==value||p->next->next==NULL) {
break;
}
p=p->next;
}
//2.如果没找到,返回-1
if (p->next->next==NULL) {
fprintf(stderr,"deletelinklist element not found\n");
return -1;
}
//3.删除节点
node_t*temp=p->next;
p->next=temp->next;
free(temp);
table->count--;
//4.将临时节点的next赋值给头指针
table->header=dummpy.next;
return 0;
}
void distorychainlist(chainlist_t *table) {
node_t dummpy;
dummpy.next=table->header;
//1.定义指针p表示待释放的节点,再定义temp拷贝p
node_t*p=dummpy.next;
node_t*temp=NULL;
//2.只要节点不为空,就释放节点
while(p) {
temp=p;
p=temp->next;
free(temp);
}
printf("chainlist distory\n");
/*node_t *p = &dummpy;
node_t *tmp;
while (p->next) {
tmp = p->next;
p->next = tmp->next;
free(tmp);
--table->count;
}
printf("LinkList have %d node!\n", table->count);*/
}
void showchainlist(chainlist_t *table) {
node_t*p=table->header;
while (p->next!=NULL) {
printf("%d\t ",p->val);
p=p->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
3.最后测试一下有没有bug
为了锻炼我们灵活管理空间的能力我们这次不在堆空间创建表头,在数据区中创建
#include <stdio.h>
#include "linklist.h"
#include "chainlist.h"
//在数据区创建表头
chainlist_t table;
void test2() {
initchainlist(&table);
for (int i=0;i<10;i++) {
insertchainlisthead(&table,100+i);
}
insertchainlistpos(&table,0,500);
deletechainlist(&table,101);
showchainlist(&table);
distorychainlist(&table);
}
int main() {
//test1();
test2();
return 0;
}
二,单向循环链表
对于链表当我们有更多需求,比如我们想把新节点放入末尾,我们会有很多这种需求,此时我们会创建一个尾指针rear指向链表最后一个元素并将最后一个元素的指针域next指向头结点,我们可以用头结点链表来实现一下
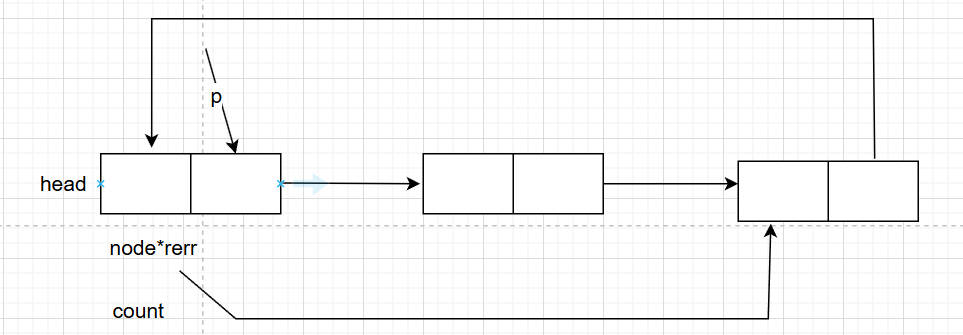
1.头文件中的接口
#ifndef LISTLOOP_H
#define LISTLOOP_H
typedef int Element_t;
typedef struct _node {
Element_t val;
struct _node *next;
}node_t;
typedef struct {
node_t head;
node_t*rear;
int count;
}looplist_t;
void initlooplist(looplist_t*table);
int insertlistloophead(looplist_t*table,Element_t val);
int insertlistlooptail(looplist_t*table,Element_t val);
void showlooplist(looplist_t*table);
int deletelooplist(looplist_t*table,Element_t val);
int distorylooplist(looplist_t*table);
#endif //LISTLOOP_H
2.把头文件中的接口一一实现
#include "listloop.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void initlooplist(looplist_t *table) {
table->head.next=table->rear=&table->head;
table->count=0;
printf("initlooplist successfully\n");
}
int insertlistloophead(looplist_t *table, Element_t val) {
node_t*newnode=malloc(sizeof(looplist_t));
if (newnode==NULL) {
fprintf(stderr,"malloc error\n");
return -1;
}
newnode->val=val;
newnode->next=table->head.next;
table->head.next=newnode;
if (table->rear==&table->head) {
table->rear=newnode;
newnode->next=&table->head;
}
table->count++;
return 0;
}
int insertlistlooptail(looplist_t *table, Element_t val) {
node_t*newnode=malloc(sizeof(node_t));
if (newnode==NULL) {
fprintf(stderr,"newnode malloc error\n");
return -1;
}
newnode->val=val;
newnode->next=table->rear->next;
table->rear->next=newnode;
table->rear=newnode;
table->count++;
return 0;
}
void showlooplist(looplist_t *table) {
node_t*p=table->head.next;
for (int i=0;i<table->count;i++) {
printf("%d\t",p->val);
p=p->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
int deletelooplist(looplist_t *table, Element_t val) {
node_t*p=&table->head;
while (p->next!=&table->head&&p->next->val!=val) {
p=p->next;
}
if (p->next==&table->head) {
printf("not found\n");
return -1;
}
node_t*temp=p->next;
p->next=temp->next;
free(temp);
table->count--;
table->rear=p->next;
return 0;
}
int distorylooplist(looplist_t *table) {
node_t*p=table->head.next;
node_t*temp=NULL;
while (p!=&table->head) {
temp=p;
p=p->next;
free(temp);
}
return 0;
}
3.最后测试有没有bug
#include "listloop.h"
void test() {
looplist_t table;
initlooplist(&table);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
insertlistlooptail(&table,100+i);
}
deletelooplist(&table,100);
showlooplist(&table);
distorylooplist(&table);
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








